vtkMultiBlockDataSet で .vtp ファイルや .vtu ファイルを束ねると、paraview でひとつのファイルを開くだけで、モデル一式を読めるようにできます。
以下の環境で動作確認しました。
- Windows 11 上の paraview 6.0.1
- Python 3.13
具体例
図 1 は、9 つの polydata ( .vtp) ファイルを束ねたものを読み込んだところです。
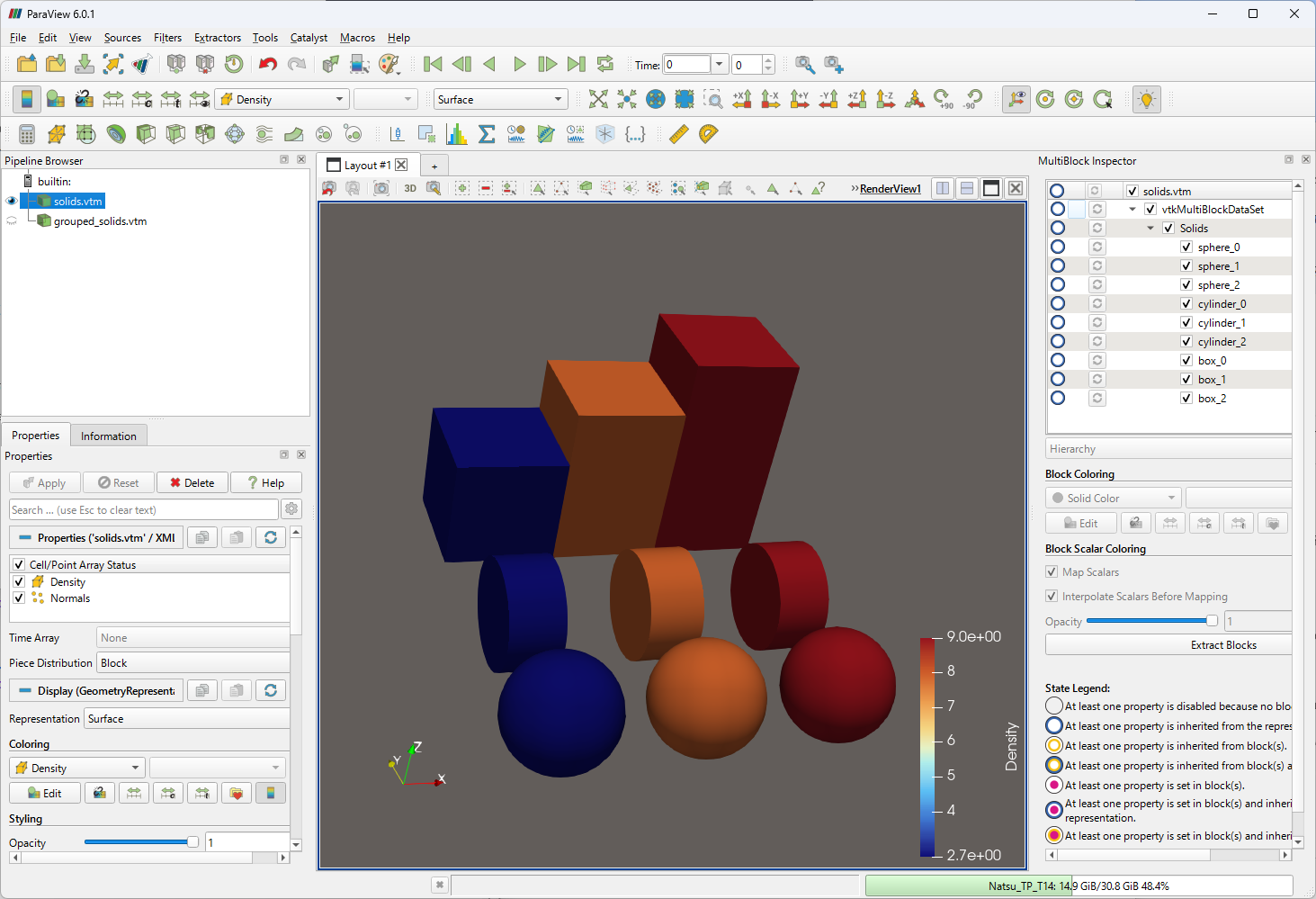
図 1: 9 つの polydata を DataSet として保持する vtkMultiBlockDataSet
paraview 6.0.1 で、 MultiBlock Inspector ウィンドウを右側に表示しています。どの Dataset (polydata) を表示するか、選択できるようになっています。
また、図 2 のように、材料ごとのブロックを作り、その中で複数の Dataset (polydata) を保持することができます。この場合、材質ごとのブロックをまとめて非表示にでき、構造データを確認するときに便利です。
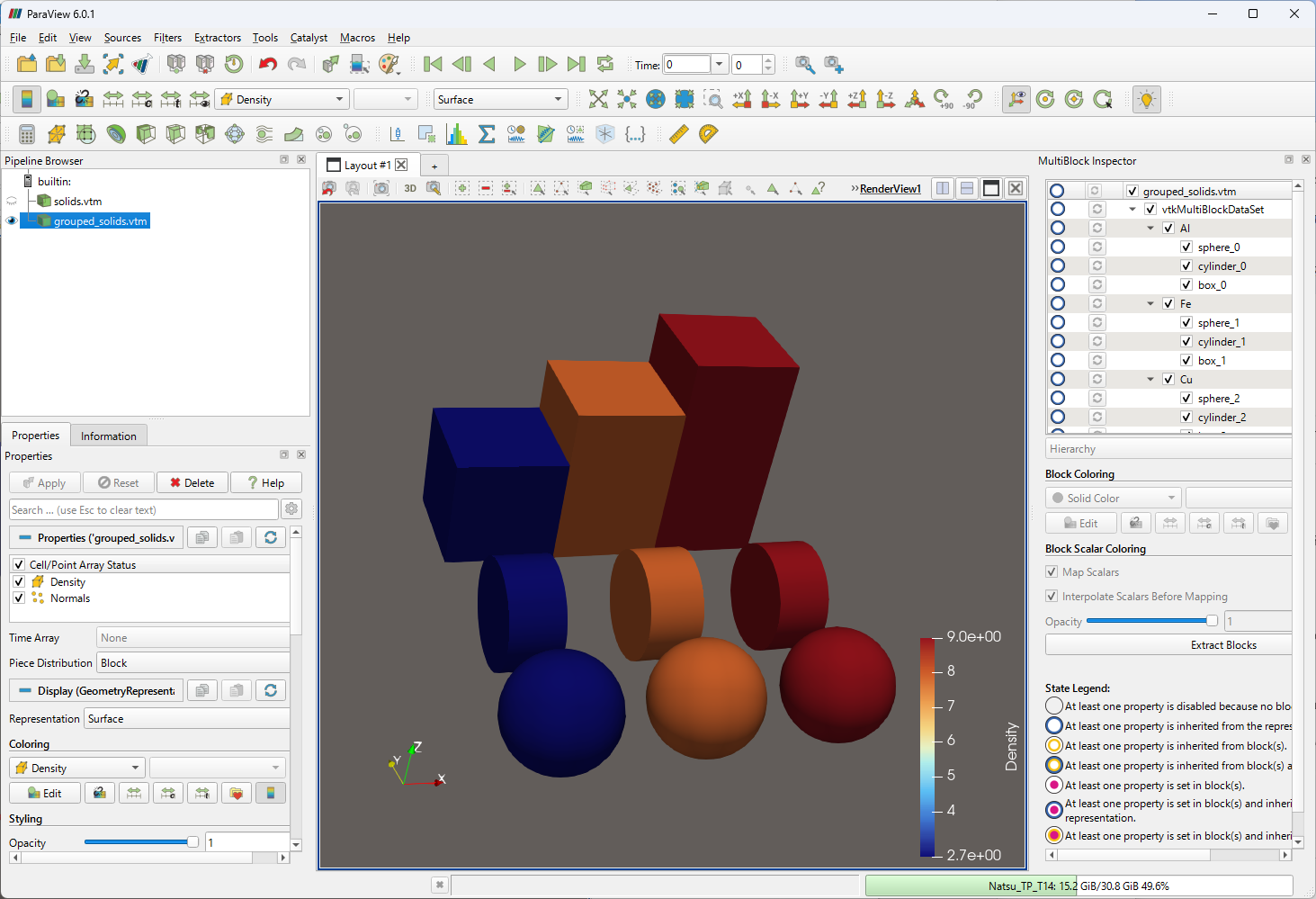
図 2: 複数の Block からなる vtkMultiBlockDataSet
ファイルの内容
このような vtkMultiBlockDataSet の .vtm ファイルは、別々の .vtp ファイルをまとめた xml 形式のファイルです。図 1 の構造は、以下のようなファイルになっています。.vtp ファイルで記述される Dataset が ブロック内に複数並んでいます。(ブロック階層を省いて、いきなり DataSet を並べても、 paraview で表示できました。)
<?xml version="1.0" ?>
<VTKFile type="vtkMultiBlockDataSet" version="1.0" byte_order="LittleEndian">
<vtkMultiBlockDataSet>
<Block name="Solids">
<DataSet name="sphere_0" file="sphere_Al.vtp"/>
<DataSet name="sphere_1" file="sphere_Fe.vtp"/>
<DataSet name="sphere_2" file="sphere_Cu.vtp"/>
<DataSet name="cylinder_0" file="cylinder_Al.vtp"/>
<DataSet name="cylinder_1" file="cylinder_Fe.vtp"/>
<DataSet name="cylinder_2" file="cylinder_Cu.vtp"/>
<DataSet name="box_0" file="box_Al.vtp"/>
<DataSet name="box_1" file="box_Fe.vtp"/>
<DataSet name="box_2" file="box_Cu.vtp"/>
</Block>
</vtkMultiBlockDataSet>
</VTKFile>
図 2 の構造では、材質の名前を付けたブロックが複数あり、それぞれのブロック内に .vtp ファイルで記述される Dataset が 複数並んでいます。
<?xml version="1.0" ?>
<VTKFile type="vtkMultiBlockDataSet" version="1.0" byte_order="LittleEndian">
<vtkMultiBlockDataSet>
<Block name="Al">
<DataSet name="sphere_0" file="sphere_Al.vtp"/>
<DataSet name="cylinder_0" file="cylinder_Al.vtp"/>
<DataSet name="box_0" file="box_Al.vtp"/>
</Block>
<Block name="Fe">
<DataSet name="sphere_1" file="sphere_Fe.vtp"/>
<DataSet name="cylinder_1" file="cylinder_Fe.vtp"/>
<DataSet name="box_1" file="box_Fe.vtp"/>
</Block>
<Block name="Cu">
<DataSet name="sphere_2" file="sphere_Cu.vtp"/>
<DataSet name="cylinder_2" file="cylinder_Cu.vtp"/>
<DataSet name="box_2" file="box_Cu.vtp"/>
</Block>
</vtkMultiBlockDataSet>
</VTKFile>
Python スクリプトで生成
このファイルを、python プログラムで生成するコード例を示します。ここでは、vtkMultiBlockDataSet の生成には、xml.etree.ElementTree を使用しました。テキストとして適度に改行を入れて見やすくするために、 minidom を使っています。xml ファイルの生コードの見やすさのためだけです。
import xml.etree.ElementTree as ET
from collections import defaultdict
from xml.dom import minidom
import numpy as np
import pyvista as pv
density = {"Al": 2.7, "Fe": 7.87, "Cu": 8.96}
materials = ["Al", "Fe", "Cu"]
datasets = []
# 球体、円柱、直方体を作成し、各々に密度データを追加して保存
for i in range(3):
sphere = pv.Sphere(center=(i * 2.5, 0, 0), radius=1.0)
surf = np.full(sphere.n_cells, density[materials[i]])
sphere.cell_data["Density"] = surf
filename = f"sphere_{materials[i]}.vtp"
sphere.save(filename)
datasets.append((f"sphere_{i}", materials[i], filename))
for i in range(3):
cylinder = pv.Cylinder(center=(i * 2.5, 2.5, 0), radius=1.0)
surf = np.full(cylinder.n_cells, density[materials[i]])
cylinder.cell_data["Density"] = surf
filename = f"cylinder_{materials[i]}.vtp"
cylinder.save(filename)
datasets.append((f"cylinder_{i}", materials[i], filename))
for i in range(3):
box = pv.Box(bounds=(i * 2 - 1.0, i * 2 + 1.0, 4.0, 6.0, 0.0, 2.0 + i))
surf = np.full(box.n_cells, density[materials[i]])
box.cell_data["Density"] = surf
filename = f"box_{materials[i]}.vtp"
box.save(filename)
datasets.append((f"box_{i}", materials[i], filename))
vtkfile = ET.Element(
"VTKFile",
{"type": "vtkMultiBlockDataSet", "version": "1.0", "byte_order": "LittleEndian"},
)
multiblock = ET.SubElement(vtkfile, "vtkMultiBlockDataSet")
block_name = "Solids"
block = ET.SubElement(multiblock, "Block", {"name": "Solids"})
for dataset in datasets:
ET.SubElement(block, "DataSet", {"name": dataset[0], "file": dataset[2]})
rough_string = ET.tostring(vtkfile, encoding="utf-8")
pretty_xml = minidom.parseString(rough_string).toprettyxml(indent=" ")
with open("solids.vtm", "w", encoding="utf-8") as f:
f.write(pretty_xml)
# 材質でグルーピング
grouped = defaultdict(list)
for name, mat, file in datasets:
grouped[mat].append((name, file))
vtkfile_g = ET.Element(
"VTKFile",
{"type": "vtkMultiBlockDataSet", "version": "1.0", "byte_order": "LittleEndian"},
)
multiblock = ET.SubElement(vtkfile_g, "vtkMultiBlockDataSet")
# BlockごとにDataSetを追加
for mat, items in grouped.items():
block = ET.SubElement(multiblock, "Block", {"name": mat})
for name, file in items:
ET.SubElement(block, "DataSet", {"name": name, "file": file})
rough_string = ET.tostring(vtkfile_g, encoding="utf-8")
pretty_xml = minidom.parseString(rough_string).toprettyxml(indent=" ")
with open("grouped_solids.vtm", "w", encoding="utf-8") as f:
f.write(pretty_xml)
参考)pyvista の pyvista.MultiBlock でも、MultiBlock の操作は可能なようです。