この記事は、Justsystems Advent Calendar 2017の23日目の記事です。
今回はElasticsearchでランキング学習をやってみます。
ランキング学習について
ランキング学習は機械学習のモデルを用いて検索ランキングを最適化することをさします。
検索結果のランキングはtf-idfやBM25、ページランクなどを使うことが多いと思いますが、ランキング学習により検索サーバーのクリックログなどに基づき順位の最適化を行うことができます。
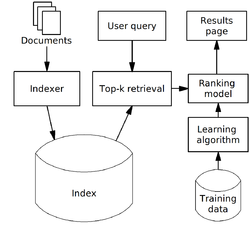
その際、処理速度などの問題から順位の最適化はトップN件のリランクという形で行われることが多いです (下図参照)。
Elasticsearchはこのようなランキング学習を行うことができるプラグインが開発されていますが、まだ詳細を確認できていなかったのでこの機会に試してみました。誰かの参考になれば幸いです。
この記事では次のことをします。
- The Movie Databaseの映画情報を用いてインデックスを作成する
- 映画と検索ユーザーの言語/嗜好ジャンルが一致する場合にクリックされやすくなる検索シミュレーションを行い、検索ログを生成する
- 検索ログを用いてランキング学習し、言語とジャンルが一致する映画が上位にリランキングされるようになることを確かめる
Elasticsearchとプラグインの導入
適当なディレクトリにElasticsearchとプラグインをダウンロード、インストールし、起動します。
cd /tmp
curl -O https://artifacts.elastic.co/downloads/elasticsearch/elasticsearch-5.6.4.zip
unzip elasticsearch-5.6.4.zip && cd elasticsearch-5.6.4
curl -O http://es-learn-to-rank.labs.o19s.com/ltr-1.0.0-RC2-es5.6.4.zip
./bin/elasticsearch-plugin install -b file:///tmp/elasticsearch-5.6.4/ltr-1.0.0-RC2-es5.6.4.zip
./bin/elasticsearch &
データのインデックス作成
The Movie Databaseの映画情報ダウンロードし、インデックスを作成します。
curl -O http://es-learn-to-rank.labs.o19s.com/tmdb.json
マッピング定義
curl -X PUT "http://localhost:9200/tmdb" '{
"mappings": {
"movie": {
"properties": {
"title": {
"type": "text"
},
"overview": {
"type": "text"
},
"genres": {
"type": "keyword"
},
"original_language": {
"type": "keyword"
}
}
}
}
}'
データをbulkリクエスト形式に整形
import json
with open("tmdb.json") as infile, open("tmdb-bulk.txt", "w") as outfile:
action = '{ "index": {} }'
fields = ["title", "overview", "genres", "original_language"]
contents = json.loads(infile.read())
for record in contents.values():
movie = {field: record[field] for field in fields if field in record}
outfile.write("%s\n%s\n" % (action, json.dumps(movie)))
データの投入
curl -XPOST -H "Content-Type:application/json" "localhost:9200/tmdb/movie/_bulk" --data-binary @tmdb-bulk.txt
教師データの生成
映画と検索ユーザーの言語/嗜好ジャンルが一致する場合にクリックされやすくなる検索シミュレーションを行い、検索ログを生成します。
検索に用いる単語リストのダンロード
curl -O https://raw.githubusercontent.com/dwyl/english-words/master/words.txt
シミュレーションの実行
import math
import random
import elasticsearch
client = elasticsearch.Elasticsearch("localhost")
queries = [word.rstrip() for word in open("words.txt")]
languages = ["en", "ja"]
genres = ['Animation', 'TV Movie', 'Mystery', 'War', 'Adventure', 'Science Fiction',
'Horror', 'Foreign', 'Music', 'Thriller', 'Family', 'Comedy', 'History',
'Western', 'Romance', 'Action', 'Drama', 'Fantasy', 'Documentary', 'Crime']
simulation_result = list()
random.shuffle(queries)
for query_id in range(100000):
# 検索クエリ、ユーザーの嗜好ジャンル、言語をランダムに選択
query = queries[query_id]
user_language = languages[random.randint(0, len(languages) - 1)]
user_genre = genres[random.randint(0, len(genres) - 1)]
# 検索の実行
body = {"query": {"multi_match": {"query": query, "fields": ["title", "overview"]}}}
result = client.search(index="tmdb", doc_type="movie", body=body)
hits = result.get("hits").get("hits")
if len(hits) == 0:
continue
# ヒットした結果をクリックするかどうかシミュレートする
hit_group = list()
for hit in hits:
source = hit["_source"]
movie_language = source["original_language"]
movie_genres = [genre["name"] for genre in source.get("genres", [])]
match_language = user_language == movie_language
match_genre = user_genre in movie_genres
logit = 0
if match_language:
# 言語がマッチした場合クリックされやすい
logit += 1
if match_genre:
# ジャンルがマッチした場合クリックされやすい
logit += 1
p = 1 - 1 / (1 + math.exp(logit))
if p > random.random():
clicked = 1
else:
clicked = 0
hit_group.append((clicked, query_id, int(match_language), int(match_genre)))
simulation_result.append(hit_group)
# xgboostの教師/テストデータとして出力
def write_result(result, outfile, groupfile):
for hit_group in result:
for clicked, query_id, match_language, match_genre in hit_group:
outfile.write("%s %s 1:%s 2:%s\n" % (clicked, query_id, match_language, match_genre))
groupfile.write("%s\n" % len(hit_group))
with open("movie.train", "w") as train, open("movie.train.group", "w") as train_group, \
open("movie.test", "w") as test, open("movie.test.group", "w") as test_group, \
open("movie.vali", "w") as vali, open("movie.vali.group", "w") as vali_group:
result_length = len(simulation_result)
random.shuffle(simulation_result)
write_result(simulation_result[:int(0.8 * result_length)], train, train_group)
write_result(simulation_result[int(0.8 * result_length):int(0.9 * result_length)], test, test_group)
write_result(simulation_result[int(0.9 * result_length):], vali, vali_group)
特徴の定義
データの特徴量をelasticsearchに登録していきます。
まずfeature storeという特徴の保存場所を作成します。
curl -XPUT "localhost:9200/_ltr"
次に特徴を定義します。
- ユーザーの言語とヒットした映画の言語が一致しているかどうか
- ユーザーの嗜好ジャンルとヒットした映画のジャンルが一致しているかどうか
curl -XPOST "localhost:9200/_ltr/_featureset/movie_features" -d '{
"featureset": {
"name": "movie_features",
"features": [
{
"name": "language_match",
"params": [
"user_lang"
],
"template_language": "mustache",
"template": {
"match": {
"original_language": "{{user_lang}}"
}
}
},
{
"name": "genres_match",
"params": [
"user_genres"
],
"template_language": "mustache",
"template": {
"match": {
"genres": "{{user_genres}}"
}
}
}
]
}
}'
特徴の定義はElasticsearchのクエリと対応しており、クエリで表現できるものが利用できます。
{{}}で囲われたものはmustacheテンプレートで、検索実行時に指定します。
また、Elasticsearch標準のクエリ以外にもプラグインが提供しているクエリを使うことで、tfやdfなどよく利用される特徴も定義することができます。詳細はドキュメントを参照ください。
学習の実行、モデルのアップロード
シミュレーションの条件だと線形モデルでも十分すぎますが、xgboostのペアワイズロスを用いて学習します。設定の詳細についてはxgboostのドキュメントを参照ください。
xgboostの設定ファイル
objective="rank:pairwise"
# Tree Booster Parameters
# step size shrinkage
eta = 0.1
# minimum loss reduction required to make a further partition
gamma = 1.0
# minimum sum of instance weight(hessian) needed in a child
min_child_weight = 0.1
# maximum depth of a tree
max_depth = 3
# Task parameters
# the number of round to do boosting
num_round = 2
# 0 means do not save any model except the final round model
save_period = 0
# The path of training data
data = "movie.train"
# The path of validation data, used to monitor training process, here [test] sets name of the validation set
eval[test] = "movie.vali"
# The path of test data
test:data = "movie.test"
xgboostの実行
../../xgboost movie.conf
echo -e "0 na q\n1 language_match q\n2 genres_match q" > featmap.txt
../../xgboost movie.conf task=dump model_in=0004.model name_dump=dump.json dump_format=json fmap=featmap.txt
プラグインが線形モデル、ブースティング木の予測モデルをサポートしているので、簡単にElasticsearchに取り込むことができます。
xgboostのダンプからモデルの定義ファイル出力
import json
with open("dump.json") as infile, open("model_payload.json", "w") as outfile:
model_payload = {
"model": {
"name": "movie_model",
"model": {
"type": "model/xgboost+json",
"definition": infile.read()
}
}
}
outfile.write(json.dumps(model_payload))
モデルのアップロード
curl -XPOST -H "Content-Type:application/json" "localhost:9200/_ltr/_featureset/movie_features/_createmodel" -d @model_payload.json
学習したモデルで検索する
準備が整ったので、学習モデルを用いて検索をしてみましょう。
- 言語 日本語、ジャンル SFで
starを検索
curl -XPOST "localhost:9200/tmdb/_search" -d '{
"query": {
"multi_match": {
"query": "star",
"fields": ["title", "overview"]
}
},
"rescore": {
"window_size": 1000,
"query": {
"rescore_query": {
"sltr": {
"params": {
"user_lang": "ja",
"user_genres": "Science Fiction"
},
"model": "movie_model"
}
},
"query_weight" : 0.0,
"rescore_query_weight" : 1.0
}
}
}'
top3
| タイトル | 言語 | ジャンル |
|---|---|---|
| Gantz: Perfect Answer | ja | Action, Mystery, Science Fiction |
| Fullmetal Alchemist: The Sacred Star of Milos | ja | Adventure, Fantasy, Animation, Action, Science Fiction |
| Fist of the North Star | ja | Action, Animation, Drama, Science Fiction, Thriller |
- ランキング学習を利用せずに
starを検索
curl -XPOST "localhost:9200/tmdb/_search" -d '{
"query": {
"multi_match": {
"query": "star",
"fields": ["title", "overview"]
}
}
}'
top3
| タイトル | 言語 | ジャンル |
|---|---|---|
| Star! | en | Romance, Drama, Music |
| Third Star | en | Drama |
| Afghan Star | en | Documentary, Music |
ランキング学習により、言語や嗜好ジャンルがあったものが上位にリランクできています。
まとめ
Elasticsearchでランキング学習ができるプラグインを試してみました。
xgboostで学習したモデルを簡単に利用できる点が非常に便利だと感じました。
ただ特徴の定義ごとにクエリが必要なため、特徴の数が多い場合だと大変そうだなーという印象です。
性能も見ようと思っていましたが時間が無くなってしまったのでまた今度にします。