グラフ構造を深層学習する PyG (PyTorch Geometric) を Google Colaboratory 上で使ってみました。今回は、Recurrent Graph Neural Network を使うことがテーマです。
学習済みモデルを Google Drive に保存するための準備
学習済みモデルを Google Drive に保存するため、Google Drive をマウントします。
from google.colab import drive
drive.mount('/content/drive')
Mounted at /content/drive
次のようにして Google Drive 上のディレクトリを指定します。
import os
directory_path = './drive/MyDrive/pyg_models/'
if not os.path.exists(directory_path):
os.makedirs(directory_path)
PyG (PyTorch Geometric) インストール
PyG (PyTorch Geometric) のレポジトリは https://github.com/pyg-team/pytorch_geometric にあります。また、コードはチュートリアルドキュメント https://pytorch-geometric.readthedocs.io/en/latest/index.html を参考にしています。
import os
import torch
torch.manual_seed(53)
os.environ['TORCH'] = torch.__version__
print(torch.__version__)
!pip install -q torch-scatter -f https://data.pyg.org/whl/torch-${TORCH}.html
!pip install -q torch-sparse -f https://data.pyg.org/whl/torch-${TORCH}.html
!pip install -q git+https://github.com/pyg-team/pytorch_geometric.git
import torch_geometric
1.12.0+cu113
[K |████████████████████████████████| 7.9 MB 45.1 MB/s
[K |████████████████████████████████| 3.5 MB 24.4 MB/s
[?25h Building wheel for torch-geometric (setup.py) ... [?25l[?25hdone
コード開発中は cpu を用い、max_epoch を 50 程度にしていました。ほぼ開発が終わってから、cuda を用いて max_epoch を 2000 にしました。
device = torch.device('cuda' if torch.cuda.is_available() else 'cpu')
#device = "cpu"
max_epoch = 2000
次のようにして、train_mask, val_mask, test_mask を設定します。
def train_val_test_split(data, val_ratio: float = 0.15,
test_ratio: float = 0.15):
rnd = torch.rand(len(data.x))
train_mask = [False if (x > val_ratio + test_ratio) else True for x in rnd]
val_mask = [False if (val_ratio + test_ratio >= x) and (x > test_ratio) else True for x in rnd]
test_mask = [False if (test_ratio >= x) else True for x in rnd]
return torch.tensor(train_mask), torch.tensor(val_mask), torch.tensor(test_mask)
日本の市町村の緯度経度データ
日本の市町村の緯度経度データを PyG で取り扱うためのクラスです。コードの内容について詳細は過去記事をご参照ください。
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
from scipy.spatial import distance
from torch_geometric.data import Data, InMemoryDataset
class JapaneseCities(InMemoryDataset):
def __init__(self, transform = None,
top=8,
url="https://raw.githubusercontent.com/maskot1977/toydata/main/data/cities3.txt"):
super().__init__('.', transform)
japan_df = pd.read_csv(url, header=None, sep="\t")
location = japan_df.iloc[:, -2:].values
dist_matrix = distance.cdist(location, location, metric='euclidean')
adj_matrix = []
for idxs in np.argsort(dist_matrix)[:, :top]:
adj_matrix.append(
[1 if i in idxs else 0 for i in range(len(dist_matrix))]
)
adj_matrix = np.array(adj_matrix)
embeddings = torch.tensor(japan_df.iloc[:, [-1, -2]].values,
dtype=torch.float)
edges = []
edge_attr = []
for i in range(len(adj_matrix)):
for j in range(len(adj_matrix)):
if i == j:
continue
elif adj_matrix[i][j] == 1:
edges.append([i, j])
edge_attr.append(dist_matrix[i][j])
edges = torch.tensor(edges, dtype=torch.long).T
edge_attr = torch.tensor(edge_attr, dtype=torch.float)
name2id = {}
id2name = {}
for v in japan_df.iloc[:, 1].values:
if v not in name2id.keys():
name2id[v] = len(name2id.keys())
id2name[name2id[v]] = v
ys = torch.tensor(
[name2id[v] for v in japan_df.iloc[:, 1].values], dtype=torch.long
)
data = Data(x=embeddings, edge_index=edges, y=ys, edge_attr=edge_attr)
self.data, self.slices = self.collate([data])
次のようにしてデータセットを作成します。この data はのちの工程でグローバル変数として用いられます。
dataset = JapaneseCities()
data = dataset[0].to(device)
train_mask, val_mask, test_mask = train_val_test_split(data)
data.train_mask = train_mask
data.val_mask = val_mask
data.test_mask = test_mask
学習の流れ
過去記事とは違う書き方で学習してみたいと思います。model や data は引数として与えていないので、グローバル変数から取ってくるということに注意してください。
def train():
model.train()
optimizer.zero_grad()
loss = loss_fn(model()[data.train_mask], data.y[data.train_mask])
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
return loss.detach().cpu().numpy()
def test():
model.eval()
logits = model()
accs = []
for _, mask in data('train_mask', 'val_mask', 'test_mask'):
pred = logits[mask].max(1)[1]
acc = pred.eq(data.y[mask]).sum().item() / mask.sum().item()
accs.append(acc)
return accs
Graph Attention Networks (GAT)
過去記事でも用いた Graph Attention Networks (GAT) (これは Recurrent Graph Neural Network ではありません)を今回は次のように定義します。forward の引数が self だけであることに注意してください。
class GAT(torch.nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(GAT, self).__init__()
self.hid = 32
self.in_head = 32
self.out_head = 1
self.conv1 = torch_geometric.nn.GATConv(dataset.num_features,
self.hid,
heads=self.in_head,
dropout=0.1) # dropout=0.6)
self.conv1b = torch_geometric.nn.GATConv(self.hid*self.in_head,
self.hid,
heads=self.in_head,
dropout=0.1)
self.conv2 = torch_geometric.nn.GATConv(self.hid*self.in_head,
dataset.num_classes,
heads=self.out_head,
concat=True,
dropout=0.1)
def forward(self):
x, edge_index = data.x, data.edge_index
x = torch.nn.functional.dropout(x, p=0.1, training=self.training)
x = self.conv1(x, edge_index)
x = torch.nn.functional.elu(x)
x = torch.nn.functional.dropout(x, p=0.1, training=self.training)
x = self.conv1b(x, edge_index)
x = torch.nn.functional.elu(x)
x = torch.nn.functional.dropout(x, p=0.1, training=self.training)
x = self.conv2(x, edge_index)
return torch.nn.functional.log_softmax(x, dim=1)
モデル、最適化手法、損失関数を定義します。
model_name = "GAT"
model = GAT().to(device)
optimizer = torch.optim.Adam(model.parameters(), lr=0.001)
loss_fn = torch.nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
次のようにして学習します。このコードは使いまわします。
import copy
best_loss = None
loss_hist = []
acc_hist = []
for epoch in range(1, max_epoch):
loss = train()
loss_hist.append(loss)
accs = test()
acc_hist.append(accs)
train_acc, val_acc, test_acc = accs
if best_loss is None or best_loss > loss:
best_loss = loss
best_model = copy.deepcopy(model)
best_model = best_model.to('cpu')
torch.save(
best_model.state_dict(),
"{}/{}_model.pt".format(directory_path, model_name)
)
print('Epoch: {:05d}, Train Acc: {:.5f}, '
'Val Acc: {:.5f}, Test Acc: {:.5f}, Loss: {}'.format(
epoch, train_acc, val_acc, test_acc, loss))
Epoch: 00001, Train Acc: 0.18740, Val Acc: 0.18742, Test Acc: 0.18700, Loss: 12.414194107055664
Epoch: 00002, Train Acc: 0.12604, Val Acc: 0.11817, Test Acc: 0.12384, Loss: 8.90912914276123
Epoch: 00019, Train Acc: 0.14760, Val Acc: 0.12770, Test Acc: 0.12879, Loss: 8.612857818603516
Epoch: 00020, Train Acc: 0.18740, Val Acc: 0.18742, Test Acc: 0.18700, Loss: 7.044679164886475
Epoch: 00022, Train Acc: 0.29685, Val Acc: 0.28971, Test Acc: 0.29412, Loss: 6.814143180847168
(以下略)
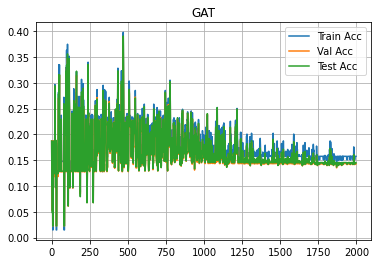
損失関数や正答率の履歴を表示してみましょう。
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
plt.title(model_name)
plt.plot(loss_hist, label="Loss")
plt.legend()
plt.yscale('log')
plt.grid()
plt.show()
plt.title(model_name)
plt.plot([acc[0] for acc in acc_hist], label="Train Acc")
plt.plot([acc[1] for acc in acc_hist], label="Val Acc")
plt.plot([acc[2] for acc in acc_hist], label="Test Acc")
plt.legend()
plt.grid()
plt.show()
学習が進むにつれて、損失関数の値は低下していってますが、正答率はほとんど向上していないようです。
Graph Neural Network Model (GNNM)
これは graph convolution に MessagePassing と MLP を導入して改良したネットワークモデルです。
class MLP(torch.nn.Module):
def __init__(self, input_dim, hid_dims, out_dim):
super(MLP, self).__init__()
self.mlp = torch.nn.Sequential()
dims = [input_dim] + hid_dims + [out_dim]
for i in range(len(dims)-1):
self.mlp.add_module(
'lay_{}'.format(i),
torch.nn.Linear(in_features=dims[i], out_features=dims[i+1])
)
if i+2 < len(dims):
self.mlp.add_module('act_{}'.format(i), torch.nn.Tanh())
def reset_parameters(self):
for i, l in enumerate(self.mlp):
if type(l) == torch.nn.Linear:
torch.nn.init.xavier_normal_(l.weight)
def forward(self, x):
return self.mlp(x)
class GNNM(torch_geometric.nn.conv.MessagePassing):
def __init__(self, n_nodes, out_channels, features_dim, hid_dims,
num_layers = 50, eps=1e-3, aggr = 'add',
bias = True, **kwargs):
super(GNNM, self).__init__(aggr=aggr, **kwargs)
self.node_states = torch.nn.Parameter(
torch.zeros((n_nodes, features_dim)), requires_grad=False
)
self.out_channels = out_channels
self.eps = eps
self.num_layers = num_layers
self.transition = MLP(features_dim, hid_dims, features_dim)
self.readout = MLP(features_dim, hid_dims, out_channels)
self.reset_parameters()
def reset_parameters(self):
self.transition.reset_parameters()
self.readout.reset_parameters()
def forward(self):
edge_index = data.edge_index
edge_weight = data.edge_attr
node_states = self.node_states
for i in range(self.num_layers):
m = self.propagate(
edge_index, x=node_states, edge_weight=edge_weight,
size=None)
new_states = self.transition(m)
with torch.no_grad():
distance = torch.norm(new_states - node_states, dim=1)
convergence = distance < self.eps
node_states = new_states
if convergence.all():
break
out = self.readout(node_states)
return torch.nn.functional.log_softmax(out, dim=-1)
def message(self, x_j, edge_weight):
return x_j if edge_weight is None else edge_weight.view(-1, 1) * x_j
def message_and_aggregate(self, adj_t, x) :
return matmul(adj_t, x, reduce=self.aggr)
def __repr__(self):
return '{}({}, num_layers={})'.format(self.__class__.__name__,
self.out_channels,
self.num_layers)
モデル、最適化手法、損失関数を定義します。
model_name = "GNNM"
model = GNNM(
data.num_nodes, dataset.num_classes, 32, [64,64,64,64,64], eps=0.01
).to(device)
optimizer = torch.optim.Adam(model.parameters(), lr=0.001)
loss_fn = torch.nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
次のようにして学習します。このコードは先程の使いまわしです。
import copy
best_loss = None
loss_hist = []
acc_hist = []
for epoch in range(1, max_epoch):
loss = train()
loss_hist.append(loss)
accs = test()
acc_hist.append(accs)
train_acc, val_acc, test_acc = accs
if best_loss is None or best_loss > loss:
best_loss = loss
best_model = copy.deepcopy(model)
best_model = best_model.to('cpu')
torch.save(
best_model.state_dict(),
"{}/{}_model.pt".format(directory_path, model_name)
)
print('Epoch: {:05d}, Train Acc: {:.5f}, '
'Val Acc: {:.5f}, Test Acc: {:.5f}, Loss: {}'.format(
epoch, train_acc, val_acc, test_acc, loss))
Epoch: 00001, Train Acc: 0.16086, Val Acc: 0.15756, Test Acc: 0.16409, Loss: 2.4063360691070557
Epoch: 00002, Train Acc: 0.17745, Val Acc: 0.17027, Test Acc: 0.17399, Loss: 2.3022396564483643
Epoch: 00003, Train Acc: 0.21891, Val Acc: 0.18297, Test Acc: 0.19071, Loss: 2.25955867767334
Epoch: 00004, Train Acc: 0.22720, Val Acc: 0.21537, Test Acc: 0.21176, Loss: 2.222214460372925
Epoch: 00005, Train Acc: 0.18740, Val Acc: 0.18679, Test Acc: 0.18638, Loss: 2.203711986541748
(以下略)
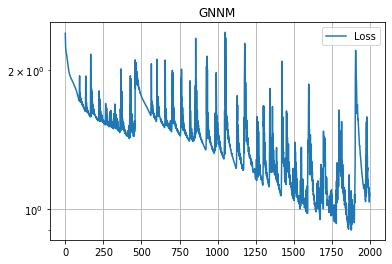
損失関数や正答率の履歴を表示してみましょう。
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
plt.title(model_name)
plt.plot(loss_hist, label="Loss")
plt.legend()
plt.yscale('log')
plt.grid()
plt.show()
plt.title(model_name)
plt.plot([acc[0] for acc in acc_hist], label="Train Acc")
plt.plot([acc[1] for acc in acc_hist], label="Val Acc")
plt.plot([acc[2] for acc in acc_hist], label="Test Acc")
plt.legend()
plt.grid()
plt.show()
学習が収束してない気がしますが、先程のGATよりは良い成績が出てます。
Gated Graph Neural Network (GGNN)
こちらは graph convolution の MessagePassing に GRU (gated recurrent unit) を導入したネットワークです。
class GatedGraphConv(torch_geometric.nn.conv.MessagePassing):
def __init__(self, out_channels, num_layers, aggr = 'add',
bias = True, **kwargs):
super(GatedGraphConv, self).__init__(aggr=aggr, **kwargs)
self.out_channels = out_channels
self.num_layers = num_layers
self.weight = torch.nn.Parameter(torch.Tensor(num_layers, out_channels, out_channels))
self.rnn = torch.nn.GRUCell(out_channels, out_channels, bias=bias)
self.reset_parameters()
def reset_parameters(self):
torch_geometric.nn.inits.uniform(self.out_channels, self.weight)
self.rnn.reset_parameters()
def forward(self, data):
x = data.x
edge_index = data.edge_index
edge_weight = data.edge_attr
if x.size(-1) > self.out_channels:
raise ValueError('The number of input channels is not allowed to '
'be larger than the number of output channels')
if x.size(-1) < self.out_channels:
zero = x.new_zeros(x.size(0), self.out_channels - x.size(-1))
x = torch.cat([x, zero], dim=1)
for i in range(self.num_layers):
m = torch.matmul(x, self.weight[i])
m = self.propagate(edge_index, x=m, edge_weight=edge_weight,
size=None)
x = self.rnn(m, x)
return x
def message(self, x_j, edge_weight):
return x_j if edge_weight is None else edge_weight.view(-1, 1) * x_j
def message_and_aggregate(self, adj_t, x):
return matmul(adj_t, x, reduce=self.aggr)
def __repr__(self):
return '{}({}, num_layers={})'.format(self.__class__.__name__,
self.out_channels,
self.num_layers)
class GGNN(torch.nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(GGNN, self).__init__()
self.conv = GatedGraphConv(1433, 3)
self.mlp = MLP(1433, [32,32,32], dataset.num_classes)
def forward(self):
x = self.conv(data)
x = self.mlp(x)
return torch.nn.functional.log_softmax(x, dim=-1)
モデル、最適化手法、損失関数を定義します。
model_name = "GGNN"
model = GGNN().to(device)
optimizer = torch.optim.Adam(model.parameters(), lr=0.001)
loss_fn = torch.nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
次のようにして学習します。このコードは先程の使いまわしです。
import copy
best_loss = None
loss_hist = []
acc_hist = []
for epoch in range(1, max_epoch):
loss = train()
loss_hist.append(loss)
accs = test()
acc_hist.append(accs)
train_acc, val_acc, test_acc = accs
if best_loss is None or best_loss > loss:
best_loss = loss
best_model = copy.deepcopy(model)
best_model = best_model.to('cpu')
torch.save(
best_model.state_dict(),
"{}/{}_model.pt".format(directory_path, model_name)
)
print('Epoch: {:05d}, Train Acc: {:.5f}, '
'Val Acc: {:.5f}, Test Acc: {:.5f}, Loss: {}'.format(
epoch, train_acc, val_acc, test_acc, loss))
Epoch: 00001, Train Acc: 0.18242, Val Acc: 0.17408, Test Acc: 0.17833, Loss: 2.4117162227630615
Epoch: 00002, Train Acc: 0.23051, Val Acc: 0.20457, Test Acc: 0.21610, Loss: 2.334713935852051
Epoch: 00003, Train Acc: 0.23715, Val Acc: 0.22935, Test Acc: 0.22910, Loss: 2.3105783462524414
Epoch: 00004, Train Acc: 0.23715, Val Acc: 0.22490, Test Acc: 0.22972, Loss: 2.279224395751953
Epoch: 00005, Train Acc: 0.20232, Val Acc: 0.19886, Test Acc: 0.19876, Loss: 2.258718252182007
(以下略)
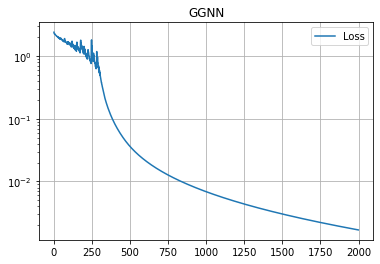
損失関数や正答率の履歴を表示してみましょう。
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
plt.title(model_name)
plt.plot(loss_hist, label="Loss")
plt.legend()
plt.yscale('log')
plt.grid()
plt.show()
plt.title(model_name)
plt.plot([acc[0] for acc in acc_hist], label="Train Acc")
plt.plot([acc[1] for acc in acc_hist], label="Val Acc")
plt.plot([acc[2] for acc in acc_hist], label="Test Acc")
plt.legend()
plt.grid()
plt.show()
今まで試したどのモデルよりも早く収束し、損失関数はまだまだ下がりそうですが、予測性能は Train ACC = 1.0 に到達し頭打ちになりました。
保存したモデルの読み出し
次のようにして保存したモデルを読み出して予測に使えます。
model_path = "{}/{}_model.pt".format(directory_path, "GAT")
gat_model = GAT().to(device)
gat_model.load_state_dict(
torch.load(model_path, map_location=torch.device('cpu'))
)
_, gat_pred = gat_model().max(dim=1)
gat_pred
tensor([ 0, 0, 0, ..., 10, 10, 10], device='cuda:0')
model_path = "{}/{}_model.pt".format(directory_path, "GNNM")
gnnm_model = GNNM(
data.num_nodes, dataset.num_classes, 32, [64,64,64,64,64], eps=0.01
).to(device)
gnnm_model.load_state_dict(
torch.load(model_path, map_location=torch.device('cpu'))
)
_, gnnm_pred = gnnm_model().max(dim=1)
gnnm_pred
tensor([ 1, 1, 0, ..., 10, 10, 10], device='cuda:0')
model_path = "{}/{}_model.pt".format(directory_path, "GGNN")
ggnn_model = GGNN().to(device)
ggnn_model.load_state_dict(
torch.load(model_path, map_location=torch.device('cpu'))
)
_, ggnn_pred = ggnn_model().max(dim=1)
ggnn_pred
tensor([ 0, 0, 0, ..., 10, 10, 10], device='cuda:0')