Constant Value Tensors
zeros
numpyのzerosみたいなもの
TensorのデータタイプとShapeを指定する
import tensorflow as tf
x = tf.zeros([1], dtype=tf.float32)
with tf.Session() as sess:
print(x.eval())
[ 0.]
import tensorflow as tf
x = tf.zeros([10], dtype=tf.float32)
with tf.Session() as sess:
print(x.eval())
[ 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0.]
2x10のTensorの例
import tensorflow as tf
x = tf.zeros([2,10], dtype=tf.float32)
with tf.Session() as sess:
print(x.eval())
[[ 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0.]
[ 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0.]]
ones
numpyのonesみたいなもの
TensorのデータタイプとShapeを指定する
import tensorflow as tf
x = tf.ones([2,10], dtype=tf.float32)
with tf.Session() as sess:
print(x.eval())
[[ 1. 1. 1. 1. 1. 1. 1. 1. 1. 1.]
[ 1. 1. 1. 1. 1. 1. 1. 1. 1. 1.]]
fill
定数のTensorを作る
dtypeが指定できない
import tensorflow as tf
x = tf.fill([2,10], 9.)
with tf.Session() as sess:
print(x.eval())
[[ 9. 9. 9. 9. 9. 9. 9. 9. 9. 9.]
[ 9. 9. 9. 9. 9. 9. 9. 9. 9. 9.]]
constant
定数のTensorを作る
import tensorflow as tf
x = tf.constant(9,shape=[2,10],dtype=tf.float32)
with tf.Session() as sess:
print(x.eval())
[[ 9. 9. 9. 9. 9. 9. 9. 9. 9. 9.]
[ 9. 9. 9. 9. 9. 9. 9. 9. 9. 9.]]
In [8]: x = tf.constant(9,shape=[2,10],dtype=tf.int32)
...: with tf.Session() as sess:
...: print(x.eval())
...:
...:
[[9 9 9 9 9 9 9 9 9 9]
[9 9 9 9 9 9 9 9 9 9]]
import tensorflow as tf
import numpy as np
x = tf.constant(np.arange(20).astype(float),shape=[2,10],dtype=tf.float32)
with tf.Session() as sess:
print(x.eval())
[[ 0. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9.]
[ 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19.]]
Random Tensors
Tensorをランダムな値で初期化する。
Weightの初期化でよく使われる
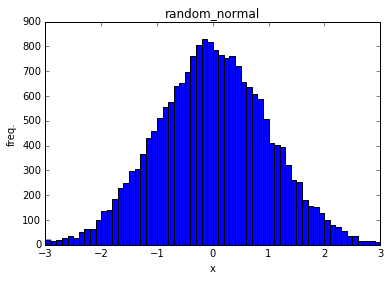
random_normal
Tensorを正規分布なランダム値で初期化する
import tensorflow as tf
x = tf.random_normal(shape=[20000],mean=0.0, stddev=1.0,dtype=tf.float32)
with tf.Session() as sess:
y = x.eval()
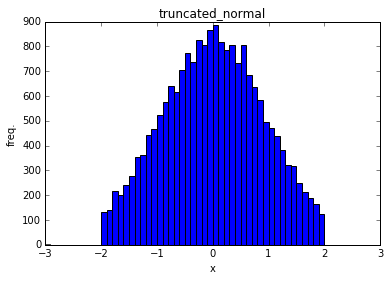
truncated_normal
Tensorを正規分布かつ標準偏差の2倍までのランダムな値で初期化する
import tensorflow as tf
x = tf.truncated_normal(shape=[20000],mean=0.0, stddev=1.0,dtype=tf.float32)
with tf.Session() as sess:
y = x.eval()
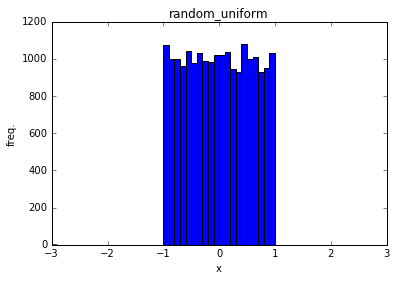
random_uniform
Tensorを一様分布なランダム値で初期化する
import tensorflow as tf
x = tf.random_uniform(shape=[20000], minval=-1.0,maxval=1.0,dtype=tf.float32)
with tf.Session() as sess:
y = x.eval()
set_random_seed
randomを使用すると再現性がなくなるが、seedを指定するとこで同じ値を取り出せる。
指定の仕方は、operationに指定するか、set_random_seedでgraph levelで指定する方法がある。
import tensorflow as tf
a = tf.random_uniform([1])
print('session1')
with tf.Session() as sess:
print(a.eval())
print(a.eval())
print('session2')
with tf.Session() as sess:
print(a.eval())
print(a.eval())
session1
[ 0.85636878]
[ 0.81764412]
session2
[ 0.36246026]
[ 0.87940264]
import tensorflow as tf
a = tf.random_uniform([1],seed=1234)
print('session1')
with tf.Session() as sess:
print(a.eval())
print(a.eval())
print('session2')
with tf.Session() as sess:
print(a.eval())
print(a.eval())
session1
[ 0.84830701]
[ 0.64822805]
session2
[ 0.84830701]
[ 0.64822805]
import tensorflow as tf
tf.set_random_seed(1234)
a = tf.random_uniform([1])
b = tf.random_uniform([1])
print('session1')
with tf.Session() as sess:
print(a.eval())
print(a.eval())
print(b.eval())
print(b.eval())
print('session2')
with tf.Session() as sess:
print(a.eval())
print(a.eval())
print(b.eval())
print(b.eval())
session1
[ 0.340114]
[ 0.65625393]
[ 0.78275204]
[ 0.14843035]
session2
[ 0.340114]
[ 0.65625393]
[ 0.78275204]
[ 0.14843035]
Shapes and Shaping
Shape
Tensorのサイズ(Sharp)を取り出す。
import tensorflow as tf
x = tf.constant(np.arange(60.),shape=[3,4,5],dtype=tf.float32)
with tf.Session() as sess:
print(x.eval())
[[[ 0. 1. 2. 3. 4.]
[ 5. 6. 7. 8. 9.]
[ 10. 11. 12. 13. 14.]
[ 15. 16. 17. 18. 19.]]
[[ 20. 21. 22. 23. 24.]
[ 25. 26. 27. 28. 29.]
[ 30. 31. 32. 33. 34.]
[ 35. 36. 37. 38. 39.]]
[[ 40. 41. 42. 43. 44.]
[ 45. 46. 47. 48. 49.]
[ 50. 51. 52. 53. 54.]
[ 55. 56. 57. 58. 59.]]]
get_shape()でサイズを取得する場合
TypeはTensorShapeになっている。
import tensorflow as tf
s = x.get_shape()
print(type(s))
print(s)
<class 'tensorflow.python.framework.tensor_shape.TensorShape'>
(3, 4, 5)
tf.shape()でサイズを取得する場合
Typeはoperationになっている。
import tensorflow as tf
s = tf.shape(x)
print(type(s))
print(s)
<class 'tensorflow.python.framework.ops.Tensor'>
Tensor("Shape:0", shape=(3,), dtype=int32)
get_shape(), tf.shape()
tf.shape()はplaceholderなどで、後でサイズが決まるような場合に使用する。
x = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, shape=[None,32])
例えばplaceholderと同じサイズのTensorを作る場合にget_shapeを使用するとエラーになる
y = tf.ones(shape=x.get_shape())
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "<ipython-input-23-366d94fbb0a4>", line 1, in <module>
y = tf.ones(shape=x.get_shape())
File "/home/user/anaconda2/envs/tensorflow/lib/python2.7/site-packages/tensorflow/python/ops/array_ops.py", line 699, in ones
shape = ops.convert_to_tensor(shape, name="shape")
File "/home/user/anaconda2/envs/tensorflow/lib/python2.7/site-packages/tensorflow/python/framework/ops.py", line 529, in convert_to_tensor
ret = conversion_func(value, dtype=dtype, name=name, as_ref=as_ref)
File "/home/user/anaconda2/envs/tensorflow/lib/python2.7/site-packages/tensorflow/python/ops/constant_op.py", line 195, in _tensor_shape_tensor_conversion_function
"Cannot convert a partially known TensorShape to a Tensor: %s" % s)
ValueError: Cannot convert a partially known TensorShape to a Tensor: (?, 32)
このような場合にはtf.shapeを使用する。
y = tf.ones(shape=tf.shape(x))
import tensorflow as tf
x = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, shape=[None,32])
y = tf.ones(shape=tf.shape(x))
z = y + x
with tf.Session() as sess:
# sess.run(y)
b = np.arange(3*32).reshape((3,32))
print(sess.run(z, feed_dict={x:b}))
[[ 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14.
15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. 21. 22. 23. 24. 25. 26. 27. 28.
29. 30. 31. 32.]
[ 33. 34. 35. 36. 37. 38. 39. 40. 41. 42. 43. 44. 45. 46.
47. 48. 49. 50. 51. 52. 53. 54. 55. 56. 57. 58. 59. 60.
61. 62. 63. 64.]
[ 65. 66. 67. 68. 69. 70. 71. 72. 73. 74. 75. 76. 77. 78.
79. 80. 81. 82. 83. 84. 85. 86. 87. 88. 89. 90. 91. 92.
93. 94. 95. 96.]]
このようにtf.shapeの一部分を使用して[]でくくるとListになってしまう。
print(type([tf.shape(x)[0],1]))
<class 'list'>
この場合はtf.packを使用してoperationにする。
この場合はtf.stackを使用してoperationにする。(packはstackになったようです)
print(type(tf.stack([tf.shape(x)[0],1])))
<class 'tensorflow.python.framework.ops.Tensor'>
Slicing and Joining
※concat,splitの引数の順番が変更になったので修正しました。
slice
Tensorの一部分を取り出す。
beginで開始場所、sizeで切り出す大きさを指定する。
import tensorflow as tf
n = np.arange(25).reshape((1,5,5))
x = tf.concat([n, n*10, n*100],0)
with tf.Session() as sess:
print(x.eval())
[[[ 0 1 2 3 4]
[ 5 6 7 8 9]
[ 10 11 12 13 14]
[ 15 16 17 18 19]
[ 20 21 22 23 24]]
[[ 0 10 20 30 40]
[ 50 60 70 80 90]
[ 100 110 120 130 140]
[ 150 160 170 180 190]
[ 200 210 220 230 240]]
[[ 0 100 200 300 400]
[ 500 600 700 800 900]
[1000 1100 1200 1300 1400]
[1500 1600 1700 1800 1900]
[2000 2100 2200 2300 2400]]]
下記の例では、6の位置から、0次元方向に3,1次元方向に2、3次元方向に4つ分取り出す。
import tensorflow as tf
y = tf.slice(x, [0,1,1], [3,2,4])
with tf.Session() as sess:
print(y.eval())
[[[ 6 7 8 9]
[ 11 12 13 14]]
[[ 60 70 80 90]
[ 110 120 130 140]]
[[ 600 700 800 900]
[1100 1200 1300 1400]]]
concat
Tensorを結合する。
import tensorflow as tf
x = tf.ones([3,4], dtype=tf.float32)
y = tf.constant(2,shape=[3,4], dtype=tf.float32)
with tf.Session() as sess:
print(x.eval())
print(y.eval())
[[ 1. 1. 1. 1.]
[ 1. 1. 1. 1.]
[ 1. 1. 1. 1.]]
[[ 2. 2. 2. 2.]
[ 2. 2. 2. 2.]
[ 2. 2. 2. 2.]]
最初の引数2番目の引数で結合するDimensionを決定する。
2次元のTensorで、Dimensionが0の場合は、結果はz1のように[[xxxx],[xxxx],[yyyy],[yyyy]...]という並びのTensorになる。
Dimensionが1の場合は、結果はz2のように[[xxxxyyyy],[xxxxyyyy],...]という並びのTensorになる。
import tensorflow as tf
z1 = tf.concat([x, y],0)
z2 = tf.concat([x, y],1)
with tf.Session() as sess:
print('z1')
print(z1.eval())
print('z2')
print(z2.eval())
z1
[[ 1. 1. 1. 1.]
[ 1. 1. 1. 1.]
[ 1. 1. 1. 1.]
[ 2. 2. 2. 2.]
[ 2. 2. 2. 2.]
[ 2. 2. 2. 2.]]
z2
[[ 1. 1. 1. 1. 2. 2. 2. 2.]
[ 1. 1. 1. 1. 2. 2. 2. 2.]
[ 1. 1. 1. 1. 2. 2. 2. 2.]]
import tensorflow as tf
x = tf.ones([3,4,5], dtype=tf.float32)
y = tf.constant(2,shape=[3,4,5], dtype=tf.float32)
with tf.Session() as sess:
print(x.eval())
print(y.eval())
[[[ 1. 1. 1. 1. 1.]
[ 1. 1. 1. 1. 1.]
[ 1. 1. 1. 1. 1.]
[ 1. 1. 1. 1. 1.]]
[[ 1. 1. 1. 1. 1.]
[ 1. 1. 1. 1. 1.]
[ 1. 1. 1. 1. 1.]
[ 1. 1. 1. 1. 1.]]
[[ 1. 1. 1. 1. 1.]
[ 1. 1. 1. 1. 1.]
[ 1. 1. 1. 1. 1.]
[ 1. 1. 1. 1. 1.]]]
[[[ 2. 2. 2. 2. 2.]
[ 2. 2. 2. 2. 2.]
[ 2. 2. 2. 2. 2.]
[ 2. 2. 2. 2. 2.]]
[[ 2. 2. 2. 2. 2.]
[ 2. 2. 2. 2. 2.]
[ 2. 2. 2. 2. 2.]
[ 2. 2. 2. 2. 2.]]
[[ 2. 2. 2. 2. 2.]
[ 2. 2. 2. 2. 2.]
[ 2. 2. 2. 2. 2.]
[ 2. 2. 2. 2. 2.]]]
import tensorflow as tf
z1 = tf.concat([x, y],0)
z2 = tf.concat([x, y],1)
z3 = tf.concat([x, y],2)
with tf.Session() as sess:
print('z1')
print(z1.eval())
print('z2')
print(z2.eval())
print('z3')
print(z3.eval())
z1
[[[ 1. 1. 1. 1. 1.]
[ 1. 1. 1. 1. 1.]
[ 1. 1. 1. 1. 1.]
[ 1. 1. 1. 1. 1.]]
[[ 1. 1. 1. 1. 1.]
[ 1. 1. 1. 1. 1.]
[ 1. 1. 1. 1. 1.]
[ 1. 1. 1. 1. 1.]]
[[ 1. 1. 1. 1. 1.]
[ 1. 1. 1. 1. 1.]
[ 1. 1. 1. 1. 1.]
[ 1. 1. 1. 1. 1.]]
[[ 2. 2. 2. 2. 2.]
[ 2. 2. 2. 2. 2.]
[ 2. 2. 2. 2. 2.]
[ 2. 2. 2. 2. 2.]]
[[ 2. 2. 2. 2. 2.]
[ 2. 2. 2. 2. 2.]
[ 2. 2. 2. 2. 2.]
[ 2. 2. 2. 2. 2.]]
[[ 2. 2. 2. 2. 2.]
[ 2. 2. 2. 2. 2.]
[ 2. 2. 2. 2. 2.]
[ 2. 2. 2. 2. 2.]]]
z2
[[[ 1. 1. 1. 1. 1.]
[ 1. 1. 1. 1. 1.]
[ 1. 1. 1. 1. 1.]
[ 1. 1. 1. 1. 1.]
[ 2. 2. 2. 2. 2.]
[ 2. 2. 2. 2. 2.]
[ 2. 2. 2. 2. 2.]
[ 2. 2. 2. 2. 2.]]
[[ 1. 1. 1. 1. 1.]
[ 1. 1. 1. 1. 1.]
[ 1. 1. 1. 1. 1.]
[ 1. 1. 1. 1. 1.]
[ 2. 2. 2. 2. 2.]
[ 2. 2. 2. 2. 2.]
[ 2. 2. 2. 2. 2.]
[ 2. 2. 2. 2. 2.]]
[[ 1. 1. 1. 1. 1.]
[ 1. 1. 1. 1. 1.]
[ 1. 1. 1. 1. 1.]
[ 1. 1. 1. 1. 1.]
[ 2. 2. 2. 2. 2.]
[ 2. 2. 2. 2. 2.]
[ 2. 2. 2. 2. 2.]
[ 2. 2. 2. 2. 2.]]]
z3
[[[ 1. 1. 1. 1. 1. 2. 2. 2. 2. 2.]
[ 1. 1. 1. 1. 1. 2. 2. 2. 2. 2.]
[ 1. 1. 1. 1. 1. 2. 2. 2. 2. 2.]
[ 1. 1. 1. 1. 1. 2. 2. 2. 2. 2.]]
[[ 1. 1. 1. 1. 1. 2. 2. 2. 2. 2.]
[ 1. 1. 1. 1. 1. 2. 2. 2. 2. 2.]
[ 1. 1. 1. 1. 1. 2. 2. 2. 2. 2.]
[ 1. 1. 1. 1. 1. 2. 2. 2. 2. 2.]]
[[ 1. 1. 1. 1. 1. 2. 2. 2. 2. 2.]
[ 1. 1. 1. 1. 1. 2. 2. 2. 2. 2.]
[ 1. 1. 1. 1. 1. 2. 2. 2. 2. 2.]
[ 1. 1. 1. 1. 1. 2. 2. 2. 2. 2.]]]
split
Tensorを指定した次元方向に分割する
import tensorflow as tf
n = np.arange(25).reshape((1,5,5))
x = tf.concat([n, n*10, n*100],0)
with tf.Session() as sess:
print(x.eval())
[[[ 0 1 2 3 4]
[ 5 6 7 8 9]
[ 10 11 12 13 14]
[ 15 16 17 18 19]
[ 20 21 22 23 24]]
[[ 0 10 20 30 40]
[ 50 60 70 80 90]
[ 100 110 120 130 140]
[ 150 160 170 180 190]
[ 200 210 220 230 240]]
[[ 0 100 200 300 400]
[ 500 600 700 800 900]
[1000 1100 1200 1300 1400]
[1500 1600 1700 1800 1900]
[2000 2100 2200 2300 2400]]]
0次元方向に3つに分割した例
import tensorflow as tf
y1, y2, y3 = tf.split(x, 3, 0)
with tf.Session() as sess:
print('y1')
print(y1.eval())
print('y2')
print(y2.eval())
print('y3')
print(y3.eval())
y1
[[[ 0 1 2 3 4]
[ 5 6 7 8 9]
[10 11 12 13 14]
[15 16 17 18 19]
[20 21 22 23 24]]]
y2
[[[ 0 10 20 30 40]
[ 50 60 70 80 90]
[100 110 120 130 140]
[150 160 170 180 190]
[200 210 220 230 240]]]
y3
[[[ 0 100 200 300 400]
[ 500 600 700 800 900]
[1000 1100 1200 1300 1400]
[1500 1600 1700 1800 1900]
[2000 2100 2200 2300 2400]]]
tile
import tensorflow as tf
x = tf.constant([[1,0],[0,1]])
with tf.Session() as sess:
print(x.eval())
[[1 0]
[0 1]]
繰り返したい次元方向を指定する。下記は0次元方向に2回繰り返した例。
import tensorflow as tf
y = tf.tile(x, [2,1])
with tf.Session() as sess:
print(y.eval())
[[1 0]
[0 1]
[1 0]
[0 1]]
1次元方向に2回繰り返した例
import tensorflow as tf
y = tf.tile(x, [1,2])
with tf.Session() as sess:
print(y.eval())
[[1 0 1 0]
[0 1 0 1]]
0次元方向と1次元方向に2回繰り返した例
import tensorflow as tf
y = tf.tile(x, [2,2])
with tf.Session() as sess:
print(y.eval())
[[1 0 1 0]
[0 1 0 1]
[1 0 1 0]
[0 1 0 1]]
pad
0 paddingする
import tensorflow as tf
n = np.arange(25).reshape((5,5))
x = tf.constant(n)
with tf.Session() as sess:
print(x.eval())
[[ 0 1 2 3 4]
[ 5 6 7 8 9]
[10 11 12 13 14]
[15 16 17 18 19]
[20 21 22 23 24]]
topに1、bottomに2、leftに3、rightに4つ分0 paddingした例
import tensorflow as tf
y = tf.pad(x,[[1,2],[3,4]])
with tf.Session() as sess:
print(y.eval())
[[ 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0]
[ 0 0 0 0 1 2 3 4 0 0 0 0]
[ 0 0 0 5 6 7 8 9 0 0 0 0]
[ 0 0 0 10 11 12 13 14 0 0 0 0]
[ 0 0 0 15 16 17 18 19 0 0 0 0]
[ 0 0 0 20 21 22 23 24 0 0 0 0]
[ 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0]
[ 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0]]
実行環境
Anaconda 4.4.0
python 3.5.3
tensorflow 1.3.0