Grad-CAM,Grad-CAM++,Score-CAM の実装と比較
はじめに
アルバイトや趣味で機械学習について学習している大学生です。
色々な CAM(Class Activation Map)について調べて実際に使用してみたのでまとめました。
CAM とは
CAM(Class Activation Map)とは、畳み込みニューラルネットワークがどこを注視して判断をしているのかということを可視化する手法です。
可視化するメリット
- 間違った出力をした根拠を知り、次の改善への目星をつけられる
- 正解を導き出していても周辺の背景などの関係のないものによって判断されていることが確認できる
- 人間が考えつかない要素による判断を見て新しい発見が得られる
などがあげられます。
使ってみる
今回は CAM の中で有名な Grad-CAM, Grad-CAM++, Score-CAM について実装し、比較していきます。
こちら のコードを参考にします.
使用するモデルは VGG16 です.
Grad-CAM
Grad-CAM とは
- CNN の判断根拠の可視化手法のひとつ
- Grad-CAM より前に発表された CAM を改良し、どんなモデルでも使用できるようになった.
- 論文はこちら
実装する
def GradCam(model, x, layer_name):
"""Grad-CAM function"""
cls = np.argmax(model.predict(x))
y_c = model.output[0, cls]
conv_output = model.get_layer(layer_name).output
grads = K.gradients(y_c, conv_output)[0]
# Get outputs and grads
gradient_function = K.function([model.input], [conv_output, grads])
output, grads_val = gradient_function([x])
output, grads_val = output[0, :], grads_val[0, :, :, :]
weights = np.mean(grads_val, axis=(0, 1)) # Passing through GlobalAveragePooling
cam = np.dot(output, weights) # multiply
cam = np.maximum(cam, 0) # Passing through ReLU
cam /= np.max(cam) # scale 0 to 1.0
return cam
Grad-CAM++
Grad-CAM++とは
- Grad-CAM を改良し、よりわかりやすく視覚化できるようにしたもの
- 論文はこちら
実装する
def GradCamPlusPlus(model, x, layer_name):
"""Grad-CAM++ function"""
cls = np.argmax(model.predict(x))
y_c = model.output[0, cls]
conv_output = model.get_layer(layer_name).output
grads = K.gradients(y_c, conv_output)[0]
first = K.exp(y_c) * grads
second = K.exp(y_c) * grads * grads
third = K.exp(y_c) * grads * grads * grads
gradient_function = K.function([model.input], [y_c, first, second, third, conv_output, grads])
y_c, conv_first_grad, conv_second_grad, conv_third_grad, conv_output, grads_val = gradient_function([x])
global_sum = np.sum(conv_output[0].reshape((-1,conv_first_grad[0].shape[2])), axis=0)
alpha_num = conv_second_grad[0]
alpha_denom = conv_second_grad[0] * 2.0 + conv_third_grad[0] * global_sum.reshape((1, 1, conv_first_grad[0].shape[2]))
alpha_denom = np.where(alpha_denom != 0.0, alpha_denom, np.ones(alpha_denom.shape))
alphas = alpha_num / alpha_denom # 0
weights = np.maximum(conv_first_grad[0], 0.0)
alpha_normalization_constant = np.sum(np.sum(alphas, axis=0), axis=0) # 0
alphas /= alpha_normalization_constant.reshape((1, 1, conv_first_grad[0].shape[2])) # NAN
deep_linearization_weights = np.sum((weights * alphas).reshape((-1, conv_first_grad[0].shape[2])), axis=0)
cam = np.sum(deep_linearization_weights * conv_output[0], axis=2)
cam = np.maximum(cam, 0) # Passing through ReLU
cam /= np.max(cam) # scale 0 to 1.0
return cam
Score-CAM
Score-CAM とは
- 2019 年 10 月に発表された比較的新しい可視化手法
- Grad-CAM や Grad-CAM++で使用されていた勾配への依存を取り除いた可視化手法
- 論文はこちら
実装する
def softmax(x):
"""softmax"""
return np.exp(x) / np.sum(np.exp(x), axis=1, keepdims=True)
def ScoreCam(model, x, layer_name, max_N=-1):
"""Score-CAM function"""
cls = np.argmax(model.predict(img_array))
act_map_array = Model(inputs=model.input, outputs=model.get_layer(layer_name).output).predict(img_array)
# extract effective maps
if max_N != -1:
act_map_std_list = [np.std(act_map_array[0,:,:,k]) for k in range(act_map_array.shape[3])]
unsorted_max_indices = np.argpartition(-np.array(act_map_std_list), max_N)[:max_N]
max_N_indices = unsorted_max_indices[np.argsort(-np.array(act_map_std_list)[unsorted_max_indices])]
act_map_array = act_map_array[:,:,:,max_N_indices]
input_shape = model.layers[0].output_shape[0][1:] # get input shape
# 1. upsampled to original input size
act_map_resized_list = [cv2.resize(act_map_array[0,:,:,k], input_shape[:2], interpolation=cv2.INTER_LINEAR) for k in range(act_map_array.shape[3])]
# 2. normalize the raw activation value in each activation map into [0, 1]
act_map_normalized_list = []
for act_map_resized in act_map_resized_list:
if np.max(act_map_resized) - np.min(act_map_resized) != 0:
act_map_normalized = act_map_resized / (np.max(act_map_resized) - np.min(act_map_resized))
else:
act_map_normalized = act_map_resized
act_map_normalized_list.append(act_map_normalized)
# 3. project highlighted area in the activation map to original input space by multiplying the normalized activation map
masked_input_list = []
for act_map_normalized in act_map_normalized_list:
masked_input = np.copy(img_array)
for k in range(3):
masked_input[0,:,:,k] *= act_map_normalized
masked_input_list.append(masked_input)
masked_input_array = np.concatenate(masked_input_list, axis=0)
# 4. feed masked inputs into CNN model and softmax
pred_from_masked_input_array = softmax(model.predict(masked_input_array))
# 5. define weight as the score of target class
weights = pred_from_masked_input_array[:,cls]
# 6. get final class discriminative localization map as linear weighted combination of all activation maps
cam = np.dot(act_map_array[0,:,:,:], weights)
cam = np.maximum(0, cam) # Passing through ReLU
cam /= np.max(cam) # scale 0 to 1.0
return cam
各 CAM の実行
コード全文
from tensorflow.keras.models import Model
from tensorflow.keras.applications.vgg16 import VGG16, preprocess_input,decode_predictions
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import cv2
import numpy as np
import tensorflow as tf
from tensorflow.keras import backend as K
from tensorflow.keras.models import Model
import gc
import tensorflow.keras
import tensorflow as tf
from tensorflow.python.framework import ops
from tensorflow.keras.applications.vgg16 import preprocess_input
from tensorflow.keras.preprocessing.image import load_img, img_to_array
tf.compat.v1.disable_eager_execution()
def sigmoid(x, a, b, c):
return c / (1 + np.exp(-a * (x-b)))
def superimpose(original_img_path, cam, emphasize=False):
img_bgr = cv2.imread(original_img_path)
heatmap = cv2.resize(cam, (img_bgr.shape[1], img_bgr.shape[0]))
if emphasize:
heatmap = sigmoid(heatmap, 50, 0.5, 1)
heatmap = np.uint8(255 * heatmap)
heatmap = cv2.applyColorMap(heatmap, cv2.COLORMAP_JET)
hif = .8
superimposed_img = heatmap * hif + img_bgr
superimposed_img = np.minimum(superimposed_img, 255.0).astype(np.uint8) # scale 0 to 255
superimposed_img_rgb = cv2.cvtColor(superimposed_img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)
return superimposed_img_rgb
def GradCam(model, x, layer_name):
"""Grad-CAM function"""
cls = np.argmax(model.predict(x))
y_c = model.output[0, cls]
conv_output = model.get_layer(layer_name).output
grads = K.gradients(y_c, conv_output)[0]
# Get outputs and grads
gradient_function = K.function([model.input], [conv_output, grads])
output, grads_val = gradient_function([x])
output, grads_val = output[0, :], grads_val[0, :, :, :]
weights = np.mean(grads_val, axis=(0, 1)) # Passing through GlobalAveragePooling
cam = np.dot(output, weights) # multiply
cam = np.maximum(cam, 0) # Passing through ReLU
cam /= np.max(cam) # scale 0 to 1.0
return cam
def GradCamPlusPlus(model, x, layer_name):
"""Grad-CAM++ function"""
cls = np.argmax(model.predict(x))
y_c = model.output[0, cls]
conv_output = model.get_layer(layer_name).output
grads = K.gradients(y_c, conv_output)[0]
first = K.exp(y_c) * grads
second = K.exp(y_c) * grads * grads
third = K.exp(y_c) * grads * grads * grads
gradient_function = K.function([model.input], [y_c, first, second, third, conv_output, grads])
y_c, conv_first_grad, conv_second_grad, conv_third_grad, conv_output, grads_val = gradient_function([x])
global_sum = np.sum(conv_output[0].reshape((-1,conv_first_grad[0].shape[2])), axis=0)
alpha_num = conv_second_grad[0]
alpha_denom = conv_second_grad[0] * 2.0 + conv_third_grad[0] * global_sum.reshape((1, 1, conv_first_grad[0].shape[2]))
alpha_denom = np.where(alpha_denom != 0.0, alpha_denom, np.ones(alpha_denom.shape))
alphas = alpha_num / alpha_denom # 0
weights = np.maximum(conv_first_grad[0], 0.0)
alpha_normalization_constant = np.sum(np.sum(alphas, axis=0), axis=0) # 0
alphas /= alpha_normalization_constant.reshape((1, 1, conv_first_grad[0].shape[2])) # NAN
deep_linearization_weights = np.sum((weights * alphas).reshape((-1, conv_first_grad[0].shape[2])), axis=0)
cam = np.sum(deep_linearization_weights * conv_output[0], axis=2)
cam = np.maximum(cam, 0) # Passing through ReLU
cam /= np.max(cam) # scale 0 to 1.0
return cam
def read_and_preprocess_img(path, size=(224,224)):
img = load_img(path, target_size=size)
x = img_to_array(img)
x = np.expand_dims(x, axis=0)
x = preprocess_input(x)
return x
def softmax(x):
"""softmax"""
return np.exp(x) / np.sum(np.exp(x), axis=1, keepdims=True)
def ScoreCam(model, x, layer_name, max_N=-1):
"""Score-CAM function"""
cls = np.argmax(model.predict(img_array))
act_map_array = Model(inputs=model.input, outputs=model.get_layer(layer_name).output).predict(img_array)
# extract effective maps
if max_N != -1:
act_map_std_list = [np.std(act_map_array[0,:,:,k]) for k in range(act_map_array.shape[3])]
unsorted_max_indices = np.argpartition(-np.array(act_map_std_list), max_N)[:max_N]
max_N_indices = unsorted_max_indices[np.argsort(-np.array(act_map_std_list)[unsorted_max_indices])]
act_map_array = act_map_array[:,:,:,max_N_indices]
input_shape = model.layers[0].output_shape[0][1:] # get input shape
# 1. upsampled to original input size
act_map_resized_list = [cv2.resize(act_map_array[0,:,:,k], input_shape[:2], interpolation=cv2.INTER_LINEAR) for k in range(act_map_array.shape[3])]
# 2. normalize the raw activation value in each activation map into [0, 1]
act_map_normalized_list = []
for act_map_resized in act_map_resized_list:
if np.max(act_map_resized) - np.min(act_map_resized) != 0:
act_map_normalized = act_map_resized / (np.max(act_map_resized) - np.min(act_map_resized))
else:
act_map_normalized = act_map_resized
act_map_normalized_list.append(act_map_normalized)
# 3. project highlighted area in the activation map to original input space by multiplying the normalized activation map
masked_input_list = []
for act_map_normalized in act_map_normalized_list:
masked_input = np.copy(img_array)
for k in range(3):
masked_input[0,:,:,k] *= act_map_normalized
masked_input_list.append(masked_input)
masked_input_array = np.concatenate(masked_input_list, axis=0)
# 4. feed masked inputs into CNN model and softmax
pred_from_masked_input_array = softmax(model.predict(masked_input_array))
# 5. define weight as the score of target class
weights = pred_from_masked_input_array[:,cls]
# 6. get final class discriminative localization map as linear weighted combination of all activation maps
cam = np.dot(act_map_array[0,:,:,:], weights)
cam = np.maximum(0, cam) # Passing through ReLU
cam /= np.max(cam) # scale 0 to 1.0
return cam
from tensorflow.keras.preprocessing.image import load_img
from tensorflow.keras.applications.vgg16 import VGG16, preprocess_input, decode_predictions
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import cv2
import numpy as np
model = VGG16(include_top=True, weights='imagenet')
layer_name = 'block5_conv3'
img_path = 'mitte44034_TP_V4.jpg'
orig_img = np.array(load_img(img_path),dtype=np.uint8)
img_array = read_and_preprocess_img(img_path, size=(224,224))
predictions = model.predict(img_array)
top = decode_predictions(predictions, top=5)[0]
print(img_path)
print("class activation map for:",top[0])
grad_cam=GradCam(model,img_array,layer_name)
grad_cam_superimposed = superimpose(img_path, grad_cam)
grad_cam_emphasized = superimpose(img_path, grad_cam, emphasize=True)
grad_cam_plus_plus=GradCamPlusPlus(model,img_array,layer_name)
grad_cam_plus_plus_superimposed = superimpose(img_path, grad_cam_plus_plus)
grad_cam_plus_plus_emphasized = superimpose(img_path, grad_cam_plus_plus, emphasize=True)
score_cam=ScoreCam(model,img_array,layer_name)
score_cam_superimposed = superimpose(img_path, score_cam)
score_cam_emphasized = superimpose(img_path, score_cam, emphasize=True)
nrows = 2
ncols = 4
fig, ax = plt.subplots(nrows=nrows,ncols=ncols, figsize=(18, 11))
ax[0,0].imshow(orig_img)
ax[0,0].set_title("input image")
ax[0,1].imshow(grad_cam_superimposed)
ax[0,1].set_title("Grad-CAM")
ax[0,2].imshow(grad_cam_plus_plus_superimposed)
ax[0,2].set_title("Grad-CAM++")
ax[0,3].imshow(score_cam_superimposed)
ax[0,3].set_title("Score-CAM")
ax[1,0].imshow(orig_img)
ax[1,0].set_title("input image")
ax[1,1].imshow(grad_cam_emphasized)
ax[1,1].set_title("Grad-CAM emphasized")
ax[1,2].imshow(grad_cam_plus_plus_emphasized)
ax[1,2].set_title("Grad-CAM++ emphasized")
ax[1,3].imshow(score_cam_emphasized)
ax[1,3].set_title("Score-CAM emphasized")
for i in range(nrows):
for j in range(ncols):
ax[i,j].axis('off')
plt.show()
猫の画像で試した結果を以下に示します.
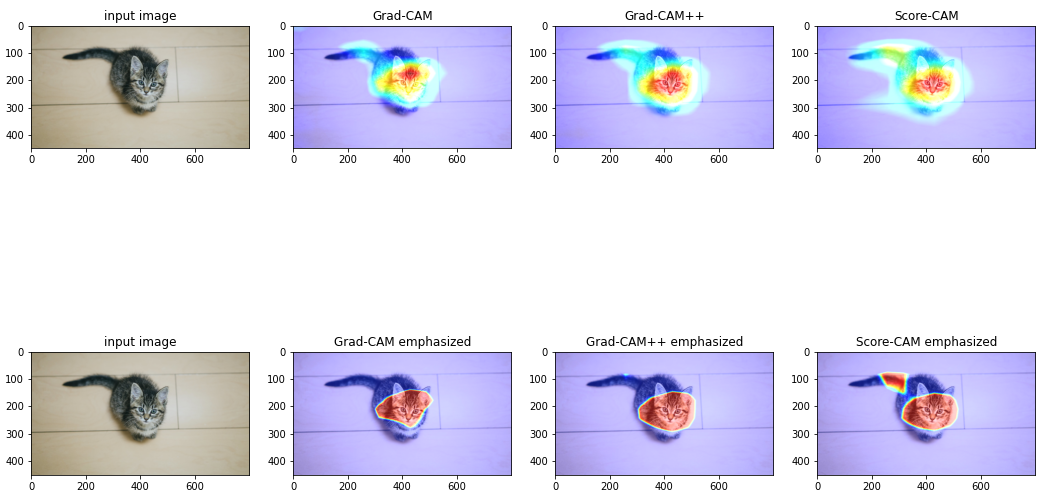
一段目左から順番にオリジナルの画像,Grad-CAM,Grad-CAM++,Score-CAM になります.
二段目は一段目の結果について強調表示です.
画像から、ぶち猫(tabby)と判断するにあたって主に顔を見て判断しているとわかります.
次にホオジロ(鳥)の画像でも試してみます
結果は以下の通りになりました.
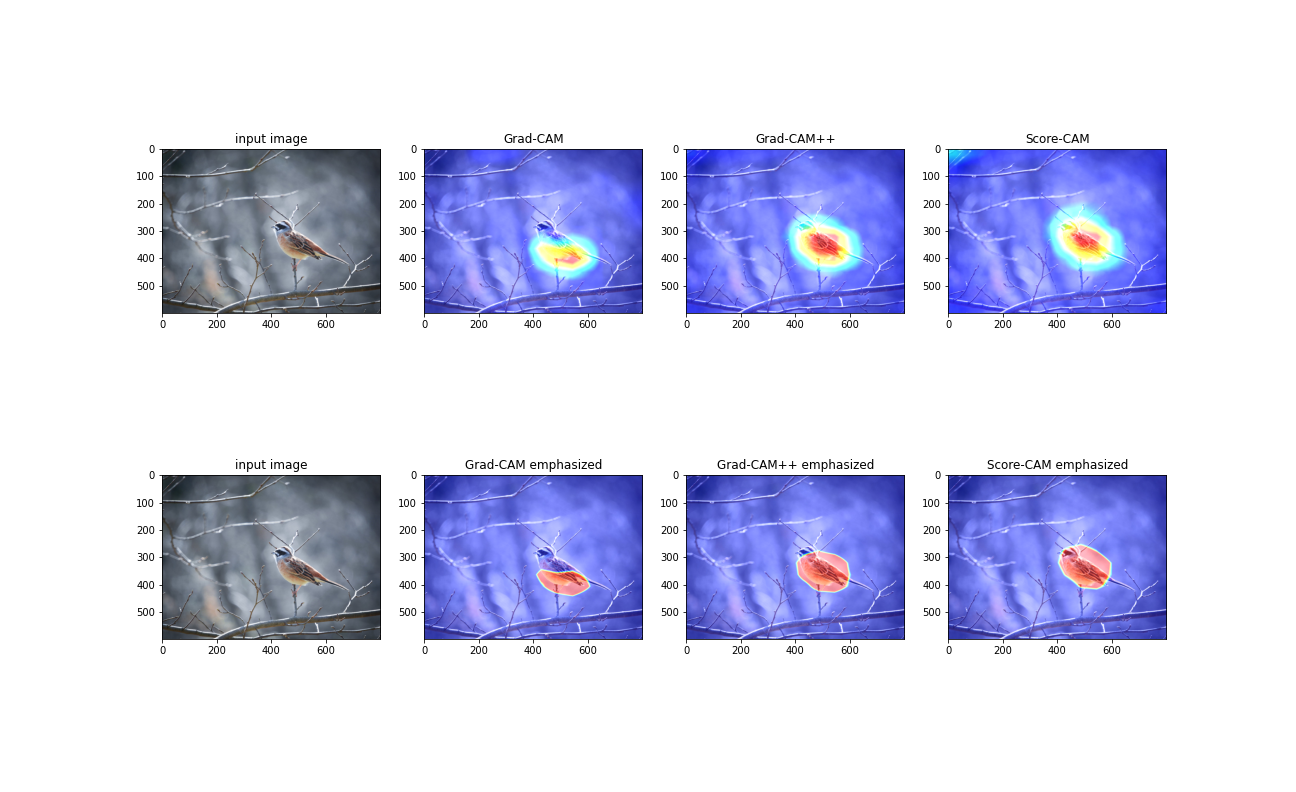
Grad-CAM では、鳥の下部分を見ているとなっていますが、Grad-CAM++や Score-CAM では鳥全体を見て判断しているとわかります.
まとめ
Grad-CAM では他の CAM に比べると局所的な部分を見ているようなヒートマップになり、Grad-CAM++と Score-CAM は似た結果となりました.
さらに論文にて指摘されている通り、Grad-CAM では任意のヒートマップを出力することができるようになると言われており、モデルの信憑性が失われることになります.
特別な理由がなければ Grad-CAM よりも Grad-CAM++や Score-CAM を使うべきだと感じました.