回帰モデルで予測の分散を考慮できるモデルとして、ガウス過程回帰があります。でもあれはあれでけっこうクセがあると思ってて、他の回帰モデルでも予測の分散を考慮できたらなと思ってました。そこで、アンサンブル手法として知られる Bagging や Blending を使えば良いと思ったので試してみました。
予測したい関数
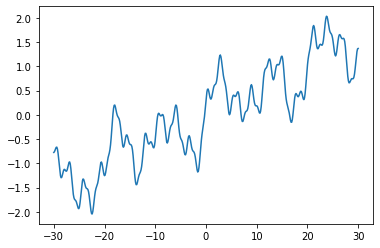
ここでは、単純のため以下のような1変数関数を用います。
import numpy as np
f = lambda x: 0.05*x+0.2*np.sin(x) + 0.3*np.cos(2.1*x) + 0.5*np.sin(0.61*x) + 0.2*np.sin(x/3.1) + 0.1*np.sin(5.1*x)
図示したらこんな感じ。
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
x_domain = np.linspace(-30, 30, 500) # 関数の範囲
plt.plot(x_domain, f(x_domain))
plt.show()
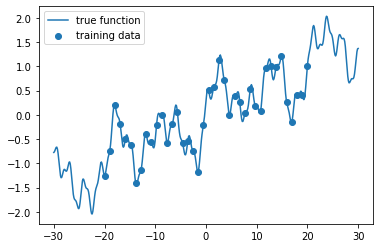
下記のように訓練データを取得して、それを学習させてみたいと思います。
x_train = np.linspace(-20, 20, 40) # 訓練データ
plt.scatter(x_train, f(x_train), label="training data")
plt.plot(x_domain, f(x_domain), label="true function")
plt.legend()
plt.show()
ガウス過程回帰
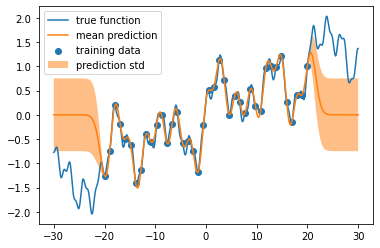
GaussianProcessRegressor を用いて、予測および予測の分散を求めます。
from sklearn.gaussian_process import GaussianProcessRegressor
from sklearn.gaussian_process.kernels import RBF
kernel = 1.0 * RBF(length_scale=1.0, length_scale_bounds=(1e-1, 10.0))
model = GaussianProcessRegressor(kernel=kernel, random_state=0)
model.fit(x_train.reshape(-1, 1), f(x_train))
y_pred, y_std = model.predict(x_domain.reshape(-1, 1), return_std=True)
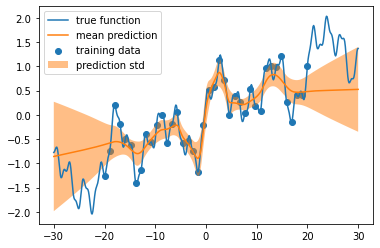
結果の図示
plt.scatter(x_train, f(x_train), label="training data")
plt.plot(x_domain, f(x_domain), label="true function")
plt.plot(x_domain, y_pred, label="mean prediction")
plt.fill_between(x_domain, y_pred-y_std, y_pred+y_std, alpha=0.5, label="prediction std")
plt.legend()
plt.show()
こんな感じで、ガウス過程って、けっこう過剰適合(過学習)しがちで、そのくせ内挿は自信過剰で、外挿はテキトーすぎる印象があるんですよねー(個人の感想です)。
アンサンブル学習器から予測の分散を求める関数
scikit-learnには数多くのアンサンブル学習器が用意されていて、平素より大変お世話になっておりますが、こんな関数が用意されてるともっと嬉しい気がするんです。
def predict_std(model, X):
y_pred = []
for base_model in model.estimators_:
y_pred.append(base_model.predict(X))
return np.array(y_pred).std(axis=0)
Blending
機械学習界隈で「Blending」と呼ばれるアンサンブルは VotingRegressor として実装されています。それを使って、たとえば MLPRegressor をアンサンブルしてみます。
from sklearn.ensemble import VotingRegressor
from sklearn.neural_network import MLPRegressor
model = VotingRegressor(
estimators = [(str(x),
MLPRegressor(
hidden_layer_sizes=[100 for x in range(10)],
max_iter=1000,
#early_stopping=True
)
) for x in range(100)]
)
model.fit(x_train.reshape(-1, 1), f(x_train))
y_pred = model.predict(x_domain.reshape(-1, 1))
y_std = predict_std(model, x_domain.reshape(-1, 1))
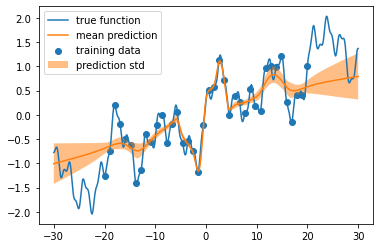
図示すると次のようになります。うーん、まだ不十分な感じだけど、ガウス過程回帰よりは、良いんじゃないですかね。
plt.scatter(x_train, f(x_train), label="training data")
plt.plot(x_domain, f(x_domain), label="true function")
plt.plot(x_domain, y_pred, label="mean prediction")
plt.fill_between(x_domain, y_pred-y_std, y_pred+y_std, alpha=0.5, label="prediction std")
plt.legend()
plt.show()
MLPRegressorには、過剰適合を防ぐ early_stopping=True というオプションがあるのですが、それを入れるとさらにザックリとした予測になります。
Bagging
次は Bagging です。
from sklearn.ensemble import BaggingRegressor
from sklearn.neural_network import MLPRegressor
model = BaggingRegressor(
base_estimator=MLPRegressor(
hidden_layer_sizes=[100 for x in range(10)],
max_iter=1000,
#early_stopping=True
),
n_estimators=100
)
model.fit(x_train.reshape(-1, 1), f(x_train))
y_pred = model.predict(x_domain.reshape(-1, 1))
y_std = predict_std(model, x_domain.reshape(-1, 1))
結果の図示
plt.scatter(x_train, f(x_train), label="training data")
plt.plot(x_domain, f(x_domain), label="true function")
plt.plot(x_domain, y_pred, label="mean prediction")
plt.fill_between(x_domain, y_pred-y_std, y_pred+y_std, alpha=0.5, label="prediction std")
plt.legend()
plt.show()
うん、このくらいが一番良い気がしますね(個人の感想です)。