1.はじめに
GIMP Python-Fuでグラデーションを描画しました。
GIMP 2.10で動作確認をしています。
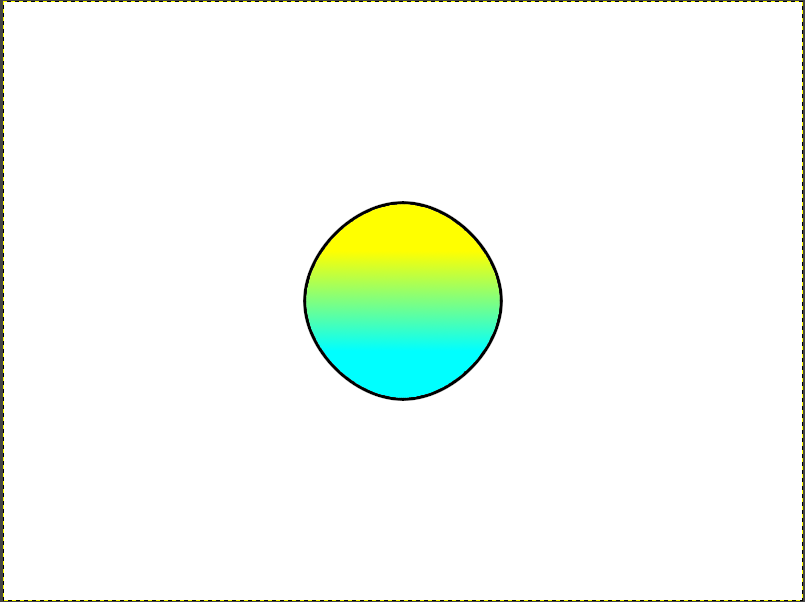
2.実行結果
円を描く正確な方法はまだ分かっていないので、曲線描画でほぼ円にしています。
追記:「鉛筆で描画」を選択していてブラシは「1. Pixel」の場合の実行結果です。「ブラシで描画」や他のブラシの場合には若干結果が変わります。
3.グラデーション関連スクリプト
背景色設定です。
グラデーションでFG_BG_RGB_MODE(前景色から背景色までRGBでグラデーション)を使用するため、追加しています。
def set_bg_color(r, g, b, a):
color = (r, g, b, a)
pdb.gimp_context_set_background(color)
以下、メイン関数の中です。
円っぽいものを描画しています。アンチエイリアスありです。
# ほぼ円
points = [
(+100, 0, 0, -50, 0, +50),
(-100, +100, +50, 0, -50, 0),
(-100, -100, 0, +50, 0, -50),
(+100, -100, -50, 0, +50, 0),
]
make_path_relative2(image, 400, 300, points, 2, TRUE)
ファジー選択で円の内側を選択しています。しきい値は150にしています。
pdb.gimp_fuzzy_select(layer, 400, 300, 150, 2, TRUE, 0, 0, 0)
グラデーション描画です。分かる範囲で記載します。
| 引数 | 引数名 | 内容 | 指定した値 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | drawable_ID | drawable | レイヤーを指定しています |
| 2 | blend_mode | FG_BG_RGB_MODE(前景色から背景色までRGBでグラデーション) | |
| 3 | paint_mode | NORMAL_MODE 色々選べるようですが未確認。GUIでも選べます | |
| 4 | gradient_type | 形状 | GRADIENT_LINEAR(線形) |
| 5 | opacity | 不透明度 | 100 |
| 6 | offset | オフセット | 0 |
| 7 | repeat | リピート形状を選べるようです | REPEAT_NONE |
| 8 | reverse | 反転 | FALSE |
| 9 | supersample | Do adaptive supersampling. | FALSE |
| 10 | max_depth | Maximum recursion levels for supersampling. | 0 |
| 11 | threshold | Supersampling threshold. | 0 |
| 12 | dither | Use dithering to reduce banding. | TRUE |
| 13 | x1 | 開始X座標 | 400 |
| 14 | y1 | 開始Y座標 | 250 |
| 15 | x2 | 終了X座標 | 400 |
| 16 | y2 | 終了Y座標 | 350 |
set_color(255, 255, 0, 1.0) # 黄色
set_bg_color(0, 255, 255, 1.0) # シアン
pdb.gimp_edit_blend(layer, FG_BG_RGB_MODE, NORMAL_MODE, GRADIENT_LINEAR, 100, 0, REPEAT_NONE, FALSE, FALSE, 0, 0, TRUE, 400, 250, 400, 350)
ファジー選択していた分を解除します。
pdb.gimp_selection_clear(image)
4.スクリプト全体
長くなっていますが、曲線描画等のためで、グラデーション部分は前出の通りわずかです。
関数はGIMP Python-Fuでパスを使用して直線・曲線を描く時に、最後を閉じないと線の欠けが発生する - Qiitaと同じですが、set_bg_color()を追加しています。
今回も下記関数は、5 分で始める GIMP Python-Fu - Qiitaのものを使用させて頂いています。
create_image()
add_layer()
set_color()
set_line_width()
display_image()
# Python-Fu のサンプル・スクリプト
# GIMP の Python-Fu コンソールにコピペして実行してください
# 画像データの作成
## 指定したサイズで画像データを作成する
### width : 画像データの幅 (px)
### height : 画像データの高さ (px)
def create_image(width, height):
# 画像データを生成
return gimp.Image(width, height, RGB)
# レイヤーの追加
## 指定した名前のレイヤーを新規に作成し、画像データに挿入する
### image : レイヤーを追加する画像データ
### name : 新規に作成するレイヤーの名前(文字列)
def add_layer(image, name):
# レイヤーの作成に必要なパラメータ
width = image.width
height = image.height
type = RGB_IMAGE
opacity = 100
mode = NORMAL_MODE
#
# パラメータをもとにレイヤーを作成
layer = gimp.Layer(image, name, width, height, type, opacity, mode)
#
# レイヤーを背景色で塗りつぶす(GIMP のデフォルトの挙動に合わせています)
layer.fill(1)
#
# 画像データの 0 番目の位置にレイヤーを挿入する
position = 0
image.add_layer(layer, position)
#
return layer
# 描画する色を変更する
## パレットの前景色を変更して描画色を設定する
### r : 赤要素 (0-255)
### g : 緑要素 (0-255)
### b : 青要素 (0-255)
### a : 透明度 (0-1.0)
def set_color(r, g, b, a):
color = (r, g, b, a)
pdb.gimp_context_set_foreground(color)
def set_bg_color(r, g, b, a):
color = (r, g, b, a)
pdb.gimp_context_set_background(color)
# 描画する線の太さを変える
## ブラシのサイズを変更して線の太さを設定する
### width : 線の太さ
def set_line_width(width):
pdb.gimp_context_set_brush_size(width)
# アンチエイリアスを設定する
## アンチエイリアスを設定する
### antialias : TRUE:有効、FALSE:無効
def set_antialias(antialias):
pdb.gimp_context_set_antialias(antialias)
# 画像の表示
## 新しいウィンドウを作成し、画像データを表示する
### image : 表示する画像データ
def display_image(image):
gimp.Display(image)
# パス作成
## パスを作成
### image : レイヤーを追加する画像データ
### points : パス座標
### mode : 0:描画しない、1:閉じないストローク(初期値)、2:閉じるストローク、3:塗りつぶし
### delete_path : TRUE:パスを削除する(初期値)、FALSE:パスを残す
def make_path(
image,
points,
mode=1,
delete_path=TRUE,
):
""" パスを作成する。 """
#
# フラグ設定
#
is_draw = FALSE
is_closed = FALSE
is_fill = FALSE
is_stroke = FALSE
if mode == 1: # 閉じないストローク
is_draw = TRUE
is_closed = FALSE
is_fill = FALSE
is_stroke = FALSE
elif mode == 2: # 閉じるストローク
is_draw = TRUE
is_closed = TRUE
is_fill = FALSE
is_stroke = FALSE
elif mode == 3: # 塗りつぶし
is_draw = TRUE
is_closed = TRUE # TRUE/FALSEどちらでも変わらない
is_fill = TRUE
is_stroke = FALSE
elif mode == 4: # 閉じないストローク(アンチエイリアスが効かない)
is_draw = TRUE
is_closed = FALSE # 効かない
is_fill = FALSE
is_stroke = TRUE
elif mode == 5: # 閉じるストローク(アンチエイリアスが効かない)
is_draw = TRUE
is_closed = TRUE
is_fill = FALSE
is_stroke = TRUE
#
vectors = pdb.gimp_vectors_new(image, 'path') # パス新規作成
pdb.gimp_image_add_vectors(image, vectors, 0) # パスを画像に追加
#
# パスとしてストロークを追加
#
stroke_id = pdb.gimp_vectors_stroke_new_from_points(vectors, 0,
len(points), points, is_closed)
#
# パスを表示
#
pdb.gimp_vectors_set_visible(vectors, TRUE)
#
# 描画するよう指定されてたら、パスから選択範囲を作って描画する。
#
if is_draw:
#
# 選択範囲解除
#
pdb.gimp_selection_none(image)
#
# パスから選択範囲作成
#
pdb.gimp_vectors_to_selection(
vectors,
CHANNEL_OP_REPLACE,
TRUE,
FALSE,
0,
0,
)
#
# 前景色で描画
#
drawable = pdb.gimp_image_active_drawable(image)
if is_fill:
pdb.gimp_edit_fill(drawable, FOREGROUND_FILL)
elif is_stroke:
pdb.gimp_edit_stroke(drawable)
else:
pdb.gimp_drawable_edit_stroke_item(drawable, vectors)
#
# 選択範囲解除
#
pdb.gimp_selection_none(image)
#
# パス削除が指定されていたらパスを削除する。
#
if delete_path:
# パス削除
#
pdb.gimp_image_remove_vectors(image, vectors)
#
return
def get_absolute_point(list):
""" """
rlist = []
for pos in list:
if len(pos) == 6:
(x, y, rx1, ry1, rx2, ry2) = pos
x1 = x + rx1
y1 = y + ry1
x2 = x + rx2
y2 = y + ry2
else:
(x, y) = pos
x1 = x
y1 = y
x2 = x
y2 = y
rlist.extend([
x1,
y1,
x,
y,
x2,
y2,
])
return rlist
# 絶対座標取得
def get_absolute_point2(x, y, list):
""" """
rlist = []
bx = x
by = y
for pos in list:
if len(pos) == 6:
(rx0, ry0, rx1, ry1, rx2, ry2) = pos
bx = bx + rx0
by = by + ry0
x1 = bx + rx1
y1 = by + ry1
x2 = bx + rx2
y2 = by + ry2
else:
(rx0, ry0) = pos
bx = bx + rx0
by = by + ry0
x1 = bx
y1 = by
x2 = bx
y2 = by
rlist.extend([
x1,
y1,
bx,
by,
x2,
y2,
])
return rlist
# パス作成(相対座標指定)
## パスを作成
### image : レイヤーを追加する画像データ
### points : パス座標
### mode : 0:描画しない、1:最後を閉じないストローク(初期値)、2:最後を閉じるストローク、3:塗りつぶし
### delete_path : TRUE:パスを削除する(初期値)、FALSE:パスを残す
def make_path_relative(
image,
points,
mode=1,
delete_path=TRUE,
):
""" パスを作成する。 """
new_points = get_absolute_point(points)
make_path(image, new_points, mode, delete_path)
# パス作成(座標・アンカー・制御点相対座標指定)
## パスを作成
### image : レイヤーを追加する画像データ
### x : 開始X座標
### y : 開始Y座標
### points : パス座標
### mode : 0:描画しない、1:最後を閉じないストローク(初期値)、2:最後を閉じるストローク、3:塗りつぶし
### delete_path : TRUE:パスを削除する(初期値)、FALSE:パスを残す
def make_path_relative2(
image,
x,
y,
points,
mode=1,
delete_path=TRUE,
):
""" パスを作成する。 """
new_points = get_absolute_point2(x, y, points)
make_path(image, new_points, mode, delete_path)
# メイン
def main():
set_bg_color(255, 255, 255, 1.0)
image = create_image(800, 600)
layer = add_layer(image, "背景")
#layer = add_layer(image, "テスト")
set_color(0, 0, 0, 1.0)
set_line_width(10)
set_antialias(TRUE)
# 値は(アンカーX, Y[, 制御開始点増分X, Y, 制御終了点増分X, Y])
#
# ほぼ円
points = [
(+100, 0, 0, -50, 0, +50),
(-100, +100, +50, 0, -50, 0),
(-100, -100, 0, +50, 0, -50),
(+100, -100, -50, 0, +50, 0),
]
make_path_relative2(image, 400, 300, points, 2, TRUE)
#
pdb.gimp_fuzzy_select(layer, 400, 300, 150, 2, TRUE, 0, 0, 0)
set_color(255, 255, 0, 1.0) # 黄色
set_bg_color(0, 255, 255, 1.0) # シアン
pdb.gimp_edit_blend(layer, FG_BG_RGB_MODE, NORMAL_MODE, GRADIENT_LINEAR, 100, 0, REPEAT_NONE, FALSE, FALSE, 0, 0, TRUE, 400, 250, 400, 350)
pdb.gimp_selection_clear(image)
#
display_image(image)
main()