環境
この記事は以下の環境で動いています。
| 項目 | 値 |
|---|---|
| CPU | Core i5-8250U |
| Ubuntu | 20.04 |
| ROS | Noetic |
| Gazebo | 11.9.0 |
インストールについてはROS講座02 インストールを参照してください。
またこの記事のプログラムはgithubにアップロードされています。ROS講座11 gitリポジトリを参照してください。
概要
ロボットの重要な入力データとして画像があります。ROSでは画像処理はOpenCVを使って行います。ROSのバージョンとOpenCVのバージョンは紐づけられていて、NoeticではOpenCV4を使います。ROSをインストールしたときにOpenCVもインストールされるので、特に追加でインストールをする必要はありません。
シミュレーション環境の用意
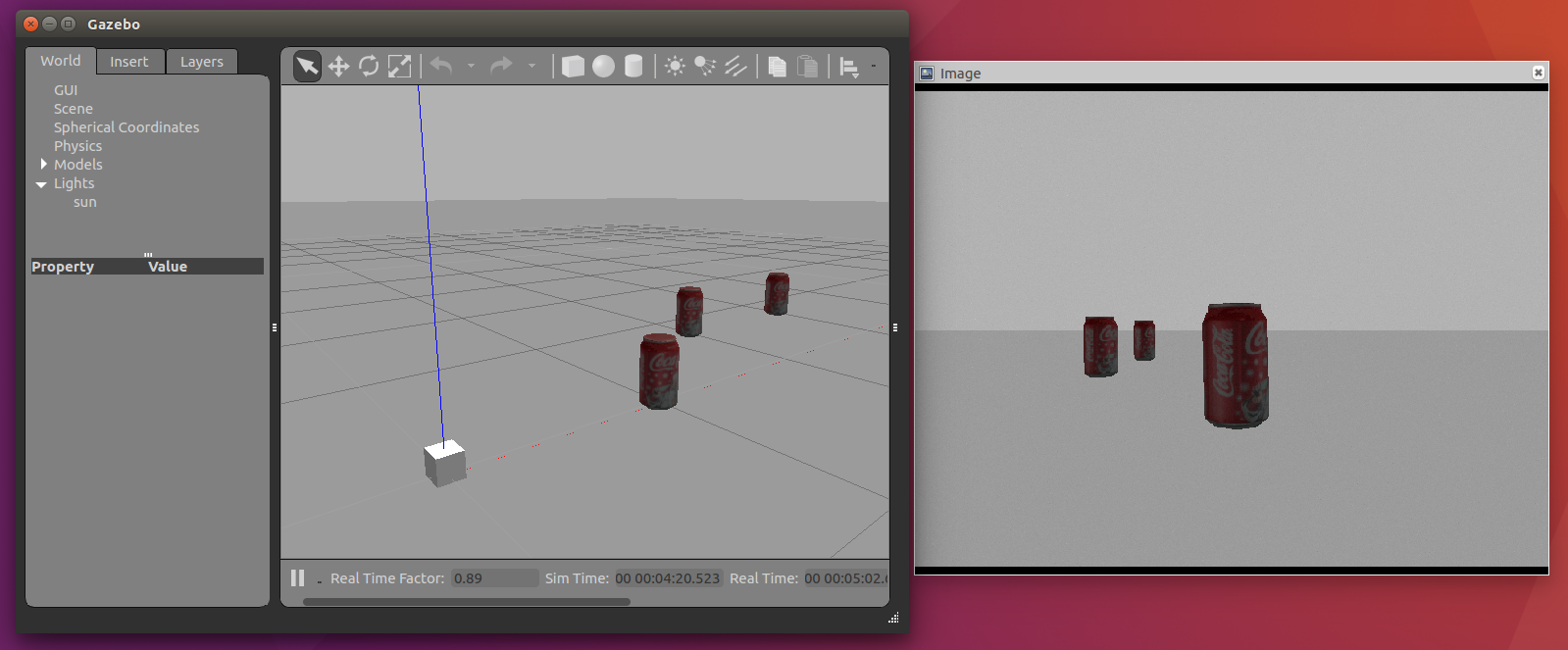
毎回実際のWebカメラをつないで実験するのは大変なのでシミュレーションで環境構築をします。カメラとカメラで写す対象のコーラの缶があるシミュレーション環境を用意します。
シミュレーターへの光源の追加
シミュレーターの初期設定ではワールド内がだいぶ暗く映ります。画像処理に影響が出そうなので光源を追加します。
ソースコード
sdf
カメラのついているモデルを作成します。
sim_env_lecture/models/sensor_station/model.sdf
world
カメラで写すコーラ缶と追加のライトがあるWorldです。
<?xml version="1.0" ?>
<sdf version='1.6'>
<world name='default'>
<include>
<uri>model://sun</uri>
</include>
<include>
<uri>model://ground_plane</uri>
</include>
<include>
<name>sensor_station</name>
<uri>model://sensor_station</uri>
<pose>0 0 0 0 0 0</pose>
</include>
<include>
<name>coke0</name>
<uri>model://coke_can</uri>
<pose>1 0 0 0 0 0</pose>
</include>
<include>
<name>coke1</name>
<uri>model://coke_can</uri>
<pose>2 -0.7 0 0 0 0</pose>
</include>
<include>
<name>coke2</name>
<uri>model://coke_can</uri>
<pose>1.5 0.7 0 0 0 0</pose>
</include>
<light name='user_spot_light_0' type='spot'>
<pose frame=''>0 0 1 0 -0.9 0</pose>
<diffuse>0.5 0.5 0.5 1</diffuse>
<specular>0.4 0.4 0.4 1</specular>
<direction>0 0 -1</direction>
<attenuation>
<range>20</range>
<constant>0.5</constant>
<linear>0.01</linear>
<quadratic>0.001</quadratic>
</attenuation>
<cast_shadows>0</cast_shadows>
<spot>
<inner_angle>0.6</inner_angle>
<outer_angle>1</outer_angle>
<falloff>1</falloff>
</spot>
</light>
</world>
</sdf>
launch
軌道を行うlaunchファイルです。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<launch>
<arg name="model" default="$(find cam_lecture)/urdf/camera_sim.urdf" />
<arg name="rvizconfig" default="$(find cam_lecture)/rviz/camera_sim.rviz" />
<param name="robot_description" type="str" textfile="$(arg model)"/>
<include file="$(find gazebo_ros)/launch/empty_world.launch">
<arg name="world_name" value="$(find cam_lecture)/world/camera_sim.world" />
<arg name="paused" value="false"/>
<arg name="use_sim_time" value="true"/>
<arg name="gui" value="true"/>
<arg name="headless" value="false"/>
<arg name="debug" value="false"/>
</include>
<node name="spawn_urdf" pkg="gazebo_ros" type="spawn_model" args="-param robot_description -urdf -model camera_robot" />
<node name="robot_state_publisher" pkg="robot_state_publisher" type="robot_state_publisher" />
<node name="rviz" pkg="rviz" type="rviz" args="-d $(arg rvizconfig)" required="true" />
</launch>
実行
各ターミナルごとに実行前にsource ~/catkin_ws/devel/setup.bashを実行する必要があります。
roslaunch gazebo_ros empty_world.launch world_name:=sensor_station_coke.world
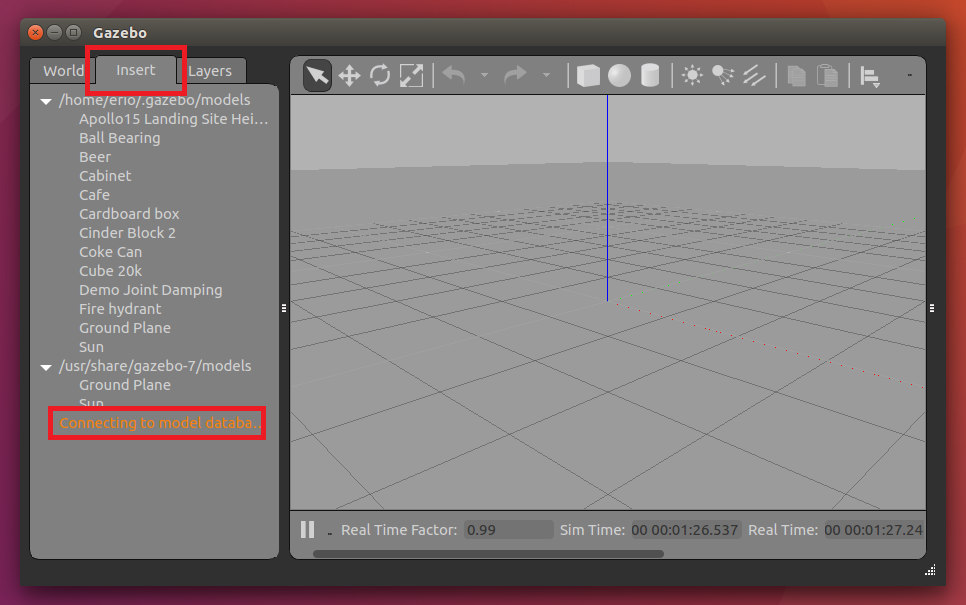
コーラ缶が出現しないときの対処法
Gazeboのバージョンによってはコーラ缶がデフォルトで入っていないことがあります。その対処法を説明します。
- まずターミナルで
gazeboを打ってgazeboを起動します。 - insetタブをクリックします。
- Connectting to model database をクリックします。
- この中でcoke_canがあるのでそれをクリックした後に3Dビュー上で適当な位置に出現させます。
- gazeboを終了します。
簡単な画像処理を行う
opencv-appというOpenCVの処理を行うためのROSパッケージがあります。これにはエッジ検出や顔検出などを行うノードが入っています。これを使って赤色を検出してみましょう。
インストール
sudo apt-get install -y ros-noetic-opencv-apps
ソースコード
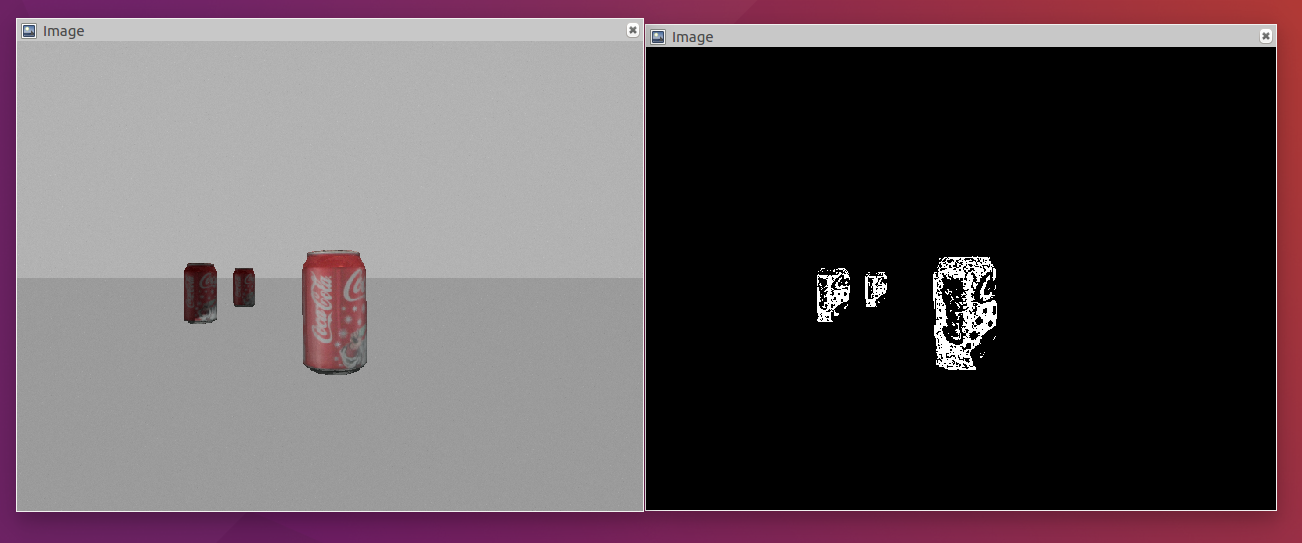
画像をhsv表記に変換してh:330~360、s:80~200、v:0~256の間の色を検出します。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<launch>
<include file="$(find gazebo_ros)/launch/empty_world.launch">
<arg name="world_name" value="sensor_station_coke.world" />
</include>
<node name="hsv_color_filter" pkg="opencv_apps" type="hsv_color_filter" >
<remap from="/image" to="/head_camera/image_raw" />
<remap from="~image" to="output/image_raw" />
<param name="h_limit_max" value="360" />
<param name="h_limit_min" value="330" />
<param name="s_limit_max" value="200" />
<param name="s_limit_min" value="80" />
<param name="v_limit_max" value="256" />
<param name="v_limit_min" value="0" />
</node>
<node name="original_image_view" pkg="image_view" type="image_view" >
<remap from="image" to="/head_camera/image_raw"/>
</node>
<node name="filtered_image_view" pkg="image_view" type="image_view" >
<remap from="image" to="/output/image_raw"/>
</node>
</launch>
実行
各ターミナルごとに実行前にsource ~/catkin_ws/devel/setup.bashを実行する必要があります。
roslaunch cam_lecture opencv_app_example.launch
以下のようにコーラ缶の赤い部分のみが抽出されます。
pythonで画像処理を行う
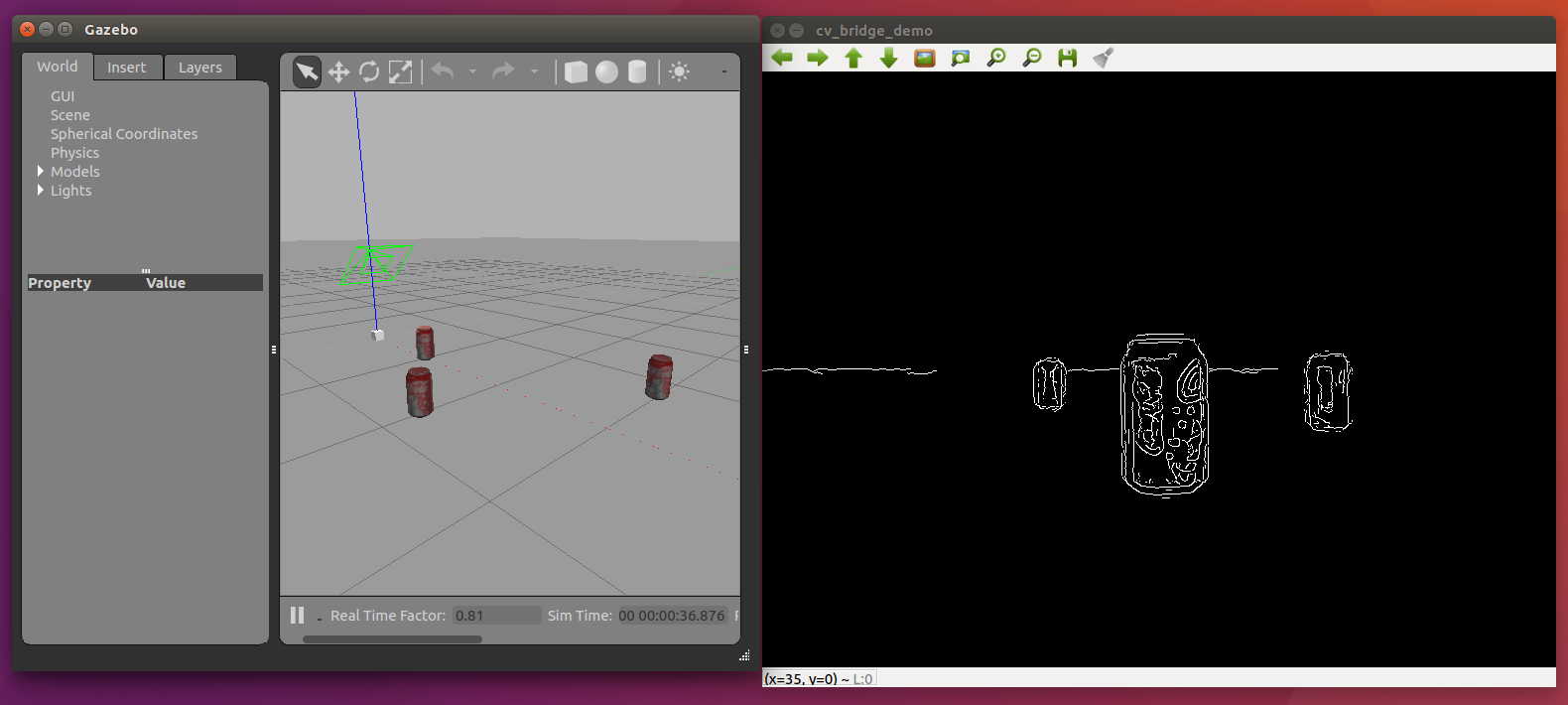
次にOpenCVを使った画像処理を行ってみます。ROS講座では主にC++でプログラムを紹介していきますが、ここではpythonで書いてみます。
今回はImage型の画像を取得してそれをcannyフィルタをかけてImage型で出すノードを作ります。
ソースコード
以下のようなモダンな書き方をします。機能を持つクラスを作成してからそのクラスを実行します。
# !/usr/bin/env python3
import rospy
import sys
import cv2
from sensor_msgs.msg import Image, CameraInfo
from cv_bridge import CvBridge, CvBridgeError
import numpy as np
class cvBridgeDemo:
def __init__(self):
self.node_name = "cv_bridge_demo"
rospy.init_node(self.node_name)
rospy.on_shutdown(self.cleanup)
self.bridge = CvBridge()
self.image_sub = rospy.Subscriber("/head_camera/image_raw", Image, self.image_callback, queue_size=1)
self.image_pub = rospy.Publisher("/output/image_raw", Image, queue_size=1)
def image_callback(self, ros_image):
try:
input_image = self.bridge.imgmsg_to_cv2(ros_image, "bgr8")
except CvBridgeError as e:
print(e)
output_image = self.process_image(input_image)
self.image_pub.publish(self.bridge.cv2_to_imgmsg(output_image, "mono8"))
cv2.imshow(self.node_name, output_image)
cv2.waitKey(1)
def process_image(self, frame):
grey = cv2.cvtColor(frame, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
blur = cv2.blur(grey, (7, 7))
edges = cv2.Canny(blur, 15.0, 30.0)
return edges
def cleanup(self):
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
if __name__ == '__main__':
cvBridgeDemo()
rospy.spin()
- まずは
__init__の部分が実行されます。この中のself.image_sub = rospy.Subscriber("input_image", Image, self.image_callback, queue_size=1)とself.image_pub = rospy.Publisher("output_image", Image, queue_size=1)でpubliser、subscriberの登録をしています。 - 画像をsubすると
image_callback(self, ros_image)が実行されます。この中のinput_image = self.bridge.imgmsg_to_cv2(ros_image, "bgr8")でROSの形式からOpenCVの形式(実質はnumpy)に変換します。カラー画像なのでbgr8と指定します。 - 処理の本体は
process_image(self, frame)にいます。この中ではカラー(3ch)からグレー(1ch)に変換、ぼかし、Cannyエッジ検出の段階を踏んでエッジ検出をしています。
self.image_pub.publish(self.bridge.cv2_to_imgmsg(output_image, "mono8"))で処理した画像をpubします。グレー画像なのでmono8で変換します。 - 最後に
cv2.imshow(self.node_name, output_image)とcv2.waitKey(1)で変換後の画像を新しくウィンドウを作って表示します。cv2.waitKey(1)があることでプログラムがwaitして、その間にウィンドウが描画されます。ないとウィンドウが正しく表示されません。ちなみにcv2.waitKey(0)ではキー入力があるまで無限に待ちます。
起動用のlaunchが以下になります。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<launch>
<include file="$(find gazebo_ros)/launch/empty_world.launch">
<arg name="world_name" value="sensor_station_coke.world" />
</include>
<node name="edge_filter" pkg="cam_lecture" type="edge_filter.py" />
<node name="original_image_view" pkg="image_view" type="image_view" >
<remap from="image" to="/head_camera/image_raw"/>
</node>
<node name="filtered_image_view" pkg="image_view" type="image_view" >
<remap from="image" to="/output/image_raw"/>
</node>
</launch>
実行
roslaunch cam_lecture sim_edge_filter.launch
参考
opencv-apps
ROSwiki cv_bridge tutorial