こんにちは!Railsエンジニア歴10ヶ月のshin1rokです!
プログラミング初心者の友人に検索機能の実装方法を伝授したので、その内容を公開します。
バージョン
- Ruby 2.6.3
- Rails 5.2.3
- bootstrap 4.3.1(レイアウト調整のため。検索機能実装に必須ではない。)
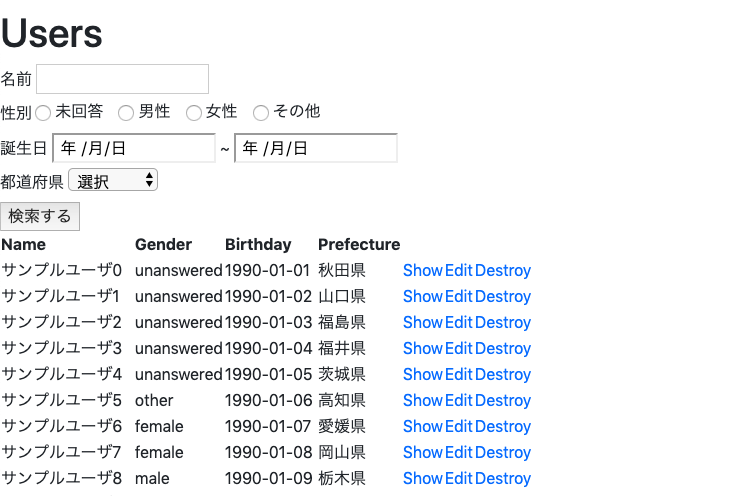
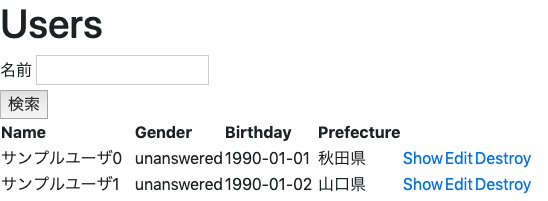
完成イメージ
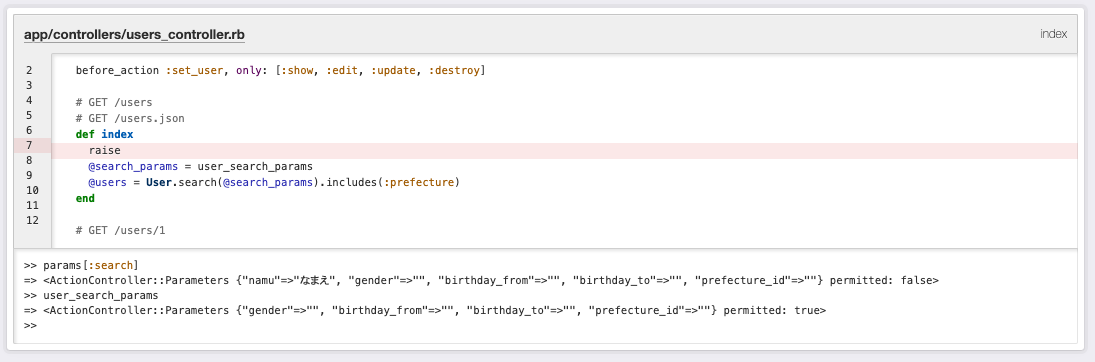
コード
# app/views/users/index.html.erb
<p id="notice"><%= notice %></p>
<h1>Users</h1>
<div class="search-form">
<%= form_with(scope: :search, url: users_path, method: :get, local: true) do |f| %>
<div class="field">
<%= f.label(:name, User.human_attribute_name(:name)) %>
<%= f.text_field :name, value: @search_params[:name] %>
</div>
<div class="field">
<%= f.label(:gender, User.human_attribute_name(:gender)) %>
<%= f.collection_radio_buttons(:gender, User.genders, :first, :first) do |r| %>
<%= tag.div(class: 'form-check form-check-inline') do %>
<%= r.radio_button(checked: r.value == @search_params[:gender], class: 'form-check-input') + f.label(User.human_attribute_name("gender.#{r.text}"), class: 'form-check-label') %>
<% end %>
<% end %>
</div>
<div class="field">
<%= f.label(:birthday, User.human_attribute_name(:birthday)) %>
<%= f.date_field :birthday_from, value: @search_params[:birthday_from] %> ~ <%= f.date_field :birthday_to, value: @search_params[:birthday_to] %>
</div>
<div class="field">
<%= f.label(:prefecture_id, User.human_attribute_name(:prefecture_id)) %>
<%= f.collection_select(:prefecture_id, Prefecture.all, :id, :name, selected: @search_params[:prefecture_id], include_blank: t('helpers.select.include_blank')) %>
</div>
<div class="actions">
<%= f.submit(t('helpers.submit.search')) %>
</div>
<% end %>
</div>
<table>
<thead>
<tr>
<th>Name</th>
<th>Gender</th>
<th>Birthday</th>
<th>Prefecture</th>
<th colspan="3"></th>
</tr>
</thead>
<tbody>
<% @users.each do |user| %>
<tr>
<td><%= user.name %></td>
<td><%= user.gender %></td>
<td><%= user.birthday %></td>
<td><%= user.prefecture.name %></td>
<td><%= link_to 'Show', user %></td>
<td><%= link_to 'Edit', edit_user_path(user) %></td>
<td><%= link_to 'Destroy', user, method: :delete, data: { confirm: 'Are you sure?' } %></td>
</tr>
<% end %>
</tbody>
</table>
<br>
<%= link_to 'New User', new_user_path %>
class UsersController < ApplicationController
# indexアクション以外は不要なので省略しています。
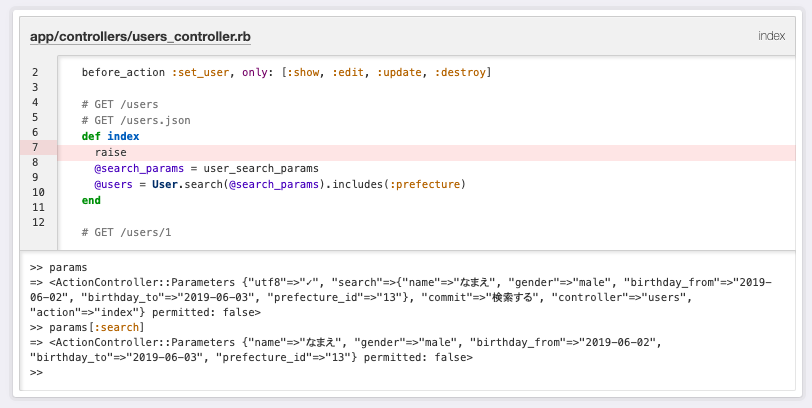
def index
@search_params = user_search_params
@users = User.search(@search_params).includes(:prefecture)
end
private
def user_search_params
params.fetch(:search, {}).permit(:name, :gender, :birthday_from, :birthday_to, :prefecture_id)
end
end
class User < ApplicationRecord
enum gender: { unanswered: 0, male: 1, female: 2, other: 9 }
belongs_to :prefecture
scope :search, -> (search_params) do
return if search_params.blank?
name_like(search_params[:name])
.gender_is(search_params[:gender])
.birthday_from(search_params[:birthday_from])
.birthday_to(search_params[:birthday_to])
.prefecture_id_is(search_params[:prefecture_id])
end
scope :name_like, -> (name) { where('name LIKE ?', "%#{name}%") if name.present? }
scope :gender_is, -> (gender) { where(gender: gender) if gender.present? }
scope :birthday_from, -> (from) { where('? <= birthday', from) if from.present? }
scope :birthday_to, -> (to) { where('birthday <= ?', to) if to.present? }
scope :prefecture_id_is, -> (prefecture_id) { where(prefecture_id: prefecture_id) if prefecture_id.present? }
end
GitHub shin1rok/rails_search_sample
事前準備
デバッグを効率よく行うためにBetter Errorsをインストールします。
使い方は公式をみていただければと思うのですが、インストール手順を記載しておきます。
1. gemfileに以下を追記する
group :development do
gem 'better_errors'
gem 'binding_of_caller'
end
2. bundle install
3. 適当なところでraiseしてインストールできていることを確認する
※プログラミング全般に言えることですが、確認を怠ると不具合が発生した際の原因の切り分けが難しくなります。めんどうに感じるかもしれませんが、1つ1つ確認しながら進めた方が結果として近道になります。
実装方針
- 検索パラメータを入力するフォームを作る(View)
- 検索パラメータを受け取る(Controller)
- 検索処理を実行する(Model)
各検索項目について
- 名前: like検索
- 性別: ラジオボタンで選択
- 誕生日: 範囲検索
- 都道府県: プルダウン選択
テーブル構成
ユーザテーブルと都道府県テーブルを作成します。
ユーザテーブルにprefecture_idを外部キーとして設定するため、都道府県テーブルから先に作成する必要があります。
ActiveRecord::Schema.define(version: 2019_05_27_215135) do
create_table "prefectures", options: "ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8", force: :cascade do |t|
t.string "name"
t.datetime "created_at", null: false
t.datetime "updated_at", null: false
end
create_table "users", options: "ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8", force: :cascade do |t|
t.string "name"
t.integer "gender", default: 0, null: false
t.date "birthday"
t.bigint "prefecture_id"
t.datetime "created_at", null: false
t.datetime "updated_at", null: false
t.index ["prefecture_id"], name: "index_users_on_prefecture_id"
end
add_foreign_key "users", "prefectures"
end
コマンド例
rails g model prefecture name:string --skip-test-unit --no-api --no-jbuilder
rails g scaffold user name:string gender:integer birthday:date prefecture:references --skip-test-unit --no-api --no-jbuilder
オプションの詳細は「rails scaffold option」とかで調べてみてください。
View
Viewで行なっていることは以下の通りです。順番に解説していきます。
- form_withで入力フォームを作る
- 検索後に検索フォームに入力された値を保持するようにする
- I18n対応
- ラジオボタンを横並びにする(Bootstrap4)
※ Viewの解説が一番難しい & 長いので、さらっと読み飛ばして、先にController, Modelを読む方がいいかもです。
再掲
# app/views/users/index.html.erb
<p id="notice"><%= notice %></p>
<h1>Users</h1>
<div class="search-form">
<%= form_with(scope: :search, url: users_path, method: :get, local: true) do |f| %>
<div class="field">
<%= f.label(:name, User.human_attribute_name(:name)) %>
<%= f.text_field :name, value: @search_params[:name] %>
</div>
<div class="field">
<%= f.label(:gender, User.human_attribute_name(:gender)) %>
<%= f.collection_radio_buttons(:gender, User.genders, :first, :first) do |r| %>
<%= tag.div(class: 'form-check form-check-inline') do %>
<%= r.radio_button(checked: r.value == @search_params[:gender], class: 'form-check-input') + f.label(User.human_attribute_name("gender.#{r.text}"), class: 'form-check-label') %>
<% end %>
<% end %>
</div>
<div class="field">
<%= f.label(:birthday, User.human_attribute_name(:birthday)) %>
<%= f.date_field :birthday_from, value: @search_params[:birthday_from] %> ~ <%= f.date_field :birthday_to, value: @search_params[:birthday_to] %>
</div>
<div class="field">
<%= f.label(:prefecture_id, User.human_attribute_name(:prefecture_id)) %>
<%= f.collection_select(:prefecture_id, Prefecture.all, :id, :name, selected: @search_params[:prefecture_id], include_blank: t('helpers.select.include_blank')) %>
</div>
<div class="actions">
<%= f.submit(t('helpers.submit.search')) %>
</div>
<% end %>
</div>
<table>
<thead>
<tr>
<th>Name</th>
<th>Gender</th>
<th>Birthday</th>
<th>Prefecture</th>
<th colspan="3"></th>
</tr>
</thead>
<tbody>
<% @users.each do |user| %>
<tr>
<td><%= user.name %></td>
<td><%= user.gender %></td>
<td><%= user.birthday %></td>
<td><%= user.prefecture.name %></td>
<td><%= link_to 'Show', user %></td>
<td><%= link_to 'Edit', edit_user_path(user) %></td>
<td><%= link_to 'Destroy', user, method: :delete, data: { confirm: 'Are you sure?' } %></td>
</tr>
<% end %>
</tbody>
</table>
<br>
<%= link_to 'New User', new_user_path %>
form_withで入力フォームを作る
入力フォームを実装するためには大きく2ステップあります。
- 入力フィールドをinputタグで作る(text_field, collection_radio_buttons, collection_select, date_fieldなど)
- 入力された情報をformタグによってサーバに送れるようにする(form_with)
Railsではそれらを効率よく作るためにViewHelper(↑のかっこ内のメソッドのことです。)が用意されています。
ViewHelperを使いこなせるようになると一気に生産性が高まるので、可能な限りViewHelperを使っていきましょう。1
とりあえず動くようにする → ブラウザからDeveloperToolsでHTMLを確認 → 正しく修正、というのを繰り返すことで少しずつ身に付いていくと思います。
※Rails5.1以上の場合、form_for, form_tagではなくて、form_withを使いましょう。
Railsガイド form_forとform_tagのform_withへの統合
form_with
form_withメソッドを用いてformタグを生成できるようにします。
検索パラメータはControllerにおいてparams[:search]のHash形式(厳密にはHashではなくActionController::Parametersオブジェクトです。)で受け取りたいので、そのように実装します。
こちらがミニマムで作成した検索フォームです。
(formだけだと検索できないので、名前の入力欄もついでに作っています。)
# erb
<%= form_with(scope: :search, url: users_path, method: :get, local: true) do |f| %>
<%= f.label(:name, '名前') %>
<%= f.text_field :name %>
<%= f.submit('検索') %>
<% end %>
# ブラウザから見たHTML
<form action="/users" accept-charset="UTF-8" method="get"><input name="utf8" type="hidden" value="✓">
<label for="search_name">名前</label>
<input type="text" name="search[name]" id="search_name">
<input type="submit" name="commit" value="検索" data-disable-with="検索">
</form>
察しの良い方は上記のerbとHTMLを見比べたらわかるかもですが、説明していきます。
scope: :search
scope: :search、f.text_field :nameとすることでparams[:search]にnameをKeyとしたHashを設定することができます。
>> params[:search][:name]
=> "なまえ"
url: users_path
urlにはinput type="submit"ボタンを押した時にどのURLにリクエストを送ればよいのかを指定します。
今回はUsersControllerのindexアクションにリクエストを送りたいのでusers_pathを指定します。
Rails - 名前付きルートにおける_pathと _urlの違いと使い分け
method: :get
検索はHTTPメソッドのGETにあたるのでmethod: :getを設定ます。
Railsガイド Web上のリソース
local: true
form_withではデフォルトでremote: trueとなっており、local: trueしない場合、XMLHttpRequest(Ajax)で通信が行われます。
XMLHttpRequestによって非同期通信を行うことができるのですが、今回は非同期通信をOFFにしたいので、local: trueにします。
By default form_with attaches the data-remote attribute submitting the form via an XMLHTTPRequest in the background if an Unobtrusive JavaScript driver, like rails-ujs, is used. See the :local option for more.
text_field(名前の入力欄)
value: @search_params[:name]とすることで検索パラメータを検索後も保持するようにしています。
<%= f.text_field :name, value: @search_params[:name] %>
# 初期表示時
<input type="text" name="search[name]" id="search_name">
# `なまえ`で検索した場合
<input value="なまえ" type="text" name="search[name]" id="search_name">
Ruby on Rails API - text_field
collection_radio_buttons(性別のラジオボタン選択)
collection_radio_buttonsでラジオボタンを作っています。
collection_radio_buttonsの実装を見てみるとこのようになっています。
def collection_radio_buttons(method, collection, value_method, text_method, options = {}, html_options = {}, &block)
@template.collection_radio_buttons(@object_name, method, collection, value_method, text_method, objectify_options(options), @default_html_options.merge(html_options), &block)
end
GitHub Rails - collection_radio_buttons
引数についてそれぞれ解説すると
- method:
params[:search][:method]のmethodに設定したいものを渡す。今回はgender - collection: ラジオボタンは1つだけでは意味がないので、ラジオボタンの項目のcollectionを設定する。今回は
User.genders - value_method: ラジオボタンの
valueに設定したい値をcollectionの要素に対するメソッドとして設定する。今回は:first - text_method: ラジオボタンの
textに設定したい値をcollectionの要素に対するメソッドとして設定する。今回は:first
collectionの要素に対するメソッド
見た目を整えるためのコードなど余計な部分を省いたシンプルなコードがこちらです。
<%= f.collection_radio_buttons(:gender, User.genders, :first, :first) do |r| %>
<!-- r.valueと@search_params[:gender]が一致した場合はcheckedにtrueを設定する-->
<%= r.radio_button(checked: r.value == @search_params[:gender]) + r.text %>
<% end %>
<input type="hidden" name="search[gender]" value="" />
<input type="radio" value="unanswered" name="search[gender]" id="search_gender_unanswered" />unanswered
<input type="radio" value="male" name="search[gender]" id="search_gender_male" />male
<input type="radio" value="female" name="search[gender]" id="search_gender_female" />female
<input type="radio" value="other" name="search[gender]" id="search_gender_other" />other
date_field(誕生日の範囲指定)
誕生日が検索できるようにするためにdate_fieldを使います。また、誕生日はピンポイントで検索しても使いづらいので入力欄を2つ作り、範囲検索できるようにします。
<%= f.date_field :birthday_from, value: @search_params[:birthday_from] %>
<input type="date" name="search[birthday_from]" id="search_birthday_from">
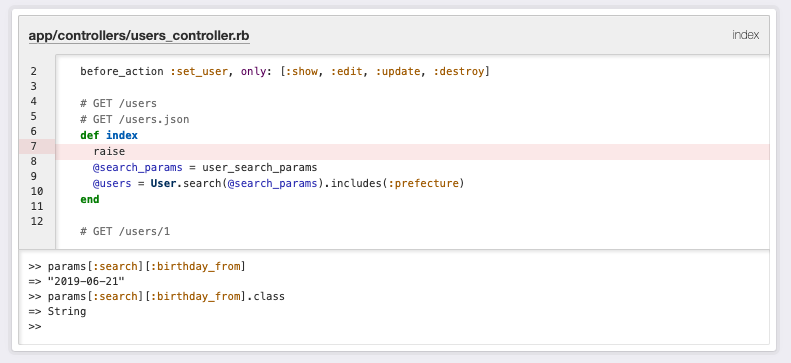
今回の検索機能では問題ないですが、birthday_fromに設定される日付はString型(ハイフン区切りの文字列)であることは認識しておいた方がよいです。
Ruby on Rails API - date_field
collection_select(都道府県のプルダウン選択)
都道府県の一覧をプルダウン選択できるようにします。
<%= f.collection_select(:prefecture_id, Prefecture.all, :id, :name, selected: @search_params[:prefecture_id], include_blank: '選択') %>
<select name="search[prefecture_id]" id="search_prefecture_id">
<option value="">選択</option>
<option value="1">北海道</option>
<option value="2">青森県</option>
省略
<option value="46">鹿児島県</option>
<option value="47">沖縄県</option>
</select>
基本的な使い方はcollection_radio_buttonsと同じです。
Ruby on Rails API - collection_select
I18n対応
I18n(Internationalization)とは、Railsアプリケーションを国際化対応させる機能です。
国際化対応と言われると難しそうに感じるかもしれませんが、ymlファイルに定義した言語ごとの文字を表示するだけです。
「国際化対応しないなら使わなくていいのでは?」と思うかもしれませんが、I18nを使うことで表記揺れ2を防ぐことにもなるので、日本限定のサービスでも使用するのが一般的です。(※筆者の観測範囲では)
インストール方法はこちらが参考になると思います。
i18nについて
使い方
検索機能に関係のある部分だけを抜粋したymlがこちらです。
ja:
activerecord:
models:
user: 'ユーザ'
attributes:
user:
name: '名前'
gender: '性別'
birthday: '誕生日'
prefecture_id: '都道府県'
user/gender:
unanswered: '未回答'
male: '男性'
female: '女性'
other: 'その他'
helpers:
select:
prompt: 選択してください
include_blank: 選択
submit:
create: 登録する
submit: 保存する
update: 更新する
search: 検索する
>> User.human_attribute_name(:gender)
=> "性別"
>> User.human_attribute_name("gender.male")
=> "男性"
>> t('helpers.select.include_blank')
=> "選択"
i18nのキーを調べる方法(nestされているパターン等)
Railsでgem無しに手軽にenumをi18nに対応させる
ラジオボタンを横並びにする(Bootstrap4)
Bootstrapを使ってラジオボタンを横並びにします。
言葉で説明するよりもコードを見比べた方がわかりやすいと思うのでコードを貼っておきます。
# erb
<%= f.collection_radio_buttons(:gender, User.genders, :first, :first) do |r| %>
<%= tag.div(class: 'form-check form-check-inline') do %>
<%= r.radio_button(checked: r.value == @search_params[:gender], class: 'form-check-input') + f.label(User.human_attribute_name("gender.#{r.text}"), class: 'form-check-label') %>
<% end %>
<% end %>
# 生成されたHTML
<input type="hidden" name="search[gender]" value="" />
<div class="form-check form-check-inline">
<input class="form-check-input" type="radio" value="unanswered" name="search[gender]" id="search_gender_unanswered" />
<label class="form-check-label" for="search_未回答">未回答</label>
</div>
<div class="form-check form-check-inline">
<input class="form-check-input" type="radio" value="male" name="search[gender]" id="search_gender_male" />
<label class="form-check-label" for="search_男性">男性</label>
</div>
<div class="form-check form-check-inline">
<input class="form-check-input" type="radio" value="female" name="search[gender]" id="search_gender_female" />
<label class="form-check-label" for="search_女性">女性</label>
</div>
<div class="form-check form-check-inline">
<input class="form-check-input" type="radio" value="other" name="search[gender]" id="search_gender_other" />
<label class="form-check-label" for="search_その他">その他</label>
</div>
Bootstrap移行ガイド - 横並び(Inline)から抜粋
<div class="form-check form-check-inline">
<input class="form-check-input" type="checkbox" id="inlineCheckbox1" value="option1">
<label class="form-check-label">1</label>
</div>
<div class="form-check form-check-inline">
<input class="form-check-input" type="checkbox" id="inlineCheckbox2" value="option2">
<label class="form-check-label">2</label>
</div>
<div class="form-check form-check-inline">
<input class="form-check-input" type="checkbox" id="inlineCheckbox3" value="option3" disabled>
<label class="form-check-label">3(無効)</label>
</div>
Controller
Controllerで行なっていることは以下の通りです。順番に解説していきます。
- 受け取った検索パラメータをチェックする(Strong Parameters)
- チェックした検索パラメータを保持する(インスタンス変数)
- 検索パラメータを元に検索する(Scope, includes)
- 検索結果を返す(インスタンス変数)
再掲
class UsersController < ApplicationController
# indexアクション以外は不要なので省略しています。
def index
@search_params = user_search_params
@users = User.search(@search_params).includes(:prefecture)
end
private
def user_search_params
params.fetch(:search, {}).permit(:name, :gender, :birthday_from, :birthday_to, :prefecture_id)
end
end
1. 受け取った検索パラメータをチェックする(Strong Parameters)
パラメータを受け取る
検索パラメータの受け取り方ですが、params[:search]の中にKey, Valueのセットで検索パラメータが渡されるHash形式(厳密にはHashではなくActionController::Parametersオブジェクトです。)で受け取りたいと思います。
params[:search]の中には{key: value}が{name: なまえ"}のHashが入っているので以下のように値を取り出すことができます。
>> params[:search][:name]
=> "なまえ"
パラメータをチェックする
RailsにはStrong Parametersという機能があります。Strong Parametersとは、システム側が意図していない値を入力された場合、サーバ側で無効化する仕組みです。悪意のあるユーザなどからの攻撃を防ぐため、受け取った値をサーバ側でチェックすることはセキュリティ上必須です。
Railsガイド(Strong Parameters)を確認してください。
Strong Parametersを利用して実装したメソッドがこちらです。
def user_search_params
params.fetch(:search, {}).permit(:name, :gender, :birthday_from, :birthday_to, :prefecture_id)
end
fetchメソッド
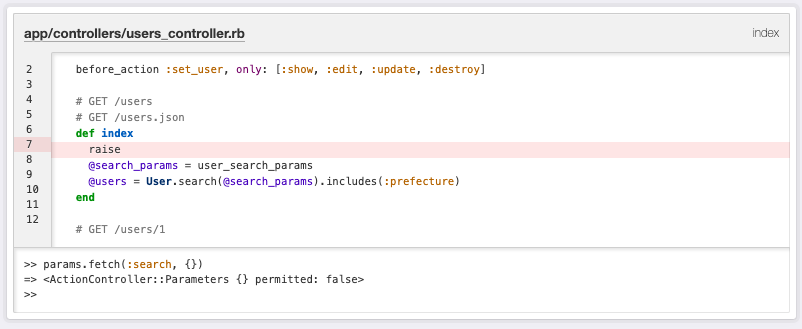
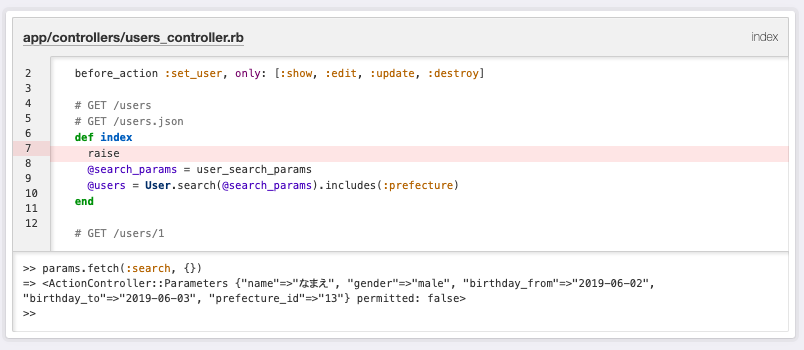
params.fetch(:search, {})は、params[:search]が空の場合{}をparams[:search]が空でない場合、params[:search]を返してくれます。
Ruby on Rails API - fetch
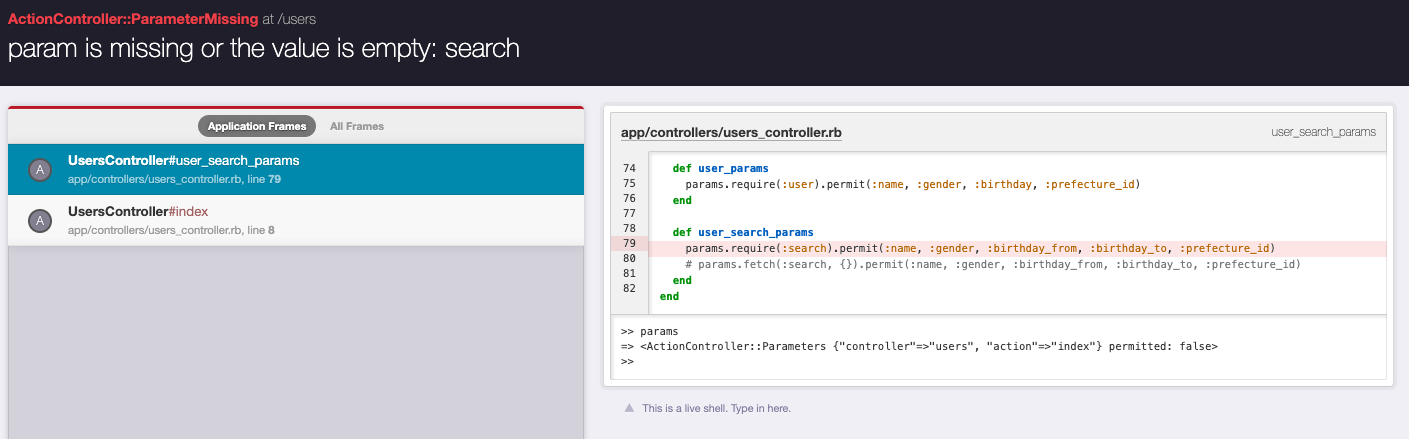
ちなみに、fetch(:search, {})をrequire(:search)に書き換えるとparams[:search]が必須、つまり検索パラメータがない場合はActionController::ParameterMissingとなり、初期表示ができなくなります。
permitメソッド
permitメソッドは許可していないKeyを切り捨てるメソッドです。user_search_paramsメソッドでは引数に指定した:name, :gender, :birthday_from, :birthday_to, :prefecture_idだけを許可して、他のKeyが渡された場合は無視します。
Ruby on Rails API - permit
例えばindex.html.erbでnameをnamuとタイポしていた場合、params[:search]ではnamuがありますが、user_search_paramsではnamuがなくなっています。
# app/views/users/index.html.erb
<%= f.text_field :namu, value: @search_params[:name] %>
2. チェックした検索パラメータを保持する(インスタンス変数)
@search_params = user_search_paramsとしてControllerで宣言/代入することで、Viewで@search_paramsを使えるようになります。
3. 検索パラメータを元に検索する(Scope, includes)
検索はこの部分です。
User.search(@search_params).includes(:prefecture)
Userモデルのsearchメソッドを呼び出して(引数は@search_params)、結果には都道府県を含みます、と。
実装の詳細を確認せずとも内容が想像できますね。プログラミングで名前重要と言われる所以でもあります。
searchメソッドはRailsのScopeという仕組みで実装しています。解説はModelの方を参照してください。
includes
includesはN + 1問題に対応するために行なっています。includesすることでSQLの発行回数を少なくすることができます。
また、N + 1問題のN + 1とは以下の合計のことです。
-
@usersを取得するためにSQLを実行する(1) -
@usersはprefecture_idを持っているけど、都道府県名は持っていないので、prefecture_idをKeyにSQLを実行する(N)
ユーザ一覧ページを初期表示した際の、SQLがこちらです。
(件数が多いと見辛いので、limit(5)しています。)
# User.search(@search_params).limit(5)
Started GET "/users" for 127.0.0.1 at 2019-06-03 22:54:28 +0900
Processing by UsersController#index as HTML
Rendering users/index.html.erb within layouts/application
Prefecture Load (0.5ms) SELECT `prefectures`.* FROM `prefectures`
↳ app/views/users/index.html.erb:28
User Load (0.6ms) SELECT `users`.* FROM `users` LIMIT 5
↳ app/views/users/index.html.erb:49
Prefecture Load (1.6ms) SELECT `prefectures`.* FROM `prefectures` WHERE `prefectures`.`id` = 5 LIMIT 1
↳ app/views/users/index.html.erb:54
Prefecture Load (0.5ms) SELECT `prefectures`.* FROM `prefectures` WHERE `prefectures`.`id` = 35 LIMIT 1
↳ app/views/users/index.html.erb:54
Prefecture Load (0.4ms) SELECT `prefectures`.* FROM `prefectures` WHERE `prefectures`.`id` = 7 LIMIT 1
↳ app/views/users/index.html.erb:54
Prefecture Load (0.5ms) SELECT `prefectures`.* FROM `prefectures` WHERE `prefectures`.`id` = 18 LIMIT 1
↳ app/views/users/index.html.erb:54
Prefecture Load (0.4ms) SELECT `prefectures`.* FROM `prefectures` WHERE `prefectures`.`id` = 8 LIMIT 1
↳ app/views/users/index.html.erb:54
Rendered users/index.html.erb within layouts/application (38.0ms)
Completed 200 OK in 188ms (Views: 180.7ms | ActiveRecord: 4.4ms)
# User.search(@search_params).includes(:prefecture).limit(5)
Started GET "/users" for 127.0.0.1 at 2019-06-03 22:55:45 +0900
Processing by UsersController#index as HTML
Rendering users/index.html.erb within layouts/application
Prefecture Load (0.7ms) SELECT `prefectures`.* FROM `prefectures`
↳ app/views/users/index.html.erb:28
User Load (0.6ms) SELECT `users`.* FROM `users` LIMIT 5
↳ app/views/users/index.html.erb:49
Prefecture Load (3.4ms) SELECT `prefectures`.* FROM `prefectures` WHERE `prefectures`.`id` IN (5, 35, 7, 18, 8)
↳ app/views/users/index.html.erb:49
Rendered users/index.html.erb within layouts/application (211.5ms)
Completed 200 OK in 400ms (Views: 313.4ms | ActiveRecord: 61.7ms)
includesなしの方はSQLの発行が6回なのに対して、includesありの方はSQLの発行が2回になっています。
仮にユーザが10万人いる場合でもincludesありの方はSQLの発行が2回で済むため、パフォーマンスがよくなります。
4. 検索結果を返す(インスタンス変数)
@usersに検索結果を代入します。
Model
Modelで行なっていることは以下の通りです。順番に解説していきます。
- Enumでgenderの値を定義する
- Active Record Associations(関連付け)でUserとPrefectureの関係を定義する
- Scopeで検索用のメソッドを定義する
再掲
class User < ApplicationRecord
enum gender: { unanswered: 0, male: 1, female: 2, other: 9 }
belongs_to :prefecture
scope :search, -> (search_params) do
return if search_params.blank?
name_like(search_params[:name])
.gender_is(search_params[:gender])
.birthday_from(search_params[:birthday_from])
.birthday_to(search_params[:birthday_to])
.prefecture_id_is(search_params[:prefecture_id])
end
scope :name_like, -> (name) { where('name LIKE ?', "%#{name}%") if name.present? }
scope :gender_is, -> (gender) { where(gender: gender) if gender.present? }
scope :birthday_from, -> (from) { where('? <= birthday', from) if from.present? }
scope :birthday_to, -> (to) { where('birthday <= ?', to) if to.present? }
scope :prefecture_id_is, -> (prefecture_id) { where(prefecture_id: prefecture_id) if prefecture_id.present? }
end
Enumでgenderの値を定義する
Enumは取りうる値の範囲が決まっている時にその値を定義することでRailsが便利な機能やメソッドを提供してくれる仕組みです。
例えば、Enumで定義していない値を設定しようとするとArgumentErrorになります。
>> User.new(gender: 3)
!! #<ArgumentError: '3' is not a valid gender>
他にも便利なメソッドが使えるようになります。
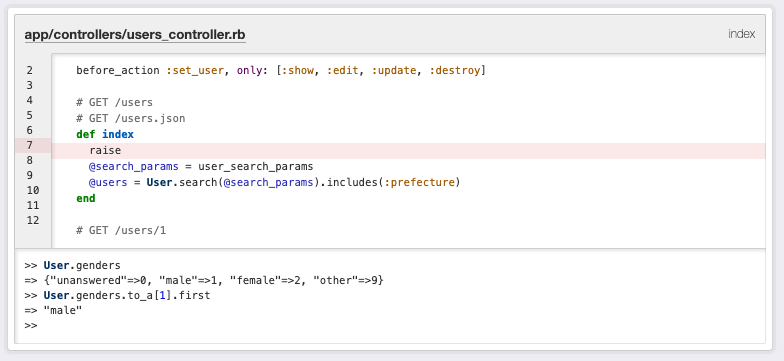
>> User.genders
=> {"unanswered"=>0, "male"=>1, "female"=>2, "other"=>9}
>> User.genders[:male]
=> 1
>> User.new(gender: 1).gender
=> "male"
>> User.new(gender: 1).male?
=> true
Ruby on Rails API - Enum
システムで「性別」の情報を扱う前に知っておくべきこと
Active Record Associations(関連付け)でUserとPrefectureの関係を定義する
belongs_to :prefectureとし、UserモデルとPrefectureモデルの関連付けを定義することで、user.prefecture.nameと書けるようになります。
(Viewで使っています。)
>> User.first.prefecture.name
=> "秋田県"
Scopeで検索用のメソッドを定義する
Scopeとは、ActiveRecordのQueryメソッドに名前を付ける機能です。戻り値はActiveRecord::Relationオブジェクトなので、ScopeからScopeを呼び出すことも可能です。
class User < ApplicationRecord
# 省略
scope :search, -> (search_params) do
# search_paramsが空の場合以降の処理を行わない。
# >> {}.blank?
# => true
return if search_params.blank?
# パラメータを指定して検索を実行する
name_like(search_params[:name])
.gender_is(search_params[:gender])
.birthday_from(search_params[:birthday_from])
.birthday_to(search_params[:birthday_to])
.prefecture_id_is(search_params[:prefecture_id])
end
# nameが存在する場合、nameをlike検索する
scope :name_like, -> (name) { where('name LIKE ?', "%#{name}%") if name.present? }
# gender_isが存在する場合、gender_isで検索する
scope :gender_is, -> (gender) { where(gender: gender) if gender.present? }
# birthdayが存在する場合、birthdayで範囲検索する
scope :birthday_from, -> (from) { where('? <= birthday', from) if from.present? }
scope :birthday_to, -> (to) { where('birthday <= ?', to) if to.present? }
# prefecture_idが存在する場合、prefecture_idで検索する
scope :prefecture_id_is, -> (prefecture_id) { where(prefecture_id: prefecture_id) if prefecture_id.present? }
end
Railsガイド(Scope)
nil? empty? blank? present? の使い分け
この記事でやっていないこと
helperへの切り出し
collection_radio_buttonsが1行になるように切り出したいですよね。こんな感じで。
class ApplicationFormBuilder < ActionView::Helpers::FormBuilder
include ActionView::Helpers::TagHelper
include ActionView::Context
def inline_radio_buttons(method:, collection:, checked:)
collection_radio_buttons(method, collection, :first, :first) do |r|
tag.div(class: 'form-check form-check-inline') do
r.radio_button(checked: r.value == checked, class: 'form-check-input') + self.label(r.text, class: 'form-check-label')
end
end
end
end
formオブジェクト
感想
普段自分が行なっていることを技術記事という形で言語化することで、深掘りできてよかったです。
今後勉強するときは「記事にできるくらいちゃんと理解しているか?」という視点を持ちつつ勉強していくぞい💪('ω'💪)