はじめに
Part1ではBPEトークナイザーを実装しました。
今回は、そのトークナイザーで処理したデータを学習・推論するための Transformerを実装します。
Transformerとは
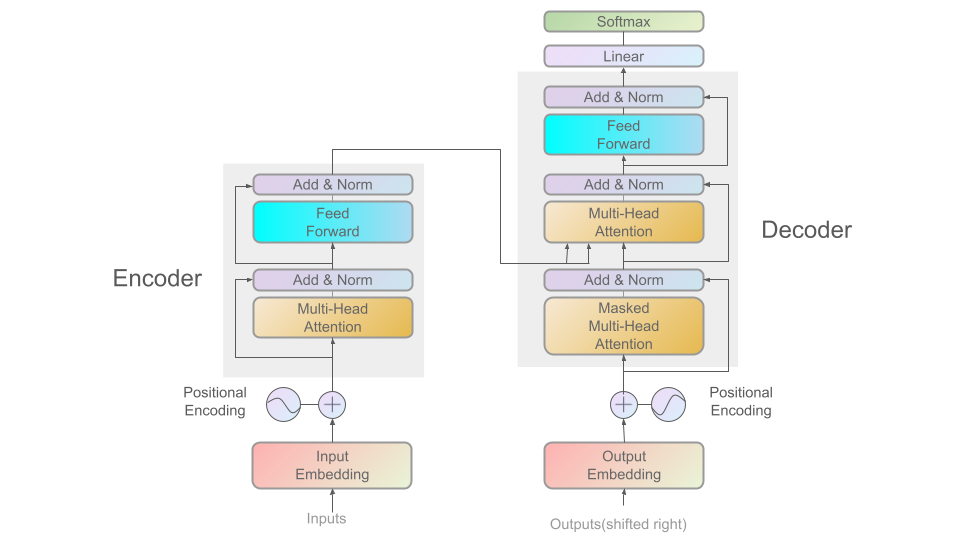
Transformerは「Attention Is All You Need」で提案されたアーキテクチャであり、GPTなどのLLMのベースとなっています。以下の図はML Visualsから引用したTransformerの全体構造です。各コンポーネントの役割については次の章で見ていきます。
なおTransformerの仕組みは以下のサイトでめちゃくちゃわかりやすく可視化されているので, まずこちらを見てみることをおすすめします。実装する際にもかなり参考にしました。
Transformerのコンポーネント実装
Transformerの各コンポーネントを実装ベースで解説していきます。コード全体はこちらに置いています。
1. Token Embedding
トークンIDから埋め込みベクトルを得るためのコンポーネントで、Input EmbeddingおよびOutput Embeddingで使用します。
class TokenEmbedding(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, vocab_size, model_dim, padding_idx=None):
super().__init__()
self.embedding = nn.Embedding(vocab_size, model_dim, padding_idx=padding_idx)
self.model_dim = model_dim
def forward(self, inputs):
return self.embedding(inputs) * sqrt(self.model_dim)
nn.Embedding is Whatとなりますが、要するに以下のコードと同じです。
class TokenEmbedding(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, vocab_size, model_dim):
super().__init__()
self.embedding = nn.Parameter(torch.randn(size=(vocab_size, model_dim)))
self.model_dim = model_dim
def forward(self, inputs):
return self.embedding[inputs] * sqrt(self.model_dim)
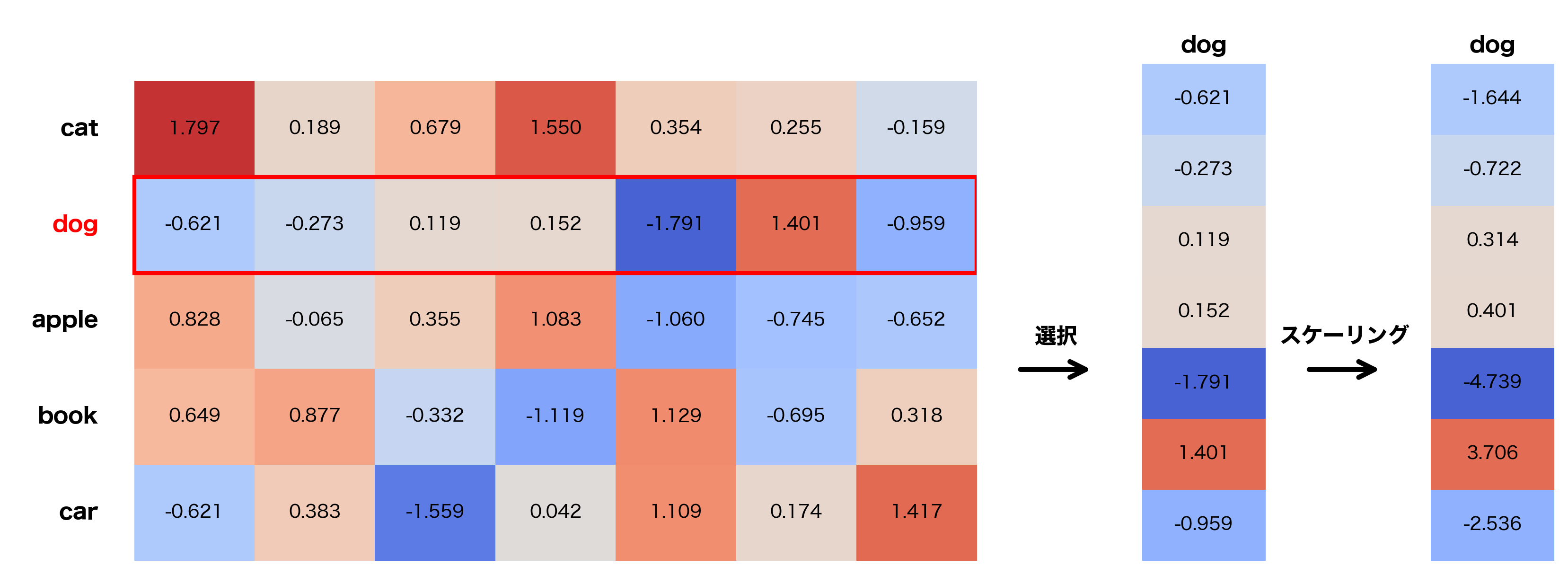
例えばvocab_size=5, model_dim=8 の場合, dogの埋め込みベクトルは以下の図のような手順で得られます(図中の数値は乱数で生成したものであり, 特に意味はないです)。
2. Positional Encoding
Transformerは再帰構造を持たないため、単語の位置情報をPositional Encodingを用いて埋め込みベクトルに加算します。
class PositionalEncoding(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, model_dim, dropout=0.1, max_len=5000):
super().__init__()
self.dropout = nn.Dropout(p=dropout)
# Positional Encoding行列
pe = torch.zeros(max_len, model_dim)
# 位置インデックス (max_len, 1)
position = torch.arange(0, max_len, dtype=torch.float).unsqueeze(1)
denominator = torch.exp(
torch.arange(0, model_dim, 2).float() * (-math.log(10000.0) / model_dim)
)
# 偶数インデックス
pe[:, 0::2] = torch.sin(position * denominator)
# 奇数インデックス
pe[:, 1::2] = torch.cos(position * denominator)
# バッチ次元を追加
pe = pe.unsqueeze(0)
self.register_buffer("pe", pe)
def forward(self, inputs):
# 入力: (batch_size, seq_len, model_dim)
seq_len = inputs.size(1)
# Positional Encodingを加算
inputs = inputs + self.pe[:, :seq_len, :]
return self.dropout(inputs)
位置pos、次元iの位置エンコーディングは以下の式で表されます:
$$PE_{(pos,2i)} = \sin\left(\frac{pos}{10000^{2i/d_{\mathrm{model}}}}\right)$$
$$PE_{(pos,2i+1)} = \cos\left(\frac{pos}{10000^{2i/d_{\mathrm{model}}}}\right)$$
${10000^{2i/d_{\mathrm{model}}}}$の部分は指数計算が不安定なので, 対数を使って以下のように変換しています:
$$10000^{2i/d_{\text{model}}} = \exp(\log(10000^{2i/d_{\text{model}}})) = \exp\left(\frac{2i}{d_{\text{model}}} \cdot \log(10000)\right)$$
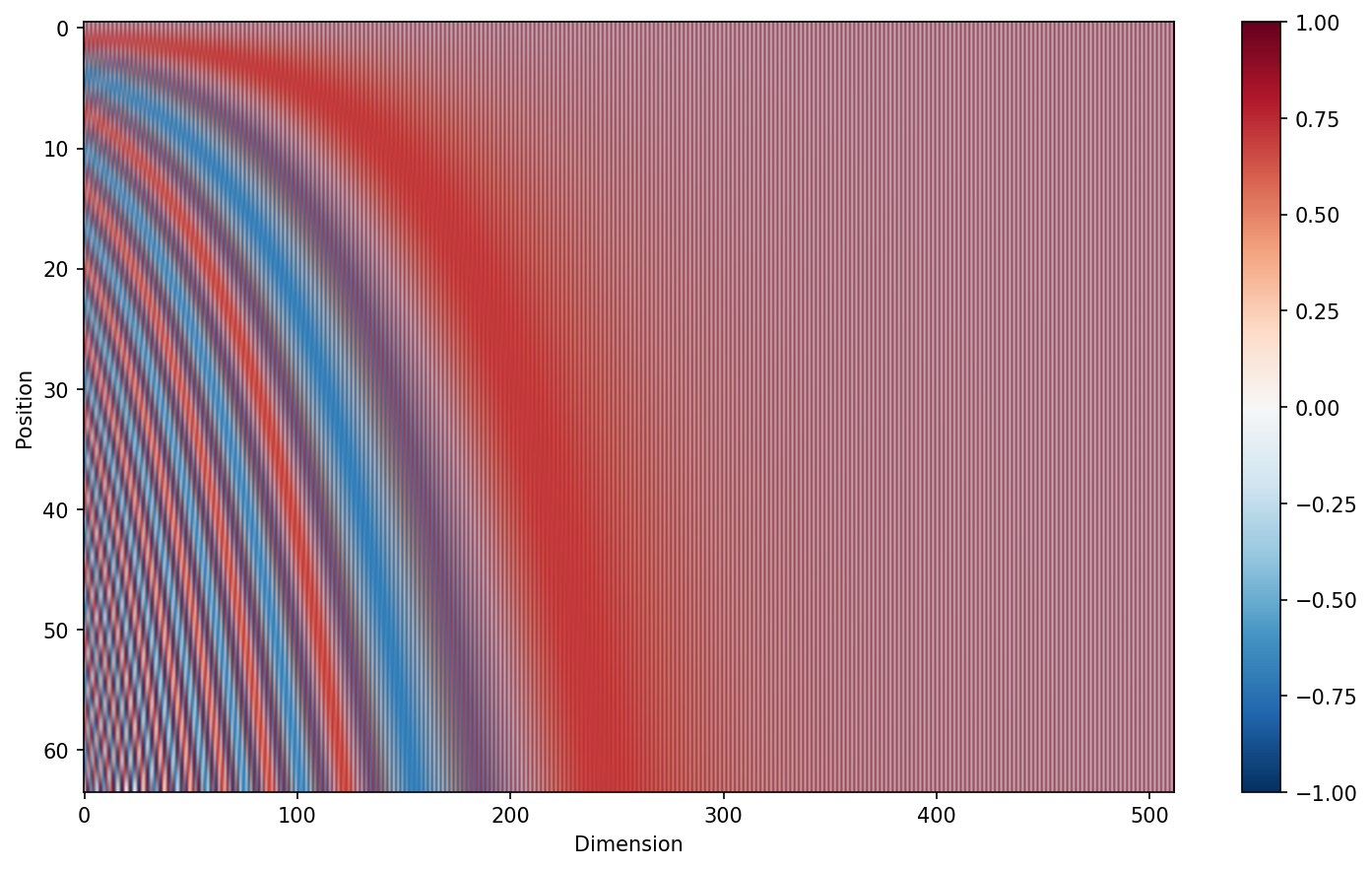
最終的に得られる位置エンコーディングpeを可視化したものが以下の図です.
3. Multi-Head Attention
Attentionは「どの単語に注目すべきか」を計算する仕組みです。Transformerでは、複数の「ヘッド」に分割して異なる観点からトークン間の関係を学習するMulti-Head Attentionを使用します。
Attentionの計算式
各ヘッドで以下の計算を行います:
$$\text{Attention}(Q, K, V) = \text{softmax}\left(\frac{QK^T}{\sqrt{d_k}}\right) V$$
実装
class MultiheadAttention(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, model_dim, head=8, dropout=0.1):
super().__init__()
if model_dim % head != 0:
raise ValueError("model_dim must be divisible by head")
# Q(query), K(key), V(value)の重みの次元
self.w_qkv_dim = model_dim // head
self.head = head
# Q, K, V: (model_dim, self.w_qkv_dim * head = model_dim)の線形変換
self.q_proj = nn.Linear(model_dim, self.w_qkv_dim * head, bias=True)
self.k_proj = nn.Linear(model_dim, self.w_qkv_dim * head, bias=True)
self.v_proj = nn.Linear(model_dim, self.w_qkv_dim * head, bias=True)
# 出力: (self.w_qkv_dim * head = model_dim, model_dim)の線形変換
self.out_proj = nn.Linear(self.w_qkv_dim * head, model_dim, bias=True)
self.dropout = nn.Dropout(p=dropout)
self.last_attention_weights = None
def forward(self, inputs, encoder_out=None, mask=None):
# input: (batch_size, seq_len, model_dim)
batch_size, seq_len, _ = inputs.shape
# (batch_size, seq_len, model_dim)
# → (batch_size, seq_len, model_dim)
query = self.q_proj(inputs)
key = self.k_proj(encoder_out if encoder_out is not None else inputs)
value = self.v_proj(encoder_out if encoder_out is not None else inputs)
# 全ヘッドのAttention計算を行列演算で行うために変形·並び替え
# (batch_size, seq_len, model_dim)
# → (batch_size, seq_len, head, w_qkv_dim)
# → (batch_size, head, seq_len, w_qkv_dim)
query = query.view(batch_size, seq_len, self.head, self.w_qkv_dim).transpose(
1, 2
)
key = key.view(batch_size, -1, self.head, self.w_qkv_dim).transpose(1, 2)
value = value.view(batch_size, -1, self.head, self.w_qkv_dim).transpose(1, 2)
# Q x K^T: (batch_size, head, seq_len, seq_len)
# key.transpose(-2, -1): (batch_size, head, w_qkv_dim, seq_len)
scores = torch.matmul(query, key.transpose(-2, -1))
# Kの次元の平方根で割る
scores /= sqrt(self.w_qkv_dim)
# マスク処理を適用(次のセクションで説明)
if mask is not None:
if mask.dim() == 2:
if encoder_out is not None: # Cross-attention
mask = mask.unsqueeze(1).unsqueeze(2)
else: # Self-attention
mask = mask.unsqueeze(0).unsqueeze(0)
elif mask.dim() == 3:
mask = mask.unsqueeze(1)
scores = scores.masked_fill(~mask, -1e9)
# softmax: (batch_size, head, seq_len, seq_len)
attention_weights = F.softmax(scores, dim=-1)
self.last_attention_weights = attention_weights
# dropout
attention_weights = self.dropout(attention_weights)
# z: (batch_size, head, seq_len, w_qkv_dim)
z = torch.matmul(attention_weights, value)
# (batch_size, head, seq_len, w_qkv_dim)
# → (batch_size, seq_len, head, w_qkv_dim)
# cf: https://qiita.com/kenta1984/items/d68b72214ce92beebbe2
z = z.transpose(1, 2).contiguous()
# (batch_size, seq_len, head, w_qkv_dim)
# → (batch_size, seq_len, head * w_qkv_dim)
z = z.view(batch_size, seq_len, self.head * self.w_qkv_dim)
# (batch_size, seq_len, model_dim)
output = self.out_proj(z)
# dropout
output = self.dropout(output)
return output
Self-Attention と Cross-Attention
Multi-Head Attentionは、Q, K, Vの入力元によって2つの使い方があります:
- Self-Attention: Q, K, V をすべて同じ入力から生成(Encoder·Decoderで使用)
- Cross-Attention: Q は Decoder、K と V は Encoder から生成(Decoderで使用)
実装では encoder_out パラメータの有無で切り替えています:
# Self-Attention: encoder_out=None
key = self.k_proj(inputs)
value = self.v_proj(inputs)
# Cross-Attention: encoder_out が指定されている
key = self.k_proj(encoder_out)
value = self.v_proj(encoder_out)
4. マスク処理
Transformerは全単語を同時に処理するため、「見てはいけない情報」を明示的にマスクする必要があります。マスクは主に2種類あります。
Padding Mask
バッチ学習では、短い文に <PAD> を追加して長さを揃えます。このパディング部分をAttentionの計算から除外する必要があります。
padding_mask = (src != PAD_IDX) # True: 有効なトークン, False: <PAD>
Causal Mask
Decoderは出力文を生成する際、未来の単語(まだ生成していない単語)を見てはならないので, マスクしてあげる必要があります。
例: I like sushi を生成する場合の各位置で見てよい/見てはいけない範囲
| 位置 | 入力 | 見てよい | 見てはいけない |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | <BOS> |
<BOS> |
I, like, sushi
|
| 1 | I |
<BOS>, I
|
like, sushi
|
| 2 | like |
<BOS>, I, like
|
sushi |
Causal Maskの構造(下三角行列):
<BOS> I like sushi
<BOS> [ 1 0 0 0 ]
I [ 1 1 0 0 ]
like [ 1 1 1 0 ]
sushi [ 1 1 1 1 ]
1: 見てよい, 0: 見てはいけない
実装では torch.tril で下三角行列を生成しています:
def create_causal_mask(seq_len, device=None):
return torch.tril(torch.ones(seq_len, seq_len, device=device)).bool()
5. Feed Forward Network
Attentionの後に適用される全結合層です。
class FeedForward(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, model_dim, dropout=0.1):
super().__init__()
self.linear_1 = nn.Linear(model_dim, model_dim * 4)
self.activation_func = nn.ReLU()
self.linear_2 = nn.Linear(model_dim * 4, model_dim)
self.dropout = nn.Dropout(p=dropout)
def forward(self, inputs):
middle = self.linear_1(inputs)
relu = self.activation_func(middle)
output = self.linear_2(relu)
# dropout
output = self.dropout(output)
return output
中間層のサイズをモデル次元の4倍にしてからもとに戻しています。
6. Encoder Layer
Self-Attention、Feed Forward、Layer Normalization、Residual Connection(残差結合, Transformerの構成図におけるブロックをスキップしている部分)を組み合わせます。
class EncoderLayer(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, model_dim):
super().__init__()
self.attention = MultiheadAttention(model_dim)
self.normalizer_1 = nn.LayerNorm(model_dim)
self.feed_forward = FeedForward(model_dim)
self.normalizer_2 = nn.LayerNorm(model_dim)
def forward(self, inputs, mask=None):
# 1. Self-Attention + Residual Connection + Layer Normalization
attention_out = self.attention(inputs, mask=mask)
normalized_1 = self.normalizer_1(inputs + attention_out)
# 2. Feed Forward + Residual Connection + Layer Normalization
feed_forward_out = self.feed_forward(normalized_1)
normalized_2 = self.normalizer_2(normalized_1 + feed_forward_out)
return normalized_2
Encoder
Encoderは複数のEncoder Layerを重ねて構成します。
class Encoder(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, model_dim, encoder_num):
super().__init__()
self.encoders = nn.ModuleList(
[EncoderLayer(model_dim) for _ in range(encoder_num)]
)
def forward(self, inputs, mask=None):
for encoder_layer in self.encoders:
inputs = encoder_layer(inputs, mask)
return inputs
7. Decoder Layer
Decoder LayerはEncoder LayerにCross-Attentionを追加した構造です。
class DecoderLayer(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, model_dim):
super().__init__()
self.masked_attention = MultiheadAttention(model_dim)
self.normalizer_1 = nn.LayerNorm(model_dim)
self.attention = MultiheadAttention(model_dim)
self.normalizer_2 = nn.LayerNorm(model_dim)
self.feed_forward = FeedForward(model_dim)
self.normalizer_3 = nn.LayerNorm(model_dim)
def forward(self, inputs, encoder_out, tgt_mask=None, src_mask=None):
# 1. Masked Self-Attention(未来の単語を見ない)
masked_attention_out = self.masked_attention(inputs, mask=tgt_mask)
normalized_1 = self.normalizer_1(inputs + masked_attention_out)
# 2. Cross-Attention(Encoderの出力を参照)
attention_out = self.attention(normalized_1, encoder_out, mask=src_mask)
normalized_2 = self.normalizer_2(normalized_1 + attention_out)
# 3. Feed Forward
feed_forward_out = self.feed_forward(normalized_2)
normalized_3 = self.normalizer_3(normalized_2 + feed_forward_out)
return normalized_3
Decoder
Decoderも複数のDecoder Layerを重ねて構成されます。
class Decoder(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, model_dim, decoder_num):
super().__init__()
self.decoders = nn.ModuleList(
[DecoderLayer(model_dim) for _ in range(decoder_num)]
)
def forward(self, inputs, encoder_out, tgt_mask=None, src_mask=None):
for decoder_layer in self.decoders:
inputs = decoder_layer(inputs, encoder_out, tgt_mask, src_mask)
return inputs
Transformerの実装
これらを組み合わせて Transformer クラスを作ります。
class Transformer(nn.Module):
def __init__(
self,
src_vocab_size,
tgt_vocab_size,
model_dim,
encoder_num,
decoder_num,
padding_idx=None,
):
super().__init__()
self.src_embedding = TokenEmbedding(src_vocab_size, model_dim, padding_idx)
self.tgt_embedding = TokenEmbedding(tgt_vocab_size, model_dim, padding_idx)
self.positional_encoding = PositionalEncoding(model_dim)
self.encoder = Encoder(model_dim, encoder_num)
self.decoder = Decoder(model_dim, decoder_num)
self.decoder_proj = nn.Linear(model_dim, tgt_vocab_size)
def forward(
self,
source_tokens,
target_tokens,
encoder_src_mask=None,
decoder_src_mask=None,
tgt_mask=None,
):
# (batch_size, source_len, model_dim)
source_embed = self.src_embedding(source_tokens)
source_embed = self.positional_encoding(source_embed)
# (batch_size, target, model_dim)
target_embed = self.tgt_embedding(target_tokens)
target_embed = self.positional_encoding(target_embed)
encoder_out = self.encoder(source_embed, encoder_src_mask)
decoder_out = self.decoder(
target_embed, encoder_out, tgt_mask, decoder_src_mask
)
output = self.decoder_proj(decoder_out)
return output
まとめ
これでTransformerモデルの実装が完成しました。
Part3 ではこのモデルを使って英日翻訳タスクを解いていきます。
参考
ゼロから作るLLM - 目次