標準誤差について : 統計WEB : 18-5. 標準偏差と標準誤差
手法の目的
母集団からの得られた標本を用いて母集団の統計量$\theta$を推定する際の、バイアスやばらつきを少なくしたり見積ったりする際に用いられます。
得られた標本を繰り返し利用し単純なシミュレーションを行う計算機統計学と呼ばれる分野の手法だそうです。
バイアスは、推定したパラメータの期待値が母集団のパラメータとズレている分のことです。
ジャックナイフ法
標本$x_1,...,x_n$を使って算出した推定量$\hat{\theta}$のバイアスを補正する方法を考えるとき、
標本$x_i$を除いたサイズ$n-1$の部分標本から推定量$\hat{\theta}$と同様にして計算される推定量を$\hat{\theta}_{(i)}$とします。
$i$を$1$から$n$まで繰り返し、
\hat{\theta}_{(1)},...,\hat{\theta}_{(i)},...,\hat{\theta}_{(n)}
と$n$個の推定量を作ります。
$n$個の推定量の平均を
\hat{\theta}_{(\cdot)} = \frac{1}{n}\sum_{i=1}^{n}\hat{\theta}_{(i)}
とします。
この時、$\hat{\theta}$のバイアスは
\widehat{bias} :=(n - 1)(\hat{\theta}_{(\cdot)} - \hat{\theta})
と定義され、それを補正した
\hat{\theta}_{jack} := \hat{\theta} - \widehat{bias} = \hat{\theta} - (n - 1)(\hat{\theta}_{(\cdot)} - \hat{\theta})
をジャックナイフ推定量といいます。
例
コインを製造する工場で5つの円形のコインを試作し、半径$r$を測ったところ、以下のような形になりました。
8.4, \quad 9.0, \quad 8.2, \quad 10.4, \quad 9.2 \quad (単位:mm)
それぞれのコインの半径の平均値を用いて、コインの面積の推定量とジャックナイフ推定量を求めましょう。
$\pi$を3.14として、推定量$\hat{\theta}$は
\hat{\theta} = \biggl( \frac{8.4 + 9.0 + 8.2 + 10.4 + 9.2}{n} \biggr)^2 \cdot \pi= 256.6058
$\hat{\theta}_{(i)}$はそれぞれ
\hat{\theta}_{(1)} = \biggl( \frac{9.0 + 8.2 + 10.4 + 9.2}{n-1} \biggr)^2 \cdot \pi = 265.7696\\
\hat{\theta}_{(2)} = \biggl( \frac{8.4 + 8.2 + 10.4 + 9.2}{n-1} \biggr)^2 \cdot \pi = 257.17385\\
\hat{\theta}_{(3)} = \biggl( \frac{8.4 + 9.0 + 10.4 + 9.2}{n-1} \biggr)^2 \cdot \pi = 268.66625\\
\hat{\theta}_{(4)} = \biggl( \frac{8.4 + 9.0 + 8.2 + 9.2}{n-1} \biggr)^2 \cdot \pi = 237.6666\\
\hat{\theta}_{(5)} = \biggl( \frac{8.4 + 9.0 + 8.2 + 10.4}{n-1} \biggr)^2 \cdot \pi = 254.34\\
なので、$\hat{\theta}_{(\cdot)}$は
\hat{\theta}_{(\cdot)} = \frac{265.7696 + 257.17385 + 268.66625 + 237.6666 + 254.34}{n} = 256.72326
よって、$\widehat{bias}$は
\widehat{bias} := (n - 1)(\hat{\theta}_{(\cdot)} - \hat{\theta}) = 4(256.72326 - 256.6058) = 0.46984
ジャックナイフ推定量$\hat{\theta}_{jack}$は
\hat{\theta}_{jack} := \hat{\theta} - \widehat{bias} = 256.6058 - 0.46984 = 256.13596
となります。
得られた標本の単純な平均を推定量とする場合、元から不偏推定量でありバイアスが発生しないので、$\hat{\theta}_{(\cdot)}$と$\hat{\theta}$は同じ値になります。
ブートストラップ法
母集団$F$からの無作為標本$\boldsymbol{x} = (x_1,...,x_n)$を取得します。
取得した標本それぞれに確率$1/n$を与えて無作為に$n$回取り出しブートストラップ標本$\boldsymbol{x}^* = (x_1^*,...,x_n^*)$を作成します。
(この時、一度選ばれた標本がまた選ばれることもあります)
このブートストラップ標本ですが、標本から何度でも抽出できます。
$b$回目のブートストラップ標本を$\boldsymbol{x}^{*(b)} = (x_1^{*(b)},...,x_n^{*(b)})$とします。
「何度でも」の回数を$B$として、$B$個のブートストラップ標本を作成することをブートストラップ法といい、標準誤差やバイアスの推定、信頼区間の構成や機械学習のブースティング等に用いられます。
標準誤差のジャックナイフ推定量
母数$\theta = \theta(F)$に関心があり、$\theta$の推定量$\hat{\theta}$が関数$T_n$を用いて$\hat{\theta} = T_n(\boldsymbol{x})$と書かれているとします。
($\theta$が母平均の場合、$\hat{\theta} = T_n({\boldsymbol{x})} = (x_1 + \cdots + x_n) / n$です)
推定量$\hat{\theta}$の標準誤差のジャックナイフ推定量を構成するために、ジャックナイフ法で行った
\hat{\theta}_{(i)} \quad と \quad \hat{\theta}_{(\cdot)}
を用いると、推定量$\hat{\theta}$の標準誤差のジャックナイフ推定量は以下で与えられます。
\widehat{se}_{jack} = \sqrt{\frac{n-1}{n}\sum_{i=1}^{n}\Bigl(\hat{\theta}_{(i)} - \hat{\theta}_{(\cdot)} \Bigr)^2}
標準誤差のブートストラップ推定量
ブートストラップ法を用いた場合の推定量$\hat{\theta}$の標準誤差の推定ですが、
$b$回目のブートストラップ標本$\boldsymbol{x}^{*(b)}$から求めた推定量を$\hat{\theta}^*(b) = T_n(\boldsymbol{x}^{*(b)})$とし、
$B$回の標本抽出から求めた
\hat{\theta}^*(1),...,\hat{\theta}^*(b),...,\hat{\theta}^*(B)
を総和してBで割ったものを
\overline{\hat{\theta}^*} = \frac{1}{B}\sum_{b=1}^{B}\hat{\theta}^*(b)
とすると、以下で与えられます。
\widehat{se}_B = \sqrt{\frac{1}{B-1}\sum_{b=1}^{B}\Bigl( \hat{\theta}^*(b) - \overline{\hat{\theta}^*}\Bigr)^2}
標準誤差の推定の場合、$B$は50~200程度で良いそうです。
また、バイアスのブートストラップ推定量は
\overline{\hat{\theta}^*} - \hat{\theta}
となります。
例
- 2019年東京都における交通事故による月別死者数
| 月 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 人数 | 11 | 9 | 9 | 12 | 5 | 8 | 7 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 18 | 15 |
import numpy as np
sample = np.array([11,9,9,12,5,8,7,12,13,14,18,15])
標本平均と標本分散を求めます。
print(sample.mean())
print(sample.var(ddof=1))
11.083333333333334
13.537878787878789
$B$を200とし、ブートストラップ標本を200個作成します。
n = len(sample)
B = 200
# 重複有等間隔で標本サンプル数と同じ数だけ取り出す を200回繰り返す
bootstrap_samples = np.array([np.random.choice(sample, size=n) for i in range(B)])
array([[ 8, 12, 11, ..., 9, 12, 9], -- それぞれの行がブートストラップ標本になっている
[ 9, 12, 12, ..., 9, 13, 18],
[11, 12, 14, ..., 15, 11, 5],
...,
[18, 15, 18, ..., 7, 7, 18],
[15, 12, 9, ..., 15, 9, 14],
[15, 5, 9, ..., 7, 13, 12]])
母平均の推定量$\hat{\theta}$とそれぞれのブートストラップ標本から取得した統計量$\hat{\theta}^*(b) $を平均した、
$\overline{\hat{\theta}^*}$を用いてバイアスのブートストラップ推定量を求め、標本平均を修正します。
# ブートストラップ標本それぞれから推定量を出して総和してBで割る
bootstrap_samples_total_mean = np.mean(bootstrap_samples, axis=1).sum() / B
# バイアスのブートストラップ推定量を求める
bootstrap_estimate_bias = bootstrap_samples_total_mean - sample_mean
print(bootstrap_estimate_bias)
-0.08458333333333456
# 修正する
sample_mean - bootstrap_estimate_bias
11.167916666666668
標本平均の標準誤差のブートストラップ推定量$\widehat{se}_B$を求めてみます。
calc_inside_sigma = np.sum((np.mean(bootstrap_samples, axis=1) - bootstrap_samples_total_mean)**2)
np.sqrt(calc_inside_sigma * (1 / (B - 1)))
0.9197442436665082
標本から標準誤差を求める場合は$\frac{\sigma}{\sqrt{n}}$なので、
standard_error = np.sqrt(sample_var) / np.sqrt(n)
standard_error
1.062147148777685
標本からの標準誤差よりも13.5%程、誤差が小さくなっています。
95%信頼区間を求める場合は、得られたブートストラップ標本の統計量分布の上位下位2.5%点を求めます。
# ブートストラップ標本のそれぞれの平均を求める
bootstrap_means = np.mean(bootstrap_samples, axis=1)
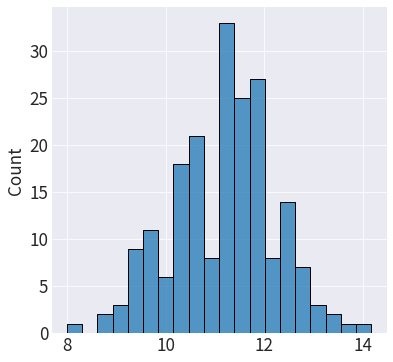
# ヒストグラムを作成
plt.figure(figsize=(6, 6))
sns.histplot(x=bootstrap_means, bins=20)
plt.show()
# 上位下位2.5%を求める
np.percentile(bootstrap_means,[2.5, 97.5])
array([ 9.16666667, 13.00416667 ])
推定される95%信頼区間は9.4125 ~ 12.5になりました。
参考
間違っている点等ありましたら、ご指摘いただけますと嬉しいです。