Models of Interaction
Client - Server
- central storage of information in always on server
- distinction between client which recieves service and server which provides service
- note that it is possible for a host to act as both a client and as a server in different intractions.
- Web, e-mail, FTP
Peerr to Peer
- distributed storage of information
- no clear distinction between clients and servers. Hosts share typically equal control of processing and data.
- Peers dynamically join and leave.
- Bit Torrent. (which is a popular P2P protocol for file distribution)
メリット
peerのupload capacityを使って、serverの負担を減らすことができる。serverはある一定のupload capacityを持っているので、たくさんのhostからアクセスがあると、一つのhostあたりにさかれるcapacityは低くなる。でも、peer to peerでhostのuplaod capacityも利用できれば、そいつらのcapacityを利用して、ほかのhostたちのためのuploadを進めることができる。
デメリット
常に同じserverが存在するわけではなく、いまserver役をしているpeerも好きなタイミングで抜けることができ、流動的に変わる。
Pure P2P architecture
- no always-on server
- arbitary end systems directly communicate
- peers are intermittently connected and change IP addresses
- Advantages
- Distributes load of serving files.
気をつけたいのは、必ずしも、uploadスピードを速くするという保証はないということ。基本的に、普通のPeerよりもserverの方が早いuploadスピードを持っているため、Peer to Peerより、client-server型の方が速くなることもあり得る。保証できる利点は、負担を分散できるという点である。
- Distributes load of serving files.
- Challenges
- How to find resources
流動的にserver役も出入りする中で、毎回提供してくれるpeerを見つけなきゃいけない。 - Fairness
ダウンロードした人がシェアにも参加する平等さ
- How to find resources
- examples:
- file distribution (BitTorrent)
- Streaming (KanKan), VoIP(Skype)
File distribution: client-server vs P2P
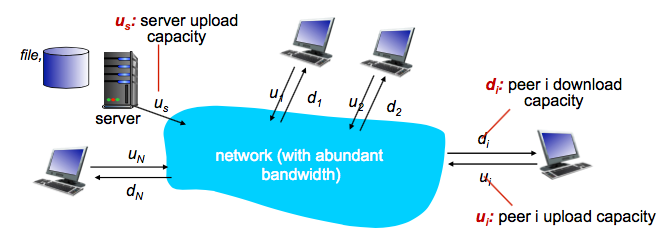
Question: how much time to distribute file(size F) from one server to N peers? - peer upload/download capacity is limited resource.
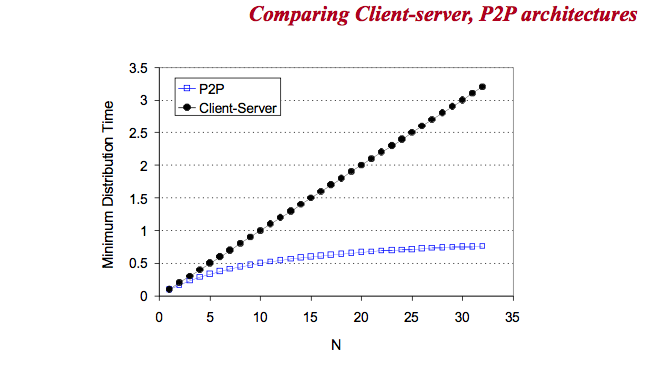
N人に分配するのにかかる時間の変化の仕方の1例。最初の一発目はどちらもserverからあげる必要があるので、かかる時間は一緒。Nが増えるにつれて、distributionにかかる時間がP2Pだと収束っぽく時間短縮できることがわかる。
P2P file distribution: BitTorrent
- flie divided into 256Kb chunks
- peers in torrent send/recieve file chunks
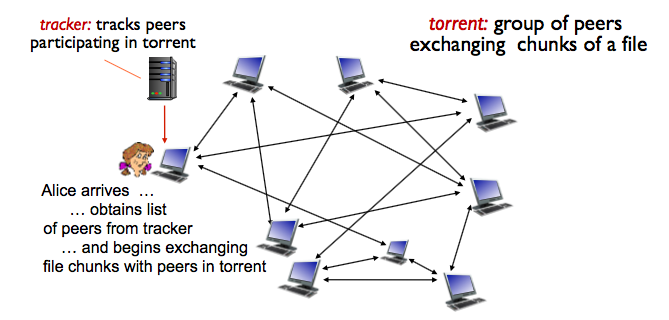
まず初めに、userはtrackerに今participatingなpeerの位置を教えてもらう。これが、p2pのservingしてくれる人の見つけ方。あるファイルのchunksをやりとりしているpeerたちのgroupをtorren(激流)と呼ぶ。
peer joinig to torrent:
-
has no chunks, but will accumulate them over time from other peers
-
registers with tracker to get list of peers, connects to subset of peers ("neighbors")
- while downloading, peer uploads chunks to other peers
- peer may change peers with whom it exchanges chunks
- churn: peers may come and go
-
Once peer has entire file, it may (selfishly) leave or (altruistically) remain in torrent
最初は、chunk全く持ってないけど、downloadingしていく中でそれを蓄積しながら、さらに同時に蓄積したシェアしていく。ほかのpeersが持っていない傾向にあるchunkを繋がってるpeerからもらうという仕組み。レアなchunk持ってるやつが消えたら困るからね。
BitTorrent: requesting, sending file chunks
requesting chunks:
- at any given time, different peers have different subsets of file chunks
- periodically, one asks each peer for list of chunks that they have
- the one requests missing chunks from peers, rarest first
sending chunks: tit-for-tat
- one sends chunks to those four peers currently sending the one's chunks at highest rate
- other peers are choked by the one (do not recieve chunks from the one)
- re-evaluate top 4 every 10 secs
- every 30 secs: randomly select another peer, starts sending chunks
- "optimistically unchoke" this peer
- newly chosen peer may join top 4