p5.jsで描ける図形についてまとめました。
この記事は以下の記事のp5.js版です。
Processing で描ける図形まとめ - Qiita
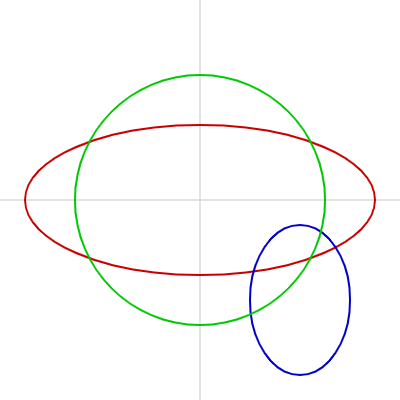
円・楕円
ellipse() や circle() で描けます。
ellipseは横の大きさと縦の大きさを別々に指定できるため、楕円が描けます。
circleは直径を指定することでまんまるの円(正円、真円)が描けます。
function setup() {
createCanvas(400, 400);
}
function draw() {
background(255);
// 中心線
strokeWeight(1);
stroke(200);
line(0, height / 2, width, height / 2);
line(width / 2, 0, width / 2, height);
noFill();
strokeWeight(2);
// 赤い楕円
stroke(200, 0, 0);
ellipse(width / 2, height / 2, 350, 150);
// 青い楕円
stroke(0, 0, 200);
ellipse(300, 300, 100, 150);
// 緑の正円
stroke(0, 200, 0);
circle(width / 2, height / 2, 250);
}
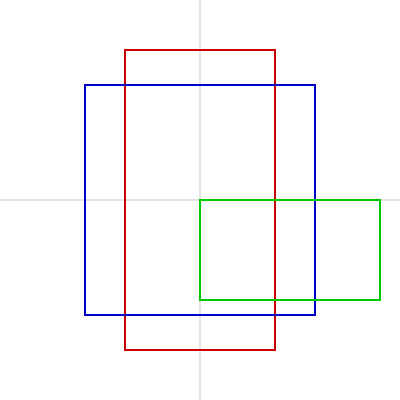
四角(長方形・正方形)
square() や rect() で描けます。
squareは辺の長さを指定することで正方形が描けます。
rectは横の大きさと縦の大きさを別々に指定できるため、長方形が描けます。
rectMode() を使うと指定した座標が四角のどこの位置を指すのか変更できます。
デフォルトでは左上が指定されるので、 rectMode(CORNER) と同じ状態になります。
function setup() {
createCanvas(400, 400);
}
function draw() {
background(255);
// 中心線
strokeWeight(1);
stroke(200);
line(0, height / 2, width, height / 2);
line(width / 2, 0, width / 2, height);
noFill();
strokeWeight(2);
// 赤い長方形
stroke(200, 0, 0);
rectMode(CENTER);
rect(width / 2, height / 2, 150, 300);
//青い正方形
stroke(0, 0, 200);
square(width / 2, height / 2, 230);
// 緑の長方形
stroke(0, 200, 0);
rectMode(CORNER);
rect(width / 2, height / 2, 180, 100);
}
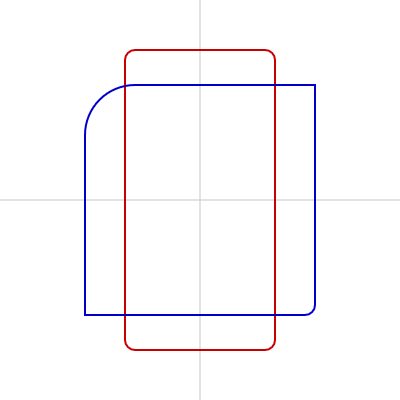
四角の角のまるみも指定できます。
位置やサイズの指定の後に4つの角のまるみを一括で指定したり、4つの角のまるみをそれぞれ指定したりできます。
function setup() {
createCanvas(400, 400);
}
function draw() {
background(255);
// 中心線
strokeWeight(1);
stroke(200);
line(0, height / 2, width, height / 2);
line(width / 2, 0, width / 2, height);
noFill();
strokeWeight(2);
// 赤い長方形、角まる
stroke(200, 0, 0);
rectMode(CENTER);
rect(width/2, height/2, 150, 300, 10);
// 青い正方形、角いろいろ
stroke(0, 0, 200);
square(width/2, height/2, 230, 50, 0, 10, 0);
}
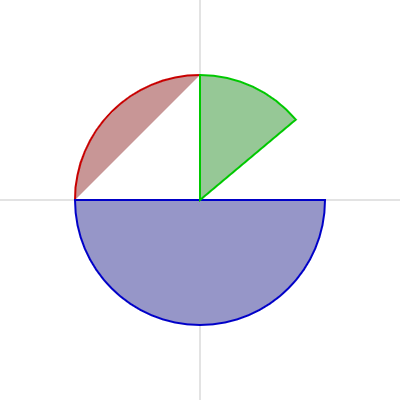
半円、パイカット図形
半円もしくはパイやピザをカットしたような図形は arc() で描けます。
オプションとしてOPEN(弧の線だけを描いて図形を閉じきらない)、CHORD(弧の線とその間の直線で図形を閉じきる)、PIE(弧と始点の間を線で結びピザのピース状に閉じきる)が指定できます。
function setup() {
createCanvas(400, 400);
}
function draw() {
background(255);
// 中心線
strokeWeight(1);
stroke(200);
line(width / 2, 0, width / 2, height);
line(0, height / 2, width, height / 2);
strokeWeight(2);
// 左上の赤い半円。線は閉じきっていない
stroke(200, 0, 0);
fill(200, 150, 150);
arc(width / 2, height / 2, 250, 250, -PI, -PI / 2, OPEN);
// 下の青い半円。線は閉じきっている
stroke(0, 0, 200);
fill(150, 150, 200);
arc(width / 2, height / 2, 250, 250, 0, PI, CHORD);
// 右上の緑のピース。線は始点を含めて閉じきっている
stroke(0, 200, 0);
fill(150, 200, 150);
arc(width / 2, height / 2, 250, 250, radians(270), radians(320), PIE);
}
angleMode() を使って、角度の指定を度数法で書く方法もあります。
function setup() {
createCanvas(400, 400);
angleMode(DEGREES);
}
function draw() {
background(255);
// 中心線
strokeWeight(1);
stroke(200);
line(width / 2, 0, width / 2, height);
line(0, height / 2, width, height / 2);
strokeWeight(2);
// 左上の赤い半円。線は閉じきっていない
stroke(200, 0, 0);
fill(200, 150, 150);
arc(width / 2, height / 2, 250, 250, -180, -90, OPEN);
// 下の青い半円。線は閉じきっている
stroke(0, 0, 200);
fill(150, 150, 200);
arc(width / 2, height / 2, 250, 250, 0, 180, CHORD);
// 右上の緑のピース。線は始点を含めて閉じきっている
stroke(0, 200, 0);
fill(150, 200, 150);
arc(width / 2, height / 2, 250, 250, 270, 320, PIE);
}
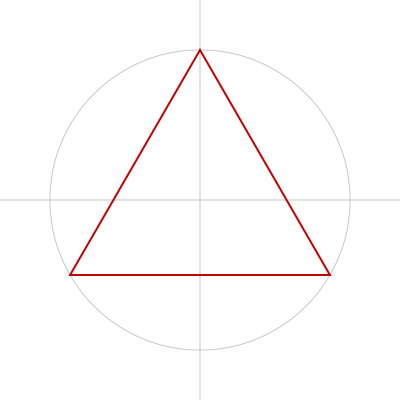
三角形
triangle() で描く方法もありますが、
beginShape()、endShape()、vertex() を使って描くと扱いやすいのでオススメです。
function setup() {
createCanvas(400, 400);
angleMode(DEGREES);
}
function draw() {
background(255);
// 中心線
strokeWeight(1);
stroke(200);
line(width / 2, 0, width / 2, height);
line(0, height / 2, width, height / 2);
// 灰色の円
stroke(200);
ellipse(width / 2, height / 2, 150 * 2, 150 * 2);
// 三角形
noFill();
strokeWeight(2);
stroke(200, 0, 0);
drawTriangle(width / 2, height / 2, 150); // 横の位置、縦の位置、円の半径
}
function drawTriangle(x, y, r) {
push();
translate(x, y); // 中心となる座標
rotate(-90);
// 円を均等に3分割する点を結び、三角形をつくる
beginShape();
for (let i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
vertex(r * cos(360 * i / 3), r * sin(360 * i / 3));
}
endShape(CLOSE);
pop();
}
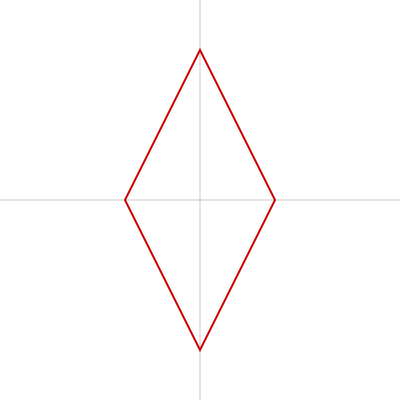
ひし形
beginShape()、endShape()、vertex() で描けます。
function setup() {
createCanvas(400, 400);
angleMode(DEGREES);
}
function draw() {
background(255);
// 中心線
strokeWeight(1);
stroke(200);
line(width / 2, 0, width / 2, height);
line(0, height / 2, width, height / 2);
// ひし形
noFill();
strokeWeight(2);
stroke(200, 0, 0);
drawDiamond(width / 2, height / 2, 150); // 横の位置、縦の位置、中心点と中心から遠い頂点までの距離
}
function drawDiamond(x, y, r) {
let R;
push();
translate(x, y);
beginShape();
for (let i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
if (i % 2 == 0) {
R = r / 2;
} else {
R = r;
}
vertex(R * cos(90 * i), R * sin(90 * i));
}
endShape(CLOSE);
pop();
}
三項演算子を使ってすっきり書くこともできます。
function setup() {
createCanvas(400, 400);
angleMode(DEGREES);
}
function draw() {
background(255);
// 中心線
strokeWeight(1);
stroke(200);
line(width / 2, 0, width / 2, height);
line(0, height / 2, width, height / 2);
// ひし形
noFill();
strokeWeight(2);
stroke(200, 0, 0);
drawDiamond(width / 2, height / 2, 150); // 横の位置、縦の位置、中心点と中心から遠い頂点までの距離
}
function drawDiamond(x, y, r) {
push();
translate(x, y);
beginShape();
for (let i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
let R = i % 2 == 0 ? r / 2 : r;
vertex(R * cos(90 * i), R * sin(90 * i));
}
endShape(CLOSE);
pop();
}
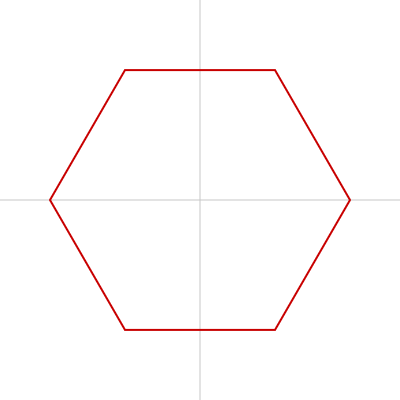
正多角形
シンプルな書き方
正五角形、正六角形、…正n角形は beginShape()、endShape()、vertex() を使って描けます。
正六角形を描く例 :
function setup() {
createCanvas(400, 400);
angleMode(DEGREES);
}
function draw() {
background(255);
// 中心線
strokeWeight(1);
stroke(200);
line(width / 2, 0, width / 2, height);
line(0, height / 2, width, height / 2);
// 正六角形
noFill();
strokeWeight(2);
stroke(200, 0, 0);
drawPolygon(width / 2, height / 2, 150, 6); // 横の位置、縦の位置、中心点と頂点までの距離、頂点数
}
function drawPolygon(x, y, r, vertexNum) {
push();
translate(x, y);
beginShape();
for (let i = 0; i < vertexNum; i++) {
vertex(r * cos(360 * i / vertexNum), r * sin(360 * i / vertexNum));
}
endShape(CLOSE);
pop();
}
数式を使った書き方
数式を利用して書く方法もあります。
数式は以下のページを参考にしました。
Parametric equation of a regular pentagon – GeoGebra
正多角形とスピログラフの数式 | シキノート
p5.jsにおいては、見た目は先述のシンプルな書き方とあまり変わらないように見えました。
function setup() {
createCanvas(400, 400);
angleMode(DEGREES);
}
function draw() {
background(255);
// 中心線
strokeWeight(1);
stroke(200);
line(width / 2, 0, width / 2, height);
line(0, height / 2, width, height / 2);
// 正六角形
noFill();
strokeWeight(2);
stroke(200, 0, 0);
drawPolygon(width / 2, height / 2, 150, 6); // 横の位置、縦の位置、中心点と頂点までの距離、頂点数
}
function drawPolygon(ox, oy, r, vertexNum) {
push();
translate(ox, oy);
beginShape();
for (let theta = 0; theta < 360; theta++) {
let pos = calcPos(r, theta, vertexNum);
let x = pos.x;
let y = pos.y;
vertex(x, y);
}
endShape(CLOSE);
pop();
}
function calcPos(r, t, num) {
let x = r * cos(t) * func(t, num);
let y = r * sin(t) * func(t, num);
let vec = createVector(x, y);
return vec;
}
function func(t, num) {
let A = cos(180 / num);
let b = 360 / num;
let B = cos(b * (t / b - floor(t / b)) - 180 / num);
return A / B;
}
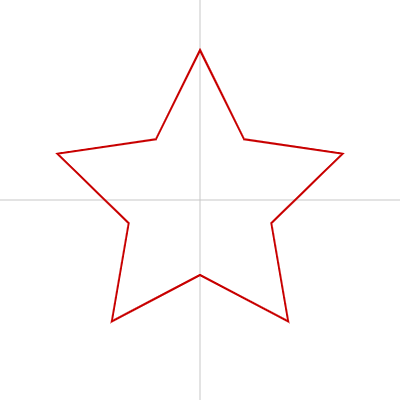
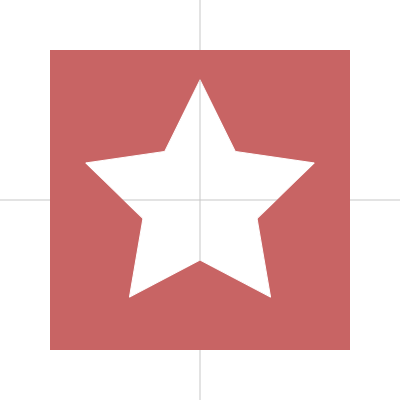
星
シンプルな描き方
星は beginShape()、endShape()、vertex() を使って描けます。
トゲの数も調整できます。
トゲの数が5つの例 :
function setup() {
createCanvas(400, 400);
angleMode(DEGREES);
}
function draw() {
background(255);
// 中心線
strokeWeight(1);
stroke(200);
line(width / 2, 0, width / 2, height);
line(0, height / 2, width, height / 2);
// 星
noFill();
strokeWeight(2);
stroke(200, 0, 0);
drawStar(width / 2, height / 2, 150, 5); // 横の位置、縦の位置、中心点とトゲの頂点までの距離、トゲの数
}
function drawStar(x, y, r, prickleNum) {
let vertexNum = prickleNum * 2; // 頂点数(トゲの数*2)
let R; // 中心点から頂点までの距離
push();
translate(x, y);
rotate(-90);
beginShape();
for (let i = 0; i < vertexNum; i++) {
R = i % 2 == 0 ? r : r / 2;
vertex(R * cos(360 * i / vertexNum), R * sin(360 * i / vertexNum));
}
endShape(CLOSE);
pop();
}
数式を使った書き方
数式を利用して書く方法もあります。
数式は以下のページを参考にしました。
正多角形とスピログラフの数式 | シキノート
p5.jsにおいては、見た目は先述のシンプルな書き方とあまり変わらないように見えました。
function setup() {
createCanvas(400, 400);
angleMode(DEGREES);
}
function draw() {
background(255);
// 中心線
strokeWeight(1);
stroke(200);
line(width / 2, 0, width / 2, height);
line(0, height / 2, width, height / 2);
// 星
noFill();
strokeWeight(2);
stroke(200, 0, 0);
drawStar(width / 2, height / 2, 150, 5); // 横の位置、縦の位置、中心点とトゲの頂点までの距離、トゲの数
}
function drawStar(ox, oy, r, prickleNum) {
push();
translate(ox, oy);
rotate(-90);
beginShape();
for (let theta = 0; theta < 360; theta++) {
let pos = calcPos(r, theta, prickleNum);
let x = pos.x;
let y = pos.y;
vertex(x, y);
}
endShape(CLOSE);
pop();
}
function calcPos(r, t, num) {
let x = r * cos(t) * func(t, num);
let y = r * sin(t) * func(t, num);
let vec = createVector(x, y);
return vec;
}
function func(t, num) {
let a = 360 / num;
let A = cos(a);
let b = acos(cos(num * t));
let B = cos(a - b / num);
return A / B;
}
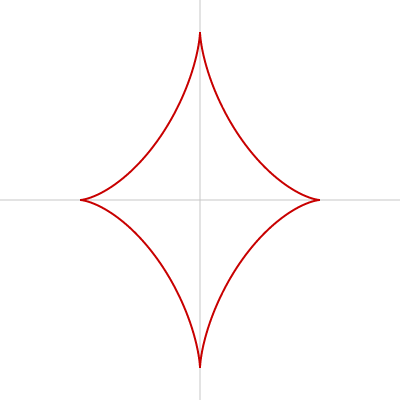
キラキラ星(アステロイド曲線 1)
キラキラな星はアステロイド曲線と呼ばれ、 beginShape()、endShape()、vertex() を使って描けます。
図形を縦方向に大きめに描くとよりそれらしくなります。
function setup() {
createCanvas(400, 400);
angleMode(DEGREES);
}
function draw() {
background(255);
// 中心線
strokeWeight(1);
stroke(200);
line(width / 2, 0, width / 2, height);
line(0, height / 2, width, height / 2);
// アステロイド曲線
noFill();
strokeWeight(2);
stroke(200, 0, 0);
drawTwinkleStar(width / 2, height / 2, 120); // 横の位置、縦の位置、中心点と横方向の頂点までの距離
}
function drawTwinkleStar(x, y, r) {
push();
translate(x, y);
beginShape();
for (let theta = 0; theta < 360; theta++) {
vertex(r * pow(cos(theta), 3), r * 1.4 * pow(sin(theta), 3));
}
endShape(CLOSE);
pop();
}
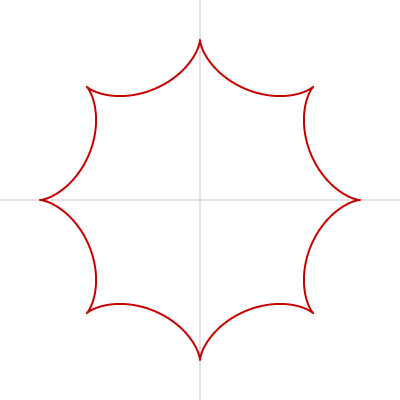
びっくり吹き出し(アステロイド曲線 2)
漫画でよく見かける
_人人人人人人人人人人_
> びっくり吹き出し <
 ̄Y^Y^Y^Y^Y^Y^Y^Y^Y ̄
はアステロイド曲線で表現でき、 beginShape()、endShape()、vertex() を使って描けます。
function setup() {
createCanvas(400, 400);
angleMode(DEGREES);
}
function draw() {
background(255);
// 中心線
strokeWeight(1);
stroke(200);
line(width / 2, 0, width / 2, height);
line(0, height / 2, width, height / 2);
// アステロイド曲線
noFill();
strokeWeight(2);
stroke(200, 0, 0);
strokeJoin(ROUND);
drawAstroid(width / 2, height / 2, 20, 8); // 横の位置、縦の位置、大きさ調整用変数、トゲの数
}
function drawAstroid(ox, oy, r, vertexNum) {
vertexNum -= 1;
push();
translate(ox, oy);
beginShape();
for (let theta = 0; theta < 360; theta++) {
let x = r * (vertexNum * cos(theta) + cos(-vertexNum * theta));
let y = r * (vertexNum * sin(theta) + sin(-vertexNum * theta));
vertex(x, y);
}
endShape();
pop();
}
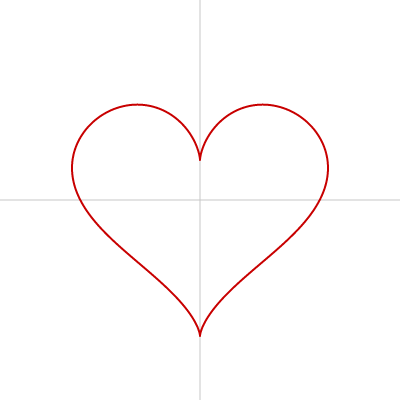
ハート
ハートは beginShape()、endShape()、vertex() を使って描けます。
strokeJoin() を利用して線のつなぎ目をなめらかにしています。
function setup() {
createCanvas(400, 400);
angleMode(DEGREES);
}
function draw() {
background(255);
// 中心線
strokeWeight(1);
stroke(200);
line(width / 2, 0, width / 2, height);
line(0, height / 2, width, height / 2);
// ハート
noFill();
strokeWeight(2);
stroke(200, 0, 0);
strokeJoin(ROUND); //線のつなぎ目について設定
drawHeart(width / 2, height / 2, 8); // 横の位置、縦の位置、大きさ調整用変数
}
function drawHeart(ox, oy, size) {
push();
translate(ox, oy);
beginShape();
for (let theta = 0; theta < 360; theta++) {
let x = size * (16 * sin(theta) * sin(theta) * sin(theta));
let y = (-1) * size * (13 * cos(theta) - 5 * cos(2 * theta) -
2 * cos(3 * theta) - cos(4 * theta));
vertex(x, y);
}
endShape(CLOSE);
pop();
}
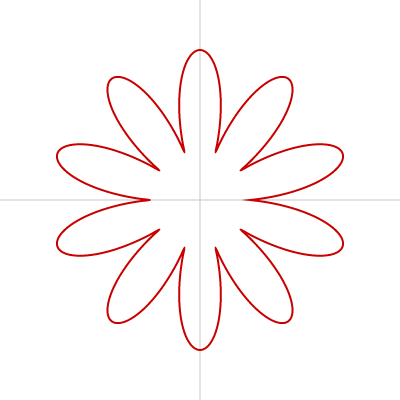
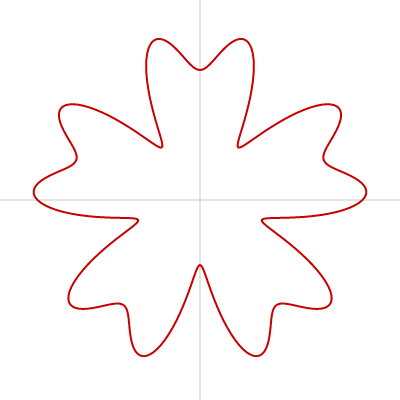
花
お花は beginShape()、endShape()、vertex() を使って描けます。
function setup() {
createCanvas(400, 400);
angleMode(DEGREES);
}
function draw() {
background(255);
// 中心線
strokeWeight(1);
stroke(200);
line(width / 2, 0, width / 2, height);
line(0, height / 2, width, height / 2);
// 花
noFill();
strokeWeight(2);
stroke(200, 0, 0);
drawFlower(width / 2, height / 2, 100); // 横の位置、縦の位置、大きさ調整用変数
}
function drawFlower(ox, oy, r) {
push();
translate(ox, oy);
beginShape();
for (let theta = 0; theta < 360; theta++) {
let R = r * abs(sin(theta * 5)) + r / 2;
let x = R * cos(theta);
let y = R * sin(theta);
curveVertex(x, y);
}
endShape(CLOSE);
pop();
}
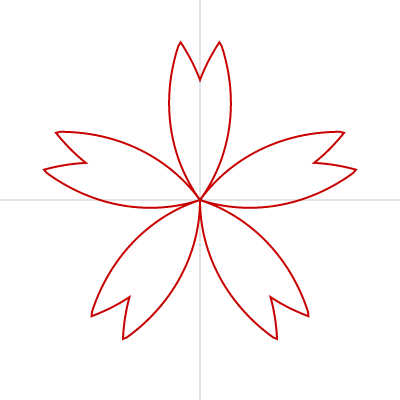
桜
花びらが分かれているタイプ
花びらがそれぞれ分かれていて、先端に鋭い切れ込みの入った桜の花は、 beginShape()、endShape()、vertex() を使って描けます。
数式は以下の記事を参考にさせていただきました。
花の曲線を描く - CinderellaJapan
function setup() {
createCanvas(400, 400);
angleMode(DEGREES);
}
function draw() {
background(255);
// 中心線
strokeWeight(1);
stroke(200);
line(width / 2, 0, width / 2, height);
line(0, height / 2, width, height / 2);
// 桜
noFill();
strokeWeight(2);
stroke(200, 0, 0);
drawSakura(width / 2, height / 2, 200); // 横の位置、縦の位置、大きさ調整用変数
}
function drawSakura(ox, oy, or) {
let petalNum = 5; // 花びらの数
push();
translate(ox, oy);
rotate(90);
beginShape();
for (let theta = 0; theta < 360; theta++) {
let A = petalNum / 180 * theta;
let md = floor(A) % 2;
let r = pow(-1, md) * (A - floor(A)) + md;
let R = r + 2 * calcH(r);
let x = or * R * cos(theta);
let y = or * R * sin(theta);
vertex(x, y);
}
endShape(CLOSE);
pop();
}
function calcH(x) {
if (x < 0.8) {
return 0;
} else {
return 0.8 - x;
}
}
花びらが分かれていないタイプ
花びらが分かれていない、丸みのある桜の花は、 beginShape()、endShape()、vertex() を使って描けます。
数式は以下の記事を参考にさせていただきました。
~スーパーバラ曲線を作ろう~
function setup() {
createCanvas(400, 400);
angleMode(DEGREES);
}
function draw() {
background(255);
// 中心線
strokeWeight(1);
stroke(200);
line(width / 2, 0, width / 2, height);
line(0, height / 2, width, height / 2);
// 桜
noFill();
strokeWeight(2);
stroke(200, 0, 0);
drawSakura(width / 2, height / 2, 130); // 横の位置、縦の位置、大きさ調整用変数
}
function drawSakura(ox, oy, or) {
push();
translate(ox, oy);
beginShape();
for (let theta = 0; theta < 360; theta++) {
let A = (sin(theta * 5) + cos(theta * 10)) / 2.0;
let B = A * 0.5 + 1.0;
let R = or * B;
let x = R * sin(theta + 90);
let y = R * cos(theta + 90);
vertex(x, y);
}
endShape(CLOSE);
pop();
}
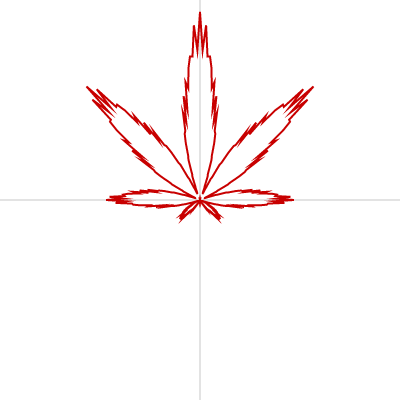
葉 (麻の葉、紅葉、楓)
葉っぱは beginShape()、endShape()、vertex() を使って描けます。
function setup() {
createCanvas(400, 400);
angleMode(DEGREES);
}
function draw() {
background(255);
// 中心線
strokeWeight(1);
stroke(200);
line(width / 2, 0, width / 2, height);
line(0, height / 2, width, height / 2);
// 葉っぱ
noFill();
strokeWeight(2);
stroke(200, 0, 0);
noFill();
drawLeaf(width / 2, height / 2, 45); // 横の位置、縦の位置、大きさ調整用変数
}
function drawLeaf(ox, oy, r) {
push();
translate(ox, oy);
beginShape();
for (let theta = 0; theta < 360; theta++) {
let R = -r * (1 + (9.0 / 10.0) * cos(8 * theta)) * (1 + (1.0 / 10.0) * cos(24 * theta)) * ((9.0 / 10.0) + (1.0 / 10.0) * cos(200 * theta)) * (1 + sin(theta));
let x = R * cos(theta);
let y = R * sin(theta);
vertex(x, y);
}
endShape(CLOSE);
pop();
}
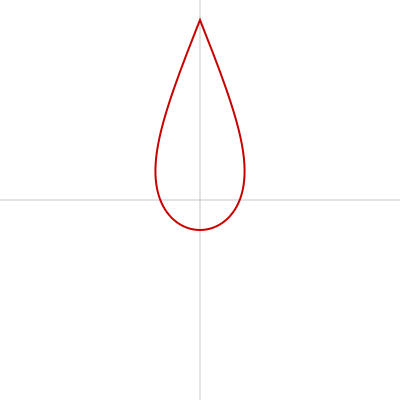
しずく
涙のようなしずく型の図形は beginShape()、endShape()、vertex() を使って描けます。
コード中、Aという変数がありますが、この値を小さくすると丸みのある形になり、大きくすると細く鋭い形になります。
function setup() {
createCanvas(400, 400);
angleMode(DEGREES);
}
function draw() {
background(255);
// 中心線
strokeWeight(1);
stroke(200);
line(width / 2, 0, width / 2, height);
line(0, height / 2, width, height / 2);
// しずく
noFill();
strokeWeight(2);
stroke(200, 0, 0);
drawDrop(width / 2, height / 2, 180, 5); // 横の位置、縦の位置、大きさ調整用変数、鋭さ調整用変数
}
function drawDrop(x, y, r, A) {
push();
translate(x, y);
rotate(-90);
beginShape();
for (let theta = 0; theta < 360; theta++) {
let R = r / (A * sin(theta / 2) + 1);
vertex(R * cos(theta), R * sin(theta));
}
endShape(CLOSE);
pop();
}
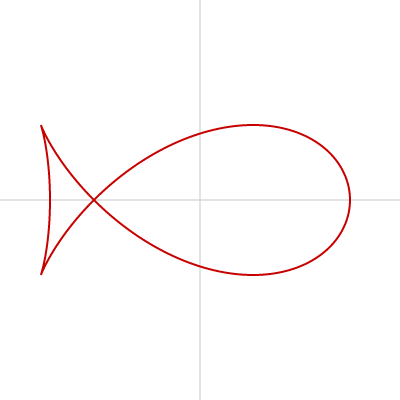
魚
魚の形は beginShape()、endShape()、vertex() を使って描けます。
数式は以下のページを参考にしました。
Fish curve - Wikipedia
function setup() {
createCanvas(400, 400);
angleMode(DEGREES);
}
function draw() {
background(255);
// 中心線
strokeWeight(1);
stroke(200);
line(width / 2, 0, width / 2, height);
line(0, height / 2, width, height / 2);
// 魚
noFill();
strokeWeight(2);
stroke(200, 0, 0);
drawFish(width / 2, height / 2, 150); // 横の位置、縦の位置、大きさ調整用変数
}
function drawFish(ox, oy, r) {
push();
translate(ox, oy);
beginShape();
for (let theta = 0; theta < 360; theta++) {
let x = r * cos(theta) - r * pow(sin(theta), 2) / sqrt(2);
let y = r * cos(theta) * sin(theta);
vertex(x, y);
}
endShape(CLOSE);
pop();
}
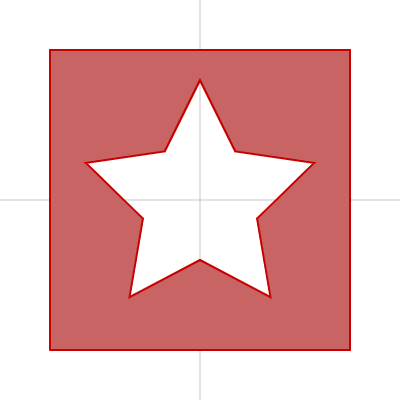
穴あき図形
beginContour()、endContour()を使った書き方
ドーナツのように穴のあいた図形は beginContour()、beginShape()、endShape()、vertex()、endContour() を使って描けます。
let R; // 星(穴)の大きさ調整用
const vertexNum = 10; // 星の頂点数
const w = 300; // 図形の外枠の横の長さ
const h = 300; // 図形の外枠の縦の長さ
function setup() {
createCanvas(400, 400);
angleMode(DEGREES);
}
function draw() {
background(255);
// 中心線
strokeWeight(1);
stroke(200);
line(0, height / 2, width, height / 2);
line(width / 2, 0, width / 2, height);
// 星形穴あき図形
noFill();
strokeWeight(2);
stroke(200, 0, 0);
fill(200, 100, 100);
push();
translate(width / 2, height / 2);
rotate(-90);
beginShape();
vertex(-w / 2, -h / 2);
vertex(w / 2, -h / 2);
vertex(w / 2, h / 2);
vertex(-w / 2, h / 2);
beginContour();
for (let i = vertexNum; i > 0; i--) {
R = i % 2 == 0 ? w * 0.4 : w * 0.2;
vertex(R * cos(360 * i / vertexNum), R * sin(360 * i / vertexNum));
}
endContour();
endShape(CLOSE);
pop();
}
erase()を使った書き方
p5.jsでは createGraphics() と erase() の組み合わせでも穴あき図形が描けます。
let R; // 星(穴)の大きさ調整用
const vertexNum = 10; // 星の頂点数
const w = 300; // 図形の外枠の横の長さ
const h = 300; // 図形の外枠の縦の長さ
let pg; // 図形の外枠を描くためのgraphics用
function setup() {
createCanvas(400, 400);
angleMode(DEGREES);
// 画像の基準点を中央に変更
imageMode(CENTER);
// 四角いgraphicsを生成
pg = createGraphics(w, h);
}
function draw() {
background(255);
// 中心線
strokeWeight(1);
stroke(200);
line(0, height / 2, width, height / 2);
line(width / 2, 0, width / 2, height);
// pgに対して描画
pg.angleMode(DEGREES);
pg.background(200, 100, 100);
// 以降の描画はpgから削除される
pg.erase();
// 星型の図形を描画
pg.push();
pg.translate(pg.width / 2, pg.height / 2);
pg.rotate(-90);
pg.beginShape();
for (let i = vertexNum; i > 0; i--) {
R = i % 2 == 0 ? w * 0.4 : w * 0.2;
pg.vertex(R * cos(360 * i / vertexNum), R * sin(360 * i / vertexNum));
}
pg.endShape(CLOSE);
pg.pop();
// pgを表示
image(pg, width / 2, height / 2);
}