1. はじめに
この記事では、以下のUdemyのコースに紹介されているLangGraphのTool CallingでMCP Serverを利用する方法をご紹介します。
MCP Crash Course: Complete Model Context Protocol in a Day
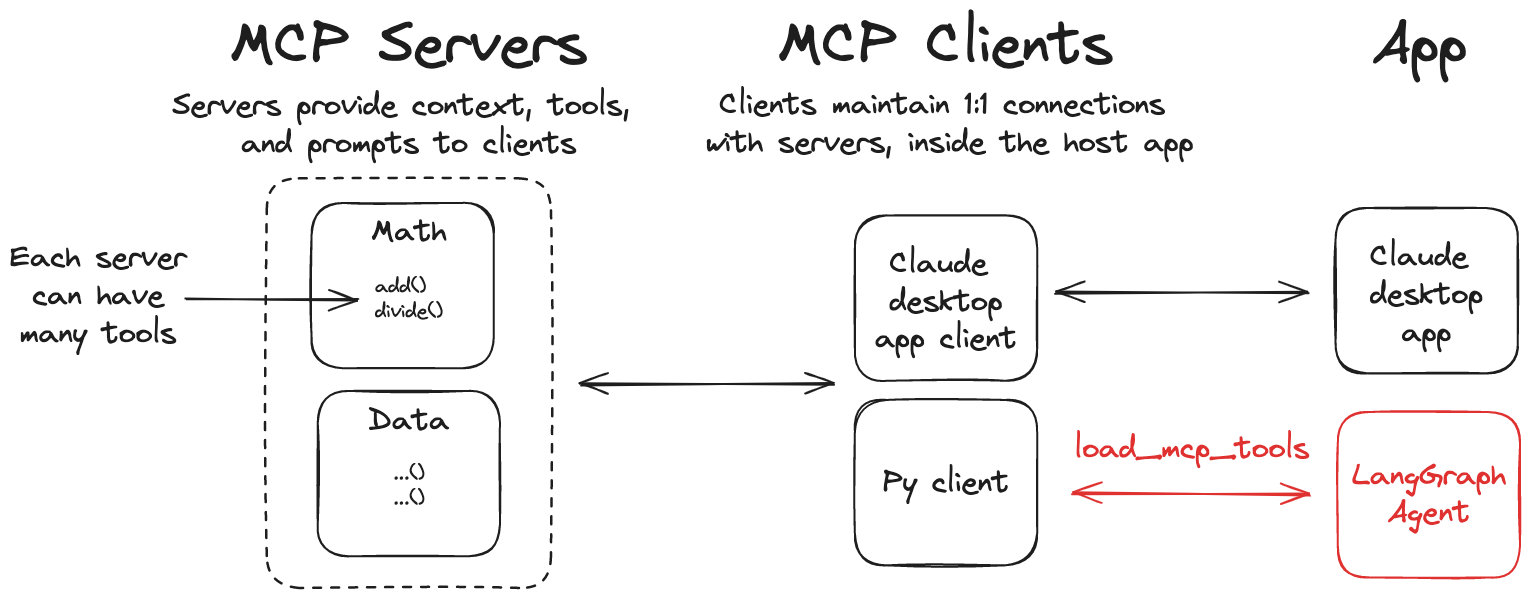
LnagGraphのエージェント内でMCP Serverのtoolsを使用するために、LangChain MCP Adaptersというライブラリを使用します。LangChain MCP AdaptersはMCPのToolオブジェクトをLangChainのToolオブジェクトに変換し、LangChain, LangGraph内でMCPのToolを使えるようにしてくれます。また、複数のMCP Serverに接続し、Toolを利用するクライアントの実装も可能です。
今回は、MCP Serverではなく、MCP Client側の実装に重点をおいて説明していきます。(下図 py clientの部分)
2. 実装したLangGraphエージェントの概要
今回実装したLangGraphのエージェントは、ソースコードはLangChan MCP AdaptersのGithub上のQuickstartを元にしています。
利用するMCP Serverは足し算と掛け算を行うToolsを提供しています。エージェントはこれらのToolsを利用して計算を行い、最終的な結果をユーザーへ返却します。
import asyncio
import os
from dotenv import load_dotenv
from langchain_core.messages import HumanMessage
from langchain_mcp_adapters.tools import load_mcp_tools
from langchain_openai import ChatOpenAI
from langgraph.prebuilt import create_react_agent
from mcp import ClientSession, StdioServerParameters
from mcp.client.stdio import stdio_client
load_dotenv()
llm = ChatOpenAI() # Change here depending on your LLM
stdio_server_params = StdioServerParameters(
command="python",
args=["absolutePath/to/math_server.py"]
)
async def main():
async with stdio_client(stdio_server_params) as (read, write):
async with ClientSession(read_stream=read, write_stream=write) as session:
await session.initialize()
print("session initialized")
# list_tools()ではMCPのtoolオブジェクトが取得できることを確認
mcp_tools = await session.list_tools()
print(mcp_tools)
# load_mcp_tools(session)で、LangChainのtoolオブジェクトに変換されていることを確認
tools = await load_mcp_tools(session)
print(tools)
agent = create_react_agent(llm, tools)
result = await agent.ainvoke({"messages": [HumanMessage(content = "What is 54 + 2 * 3?")]})
print(result["messages"][-1].content)
if __name__ == "__main__":
asyncio.run(main())
MCP Serverを立ち上げた状態で上記のソースコードを実行すると、以下のような結果が表示されます。
54 + 2 * 3 = 60
※使用するモデルによって多少結果は異なります。
実行時に、MCP ServerのToolsがどのような手順で利用されているかについては、後述の4. Tool Callingの挙動で説明します。
3. コードの詳細
StdioServerParameters
MCP Serverの実行方法を定義します。
command : 実行コマンド
args : 引数 ※実行するファイルへのパスは、絶対パスで記述する必要があります。
stdio_server_params = StdioServerParameters(
command="python",
args=["absolute path to math_server.py"]
)
stdio_client
stdio_clientは、MCP Host(今回の場合エージェント)のためのプロキシのようなものです。
クライアントには、以下の2つの情報が必要です。
- MCP Serverの実行方法
- MCP Serverとの通信方法
上記で定義したstdio_server_paramsを渡すことで、これらの2つ情報をクライアントへ渡すことができます。
クライアントのstdioトランスポートにより標準入出力ストリームを介した通信が可能になりread,writeは、それぞれ読み込みと書き込みのストリームオブジェクトです。
async with stdio_client(stdio_server_params) as (read, write):
ClientSession
クライアントはSession経由でMCP Serverへ接続します。
ClientSessionの引数のread_streamとwrite_streamには、それぞれ前述のread,とwriteを渡します。
async with ClientSession(read_stream=read, write_stream=write) as session:
load_mcp_tools
MCPのToolオブジェクトをLangChainのToolオブジェクトに変換します。
tools = await load_mcp_tools(session)
コンソールにMCPのToolオブジェクトと、変換後のLangChainのToolオブジェクトを出力させているので違いを確認してみましょう。
-
session.list_tools()で取得したMCPのToolオブジェクト
Processing request of type ListToolsRequest
meta=None nextCursor=None tools=[Tool(name='add', title=None, description='Add two numbers', inputSchema={'properties': {'a': {'title': 'A', 'type': 'integer'}, 'b': {'title': 'B', 'type': 'integer'}}, 'required': ['a', 'b'], 'title': 'addArguments', 'type': 'object'}, outputSchema={'properties': {'result': {'title': 'Result', 'type': 'integer'}}, 'required': ['result'], 'title': 'addOutput', 'type': 'object'}, annotations=None, meta=None), Tool(name='multiply', title=None, description='Multiply two numbers', inputSchema={'properties': {'a': {'title': 'A', 'type': 'integer'}, 'b': {'title': 'B', 'type': 'integer'}}, 'required': ['a', 'b'], 'title': 'multiplyArguments', 'type': 'object'}, outputSchema={'properties': {'result': {'title': 'Result', 'type': 'integer'}}, 'required': ['result'], 'title': 'multiplyOutput', 'type': 'object'}, annotations=None, meta=None)]
-
load_mcp_tools(session)で取得した、LangChainのToolに変換後のオブジェクト
LangChainのクラスであるStructuredToolコンソールに出力されているのが確認できます。
Processing request of type ListToolsRequest
[StructuredTool(name='add', description='Add two numbers', args_schema={'properties': {'a': {'title': 'A', 'type': 'integer'}, 'b': {'title': 'B', 'type': 'integer'}}, 'required': ['a', 'b'], 'title': 'addArguments', 'type': 'object'}, response_format='content_and_artifact', coroutine=<function convert_mcp_tool_to_langchain_tool.<locals>.call_tool at 0x110f476a0>), StructuredTool(name='multiply', description='Multiply two numbers', args_schema={'properties': {'a': {'title': 'A', 'type': 'integer'}, 'b': {'title': 'B', 'type': 'integer'}}, 'required': ['a', 'b'], 'title': 'multiplyArguments', 'type': 'object'}, response_format='content_and_artifact', coroutine=<function convert_mcp_tool_to_langchain_tool.<locals>.call_tool at 0x110f47740>)]
4. Tool Callingの挙動
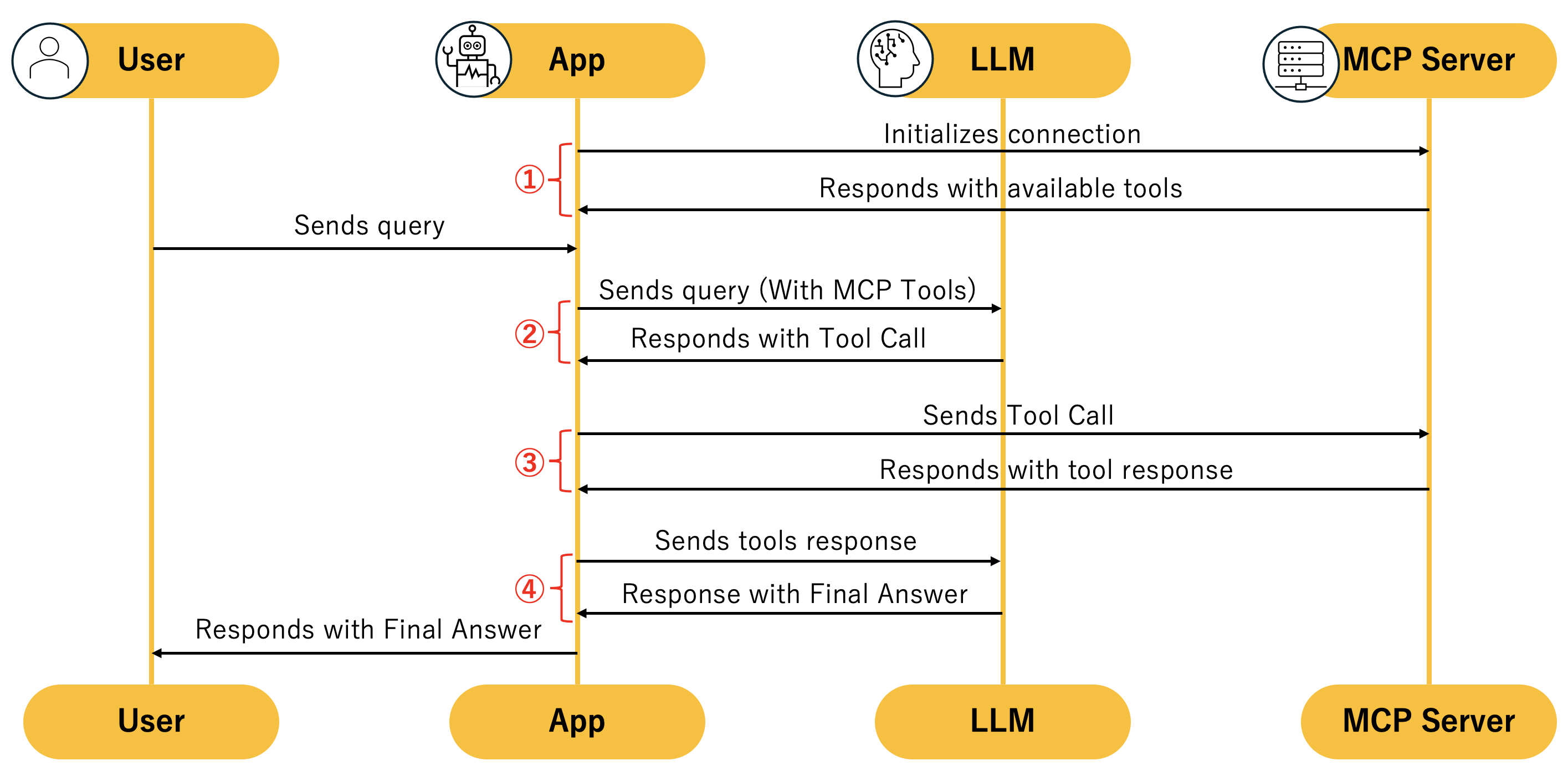
下の図の①〜④について順番に説明していきます。
① Initializes connection
はじめに、ソースコードの以下の部分が実行され、MCP Serverと接続します。
await session.initialize()
MCP Serverからは、利用可能なToolが返却されます。
② Sends query(with MCP Tools)
ユーザーからリクエストがあると、そのリクエストの内容と一緒に①で取得したMCP ToolをLLMへ渡します。
LLMからは実行するMCP ToolのTool Callが返却されます。
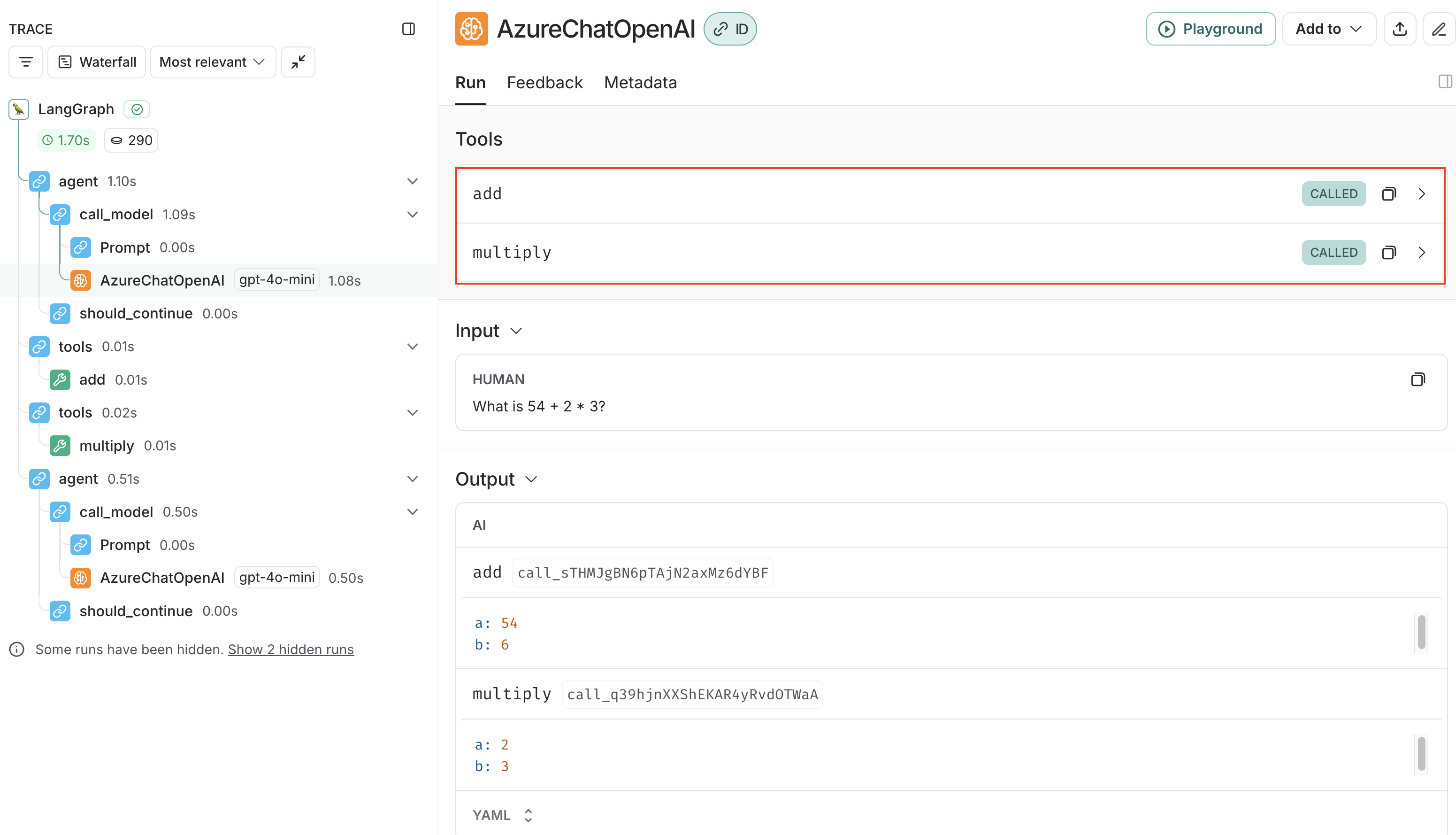
LangSmithの画面で確認すると、addとmultiplyの2つのtoolが「CALLED」となっています。
これは、LLMがこの2つのtoolをtool callすると判断したことを表しており、addとmultiplyの2つのTool Callがレスポンスとして返却されます。
③ Sends Tool Call
コンソールの出力でも、Tool Callが2回行われているのが確認できます。(addとmultiplyがそれぞれTool Callされている。)
Processing request of type CallToolRequest
Processing request of type CallToolRequest
続いて、MCP Serverへ、2と3を引数に掛け算のリクエストが実行され、multipyが実行されます。outputの6を得ます。
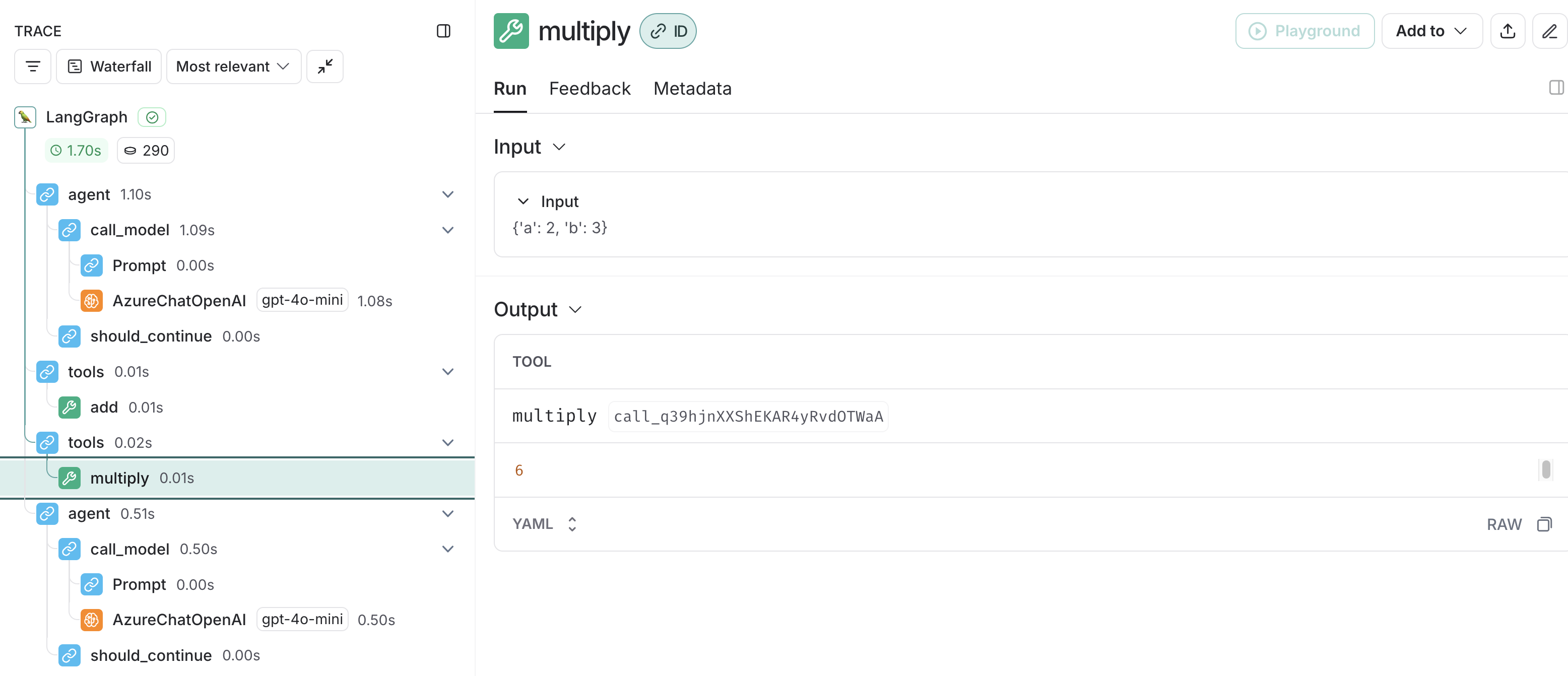
そして、54と6を引数に、足し算のリクエストが実行され、addが実行されます。
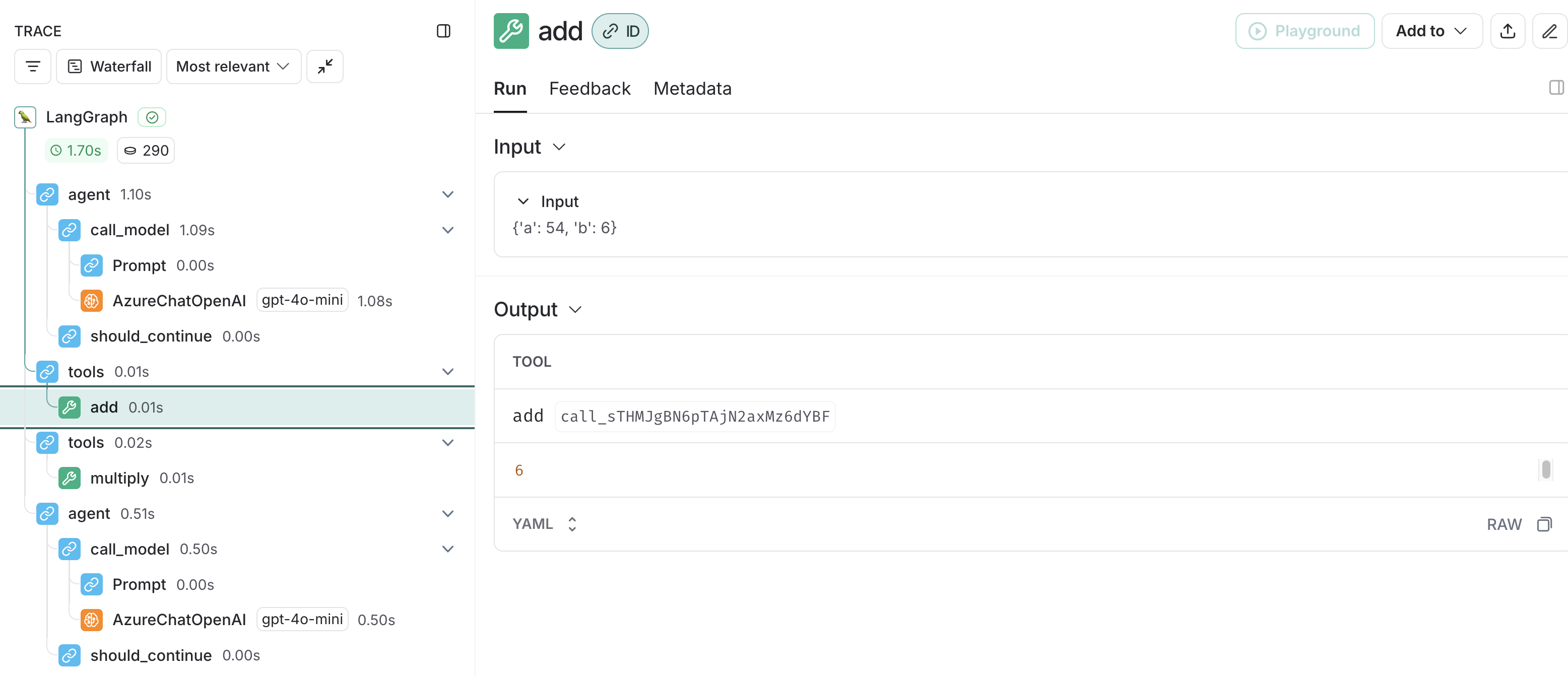
④ Sends tools response
最後に、Tool Callingで得られた結果を含めてLLMへのリクエストが実行され、最終的な結果が返却されます。
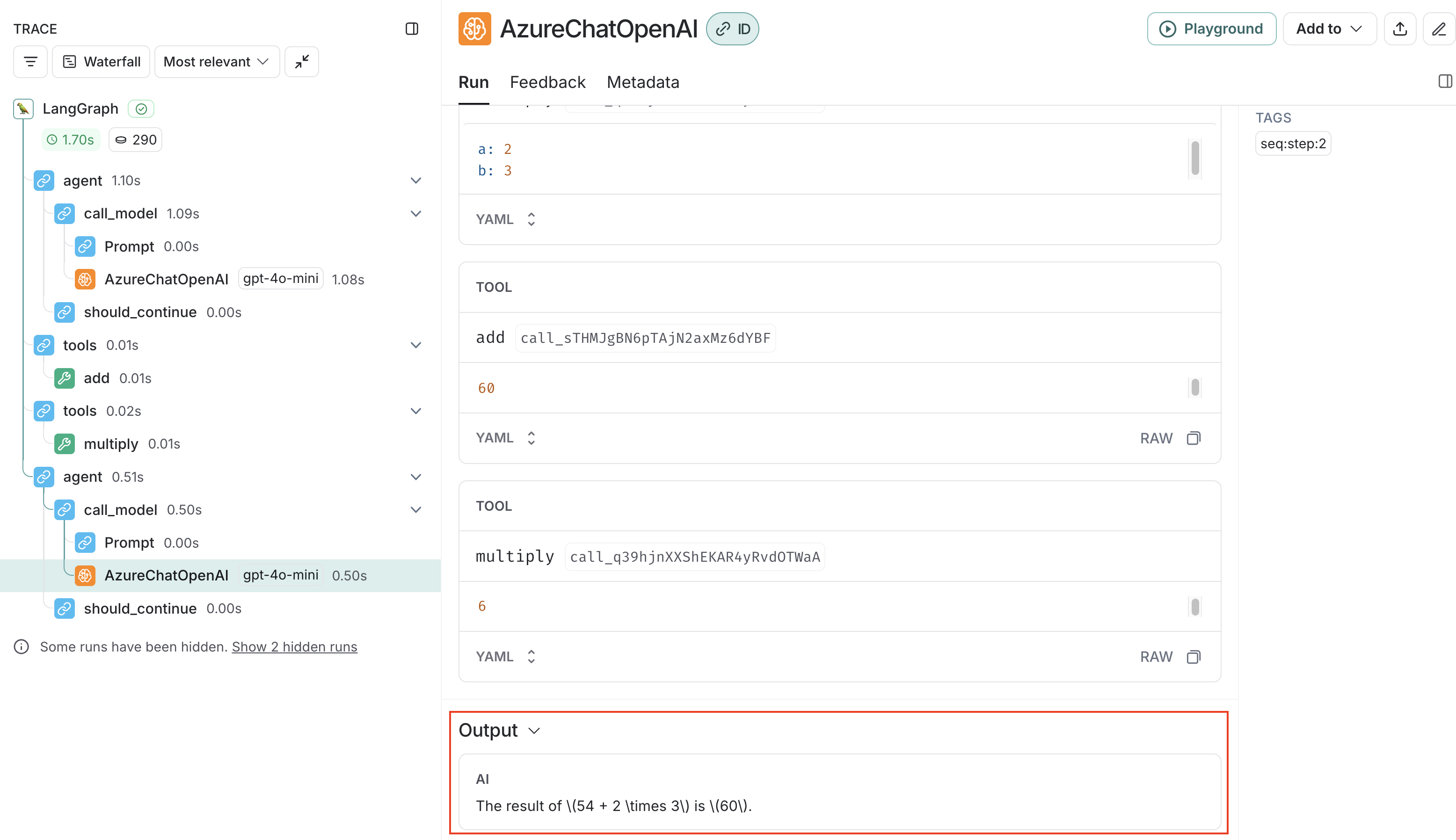
7. 補足:使用したMCP Server
LangChain MPC AdaptersのGithubのREADME.mdにあるサンプルのmath_server.pyを使用しました。
# math_server.py
from mcp.server.fastmcp import FastMCP
mcp = FastMCP("Math")
@mcp.tool()
def add(a: int, b: int) -> int:
"""Add two numbers"""
return a + b
@mcp.tool()
def multiply(a: int, b: int) -> int:
"""Multiply two numbers"""
return a * b
if __name__ == "__main__":
mcp.run(transport="stdio")
6. 参考リンク
Udemyのコース