はじめに
advent calendarを書くのが初めてなのでなんとなく緊張していますがよろしくお願いします。。
JUCEでopenGL/シェーダー(GLSL)を簡易的に使いたいということで、2Dのシェーダーに特化したjuce::OpenGLGraphicsContextCustomShaderを使用してみた備忘録になります。
ここではJUCE6.1.0+Macで試した際の例で紹介します。(Windowsでもそこまで大きく変わらないかと思います)
ちなみにopenGLが何なのかについてはこの記事では省略します。
今回のサンプル
シェーダー/GLSLとは
シェーダーとは3DCGで立体に対して陰影をつける処理を行うプログラムを指します。
JUCEではGLSL(openGL Shading Language)を使用して描画処理に対してカスタマイズを行なうことができます。
これは3Dだけではなく2Dの描画にも応用することができます。
シェーダーの種類
JUCEで使用する場合は主に以下の操作を行うことができます。
vertex shader - 図形の頂点位置/頂点色/頂点法線の操作
fragment shader - ピクセル情報の操作
geometry shader - 点/線/三角形などのプリミティブの増減や変更操作
拡張子
シェーダーファイルの拡張子には便宜的に以下が使われるイメージですがこちらは特に何でも構いません。
vertex shader - .vert
fragment shader - .frag
geometry shader - .geom
何かしらのshader - .shader / .glsl
今回の記事ではfragment shaderのみ扱います。
参考URL
はじめてシェーダーを学びたいという方におすすめです。自分も最初こちらで勉強しました。
とても分かりやすく、応用できるようになりたい方に良さそうです。
網羅されている範囲が広いのでこちらも応用できるようになりたい方におすすめです。リファレンスとしても度々参照させて頂いています。
juce_openglモジュール
JUCEでopenGL/シェーダー(GLSL)を使用するには
"Modules"の"juce_opengl"にチェックを入れ、プロジェクトを作成します。

プロジェクト作成後に入れたくなった場合は"Mudules"の+ボタン > Add a module > Global JUCE modules path > juce_opengl を追加します。

シェーダーファイル
JUCEのOpenGLのサンプルでも見られるようにシェーダーをソースコードに直書きすることも可能ですが、個人的に外部ファイルとして用意したシェーダーファイルを読み込めるようにしておくことをおすすめします。
これにより、アプリケーション/プラグインの実行中にリアルタイムにシェーダーを編集しながら実行中のアプリケーション/プラグインで確認することができます。
ちなみにDebugモードで実行するとシェーダーファイルに変更を加えてエラーがあった場合は内部のjassertfalseで落ちてしまうので、エラーで止まらないReleaseモードで編集するなど対策する必要があります。
ビルドしたアプリケーション/プラグインのResourceフォルダにシェーダーを含める場合は以下を行います。(反対に含めたくない場合はJUCE公式サンプルのようにシェーダーをソースコードに直書きします。)
ProjucerのPluginProcessor.hなどがあるソース一覧に既に作成しておいたシェーダーファイルをドラッグアンドドロップするか
ソース一覧で右クリック > Add New cpp File で
プロジェクトディレクトリ直下にResourcesフォルダを作成し、そこにファイル名.シェーダー拡張子の名前を付けて保存します。
拡張子が.cppではないけどどうする?みたいなことを聞かれるのでキャンセル以外で適当に答えて、
作成後のファイルを右クリック > Compileのチェックを外し、Rename File...で拡張子を.シェーダー拡張子に再び変更します。
さらに、シェーダーファイルを右クリックして表示される項目に
Binary Resource
Xcode Resource
のチェック項目があるのでXcodeResourceにのみチェックをつけます。これによってProjucerで吐き出した後のXcodeプロジェクトにResourceが追加された状態になり、またビルド後も自動的にアプリケーション内部のResourcesフォルダにファイルが追加されるようになります。
Macの場合のTips
Macの場合、Finderで空のテキストファイルがショートカットなどで作成できないので
Finderのウインドウの上側(ツールバー)を右クリック > ツールバーをカスタマイズ
Finderの上側に任意のアプリケーションをドラッグアンドドロップして配置しておくことができます。

自分の場合はよく使うテキストエディタ(VSCode)を置いておき、空のテキストファイルを作成したいフォルダをこのテキストエディタアイコンまでドラッグすると
このテキストエディタで開くことができるのでそこから作成したり改変したりしています。
JUCEでシェーダーを扱うシンプルな例(Uniformを使わない2D描画)
まず最初にインタラクションのないfragment shaderのみの2D描画の例です。
まずシェーダーファイルとして以下のようなshaderを用意します。
これは単純に各ピクセルを赤色にしています。
void main() {
gl_FragColor = vec4(1.0, 0.0, 0.0, 1.0);
}
コンポーネントとして以下を作成します。
# pragma once
# include <JuceHeader.h>
class OpenGLSimple: public juce::Component, public juce::Timer {
public:
OpenGLSimple();
~OpenGLSimple();
// component
void paint (juce::Graphics&) override;
void resized() override {}
// timer
void timerCallback() override;
private:
void initializeFragmentByInternalSource();
void reloadShader();
juce::OpenGLContext openGLContext;
std::unique_ptr<juce::OpenGLGraphicsContextCustomShader> shader;
juce::String fragmentString;
juce::File fragmentShaderFile;
juce::Time fragmentLastModTime;
};
# include "OpenGLSimple.h"
//------------------------------------------------------------------------------
OpenGLSimple::OpenGLSimple() {
// openGLコンテキストにコンポーネントを紐づける。(ヘビーウェイト化(?))
openGLContext.attachTo (*this);
// ビルド後のResourceフォルダからシェーダーを参照するかどうか。
// falseの場合はプロジェクトのResourceフォルダ(ユーザー/JUCE/projcets/OpenGLControllerTest/Resources)から参照する
const bool isBuildResource = false;
juce::String resourcePath;
// ビルド後のプラグインのResourceディレクトリのシェーダーを参照するかどうか
if (isBuildResource) {
resourcePath = juce::File::getSpecialLocation(juce::File::SpecialLocationType::currentApplicationFile).getFullPathName();
# ifdef JUCE_MAC
resourcePath += "/Contents/Resources/";
# elif JUCE_WINDOWS
# endif
}
// 開発プロジェクトのResourceフォルダのshaderを読む
else {
resourcePath = juce::File::getSpecialLocation(juce::File::SpecialLocationType::userDocumentsDirectory).getFullPathName() + "/JUCE/projects/OpenGLControllerTest/Resources/";
}
// shaderのソースコード読み込み
fragmentShaderFile = juce::File(resourcePath + "simple.frag");
fragmentString = fragmentShaderFile.loadFileAsString();
// リアルタイム更新のために最後にアクセスした時間と変更した時間を取得
fragmentShaderFile.setLastAccessTime(juce::Time::getCurrentTime());
fragmentLastModTime = fragmentShaderFile.getLastModificationTime();
// 配布時などソースコード直書きのシェーダを参照する。
// initializeFragmentByInternalSource();
reloadShader();
startTimerHz(60);
}
//------------------------------------------------------------------------------
OpenGLSimple::~OpenGLSimple() {
stopTimer();
// openGLコンテキストへの紐付け解除
openGLContext.detach();
}
//------------------------------------------------------------------------------
void OpenGLSimple::paint (juce::Graphics& g) {
// shaderの背景、shaderで描画失敗時にも表示される。
g.fillCheckerBoard (getLocalBounds().toFloat(), 48.0f, 48.0f, juce::Colours::lightgrey, juce::Colours::white);
// shaderが有効なものであれば描画更新
if (shader.get() != nullptr)
{
shader->fillRect (g.getInternalContext(), getLocalBounds());
}
}
//------------------------------------------------------------------------------
void OpenGLSimple::timerCallback() {
// シェーダーファイルに最後にアクセスした時間から一定時間経過していれば、シェーダーファイルが変更された時間を確認して変わっていれば際描画処理を行う。
auto currentTime = juce::Time::getCurrentTime();
if (currentTime.toMilliseconds() - fragmentShaderFile.getLastAccessTime().toMilliseconds() > 1000) {
fragmentShaderFile.setLastAccessTime(currentTime);
if (fragmentLastModTime != fragmentShaderFile.getLastModificationTime()) {
fragmentLastModTime = fragmentShaderFile.getLastModificationTime();
fragmentString = fragmentShaderFile.loadFileAsString();
reloadShader();
repaint();
}
}
}
//------------------------------------------------------------------------------
void OpenGLSimple::initializeFragmentByInternalSource() {
fragmentString = juce::String(R"(
/* shader file begin */
void main() {
gl_FragColor = vec4(1.0, 0.0, 0.0, 1.0);
}
/* shader file end */
)");
}
//------------------------------------------------------------------------------
void OpenGLSimple::reloadShader() {
// シェーダー更新処理
if (shader.get() == nullptr || (shader->getFragmentShaderCode() != fragmentString)) {
// fragment shaderに変更があればshaderを更新する
if (fragmentString.isNotEmpty())
{
shader.reset (new juce::OpenGLGraphicsContextCustomShader (fragmentString));
}
}
}
親コンポーネントのコンストラクタに一部記述します。
// ComponentPeer :
// Componentクラスの内部で使用されている。
// ComponentPeer自体は抽象クラスで,プラットフォーム毎の実装が内部で用意されている
if (juce::ComponentPeer* peer = getPeer()) {
// macの場合
// 0:Software Renderer -> NSView等
// 1:CoreGraphics Renderer -> CoreGraphicsでの実装
// サンプルを見ると0の値を指定している。
peer->setCurrentRenderingEngine (0);
}
// OpenGLSimpleコンポーネントのインスタンスを追加
openGLSimple.reset(new OpenGLSimple());
addAndMakeVisible (openGLSimple);
openGLSimple.setBounds (0, 0, 400, 300);
これで実行すると赤い四角形が表示されるかと思います。
実行した状態でXCodeや各種テキストエディタで編集し、保存することで変更したシェーダーが反映されるようになります。
juce::OpenGLGraphicsContextCustomShaderのおかげで少ないコード量でfragment shaderのみ扱うことができます。
レイマーチング(後述)以外の3D描画や凝った処理をしたい場合にはこちら使えない場合もありますが、今回の記事ではこちらを使用した例について紹介していきます。
Uniformを用いた2D描画
上記のサンプルではマウスや時間、音声データなどを扱うことができないため、このままだとあまり便利ではありません。
ですがUniformとjuce::OpenGLRendererクラスを継承したコンポーネントを使うことで利用可能になります。
Uniformとは
CPUからシェーダー(GPU)に送ることができる変数のことです。
ですがComponent::paint()内でシェーダーに対してUniformを設定するだけでは使うことができません。
これは描画タイミングなどが原因のようで、juce::OpenGLRenderer::renderOpenGL()内でUniformを指定する必要があるようです。
また特定のタイミングで行う処理のため、juce::OpenGLGraphicsContextCustomShader::onShaderActivatedにUniformを設定する内容のラムダ関数を指定します。
サンプル
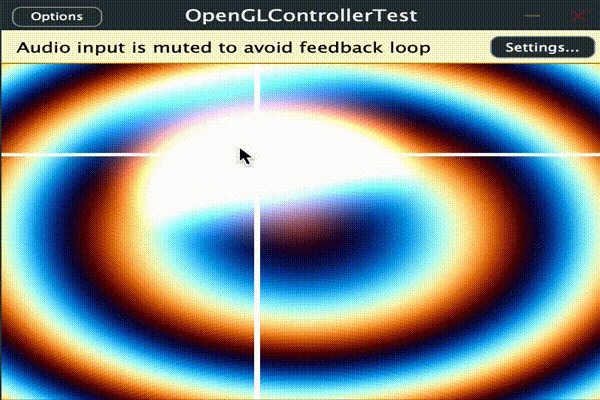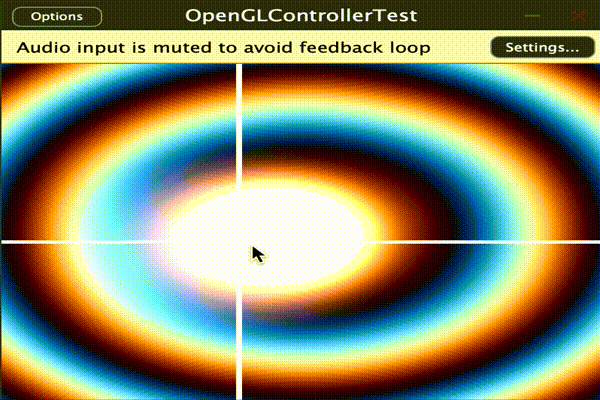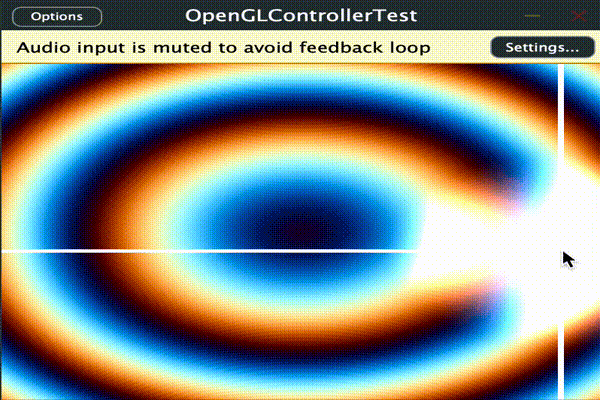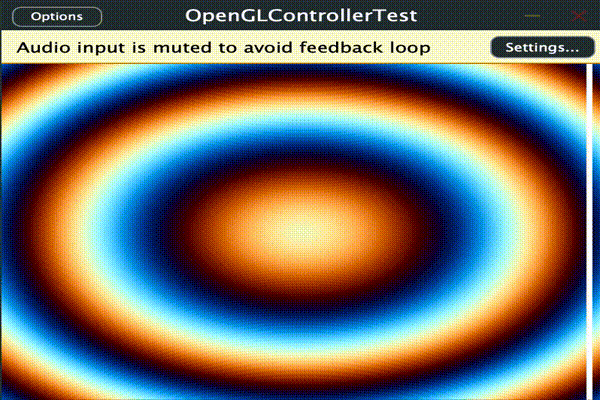
とりあえず時間、描画範囲の縦横px、パンとボリュームの値をシェーダーに渡して使用します。
このサンプルでは範囲[-1 ~ 1]の値のPARAM_PAN、 範囲[0 ~ 1]のPARAM_VOLを
audioParameterFloatとしてそれぞれマウスのXY座標と連動させています。
前述のUniformを使っていないサンプルと同じく、
C++側ではfillRect()で四角の描画しかおこなっていないため
見た目の部分に関しては、ほぼ全てシェーダーで描画処理を書いています。
詳しい解説に関してここでは省略しますが、冒頭のuniformがc++から受け取れる値です。
シェーダーのプログラムは各ピクセル毎に処理を行い、
どのピクセルなのかをgl_FragCoord.xyで取得し、諸々計算して出力色をgl_FragColorに渡します。
ここでは十字線と背景の波と半透明の円を加算合成しています。
uniform float uPan;
uniform float uVolume;
uniform float uTime;
uniform vec2 uResolution;
void main() {
float w = 0.0;
vec2 uv = gl_FragCoord.xy / uResolution.xy;
vec2 mouse = vec2((uPan + 1.0) * 0.5, uVolume);
// line
float lineWidth = 0.01;
w += step(mouse.x - lineWidth * 0.5, uv.x) * step(uv.x, mouse.x + lineWidth * 0.5);
w += step(mouse.y - lineWidth * 0.5, uv.y) * step(uv.y, mouse.y + lineWidth * 0.5);
// circle
float radius = 0.1;
w += smoothstep(radius + 0.2, radius, distance(mouse.xy, uv.xy));
// wave
float dist = distance(vec2(0.5), uv);
float r = (sin(pow(dist * 2.0, 1.5) * 10.0 - uTime + 0.0) + 1.0) * 0.5;
float g = (sin(pow(dist * 2.0, 1.5) * 10.0 - uTime + 0.75) + 1.0) * 0.5;
float b = (sin(pow(dist * 2.0, 1.5) * 10.0 - uTime + 1.4) + 1.0) * 0.5;
gl_FragColor = vec4(vec3(w) + vec3(r, g, b), 1.0);
}
uniformを使用するため、c++側ではコンポーネントをjuce::OpenGLRendererから継承させ、その他一部追記しています。
# pragma once
# include <JuceHeader.h>
# define PARAM_PAN "pan"
# define PARAM_VOL "volume"
//==============================================================================
/*
*/
class OpenGLSimpleUniform : public juce::Component, public juce::Timer, public juce::OpenGLRenderer
{
public:
OpenGLSimpleUniform(juce::AudioProcessorValueTreeState& _vts);
~OpenGLSimpleUniform() override;
// component
void paint (juce::Graphics&) override;
void resized() override {};
void mouseMove(const juce::MouseEvent& event) override;
// timer
void timerCallback() override;
// OpenGLAppComponent
void newOpenGLContextCreated() override {}; // コンテキストが作成された時に呼ばれる
void renderOpenGL() override; // 描画処理を行う
void openGLContextClosing()override {}; // コンテキスト終了時
private:
void initializeFragmentByInternalSource();
void reloadShader();
juce::OpenGLContext openGLContext;
std::unique_ptr<juce::OpenGLGraphicsContextCustomShader> shader;
juce::String fragmentString;
juce::File fragmentShaderFile;
juce::Time fragmentLastModTime;
juce::AudioProcessorValueTreeState& vts;
bool isMousePressed = false;
JUCE_DECLARE_NON_COPYABLE_WITH_LEAK_DETECTOR (OpenGLSimpleUniform)
};
//==============================================================================
OpenGLSimpleUniform::OpenGLSimpleUniform(juce::AudioProcessorValueTreeState& _vts) : vts(_vts)
{
// openGLコンテキストにコンポーネントを紐づける。(ヘビーウェイト化(?))
openGLContext.attachTo (*this);
// レンダラーとしてセット
openGLContext.setRenderer(this);
// repaint loop ON.
openGLContext.setContinuousRepainting(true);
// paint関数はrenderOpenGLから使用する
openGLContext.setComponentPaintingEnabled (false);
// opaque = 不透明であると明示するかどうか
setOpaque(false);
// ビルド後のResourceフォルダからシェーダーを参照するかどうか。
// falseの場合はプロジェクトのResourceフォルダ(ユーザー/JUCE/projcets/OpenGLControllerTest/Resources)から参照する
const bool isBuildResource = false;
juce::String resourcePath;
// ビルド後のプラグインのResourceディレクトリのシェーダーを参照するかどうか
if (isBuildResource) {
resourcePath = juce::File::getSpecialLocation(juce::File::SpecialLocationType::currentApplicationFile).getFullPathName();
# ifdef JUCE_MAC
resourcePath += "/Contents/Resources/";
# elif JUCE_WINDOWS
# endif
}
// 開発プロジェクトのResourceフォルダのshaderを読む
else {
resourcePath = juce::File::getSpecialLocation(juce::File::SpecialLocationType::userDocumentsDirectory).getFullPathName() + "/JUCE/projects/OpenGLControllerTest/Resources/";
}
// shaderのソースコード読み込み
fragmentShaderFile = juce::File(resourcePath + "simpleUniform.frag");
fragmentString = fragmentShaderFile.loadFileAsString();
// リアルタイム更新のために最後にアクセスした時間と変更した時間を取得
fragmentShaderFile.setLastAccessTime(juce::Time::getCurrentTime());
fragmentLastModTime = fragmentShaderFile.getLastModificationTime();
// 配布時などソースコード直書きのシェーダを参照する
// initializeFragmentByInternalSource();
reloadShader();
startTimerHz(60);
}
//------------------------------------------------------------------------------
OpenGLSimpleUniform::~OpenGLSimpleUniform()
{
stopTimer();
// openGLコンテキストへの紐付け解除
openGLContext.detach();
}
//------------------------------------------------------------------------------
void OpenGLSimpleUniform::paint (juce::Graphics& g)
{
auto mouseRel = getMouseXYRelative().toFloat();
auto bounds = g.getClipBounds().toFloat();
// shaderの背景、shaderで描画失敗時にも表示される。
g.fillCheckerBoard (bounds, 48.0f, 48.0f, juce::Colours::lightgrey, juce::Colours::white);
// shaderが有効なものであれば更新
if (shader.get() != nullptr)
{
shader->onShaderActivated = [&](juce::OpenGLShaderProgram& p)
{
p.setUniform("uPan", vts.getRawParameterValue(PARAM_PAN)->load());
p.setUniform("uVolume", vts.getRawParameterValue(PARAM_VOL)->load());
GLfloat uTime = (float)juce::Time::getMillisecondCounterHiRes() * 0.001f;
p.setUniform("uTime", uTime);
p.setUniform("uResolution", bounds.getWidth(), bounds.getHeight());
};
shader->fillRect (g.getInternalContext(), g.getClipBounds());
}
}
//------------------------------------------------------------------------------
void OpenGLSimpleUniform::mouseMove(const juce::MouseEvent& event) {
auto mouseRel = getMouseXYRelative().toFloat();
const auto& mappedPan = juce::jmap((float)mouseRel.x / (float)getWidth(), -1.0f, 1.0f);
vts.getRawParameterValue(PARAM_PAN)->store(juce::jmin(1.0f, juce::jmax(-1.0f, mappedPan)));
vts.getRawParameterValue(PARAM_VOL)->store(1.0f - juce::jmin(1.0f, juce::jmax(0.0f, (float)mouseRel.y / (float)getHeight())));
}
//------------------------------------------------------------------------------
void OpenGLSimpleUniform::timerCallback() {
// シェーダーファイルに最後にアクセスした時間から一定時間経過していれば、シェーダーファイルが変更された時間を確認して変わっていれば際描画処理を行う。
auto currentTime = juce::Time::getCurrentTime();
if (currentTime.toMilliseconds() - fragmentShaderFile.getLastAccessTime().toMilliseconds() > 1000) {
fragmentShaderFile.setLastAccessTime(currentTime);
if (fragmentLastModTime != fragmentShaderFile.getLastModificationTime()) {
fragmentLastModTime = fragmentShaderFile.getLastModificationTime();
fragmentString = fragmentShaderFile.loadFileAsString();
reloadShader();
}
}
}
//------------------------------------------------------------------------------
void OpenGLSimpleUniform::renderOpenGL() {
// 描画クリア
juce::OpenGLHelpers::clear (juce::Colours::black);
auto desktopScale = openGLContext.getRenderingScale();
std::unique_ptr<juce::LowLevelGraphicsContext> glContext (createOpenGLGraphicsContext (openGLContext,
juce::roundToInt (desktopScale * getWidth()),
juce::roundToInt (desktopScale * getHeight())));
if (glContext.get() == nullptr)
return;
// 描画処理
juce::Graphics g (*glContext.get());
paint (g);
}
//------------------------------------------------------------------------------
void OpenGLSimpleUniform::initializeFragmentByInternalSource() {
fragmentString = juce::String(R"(
/* shader file begin */
uniform float uTime;
uniform vec2 uMouseNorm;
uniform vec2 uResolution;
void main() {
float w = 0.0;
vec2 uv = gl_FragCoord.xy / uResolution.xy;
vec2 mouse = vec2(uMouseNorm.x, 1.0 - uMouseNorm.y);
// line
float lineWidth = 0.01;
w += step(mouse.x - lineWidth * 0.5, uv.x) * step(uv.x, mouse.x + lineWidth * 0.5);
w += step(mouse.y - lineWidth * 0.5, uv.y) * step(uv.y, mouse.y + lineWidth * 0.5);
// circle
float radius = 0.1;
w += smoothstep(radius + 0.2, radius, distance(mouse.xy, uv.xy));
// wave
float dist = distance(vec2(0.5), uv);
float r = (sin(pow(dist * 2.0, 1.5) * 10.0 - uTime + 0.0) + 1.0) * 0.5;
float g = (sin(pow(dist * 2.0, 1.5) * 10.0 - uTime + 0.75) + 1.0) * 0.5;
float b = (sin(pow(dist * 2.0, 1.5) * 10.0 - uTime + 1.4) + 1.0) * 0.5;
gl_FragColor = vec4(vec3(w) + vec3(r, g, b), 1.0);
}
/* shader file end */
)");
}
//------------------------------------------------------------------------------
void OpenGLSimpleUniform::reloadShader() {
// シェーダー更新処理
if (shader.get() == nullptr || (shader->getFragmentShaderCode() != fragmentString)) {
// fragment shaderに変更があればshaderを更新する
if (fragmentString.isNotEmpty())
{
shader.reset (new juce::OpenGLGraphicsContextCustomShader (fragmentString));
}
}
}
親コンポーネントのコンストラクタを一部変更します。
/* OpenGLSimpleコンポーネントをコメントアウト */
// openGLSimple.reset(new OpenGLSimple());
// addAndMakeVisible (openGLSimple);
// openGLSimple.setBounds (0, 0, 400, 300);
// OpenGLSimpleUniformコンポーネントのインスタンスを追加
openGLSimpleUniform.reset(new OpenGLSimpleUniform(audioProcessor.vts));
addAndMakeVisible (openGLSimpleUniform.get());
openGLSimpleUniform->setBounds (0, 0, 400, 300);
processorの処理に関してはここでは省略していますが簡易的なパンとボリュームを反映させたサイン波を鳴らしています。(ブツ音対策はひとまず入れてません)
レイマーチング
こちらのスライドが比較的に分かりやすいですが
レイマーチングという手法を使えばfragment shaderのみで3D表現を行うことが可能で、
通常のメッシュをc++で作成する方法に比べてモーフィングや物体同士の結合や差分、3次元上に等間隔で複数配置など有利な部分もあります。
距離関数というものを用いて図形を描画しますが以下のサイトからコピペすれば済むので慣れたら楽です。
↓こちらのサイトで距離関数が網羅されています。
GPU的に重たい処理となるようなので状況を見極めて使った方が良さそうです。。
サンプル
前述のUniformのコンポーネントで読み込むシェーダーだけ変更して試します。
simpleUniformRaymarching.fragというシェーダーファイルを用意し、読み込み部分を変更します。
// fragmentShaderFile = juce::File(resourcePath + "simpleUniform.frag");
fragmentShaderFile = juce::File(resourcePath + "simpleUniformRaymarching.frag");
simpleUniformRaymarching.fragを以下の内容にします。
uniform float uPan;
uniform float uVolume;
uniform float uTime;
uniform vec2 uResolution;
//---------------------------------------------
// you can edit value
//---------------------------------------------
// sphere
const float sphereSize = 1.0;
const vec3 spherePosition = vec3(0, 0, 0);
const vec3 sphereColor = vec3(0.9);
// area
const float areaSize = 10.0;
const float areaHalf = areaSize * 0.5;
const vec3 areaCenterPosition = vec3(0, 0, 0);
const vec3 leftWallColor = vec3(0.9, 0.1, 0.1);
const vec3 rightWallColor = vec3(0.1, 0.9, 0.1);
const vec3 wallColor = vec3(0.9);
// camera
const vec3 cameraPosition = vec3(0.0, 0.0, 8.0);
const vec3 lookAtPosition = vec3(0.0, 0.0, 0.0);
// light
const float pointLightZ = 4.0;
vec3 lightColor = vec3(1.0);
const float ambient = 0.2;
const bool enableDiffuse = true;
const bool enableSpecular = true;
const float specularCurve = 50.0;
// shadow
float shadowAmount = clamp(0.5, 0.0, 1.0);
// light fx
const bool enableLightFx = true;
const float sinFreq = 1.0;
const float sinCurve = 1.0;
const float lightFx = 0.5;
const float colorGap = 0.75;
//---------------------------------------------
// constants & variables
//---------------------------------------------
const int countMax = 30;
vec3 pointLightPosition;
const float EPS = 0.01;
const vec3 deltaX = vec3(EPS, 0, 0);
const vec3 deltaY = vec3(0, EPS, 0);
const vec3 deltaZ = vec3(0, 0, EPS);
//---------------------------------------------
// signed distance functions & operator
//---------------------------------------------
float opSubtraction( float d1, float d2 ) { return max(-d1,d2); }
vec3 opRep(vec3 p, vec3 c)
{
return mod(p+0.5*c,c)-0.5*c;
}
float sdSphere( vec3 p, float s )
{
return length(p)-s;
}
float sdBox( vec3 p, vec3 b )
{
vec3 q = abs(p) - b;
return length(max(q,0.0)) + min(max(q.x,max(q.y,q.z)),0.0);
}
float sdPlane( vec3 p, vec3 n ) {
return dot( p, n.xyz ) + 1.0;
}
//---------------------------------------------
// custom distance functions
//---------------------------------------------
float sdSphereStripe( vec3 p, float s )
{
float sphereDist = length(p)-s;
float boxDist = sdBox(opRep(p + vec3(0, uTime, 0), vec3(1, 0.5, 10.0)), vec3(s * 2.0, 0.1, s * 2.0));
return opSubtraction(boxDist, sphereDist);
}
float distFunc(vec3 p) {
float sphereDist = sdSphere(p - spherePosition, sphereSize);
float leftWallDist = sdBox(p - (areaCenterPosition + vec3(-areaHalf, 0, 0)), vec3(0.1, areaSize, areaSize));
float rightWallDist = sdBox(p - (areaCenterPosition + vec3(areaHalf, 0, 0)), vec3(0.1, areaSize, areaSize));
float topWallDist = sdBox(p - (areaCenterPosition + vec3(0, -areaHalf, 0)), vec3(areaSize, 0.1, areaSize));
float bottomWallDist = sdBox(p - (areaCenterPosition + vec3(0, areaHalf, 0)), vec3(areaSize, 0.1, areaSize));
float frontWallDist = sdBox(p - (areaCenterPosition + vec3(0, 0, -areaHalf)), vec3(areaSize, areaSize, 0.1));
float dist;
dist = min(sphereDist, leftWallDist);
dist = min(dist, rightWallDist);
dist = min(dist, topWallDist);
dist = min(dist, bottomWallDist);
dist = min(dist, frontWallDist);
return dist;
}
float sdLightSphere(vec3 p, float r) {
return sdSphere(p - pointLightPosition, r);
}
//---------------------------------------------
vec3 distFuncNormal(vec3 p) {
return normalize(vec3(distFunc(p + deltaX) - distFunc(p - deltaX),
distFunc(p + deltaY) - distFunc(p - deltaY),
distFunc(p + deltaZ) - distFunc(p - deltaZ))
);
}
vec3 distFuncColor(vec3 p, float dist) {
float sphereDist = sdSphere(p - spherePosition, sphereSize);
float leftWallDist = sdBox(p - (areaCenterPosition + vec3(-areaHalf, 0, 0)), vec3(0.1, areaSize, areaSize));
float rightWallDist = sdBox(p - (areaCenterPosition + vec3(areaHalf, 0, 0)), vec3(0.1, areaSize, areaSize));
if (abs(dist - sphereDist) < EPS) {
return sphereColor;
}
else if (abs(dist - leftWallDist) < EPS) {
return leftWallColor;
}
else if (abs(dist - rightWallDist) < EPS) {
return rightWallColor;
}
else {
return wallColor;
}
}
//---------------------------------------------
float genShadow(vec3 ro, vec3 dst){
vec3 rd = normalize(dst - ro);
float h = 0.0;
float c = 0.001;
float r = 1.0;
float shadowCoef = 0.5;
for(float t = 0.0; t < 50.0; t++){
h = distFunc(ro + rd * c);
if(h < 0.001){
return shadowCoef;
}
r = min(r, h * 16.0 / c);
c += h;
if (c > distance(ro, dst)) break;
}
return mix(shadowCoef, 1.0, r);
}
//---------------------------------------------
// custom distance functions
//---------------------------------------------
void main() {
float w = 0.0;
vec2 uv = (gl_FragCoord.xy * 2.0 - uResolution.xy) / max(uResolution.x, uResolution.y);
vec2 mouse = vec2(uPan, (uVolume - 0.5) * 2.0);
if (uResolution.y < uResolution.x) mouse.y *= (uResolution.y / uResolution.x);
else mouse.x *= (uResolution.y / uResolution.x);
vec4 color = vec4(vec3(0), 1);
// calculate camera vector
vec3 cameraDirection = normalize(lookAtPosition - cameraPosition);
vec3 cameraUp = vec3(0, 1, 0);
vec3 cameraRight = normalize(cross(cameraDirection, cameraUp));
cameraUp = normalize(cross(cameraRight, cameraDirection));
// initialize ray position & direction
vec3 rayPosition = cameraPosition;
vec3 rayDirection = normalize(cameraDirection + uv.x * cameraRight + uv.y * cameraUp);
pointLightPosition = vec3(0, 0, pointLightZ) + 4.0 * mouse.x * cameraRight + 4.0 * mouse.y * cameraUp;
for (int i = 0; i < countMax; i++) {
float dist = distFunc(rayPosition);
if (dist < EPS) {
vec3 normal = distFuncNormal(rayPosition);
vec3 pointLightVec = normalize(pointLightPosition - rayPosition);
vec3 halfLE = normalize(pointLightVec + -rayDirection);
if (enableLightFx) {
float pointLightDistance = distance(cameraPosition, rayPosition);
lightColor.r = (sin(pow(pointLightDistance * sinFreq, sinCurve) + uTime + colorGap * 0.0) + 1.0) * 0.5;
lightColor.g = (sin(pow(pointLightDistance * sinFreq, sinCurve) + uTime + colorGap * 1.0) + 1.0) * 0.5;
lightColor.b = (sin(pow(pointLightDistance * sinFreq, sinCurve) + uTime + colorGap * 2.0) + 1.0) * 0.5;
lightColor = mix(vec3(1.0), lightColor, lightFx);
}
vec3 objColor = distFuncColor(rayPosition, dist);
if (enableDiffuse) {
float diffuse = clamp(dot(normal, pointLightVec), 0.0, 1.0) + ambient;
objColor *= diffuse * lightColor;
}
if (enableSpecular) {
float specular = pow(clamp(dot(normal, halfLE), 0.0, 1.0), specularCurve);
objColor += vec3(specular) * lightColor;
}
float shadow = genShadow(rayPosition + normal * EPS, pointLightPosition);
objColor *= max(1.0 - shadowAmount, shadow);
color.rgb += objColor;
break;
}
rayPosition += dist * rayDirection;
}
color.rgb += smoothstep(0.2, 0.1, distance(mouse, uv));
gl_FragColor = color;
}
最後に
ベストプラクティスや、この部分はこういう方法が良い等ありましたら優しく指摘頂けると助かります...!
あとjuce::OpenGLGraphicsContextCustomShader使用時のテクスチャをシェーダーに渡す方法などあるのか気になっているのですがご存知の方がいれば...!
