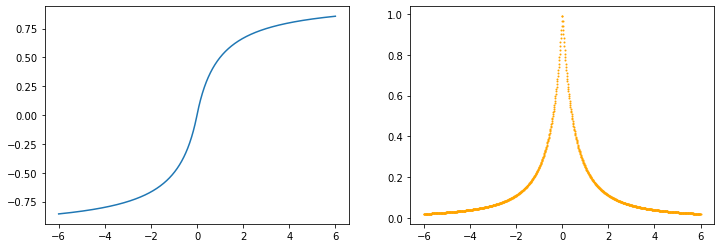はじめに
PyTorch の パッケージ TORCH.NN.FUNCTIONAL の非線形活性化関数 (Non-linear activation functions)をグラフ化しました。
目次
TORCH.NN.FUNCTIONAL 活性化関数のグラフ化
各関数のグラフをを一覧にしました。(左側の青いグラフ)
右側に微分値もあわせてグラフ化してみました。(右側のオレンジのグラフ)
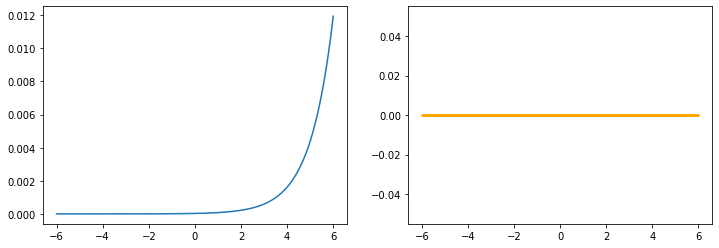
relu
import torch
import torch.nn.functional as F
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
'''
#############################################
## グラフを描画する
#############################################
'''
def drawGraph(x, y, y_dash):
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(12, 4))
ax1 = fig.add_subplot(1, 2, 1)
ax2 = fig.add_subplot(1, 2, 2)
ax1.plot(x, y)
ax2.scatter(x, y_dash, s=1, color='orange')
plt.show()
x=torch.linspace(-6, 6, 1000, dtype=torch.float, requires_grad=True)
y=F.relu(x)
z=y.sum()
z.backward()
z_dash=x.grad
drawGraph(x.detach().numpy(), y.detach().numpy(), z_dash.detach().numpy())
hardtanh
x=torch.linspace(-6, 6, 1000, dtype=torch.float, requires_grad=True)
y=F.hardtanh(x)
z=y.sum()
z.backward()
z_dash=x.grad
drawGraph(x.detach().numpy(), y.detach().numpy(), z_dash.detach().numpy())
relu6
x=torch.linspace(-6, 6, 1000, dtype=torch.float, requires_grad=True)
y=F.relu6(x)
z=y.sum()
z.backward()
z_dash=x.grad
drawGraph(x.detach().numpy(), y.detach().numpy(), z_dash.detach().numpy())
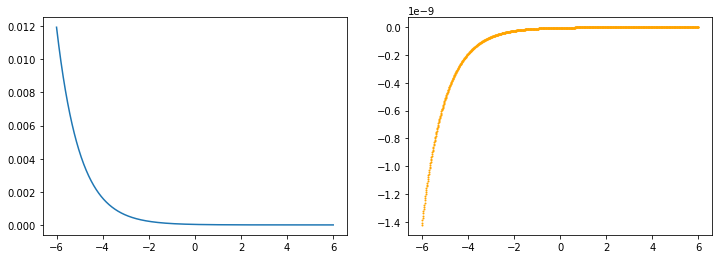
elu
x=torch.linspace(-6, 6, 1000, dtype=torch.float, requires_grad=True)
y=F.elu(x)
z=y.sum()
z.backward()
z_dash=x.grad
drawGraph(x.detach().numpy(), y.detach().numpy(), z_dash.detach().numpy())
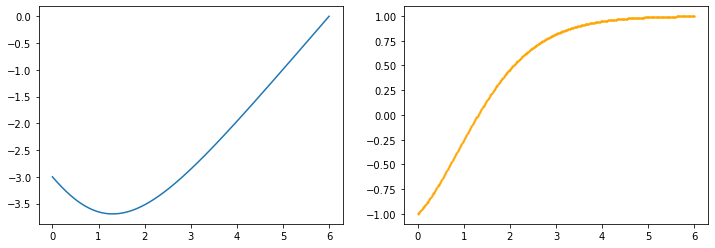
selu
x=torch.linspace(-6, 6, 1000, dtype=torch.float, requires_grad=True)
y=F.selu(x)
z=y.sum()
z.backward()
z_dash=x.grad
drawGraph(x.detach().numpy(), y.detach().numpy(), z_dash.detach().numpy())
celu
x=torch.linspace(-1, 1, 1000, dtype=torch.float, requires_grad=True)
y=F.celu(x)
z=y.sum()
z.backward()
z_dash=x.grad
drawGraph(x.detach().numpy(), y.detach().numpy(), z_dash.detach().numpy())
leaky_relu
x=torch.linspace(-6, 6, 1000, dtype=torch.float, requires_grad=True)
y=F.leaky_relu(x)
z=y.sum()
z.backward()
z_dash=x.grad
drawGraph(x.detach().numpy(), y.detach().numpy(), z_dash.detach().numpy())
prelu
x=torch.linspace(-6, 6, 1000, dtype=torch.float, requires_grad=True)
y=F.prelu(x, torch.tensor([0.25]))
z=y.sum()
z.backward()
z_dash=x.grad
drawGraph(x.detach().numpy(), y.detach().numpy(), z_dash.detach().numpy())
rrelu
x=torch.linspace(-6, 6, 1000, dtype=torch.float, requires_grad=True)
y=F.rrelu(x)
z=y.sum()
z.backward()
z_dash=x.grad
drawGraph(x.detach().numpy(), y.detach().numpy(), z_dash.detach().numpy())
glu
PyTorch の公式ドキュメント の記載を見ると、 glu は入力を2つに分け、
glu(x1,x2) = x1 * sigmoid(x2)
で計算されます。
x=torch.linspace(-6, 6, 1000, dtype=torch.float)
y=F.glu(x)
# xを2つに分解する
x1=torch.linspace(-6, 0, 500, dtype=torch.float, requires_grad=True)
x2=torch.linspace(0, 6, 500, dtype=torch.float, requires_grad=True)
y=torch.mul(x1, torch.sigmoid(x2))
z=y.sum()
z.backward()
# x1 x2 で自動微分
z_dash1=x1.grad
z_dash2=x2.grad
z_dash3=torch.add(z_dash1, z_dash2)
drawGraph(x2.detach().numpy(), y.detach().numpy(), z_dash3.detach().numpy())
gelu
x=torch.linspace(-6, 6, 1000, dtype=torch.float, requires_grad=True)
y=F.gelu(x)
z=y.sum()
z.backward()
z_dash=x.grad
drawGraph(x.detach().numpy(), y.detach().numpy(), z_dash.detach().numpy())
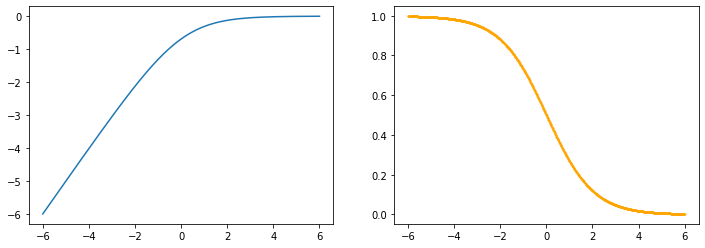
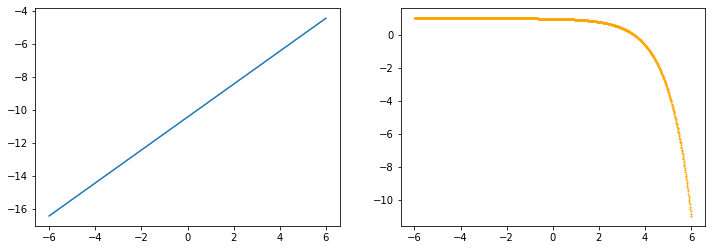
logsigmoid
x=torch.linspace(-6, 6, 1000, dtype=torch.float, requires_grad=True)
y=F.logsigmoid(x)
z=y.sum()
z.backward()
z_dash=x.grad
drawGraph(x.detach().numpy(), y.detach().numpy(), z_dash.detach().numpy())
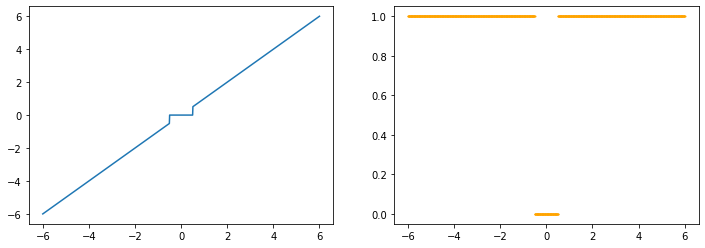
hardshrink
x=torch.linspace(-6, 6, 1000, dtype=torch.float, requires_grad=True)
y=F.hardshrink(x)
z=y.sum()
z.backward()
z_dash=x.grad
drawGraph(x.detach().numpy(), y.detach().numpy(), z_dash.detach().numpy())
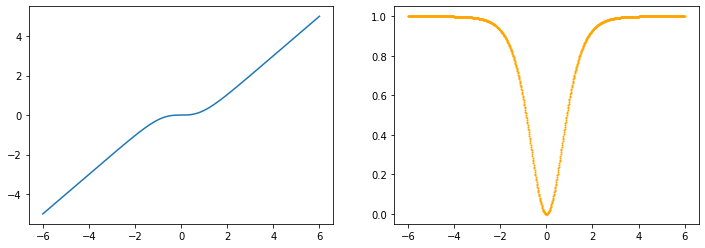
tanhshrink
x=torch.linspace(-6, 6, 1000, dtype=torch.float, requires_grad=True)
y=F.tanhshrink(x)
z=y.sum()
z.backward()
z_dash=x.grad
drawGraph(x.detach().numpy(), y.detach().numpy(), z_dash.detach().numpy())
softsign
x=torch.linspace(-6, 6, 1000, dtype=torch.float, requires_grad=True)
y=F.softsign(x)
z=y.sum()
z.backward()
z_dash=x.grad
drawGraph(x.detach().numpy(), y.detach().numpy(), z_dash.detach().numpy())
softplus
x=torch.linspace(-6, 6, 1000, dtype=torch.float, requires_grad=True)
y=F.softplus(x)
z=y.sum()
z.backward()
z_dash=x.grad
drawGraph(x.detach().numpy(), y.detach().numpy(), z_dash.detach().numpy())
softmin
x=torch.linspace(-6, 6, 1000, dtype=torch.float, requires_grad=True)
y=F.softmin(x, 0)
z=y.sum()
z.backward()
z_dash=x.grad
drawGraph(x.detach().numpy(), y.detach().numpy(), z_dash.detach().numpy())
softmax
x=torch.linspace(-6, 6, 200, dtype=torch.float)
y=F.softmax(x)
plt.plot(x.numpy(), y.numpy())
plt.show()
UserWarning: Implicit dimension choice for softmax has been deprecated. Change the call to include dim=X as an argument.
ソフトマックスは2次元だとうまくグラフ化できていないような気がします。
機会があればもう少し調べてみたいと思います。
softshrink
x=torch.linspace(-6, 6, 1000, dtype=torch.float, requires_grad=True)
y=F.softshrink(x)
z=y.sum()
z.backward()
z_dash=x.grad
drawGraph(x.detach().numpy(), y.detach().numpy(), z_dash.detach().numpy())
gumbel_softmax
x=torch.linspace(-6, 6, 200, dtype=torch.float)
y=F.gumbel_softmax(x)
plt.plot(x.numpy(), y.numpy())
plt.show()
gumbel_softmax もソフトマックスと同じくうまくグラフ化できていないようです。
log_softmax
x=torch.linspace(-6, 6, 1000, dtype=torch.float, requires_grad=True)
y=F.log_softmax(x, 0)
z=y.sum()
z.backward()
z_dash=x.grad
drawGraph(x.detach().numpy(), y.detach().numpy(), z_dash.detach().numpy())
tanh
x=torch.linspace(-6, 6, 1000, dtype=torch.float, requires_grad=True)
y=F.tanh(x)
z=y.sum()
z.backward()
z_dash=x.grad
drawGraph(x.detach().numpy(), y.detach().numpy(), z_dash.detach().numpy())
UserWarning: nn.functional.tanh is deprecated. Use torch.tanh instead.
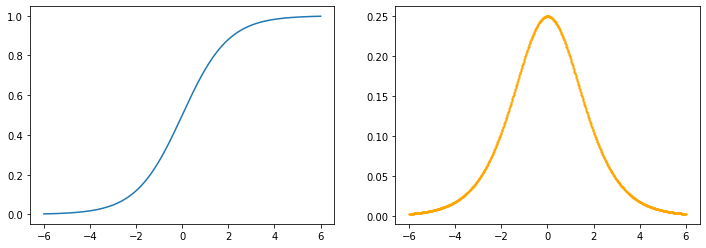
sigmoid
x=torch.linspace(-6, 6, 1000, dtype=torch.float, requires_grad=True)
y=F.sigmoid(x)
z=y.sum()
z.backward()
z_dash=x.grad
drawGraph(x.detach().numpy(), y.detach().numpy(), z_dash.detach().numpy())
UserWarning: nn.functional.sigmoid is deprecated. Use torch.sigmoid instead.
履歴
2020/04/18 初版公開