概要
DeformとはKeenan Woodall氏が公開しているUnityの無料アセットで、マルチスレッディングでメッシュを高速に変形させることができるすごいアセットです。GitHubにソースコードが公開されています。
日本語の紹介記事があります。
<参考>Unity:高速動作するメッシュ変形「Deform 1.0」が無料で使える!
今回はシェーダーの勉強として、このDeformの変形を頂点シェーダーに移植していきます。
Deformのソースコード
今回はDeformの40種類以上ある変形の中から、範囲内のメッシュを曲げるLimitedBendを選んで頂点シェーダーに移植します。
DeformのBendのソースコードの一部抜粋して見てみます。
namespace Deform
{
[Deformer (Name = "Bend", Description = "Bends a mesh", Type = typeof (BendDeformer))]
[HelpURL("https://github.com/keenanwoodall/Deform/wiki/BendDeformer")]
public class BendDeformer : Deformer, IFactor
{
//...中略...
[BurstCompile (CompileSynchronously = COMPILE_SYNCHRONOUSLY)]
public struct LimitedBendJob : IJobParallelFor
{
public float angle;
public float top;
public float bottom;
public float4x4 meshToAxis;
public float4x4 axisToMesh;
public NativeArray<float3> vertices;
public void Execute (int index)
{
var point = mul (meshToAxis, float4 (vertices[index], 1f));
var unbentPoint = point;
var angleRadians = radians (angle);
var scale = 1f / (angleRadians * (1f / (top - bottom)));
var rotation = (clamp (point.y, bottom, top) - bottom) / (top - bottom) * angleRadians;
var c = cos ((float)PI - rotation);
var s = sin ((float)PI - rotation);
point.xy = float2
(
(scale * c) + scale - (point.x * c),
(scale * s) - (point.x * s)
);
if (unbentPoint.y > top)
{
point.y += -c * (unbentPoint.y - top);
point.x += s * (unbentPoint.y - top);
}
else if (unbentPoint.y < bottom)
{
point.y += -c * (unbentPoint.y - bottom);
point.x += s * (unbentPoint.y - bottom);
}
point.y += bottom;
vertices[index] = mul (axisToMesh, point).xyz;
}
}
}
}
DeformはJob SystemやBurstコンパイラを使用して高速化を図っているようです。
<参考>【Unity】C# Job Systemを使ってみる(Burst Compilerも)
IJobParallelForを使用していることからも分かるように、Deformのほとんどの変形はポリゴンの各頂点に対して他の頂点とは独立に作用しており、またDeformで使用している数学関数ライブラリUnity.Mathematicsは関数の名前がCg/HLSLと同じなので簡単に頂点シェーダーに移植できます。
シェーダー作成
それでは頂点シェーダーを書いていきましょう。変形用の関数をDeform.cgincとして別ファイルにしておき、DeformTest.shaderからインクルードします。
# ifndef DEFORM_INCLUDED
# define DEFORM_INCLUDED
inline void swapMinMax(inout float x, inout float y){
float tmpMin = min(x, y);
float tmpMax = max(x, y);
x = tmpMin;
y = tmpMax;
}
inline float4 deformLimitedBend(float4 vertex, float4x4 meshToAxis, float4x4 axisToMesh, float angle, float top, float bottom){
if (top == bottom)
return vertex;
float4 vertex_ = mul(meshToAxis, vertex);
swapMinMax(bottom, top);
float4 unbentVertex = vertex_;
float angleRadians = radians(angle);
float scale = (top - bottom) / angleRadians;
float rotation = (clamp(vertex_.y, bottom, top) - bottom) / scale;
float s, c;
sincos((float)UNITY_PI - rotation, s, c);
vertex_.xy = float2
(
(scale - vertex_.x) * c + scale,
(scale - vertex_.x) * s
);
vertex_.xy += (unbentVertex.y > top) ? float2(s * (unbentVertex.y - top), -c * (unbentVertex.y - top)) :
((unbentVertex.y < bottom) ? float2(s * (unbentVertex.y - bottom), -c * (unbentVertex.y - bottom)) : float2(0.0,
0.0));
vertex_.y += bottom;
return mul(axisToMesh, vertex_);
}
変数名を変えたりsinとcosをsincosにまとめたりしていますが基本的に元のC#プログラムと同じことをしています。
Shader "Custom/DeformTest"
{
Properties
{
_Color ("Color", Color) = (1,1,1,1)
_MainTex ("Albedo (RGB)", 2D) = "white" {}
_Glossiness ("Smoothness", Range(0,1)) = 0.5
_Metallic ("Metallic", Range(0,1)) = 0.0
}
SubShader
{
Tags { "RenderType"="Opaque" }
LOD 200
CGPROGRAM
// Physically based Standard lighting model, and enable shadows on all light types
#pragma vertex vert
#pragma surface surf Standard noshadow
#include "UnityCG.cginc"
#include "Deform.cginc"
// Use shader model 3.0 target, to get nicer looking lighting
#pragma target 3.0
sampler2D _MainTex;
struct Input
{
float2 uv_MainTex;
};
half _Glossiness;
half _Metallic;
fixed4 _Color;
float4x4 unitMatrix(){
float4x4 m;
m._11_21_31_41 = float4(1, 0, 0, 0);
m._12_22_32_42 = float4(0, 1, 0, 0);
m._13_23_33_43 = float4(0, 0, 1, 0);
m._14_24_34_44 = float4(0, 0, 0, 1);
return m;
}
// Add instancing support for this shader. You need to check 'Enable Instancing' on materials that use the shader.
// See https://docs.unity3d.com/Manual/GPUInstancing.html for more information about instancing.
// #pragma instancing_options assumeuniformscaling
UNITY_INSTANCING_BUFFER_START(Props)
// put more per-instance properties here
UNITY_INSTANCING_BUFFER_END(Props)
void vert(inout appdata_full v)
{
float4x4 meshToAxis = unitMatrix();
float4x4 axisToMesh = unitMatrix();
#define deform(pos) deformLimitedBend(pos, unitMatrix(), unitMatrix(), 60, 1, 0)
float4 vertex = mul(meshToAxis, v.vertex);
float3 normal = mul(meshToAxis, float4(v.normal.xyz, 0));
float3 tangent = mul(meshToAxis, float4(v.tangent.xyz, 0));
float3 binormal = normalize(cross(normal, tangent));
float4 deformedVertex = deform(vertex);
float delta = 0.05;
float3 deformedVertexDeltaTangent = deform(vertex + float4(tangent, 0) * delta).xyz;
float3 deformedVertexDeltaBinormal = deform(vertex + float4(binormal, 0) * delta).xyz;
float3 deformedTangent = deformedVertexDeltaTangent - deformedVertex;
float3 deformedBinormal = deformedVertexDeltaBinormal - deformedVertex;
float3 deformedNormal = normalize(cross(deformedTangent, deformedBinormal));
v.vertex = mul(axisToMesh, deformedVertex);
v.normal = mul(axisToMesh, float4(deformedNormal.xyz, 0)).xyz;
}
void surf (Input IN, inout SurfaceOutputStandard o)
{
// Albedo comes from a texture tinted by color
fixed4 c = tex2D (_MainTex, IN.uv_MainTex) * _Color;
o.Albedo = c.rgb;
// Metallic and smoothness come from slider variables
o.Metallic = _Metallic;
o.Smoothness = _Glossiness;
o.Alpha = c.a;
}
ENDCG
}
FallBack "Diffuse"
}
頂点シェーダーでは頂点を移動して変形を行うほかに、頂点から接線および従法線方向に少し移動した座標に対しても同様に変形を行うことで法線が滑らかになるように計算しています。
<参考>【Unity】頂点シェーダーで頂点を変形した後に法線を再計算する
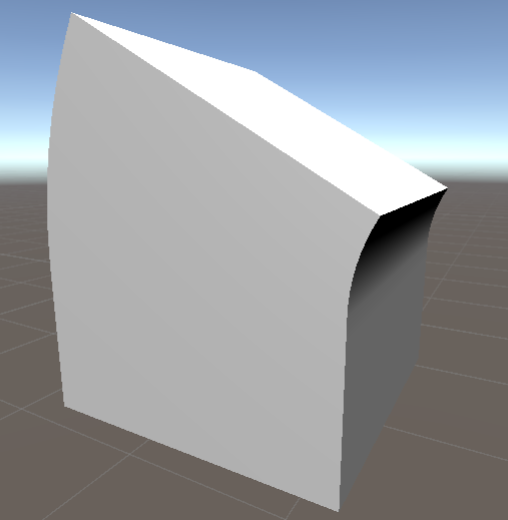
作成したシェーダーをオブジェクトに適用した結果がこちらです。なおキューブのメッシュはデフォルトのものではなくポリゴンの多いものを使っています。
結果
うまくいきました!