RemoteMediator + Paging3 + Room + ViewModel で既読機能、削除機能付きのRecyclerViewを作る。
参考
図のように既読、削除機能付きのネットワークPagingを作ろうとしたとき、RemoteMediatorを使った網羅的な解説が見当たらなかったので、いろいろと探し回って得た知見を書いておこうと思います。
特に、日本語、javaの最近のandroid技術紹介ページが少なくなっているので参考いただければと思います。
1.RemoteMediatorの設定
基本は、上記APPRNDとPREPEND両方向の読み込みに対応したRemoteMediatorの実装を参照
ここで、ネットワークからクエリしたデータに対し選りすぐって表示したいとします。
例えば、1度100件のクエリしたデータのうち90件が削除済みだった場合に10件だけを表示したい、という場合を考えてみます。このとき、1件だけでも新しくRoomにinsertするデータがある場合は読み込み終了トリガーが再セットされ、次のクエリが走ります。しかし、運悪くクエリしたデータが全て削除済みで1件も表示すべきデータがなかった場合は、次のクエリが走りません。例え次のクエリで表示したいデータがあったとしてもそこで読み込みが終了してしまいます。RemoteMediatorの場合データの信頼性は全てRoom依存なので、Roomにinsertするデータがなければこのような挙動になってしまうんですね。
であればどうすればよいかというと、クエリしたデータをすべて保存するテーブルと、削除済み、既読のアイテムのみを保存するテーブルの2つ用意し、各アイテムに対し既に削除、既読チェック用DBに存在していれば高さ0のviewとしてRecyclerViewに表示させるということを考えてみます。
こうすることでどれだけクエリ間が削除済みが続いていようが連続してクエリを走らせることができる、という訳です。
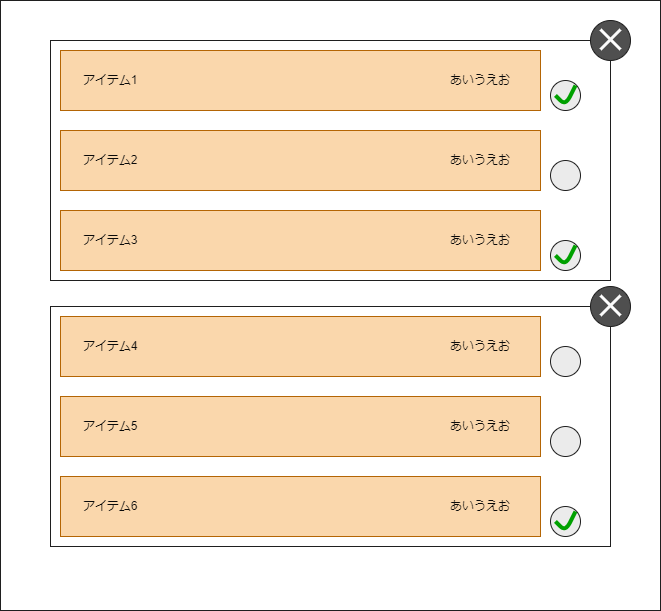
丁度、このようなイメージです。
deleted itemsは便宜上示していますが実際は見えていません。
2.ViewModelの設定
これは結構普通な書き方だと思うのですが、
このあたりの書き方もJavaのドキュメントは本当に少ないと感じました。
因みに、Paging3の初期ロードはPREFETCH_DISTANCE*3なので、
enablePlaceholders=trueとしているとき、PREFETCH_DISTANCE < PAGE_SIZE*3
が満たされているとPagingDataAdapterのアイテムにnull対策をしていないと死にます。
public LiveData<PagingData<User>> pagingDataLiveData;
private Database database;
private Dao dao;
private CoroutineScope viewModelScope;
public static final int PAGE_SIZE = 10;
public static final int PREFETCH_DISTANCE = 10;
private RemoteKeysRepository keyRepository;
private UserRepository userRepository;
private ExecutorService service;
public UserViewModel(@NonNull Application application) {
super(application);
viewModelScope = ViewModelKt.getViewModelScope(this);
database = Database.getDatabase(application);
dao = database.usersDao();
keyRepository = new RemoteKeysRepository(database);
userRepository = new UsersRepository(application);
service = Executors.newSingleThreadExecutor();
}
public LiveData<PagingData<User>> createPager(....クエリ条件等){
Pager<Integer, User> pager = new Pager<>(
new PagingConfig(PAGE_SIZE, PREFETCH_DISTANCE, true), null,
new RemoteMediator(....クエリ条件等),
() -> {
return source;
});
return PagingLiveData.cachedIn(PagingLiveData.getLiveData(pager), viewModelScope);
}
3.RecyclerView(PagingDataAdapter)の設定
基本は、上記参考文献の
【続】2020年版RecyclerViewの使い方 〜リストのアイテムに複数のレイアウトを使う〜
を踏襲しています。
public class ItemAdapter extends
PagingDataAdapter<User,
ItemAdapter.ParentViewHolder> {
private User user;
private final Context context;
private final LifecycleOwner owner;
private final ErasedUserRepository erasedRepository;
private final UserRepository repository;
private Looper mainLooper;
private Handler handler;
private BackgroundTask backgroundTask;
private ExecutorService executorService;
private PostExecutor postExecutor;
private ImageButton imageButton;
@UiThread
public void asyncExecute(User item) {
mainLooper = Looper.getMainLooper();
handler = HandlerCompat.createAsync(mainLooper);
backgroundTask = new BackgroundTask(handler,item);
executorService = Executors.newSingleThreadExecutor();
executorService.submit(backgroundTask);
}
private class BackgroundTask implements Runnable {
private final Handler _handler;
private final User _item;
public BackgroundTask(Handler handler,User item) {
_handler = handler;
_item = item;
}
@WorkerThread
@Override
public void run() {
Boolean b = erasedDao.isUserRead(_item.getId());
postExecutor = new PostExecutor(b);
_handler.post(postExecutor);
}
}
private class PostExecutor implements Runnable {
private final Boolean _b;
public PostExecutor(Boolean b){
_b = b;
}
@UiThread
@Override
public void run() {
itemImageview.setVisibility(_b ? View.INVISIBLE : View.VISIBLE);
}
}
public ItemAdapter(@NonNull DiffUtil.ItemCallback<User> itemCallback,
Context context, LifecycleOwner owner,
ErasedUserRepository erasedRepository,UserRepository repository) {
super(itemCallback);
this.context = context;
this.owner = owner;
this.erasedRepository = erasedRepository;
this.repository = repository;
}
public abstract class ParentViewHolder extends RecyclerView.ViewHolder{
abstract void bind(User item,int position);
public ParentViewHolder(@NonNull ViewBinding binding) {
super(binding.getRoot());
}
}
public class ViewHolder extends ParentViewHolder{
public ErasedUserDao erasedDao;
public UserDao dao;
public Database db;
public ViewHolder(@NonNull ItemBinding binding, Context context) {
super(binding);
this.binding = binding;
db = Database.getDatabase(context);
erasedDao = db.erasedUserDao();
dao = db.UserDao();
}
@Override
public void bind(User item,int position) {
//既読チェックメソッド
asyncExecute(item);
//削除メソッド
imageButton.setOnClickListener(v -> {
repository.getDeleteFromScreenUserList(....delete条件, (isEnd, result) -> {
if(isEnd){
List<ErasedUser> users = new ArrayList<>();
List<Integer> idList = new ArrayList<>();
for(User user: result) {
users.add(new ErasedUser(
user.getId(),
true
));
idList.add(user.getId());
}
erasedRepository.insertNewUsers(users, isEnd -> {
if(isEnd) {
repository.deleteUsers(idList);
}
});
}
});
});
//write Something else
}
}
public class ViewErasedHolder extends ParentViewHolder{
public ViewErasedHolder(ItemErasedBinding binding) {
super(binding);
}
@Override
void bind(User item, int position) {
//Anything is written
}
}
@NonNull
@Override
public ItemAdapter.ParentViewHolder onCreateViewHolder(@NonNull ViewGroup parent, int viewType) {
if(viewType == 1) {
return new ItemAdapter.ViewErasedHolder(ItemErasedBinding.inflate(LayoutInflater.from(parent.getContext()), parent, false));
}else{
return new ItemAdapter.ViewHolder(ItemBinding.inflate(LayoutInflater.from(parent.getContext()), parent, false), context);
}
}
@Override
public void onBindViewHolder(@NonNull ItemAdapter.ParentViewHolder holder, int position) {
user = getItem(position);
holder.bind(user,position);
}
@Override
public int getItemViewType(int position) {
user = getItem(position);
if(user!=null) {
if(user.isErased()) {
return 1;
}
}
return 0;
}
public static DiffUtil.ItemCallback<User> ItemCallback =
new DiffUtil.ItemCallback<User>() {
@Override
public boolean areItemsTheSame(User oldItem, User newItem) {
return oldItem.getId().equals(newItem.getId());
}
@Override
public boolean areContentsTheSame(@NonNull User oldItem, @NonNull User newItem) {
return oldItem.equals(newItem);
}
};
}
1の項で説明した、クエリしたデータをすべて保存するテーブルがdaoで、既読、削除したアイテムのみを保存するテーブルがerasedDaoに対応しています。(アイテムIDに対して既読、削除したかのフラグを所持)getItemViewTypeメソッドで各アイテムの振り分けを行い、erasedと判定された場合は空のviewで何もしない、という処理にしています。
asyncExecute(item)メソッドで既読したアイテムから未読マークを消去します。
Roomの特性として、DBの操作はバックグラウンドでなければならず、UIの操作はUIスレッドで行わなければならない
という制約があるため、少し特殊な処理になっています。
バックグラウンドでerasedDao.isUserReadメソッドで既読判定を行い、その結果を用いて既読マークの表示可否を実行しています。
このあたりの知見は、こちらの記事が大変参考になりましたので紹介しておきます。
アイテムの削除メソッドついては、バックグラウンド処理だけで済むため、Repositoryクラスを介してDB操作を行います。あとはDiffUtil.ItemCallbackが良しなにやってくれます。
Repositoryクラスの使い方の参考を挙げておきます。
public class ErasedUserRepository {
private ErasedDao dao;
public interface SearchCallback {
void onComplete(Boolean isEnd,List<User> result);
}
public ErasedUserRepository(Application application){
Database db = Database.getDatabase(application);
dao = db.erasedUserDao();
}
public void getDeleteFromScreenUserList(....Query条件,SearchCallback callback){
Executors.newSingleThreadExecutor().execute(()->{
List<User> result = dao.getDeleteFromScreenUserList(....Query条件);
callback.onComplete(result != null,result);
});
}
public void deleteUsers(List<Integer> idList){
Executors.newSingleThreadExecutor().execute(()->{
dao.deleteUsers(idList);
});
}
public void deleteUser(Integer id){
Executors.newSingleThreadExecutor().execute(()->{
dao.deleteUser(id);
});
}
public void insertUser(){
Executors.newSingleThreadExecutor().execute(()->{
dao.insert(new User(ID等....));
});
}
public void clearAll(){
Executors.newSingleThreadExecutor().execute(()->{
dao.clearAll();
});
}
}
4.Roomの設定
テーブルは
①RemoteMediator用のクエリデータをすべて保存するテーブル
②既読のアイテムを保存するテーブル
③RemoteMediator用のリモートキーを保存するテーブル
の三つ、DAOもそれぞれ①~③に対応したものを用意する必要があります(④~⑥)
@Entity(tableName="user_table")
public class User implements Comparable<User>{
@PrimaryKey
@NonNull
@ColumnInfo(name = "id")
public Integer id;
@ColumnInfo(name = "isErased")
public boolean isErased;
//....
public User(@NonNull Integer id,...) {
this.id = id;
//...
}
//getter & setter
}
@Entity(tableName="remoteKeys_table")
public class RemoteKeys {
@PrimaryKey
@NonNull
@ColumnInfo(name = "id")
public Integer id;
@ColumnInfo(name = "prevKey")
public Integer prevKey;
@ColumnInfo(name = "nextKey")
public Integer nextKey;
public RemoteKeys(@NonNull Integer recordId, Integer prevKey, Integer nextKey){
this.recordId = recordId;
this.prevKey = prevKey;
this.nextKey = nextKey;
}
//getter & setter
}
@Entity(tableName="erasedUser_table")
public class EraseUser {
@PrimaryKey
@NonNull
@ColumnInfo(name = "id")
public Integer id;
public ErasedsUser(@NonNull Integer id) {
this.id = id;
}
//getter & setter
}
@Dao
public interface UserDao {
@Insert(onConflict = OnConflictStrategy.REPLACE)
void insertAll(List<User> userList);
@Insert(onConflict = OnConflictStrategy.REPLACE)
void insert(User user);
@Query("SELECT * FROM user_table")
PagingSource<Integer, User> pagingSource();
@Query("DELETE FROM user_table")
int clearKeys();
//....
}
2.ViewModelで使うPagingSourceを取得するメソッドをここに記述します。
@Dao
public interface RemoteKeysDao {
@Insert(onConflict = OnConflictStrategy.REPLACE)
void insertAll(List<RemoteKeys> remoteKeys);
@Insert(onConflict = OnConflictStrategy.REPLACE)
void insert(RemoteKeys remoteKeys);
@Query("DELETE FROM remoteKeys_table")
int clearKeys();
//....
}
@Dao
public interface ErasedUserDao {
@Insert(onConflict = OnConflictStrategy.REPLACE)
void insertAll(List<ErasedUser> erasedUsers);
@Insert(onConflict = OnConflictStrategy.REPLACE)
void insert(ErasedUser erasedUser);
@Query("DELETE FROM erasedUser_table")
int clearKeys();
//....
}
5.MainActivityの設定
最後にこれらを表示するためのMainActivityの記述例を紹介します。
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
private ItemAdapter adapter;
private RecyclerView recyclerView;
private UserViewModel viewModel;
private Looper mainLooper;
private Handler handler;
private BackgroundTask backgroundTask;
private ExecutorService executorService;
private PostExecutor postExecutor;
private LinearLayoutManager manager;
private ErasedUserRepository erasedRepository;
private UserRepository repository;
private LiveData<PagingData<User>> pagingData;
private ActivityMainBinding binding;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
binding = ActivityMainBinding.inflate(getLayoutInflater());
}
@Override
public void onStart(){
super.onStart();
erasedRepository = new ErasedUserRepository(getApplication());
repository = new UserRepository(getApplication());
viewModel = new ViewModelProvider(this).get(UserViewModel.class);
initRecyclerView();
}
@Override
public void onResume(){
super.onResume();
asyncExecute(....);
}
@UiThread
public void asyncExecute(....) {
if(pagingData!=null&&pagingData.hasObservers()){
pagingData.removeObservers(this);
}
if(postExecutor!=null) {
handler.removeCallbacks(postExecutor);
postExecutor = null;
}
mainLooper = Looper.getMainLooper();
handler = HandlerCompat.createAsync(mainLooper);
backgroundTask = new BackgroundTask(handler,dateTimeFrom,dateTimeTo);
executorService = Executors.newSingleThreadExecutor();
executorService.submit(backgroundTask);
}
private class BackgroundTask implements Runnable {
private final Handler _handler;
....
public BackgroundTask(Handler handler,....) {
_handler = handler;
....
}
@WorkerThread
@Override
public void run() {
pagingData = viewModel.createPager(....,MainActivity.this,null);
postExecutor = new PostExecutor();
_handler.post(postExecutor);
}
}
private class PostExecutor implements Runnable {
@UiThread
@Override
public void run() {
pagingData.observe(MainActivity.this, pagingData -> {
adapter.submitData(getLifecycle(), pagingData);
}
);
}
}
public void initRecyclerView() {
recyclerView = binding.recyclerView;
manager = new LinearLayoutManager(this);
recyclerView.setLayoutManager(manager);
adapter = new ItemAdapter(ItemAdapter.ItemCallback,this,this,erasedRepository,repository);
}
@Override
public void onPause(){
if(pagingData!=null&&pagingData.hasObservers()){
pagingData.removeObservers(this);
}
super.onPause();
}
@Override
protected void onDestroy() {
super.onDestroy();
}
}
PagingSourceのクエリも、RoomのDB操作に該当するため、DBの操作(createPager)はバックグラウンドでなければならず、UIの操作(Observe)はUIスレッドで行わなければならないという制約に基づき記述します。
ここまでご覧いただきありがとうございます。
かなり複雑かつ一般化してわからないところもあると思いますので、
質問コメント、こうしたらいいよ!という助言コメントもどしどし受け付けてます。