はじめに
[2021/4/20 更新] 以前書いたものよりいい感じに書けたものがこちらです。
このリポジトリは、Kerasによる学習とMlflow RegistoryとFastAPIを組み合わせたものになっています。
普段Flaskをよく使いますが、「FastAPIはいいぞ!」と知人に進められたので簡単な画像認識APIを作って見ようと思いました。
しかし、あまりFastAPIとMLの日本語記事を見かけなかったので、メモ代わりに本記事を作成することにしました!
本記事では、開発環境を整えた後、APIサーバとフロントエンドの簡単な説明を記載しております。
今回使用したコードはすべてGithubに公開しています。
(以下実装のフォルダ構成などはGithubを前提に記載しています。サンプルモデルのダウンロードについてもREADME.mdに記載しています。)
FastAPIとは?
FlaskのようなPythonのフレームワークの1つです。
かんたんな概要と使い方のまとめは、以下の記事を参照していただけると良いと思います。(本記事でも大変お世話になりました、ありがとうございます!!)
もっと詳しく知りたい方は、FastAPIの公式チュートリアルが充実しておりオススメです!
画像認識について
今回は時間がなかったため、tensorflow.kerasのモデルを使って構築します!
具体的には、imagenetで学習されたResNet50をそのまま利用し、入力画像を1000クラスのどれに属するかを推論することとします。
(本当に使いたかったモデルは、只今絶賛学習中で間に合わなかった...)
https://www.tensorflow.org/versions/r1.15/api_docs/python/tf/keras?hl=ja
開発環境
Mac OS X Mojave
Python3.7.1(Anaconda)
環境構築
必要なPythonライブラリをインストールします。
$pip install tensorflow==1.15
$pip install fastapi
$pip install uvicorn
以下のような条件があることから、それに必要なライブラリもインストールします。
- index.htmlをRenderする
- 画像ファイルをアップロードする
- 画像を読み込み、リサイズする
$pip install Jinja
$pip install aiofiles
$pip install python-multipart
$pip install opencv-python
APIサーバ
APIサーバの実装は以下のようになりました。
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
import io
from typing import List
import cv2
import numpy as np
import tensorflow as tf
from tensorflow.keras.applications.resnet50 import decode_predictions
from fastapi import FastAPI, Request, File, UploadFile
from fastapi.staticfiles import StaticFiles
from fastapi.templating import Jinja2Templates
# 画像認識モデルの用意
global model, graph
graph = tf.get_default_graph()
model = tf.keras.models.load_model("./static/model/resnet_imagenet.h5")
# FastAPIの用意
app = FastAPI()
# static/js/post.jsをindex.htmlから呼び出すために必要
app.mount("/static", StaticFiles(directory="static"), name="static")
# templates配下に格納したindex.htmlをrenderするために必要
templates = Jinja2Templates(directory="templates")
def read_image(bin_data, size=(224, 224)):
"""画像を読み込む
Arguments:
bin_data {bytes} -- 画像のバイナリデータ
Keyword Arguments:
size {tuple} -- リサイズしたい画像サイズ (default: {(224, 224)})
Returns:
numpy.array -- 画像
"""
file_bytes = np.asarray(bytearray(bin_data.read()), dtype=np.uint8)
img = cv2.imdecode(file_bytes, cv2.IMREAD_COLOR)
img = cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)
img = cv2.resize(img, size)
return img
@app.post("/api/image_recognition")
async def image_recognition(files: List[UploadFile] = File(...)):
"""画像認識API
Keyword Arguments:
files {List[UploadFile]} -- アップロードされたファイル情報 (default: {File(...)})
Returns:
dict -- 推論結果
"""
bin_data = io.BytesIO(files[0].file.read())
img = read_image(bin_data)
with graph.as_default():
pred = model.predict(np.expand_dims(img, axis=0))
result_label = decode_predictions(pred, top=1)[0][0][1]
return {"response": result_label}
@app.get("/")
async def index(request: Request):
return templates.TemplateResponse("index.html", {"request": request})
フロントからデータを受け取る
@app.post("/api/image_recognition")
async def image_recognition(files: List[UploadFile] = File(...)):
"""画像認識API
Keyword Arguments:
files {List[UploadFile]} -- アップロードされたファイル情報 (default: {File(...)})
Returns:
dict -- 推論結果
"""
bin_data = io.BytesIO(files[0].file.read())
img = read_image(bin_data)
with graph.as_default():
pred = model.predict(np.expand_dims(img, axis=0))
result_label = decode_predictions(pred, top=1)[0][0][1]
return {"response": result_label}
今回は、FastAPIのUploadFileを使用してPOSTされる画像を取得しております。
bin_data = io.BytesIO(files[0].file.read())
ファイルは一つしかPOSTされないのでfiles[0]としており、フロント側からBASE64形式で渡されるのでAPI側でBytes配列に変換しました。
データを画像に変換する
def read_image(bin_data, size=(224, 224)):
"""画像を読み込む
Arguments:
bin_data {bytes} -- 画像のバイナリデータ
Keyword Arguments:
size {tuple} -- リサイズしたい画像サイズ (default: {(224, 224)})
Returns:
numpy.array -- 画像
"""
file_bytes = np.asarray(bytearray(bin_data.read()), dtype=np.uint8)
img = cv2.imdecode(file_bytes, cv2.IMREAD_COLOR)
img = cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)
img = cv2.resize(img, size)
return img
opencvの力を借りて、Byte配列からuint8の画像に変換します。
このとき、opencvのデフォルトフォーマットがBGRなため、RGBに変換してリサイズしました。
推論する
global model, graph
graph = tf.get_default_graph()
model = tf.keras.models.load_model("./static/model/resnet_imagenet.h5")
...
with graph.as_default():
pred = model.predict(np.expand_dims(img, axis=0))
result_label = decode_predictions(pred, top=1)[0][0][1]
事前にresnet_imagenet.h5を作成しておき、それをファイル上部で読み込んでいます。
推論処理自体は、with graph.as_default() でグローバルで設定したTensorFlowのグラフにこのスレッドでのコンテキストを固定して、predict関数で推論しています。
今回はtf.kerasのResNet50を使っていることから、predictの結果をラベルに変換するdecode_predictionsを使って推論結果を取得しています。
他のモデルや自作モデルも、プロジェクトディレクトリのどこかに.h5ファイルを保存しておき、それをload_modelすることで、この実装のように使うことができるかと思います。
フロント実装
こちらを参考にさせていただきました。(ありがとうございます!)
<html>
<head>
<meta http-qeuiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=utf-8">
<title>Fastapi 画像認識テスト</title>
<script src="//code.jquery.com/jquery-2.2.3.min.js"></script>
<script src="/static/js/post.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<!-- ファイル選択ボタン -->
<div style="width: 500px">
<form enctype="multipart/form-data" method="post">
<input type="file" name="userfile" accept="image/*">
</form>
</div>
<!-- 画像表示領域 -->
<canvas id="canvas" width="0" height="0"></canvas>
<!-- アップロード開始ボタン -->
<button class="btn btn-primary" id="post">投稿</button>
<br>
<h2 id="result"></h2>
</body>
</html>
// 画像をリサイズして、HTMLで表示する
$(function () {
var file = null;
var blob = null;
const RESIZED_WIDTH = 300;
const RESIZED_HEIGHT = 300;
$("input[type=file]").change(function () {
file = $(this).prop("files")[0];
// ファイルチェック
if (file.type != "image/jpeg" && file.type != "image/png") {
file = null;
blob = null;
return;
}
var result = document.getElementById("result");
result.innerHTML = "";
// 画像をリサイズする
var image = new Image();
var reader = new FileReader();
reader.onload = function (e) {
image.onload = function () {
var width, height;
// 縦or横の長い方に合わせてリサイズする
if (image.width > image.height) {
var ratio = image.height / image.width;
width = RESIZED_WIDTH;
height = RESIZED_WIDTH * ratio;
} else {
var ratio = image.width / image.height;
width = RESIZED_HEIGHT * ratio;
height = RESIZED_HEIGHT;
}
var canvas = $("#canvas").attr("width", width).attr("height", height);
var ctx = canvas[0].getContext("2d");
ctx.clearRect(0, 0, width, height);
ctx.drawImage(
image,
0,
0,
image.width,
image.height,
0,
0,
width,
height
);
// canvasからbase64画像データを取得し、POST用のBlobを作成する
var base64 = canvas.get(0).toDataURL("image/jpeg");
var barr, bin, i, len;
bin = atob(base64.split("base64,")[1]);
len = bin.length;
barr = new Uint8Array(len);
i = 0;
while (i < len) {
barr[i] = bin.charCodeAt(i);
i++;
}
blob = new Blob([barr], { type: "image/jpeg" });
console.log(blob);
};
image.src = e.target.result;
};
reader.readAsDataURL(file);
});
// アップロード開始ボタンがクリックされたら
$("#post").click(function () {
if (!file || !blob) {
return;
}
var name,
fd = new FormData();
fd.append("files", blob);
// API宛にPOSTする
$.ajax({
url: "/api/image_recognition",
type: "POST",
dataType: "json",
data: fd,
processData: false,
contentType: false,
})
.done(function (data, textStatus, jqXHR) {
// 通信が成功した場合、結果を出力する
var response = JSON.stringify(data);
var response = JSON.parse(response);
console.log(response);
var result = document.getElementById("result");
result.innerHTML = "この画像...「" + response["response"] + "」やんけ";
})
.fail(function (jqXHR, textStatus, errorThrown) {
// 通信が失敗した場合、エラーメッセージを出力する
var result = document.getElementById("result");
result.innerHTML = "サーバーとの通信が失敗した...";
});
});
});
ajaxを使って画像認識APIへPOSTを行い、結果を表示しています。
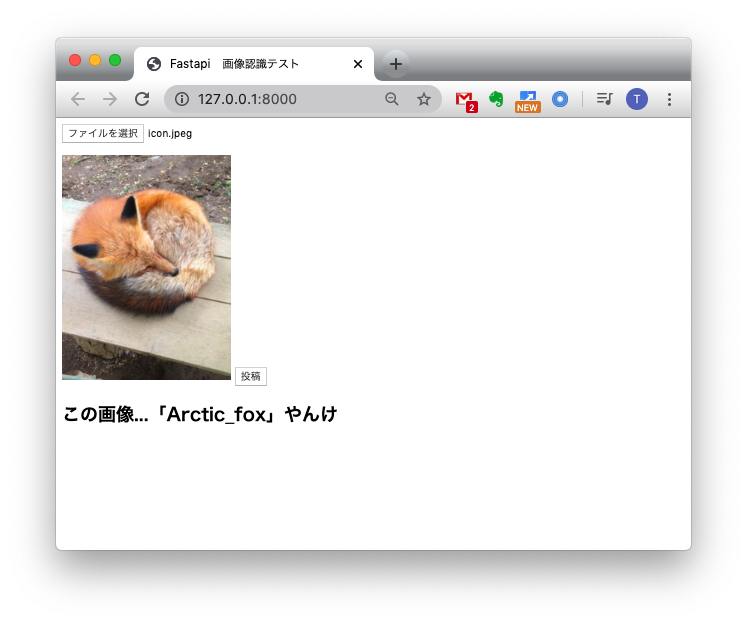
動作確認
(フロントをもうちょっとオサレにしたかったのですが...)
おわりに
FastAPIのお勉強に画像認識APIを作ってみました。
今回作った実装がベストプラクティスではないと思いますが、動くものをつくることができてよかったかと思います。
今後どのフレームワークを使って仕事をするかわかりませんが、FastAPIは割と使いやすくてFlaskから乗り換えようかなぁと思いました。
最後となりますが、参考にさせていただいた皆様に感謝いたします!