はじめに
Scikit-Learnで線形回帰をやってみます。一連の流れのコードを書いてみます。
データセット
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
from sklearn.linear_model import LinearRegression
from sklearn.metrics import mean_squared_error, r2_score
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# 1. Dataset Load
datasets = 'datasets/Boston.csv'
df = pd.read_csv(datasets)
print(f'columns: {df.columns}')
print(df.head())
print(df.describe())
結果
columns: Index(['crim', 'zn', 'indus', 'chas', 'nox', 'rm', 'age', 'dis', 'rad', 'tax',
'ptratio', 'black', 'lstat', 'medv'],
dtype='object')
crim zn indus chas nox ... tax ptratio black lstat medv
0 0.00632 18.0 2.31 0 0.538 ... 296 15.3 396.90 4.98 24.0
1 0.02731 0.0 7.07 0 0.469 ... 242 17.8 396.90 9.14 21.6
2 0.02729 0.0 7.07 0 0.469 ... 242 17.8 392.83 4.03 34.7
3 0.03237 0.0 2.18 0 0.458 ... 222 18.7 394.63 2.94 33.4
4 0.06905 0.0 2.18 0 0.458 ... 222 18.7 396.90 5.33 36.2
crim zn indus ... black lstat medv
count 506.000000 506.000000 506.000000 ... 506.000000 506.000000 506.000000
mean 3.613524 11.363636 11.136779 ... 356.674032 12.653063 22.532806
std 8.601545 23.322453 6.860353 ... 91.294864 7.141062 9.197104
min 0.006320 0.000000 0.460000 ... 0.320000 1.730000 5.000000
25% 0.082045 0.000000 5.190000 ... 375.377500 6.950000 17.025000
50% 0.256510 0.000000 9.690000 ... 391.440000 11.360000 21.200000
75% 3.677083 12.500000 18.100000 ... 396.225000 16.955000 25.000000
max 88.976200 100.000000 27.740000 ... 396.900000 37.970000 50.000000
目的変数、説明変数指定
Scikit-learnはnumpy arrayを使います。素晴らしいnumpy生態系。
したがって、Pandasのdataframeをnumpy arrayに変換します。
# 2. Dataset
target = df['medv'].to_numpy()
print(type(target))
features = df.iloc[:,:-1].to_numpy()
print(type(features))
print(target.shape)
print(features.shape)
結果
<class 'numpy.ndarray'>
<class 'numpy.ndarray'>
(506,)
(506, 13)
学習データ、テストデータ分離
# 3. Splitting the dataset into training and testing sets
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(features, target, test_size=0.2, random_state= 123)
print(X_train.shape)
print(X_test.shape)
print(y_train.shape)
print(y_test.shape)
結果
(404, 13)
(102, 13)
(404,)
(102,)
学習
# 4. Model Training
regression = LinearRegression()
model = regression.fit(X=X_train, y=y_train)
print(model.coef_)
print(model.intercept_)
結果
[-9.87931696e-02 4.75027102e-02 6.69491841e-02 1.26954150e+00
-1.54697747e+01 4.31968412e+00 -9.80167937e-04 -1.36597953e+00
2.84521838e-01 -1.27533606e-02 -9.13487599e-01 7.22553507e-03
-5.43790245e-01]
31.835164121206805
評価
RMSEと決定係数R2を出します。
後、線形回帰式の重みと切片です。
# 5.Model Evaluation
y_test_predict = model.predict(X_test)
rmse = np.sqrt(mean_squared_error(y_test, y_test_predict))
r2 = r2_score(y_true=y_test, y_pred=y_test_predict)
print('The model performance for the testing set')
print(f'RMSE is {rmse}')
print(f'R2 Score is {r2}')
print(f'coefficeints are {model.coef_}')
print(f'intercept_ is {model.intercept_}')
R2スコアが0.659、モデルは悪くないですね。
結果
The model performance for the testing set
RMSE is 5.3096596650321715
R2 Score is 0.6592466510354096
coefficeints are [-9.87931696e-02 4.75027102e-02 6.69491841e-02 1.26954150e+00
-1.54697747e+01 4.31968412e+00 -9.80167937e-04 -1.36597953e+00
2.84521838e-01 -1.27533606e-02 -9.13487599e-01 7.22553507e-03
-5.43790245e-01]
intercept_ is 31.835164121206805
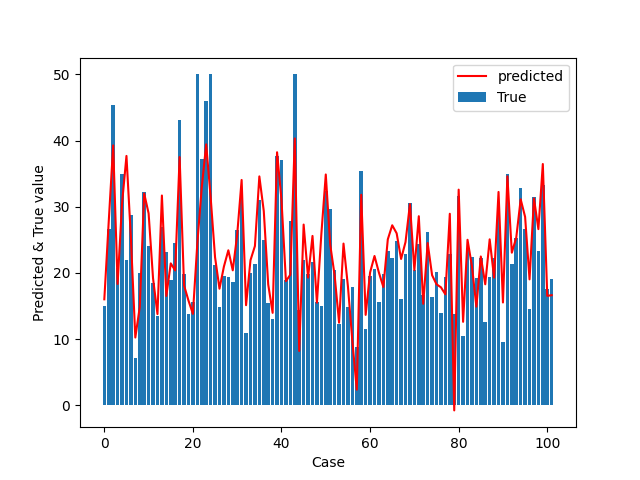
描画
True値をBarグラフで、予測値を実線で表記します。
# Plot
print(y_test.shape)
x = np.arange(0, 102 )
fig = plt.figure()
ax = fig.add_subplot(1,1,1)
ax.bar(x, y_test, label='True')
ax.plot(x,y_test_predict, color ='red', label = 'predicted')
ax.set_xlabel('Case')
ax.set_ylabel('Predicted & True value')
ax.legend()
plt.show()