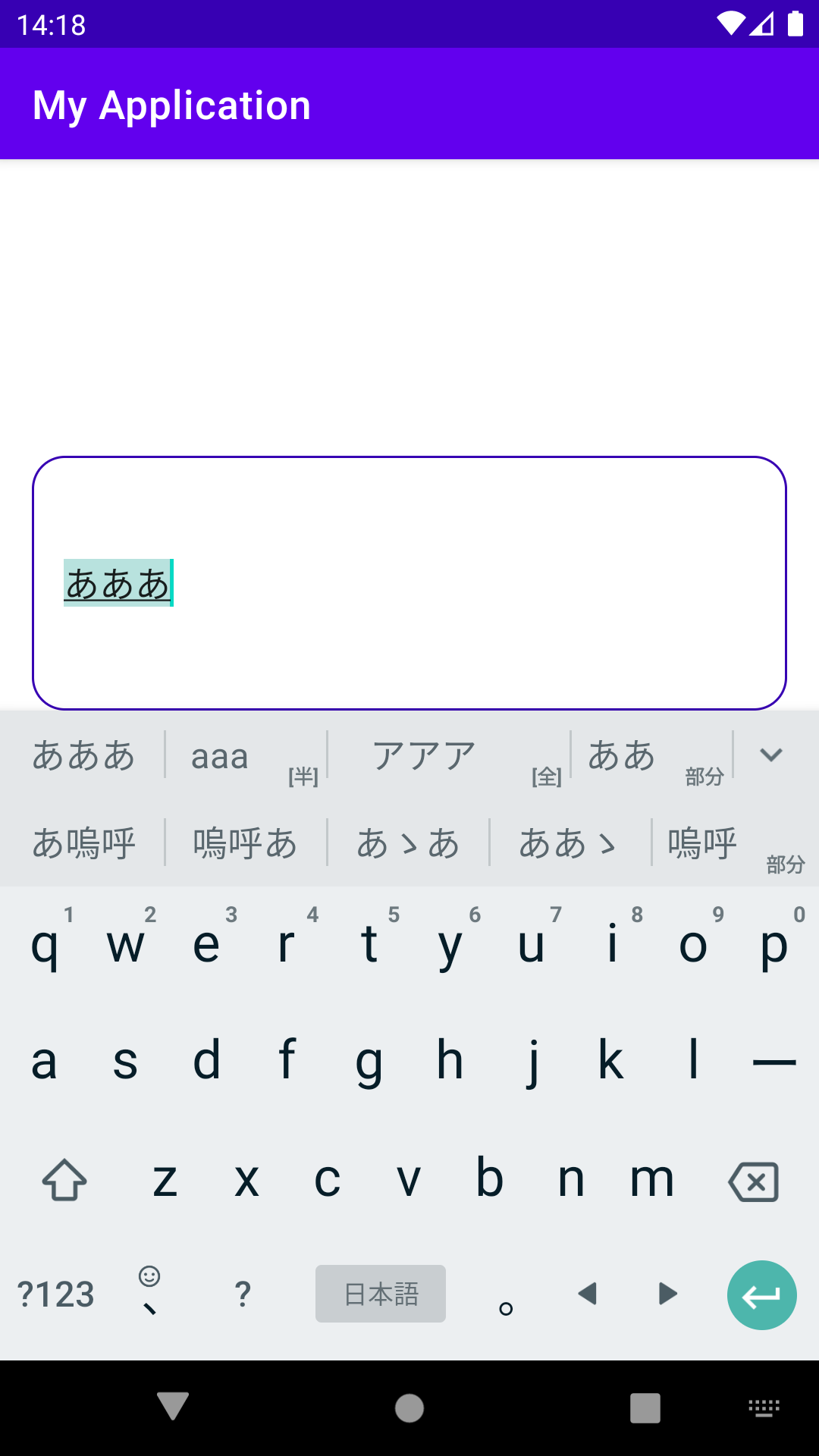
ScrollViewなどスクロール可能なViewの上にあるEditTextにフォーカスをあて、ソフトキーボードで入力するとき、日本語の場合は特に変換候補が複数行にわたって表示されるなど、表示可能なエリアが入力に応じて変動します。
デフォルトのEditTextを使っている場合、そのEditTextが画面内に収まるようにスクロールしてくれるのですが、入力文字数を表示するカウンターなど、EditTextの下にある要素も見える位置までスクロールして欲しい!ということがあるかと思います。
TextInputLayoutとTextInputEditTextを使えばそのような動作になります。
同様の動作を他の要素でもやりたい。という場合どうすれば良いかの説明です。
| ScrollViewの上のEditTextを配置 | 入力中はEditTextの範囲が画面内に収まる位置にスクロールされる | EditTextだけでなく、下のテキストまで見えて欲しい |
|---|---|---|
 |
 |
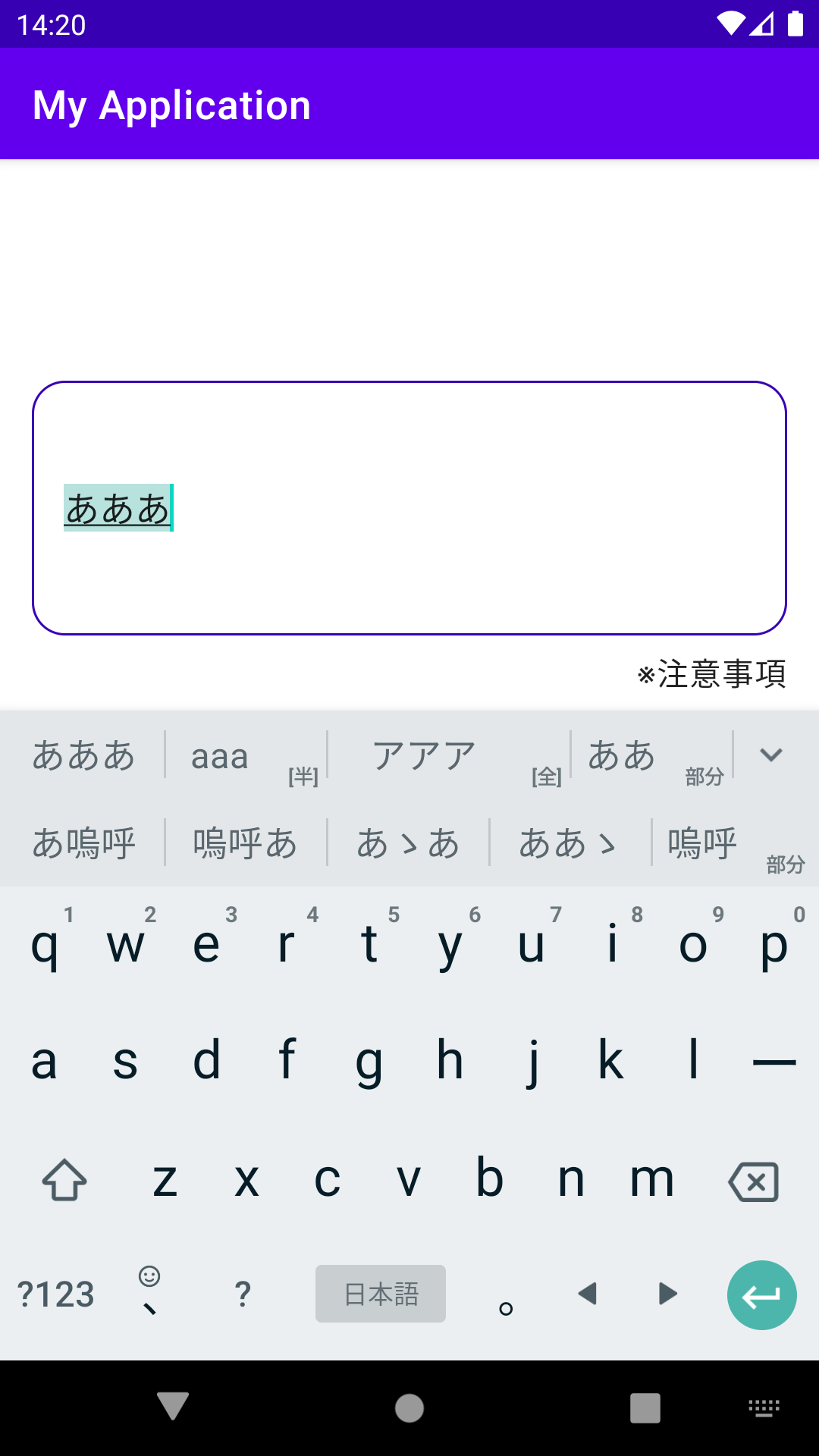 |
親Viewの領域が画面内に収まるようスクロールするEditText
EditTextへの入力中、入力しているところが見えるようにスクロールされる仕組みはrequestRectangleOnScreenで実装されています。EditTextを拡張したクラスを作成し、requestRectangleOnScreenをoverrideすることでこの動作を変更することができます。
上記画像の例では、EditTextとその下のTextViewを囲うViewGroupがあり、そのViewGroupが見える位置にスクロールするように実装するには以下のようにします。
class MyEditText @JvmOverloads constructor(
context: Context,
attrs: AttributeSet? = null,
defStyleAttr: Int = R.attr.editTextStyle,
) : AppCompatEditText(context, attrs, defStyleAttr) {
override fun requestRectangleOnScreen(rectangle: Rect?, immediate: Boolean): Boolean {
val parentView = (parent as? View)
return if (parentView == null) {
super.requestRectangleOnScreen(rectangle, immediate)
} else {
val rect = Rect()
parentView.getDrawingRect(rect)
parentView.requestRectangleOnScreen(rect, immediate)
}
}
}
requestRectangleOnScreenはTextViewのonPreDraw/updateAfterEditからbringPointIntoViewを経由してコールされており、フォーカスの変化や入力テキストの変化時にこのViewを画面内に収めるためにコールされます。引数のrectangleには入力中のテキストの領域などがはいっています。
ここで、parentViewのDrawingRect、つまり、そのView自身の相対座標で表示されている領域を表すRectを取得し、その値をそのViewのrequestRectangleOnScreenに渡します。こうすると、そのViewが画面内に収まるようにスクロールが行われます。
親レイアウトにしているのは単にこのEditTextからアクセスしやすいというだけなので、別途引数などで渡すことができるのであれば、親子関係のないViewでも問題ありません。そのViewが見える範囲へスクロールされます。
以上です
requestRectangleOnScreenってなにやってるの?
やり方としてはもう終わりなのですが、requestRectangleOnScreenってどういう仕組みになっているか?というか引数の意味も分からなかったので調べました。
requestRectangleOnScreenの実装はViewで行われています。
public boolean requestRectangleOnScreen(Rect rectangle, boolean immediate) {
if (mParent == null) {
return false;
}
View child = this;
RectF position = (mAttachInfo != null) ? mAttachInfo.mTmpTransformRect : new RectF();
position.set(rectangle);
ViewParent parent = mParent;
boolean scrolled = false;
while (parent != null) {
rectangle.set((int) position.left, (int) position.top,
(int) position.right, (int) position.bottom);
scrolled |= parent.requestChildRectangleOnScreen(child, rectangle, immediate);
if (!(parent instanceof View)) {
break;
}
// move it from child's content coordinate space to parent's content coordinate space
position.offset(child.mLeft - child.getScrollX(), child.mTop -child.getScrollY());
child = (View) parent;
parent = child.getParent();
}
return scrolled;
}
ちょっとややこしいですが、やっていることは、親Viewにたいして、子View相対座標でのrectangleを指定して requestChildRectangleOnScreen をコール、そしてrectangleを親Viewの相対座標に変更した上で、さらにその親にと親がViewでなくなるまで繰り返します。
requestChildRectangleOnScreenの実装を見てみます。
@Override
public boolean requestChildRectangleOnScreen(View child, Rect rectangle, boolean immediate) {
return false;
}
はい、ViewGroupはスクロール機能を持っていないため、空実装です。FrameLayoutやLinearLayoutも同様です。
ではScrollViewの実装を見てみましょう。
@Override
public boolean requestChildRectangleOnScreen(View child, Rect rectangle,
boolean immediate) {
// offset into coordinate space of this scroll view
rectangle.offset(child.getLeft() - child.getScrollX(),
child.getTop() - child.getScrollY());
return scrollToChildRect(rectangle, immediate);
}
子Viewの相対座標で渡されたrectangleを自身の相対座標に変換して、scrollToChildRectをコールしていますね。
引数のrectangleをワーキングメモリとして使ってしまっていますが、requestRectangleOnScreenの実装を見ればわかるとおり、中身を書き換えてしまっても次のループでリセットされるようになっているため、外部に影響はありません。
scrollToChildRect を見てみましょう。
private boolean scrollToChildRect(Rect rect, boolean immediate) {
final int delta = computeScrollDeltaToGetChildRectOnScreen(rect);
final boolean scroll = delta != 0;
if (scroll) {
if (immediate) {
scrollBy(0, delta);
} else {
smoothScrollBy(0, delta);
}
}
return scroll;
}
computeScrollDeltaToGetChildRectOnScreenでrectからスクロール量を計算して、自身をスクロールさせています。
computeScrollDeltaToGetChildRectOnScreenを見てみましょう。
protected int computeScrollDeltaToGetChildRectOnScreen(Rect rect) {
if (getChildCount() == 0) return 0;
int height = getHeight();
int screenTop = getScrollY();
int screenBottom = screenTop + height;
int fadingEdge = getVerticalFadingEdgeLength();
// leave room for top fading edge as long as rect isn't at very top
if (rect.top > 0) {
screenTop += fadingEdge;
}
// leave room for bottom fading edge as long as rect isn't at very bottom
if (rect.bottom < getChildAt(0).getHeight()) {
screenBottom -= fadingEdge;
}
int scrollYDelta = 0;
if (rect.bottom > screenBottom && rect.top > screenTop) {
// need to move down to get it in view: move down just enough so
// that the entire rectangle is in view (or at least the first
// screen size chunk).
if (rect.height() > height) {
// just enough to get screen size chunk on
scrollYDelta += (rect.top - screenTop);
} else {
// get entire rect at bottom of screen
scrollYDelta += (rect.bottom - screenBottom);
}
// make sure we aren't scrolling beyond the end of our content
int bottom = getChildAt(0).getBottom();
int distanceToBottom = bottom - screenBottom;
scrollYDelta = Math.min(scrollYDelta, distanceToBottom);
} else if (rect.top < screenTop && rect.bottom < screenBottom) {
// need to move up to get it in view: move up just enough so that
// entire rectangle is in view (or at least the first screen
// size chunk of it).
if (rect.height() > height) {
// screen size chunk
scrollYDelta -= (screenBottom - rect.bottom);
} else {
// entire rect at top
scrollYDelta -= (screenTop - rect.top);
}
// make sure we aren't scrolling any further than the top our content
scrollYDelta = Math.max(scrollYDelta, -getScrollY());
}
return scrollYDelta;
}
ちょと長いメソッドですがやっていることはシンプルですね。fadingEdigがあればそれをよけるように、指定されたrect範囲が画面内に収まる最短のスクロール量を計算しています。
指定された領域の高さが表示可能範囲より高い場合、画面下からは上端が収まるまで、画面上からは下端が収まるまでと、最短のスクロール量になっていますね。
同様にRecyclerViewなどもrequestChildRectangleOnScreenが実装されていて、指定領域が見えるような位置までのスクロールを行います。
以上です