概要
前回、Gtk-rs(GTK+のRustバインディング)を使ってタブ型のテキストエディタを作成しました。今回さらにGTK+の他のウィジェットを使ったアプリを作っていきたいと思います。
前提
この記事を読むにあたり、GTK+のチュートリアルを終えた程度の知識とRustの基本知識は必要です。
以前書いたRustを使ったGTK+の入門記事の続きの位置づけになります。
要点
この記事に書かれている内容の要点(自分が得られた知識)は以下になります。
- GTK+のTreeViewとTreeModelの扱い方
- GTK+のその他ウィジェット(Paned、MenuButton、ComboBox等)の扱い方
- マルチスレッドを使ったGUIアプリの作り方
- pcapライブラリを使ったパケットキャプチャ
- スクリプト言語によりアプリケーションの機能を拡張できるようにする方法
作るアプリ
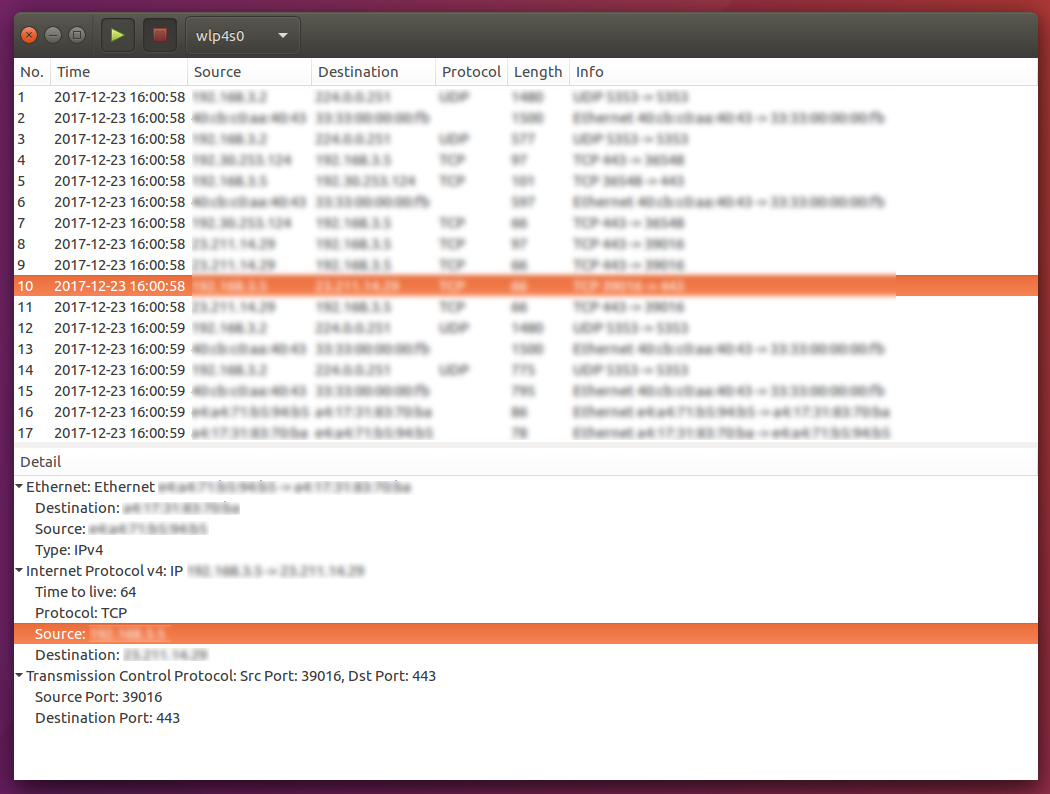
GTK+のTreeViewとTreeModelを使ったアプリを作りたいのですが、TreeViewに表示させるデータを事前に準備したりするのが面倒なのでLANアナライザを作ることにしました。LANアナライザといえばやはりWireSharkが有名ですので、アプリ名はWireShakeにしておきます。機能としてはシンプルに、パケットのキャプチャと、キャプチャしたパケットの情報を表示するだけにします。以下のような画面で、上部のコンボボックスからキャプチャしたいNICを選択し、再生ボタンをクリックするとキャプチャが開始します。するとNICに入ってきたパケットが画面上半分のリスト表示領域にほぼリアルタイムで表示されていきます。このリストからいずれかのパケットをクリックすると、画面下半分の詳細表示領域にそのパケットの詳細な情報を表示します。キャプチャを止めるには上部の停止ボタンをクリックします。
環境準備
本記事では以下の環境で作業を進めます。
- OS: Ubuntu 16.04 LTS
- 言語: Rust 1.22.1 (https://www.rust-lang.org/)
- GTK+ライブラリ: GTK+ 3.18 (https://www.gtk.org/)
- Rustバインディング: Gtk-rs 0.2.0 (http://gtk-rs.org/)
前記事ではRustのバージョン1.16.0を使っていたので、必要に応じて最新バージョンにしておきます。1
rustup update
その他必要なクレートやライブラリは必要になったら都度インストールしていきます。
ウィンドウを構成する
早速取り掛かります。
まずはCargoでプロジェクトを作成します。
~$ cargo new --bin wire_shake
以下のようにCargo.tomlを準備します。
[package]
name = "wire_shake"
version = "0.1.0"
authors = ["Your Name <Yourt Email>"]
[dependencies]
gio= "0.2.0"
[dependencies.gtk]
version = "0.2.0"
features = ["v3_16"]
次に、冒頭で紹介したようなウィンドウを表示するコードを書いていきます。
main.rsを以下のように修正します。
extern crate gtk;
extern crate gio;
use std::env::Args;
use gio::{
SimpleActionExt, ActionMapExt, ApplicationExt
};
use gtk::{
WidgetExt, GtkApplicationExt
};
mod win;
fn init_actions(app: >k::Application) {
//アプリケーションを終了するアクションを作成
let quit_action = gio::SimpleAction::new("quit", None);
{
let app = app.clone();
//quit_actionのactivateシグナルにハンドラを紐付ける
quit_action.connect_activate(move |_, _| {
//アプリケーションを終了させる
app.quit();
});
}
//アプリケーションにquit_actionを追加する
app.add_action(&quit_action);
}
fn init_accels(app: >k::Application) {
//キーボード・ショートカットCtrl-qにアプリケーションの"quit"アクションを紐付ける
app.add_accelerator("<Ctrl>q", "app.quit", None);
}
fn run(args: Args) {
match gtk::Application::new("com.github.koji-m.wire_shake", gio::APPLICATION_HANDLES_OPEN) {
Ok(app) => {
{
//アプリケーション起動時に発生するstartupシグナルに対するハンドラを紐付ける
app.connect_startup(move |app| {
init_actions(app);
init_accels(app);
});
}
{
//startupシグナルに続いて発生するactivateシグナルに対するハンドラを紐付ける
app.connect_activate(move |app| {
//ウィンドウを生成する
let w = win::create(app);
//ウィンドウとウィンドウ内のウィジェットを全て表示する
w.show_all();
});
}
//コマンドライン引数の処理(使わないが一応書いておく)
let args: Vec<String> = args.collect();
let argv: Vec<&str> = args.iter().map(|s| s.as_ref()).collect();
app.run(argv.as_slice());
},
Err(_) => {
println!("Application startup error");
}
};
}
fn main() {
run(std::env::args());
}
特に難しいところはないので引き続きwin.rsを作成。
extern crate gtk;
extern crate gio;
use std::path::Path;
use gio::{
SimpleActionExt, ActionMapExt
};
use gtk::{
WindowExt
};
fn init_action(win: >k::ApplicationWindow) {
let start_capture_action = gio::SimpleAction::new("start-capture", None);
let stop_capture_action = gio::SimpleAction::new("stop-capture", None);
//アプリ起動直後はキャプチャストップアクションを無効にしておく
stop_capture_action.set_enabled(false);
{
start_capture_action.connect_activate(move |_, _| {
println!("start capture");
});
}
{
stop_capture_action.connect_activate(move |_, _| {
println!("stop capture");
});
}
win.add_action(&start_capture_action);
win.add_action(&stop_capture_action);
}
pub fn create(app: >k::Application) -> gtk::ApplicationWindow {
//GtkBuilderを使ってUI(win.ui)オブジェクトを読み込む
let builder = gtk::Builder::new_from_file(Path::new("./ui/win.ui"));
//UIオブジェクトからid=windowのオブジェクト(下記win.uiの定義参照)を取得する
let win: gtk::ApplicationWindow = builder.get_object("window").unwrap();
//ウィンドウにアプリケーションを紐付ける
win.set_application(Some(app));
init_action(&win);
win
}
こちらも特に難しいところはないです。起動直後はキャプチャストップボタンを押せない状態にしたいので、ボタンに紐付けるアクションを無効な状態に設定しておきます。UIは全てGtkBuilderを使って生成します。プロジェクトディレクトリ配下にuiディレクトを作成して、その中に以下のようにXMLファイルwin.uiを作成します。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<interface>
<object class="GtkApplicationWindow" id="window">
<property name="default-width">1024</property>
<property name="default-height">768</property>
<!-- ウィンドウ上部のタイトルバーの定義 -->
<child type="titlebar">
<!-- GtkHeaderBarウィジェットを設定してその中に配置するウィジェットを設置していく -->
<object class="GtkHeaderBar" id="header-menubar">
<property name="visible">True</property>
<!-- 閉じる・最小化・最大化ボタンを表示する -->
<property name="show_close_button">True</property>
<child>
<!-- キャプチャスタートボタンの定義 -->
<object class="GtkMenuButton" id="start-button">
<property name="visible">True</property>
<property name="valign">center</property>
<!-- ボタンに表示するイメージはこのファイルの最後の方にstart-capture-imageとして定義している -->
<property name="image">start-capture-image</property>
<!-- ボタンをクリックしたときのアクションをwin.rsで定義したstart-captureに指定 -->
<property name="action_name">win.start-capture</property>
</object>
<packing>
<property name="pack_type">start</property>
</packing>
</child>
<child>
<!-- キャプチャストップボタンも同様に定義 -->
<object class="GtkMenuButton" id="stop-button">
<property name="visible">True</property>
<property name="valign">center</property>
<property name="image">stop-capture-image</property>
<property name="action_name">win.stop-capture</property>
</object>
<packing>
<property name="pack_type">start</property>
</packing>
</child>
<child>
<!-- NICを選択するためのコンボボックスを定義 -->
<object class="GtkComboBoxText" id="if-combobox">
<property name="visible">True</property>
<property name="valign">center</property>
</object>
<packing>
<property name="pack_type">start</property>
</packing>
</child>
</object>
</child>
<!-- ウィンドウのメインコンテツ部分を定義 -->
<child>
<!-- ウィンドウは上下二分割して上半分はパケット一覧、下半分はパケットの詳細を表示するため、GtkPaneを使用する -->
<object class="GtkPaned" id="pane">
<property name="visible">True</property>
<property name="orientation">vertical</property>
<!-- 分割する位置をウィンドウの上下真ん中に指定 -->
<property name="position">384</property>
<!-- 上半分のコンテンツを定義 -->
<child>
<object class="GtkScrolledWindow" id="list_window">
<property name="visible">True</property>
<child>
<!-- キャプチャしたパケットのリストを表示するためにGtkTreeViewを設置 -->
<object class="GtkTreeView" id="list_view">
<property name="visible">True</property>
</object>
</child>
</object>
<packing>
</packing>
</child>
<!-- 下半分のコンテンツを定義 -->
<child>
<object class="GtkScrolledWindow" id="detail_window">
<property name="visible">True</property>
<child>
<!-- パケットリストの中から選択したパケットの詳細情報を表示するためにGtkTreeViewを設置 -->
<object class="GtkTreeView" id="detail_view">
<property name="visible">True</property>
</object>
</child>
</object>
<packing>
</packing>
</child>
</object>
</child>
</object>
<!-- キャプチャスタートボタンに表示するイメージの定義 -->
<object class="GtkImage" id="start-capture-image">
<property name="visible">True</property>
<property name="tooltip_text">Start capture</property>
<!-- ビルトインのアイコンイメージとしてmedia-playback-startを指定 -->
<property name="icon_name">media-playback-start</property>
</object>
<!-- キャプチャストップボタンも同様に定義 -->
<object class="GtkImage" id="stop-capture-image">
<property name="visible">True</property>
<property name="tooltip_text">Stop capture</property>
<property name="icon_name">media-playback-stop</property>
</object>
</interface>
ウィンドウの構成としては、GtkApplicationWindowの中に設置したGtkPanedによってウィンドウを上下2分割し、各々の中に(スクロール表示できるように)GtkScrolledWindowでラップしたGtkTreeViewを設置しています。
GtkTreeViewを使う部分はMVC(Model View Controller)パターンに従ってアプリケーションを構成していきます。MVCとGTK+のウィジェットの対応は以下のようになっています。(これらを扱うControllerを書いていきます。)
- Model
- GtkTreeModelインターフェイスを実装したウィジェット。自前でも実装できるが、基本GtkListStoreとGtkTreeStoreを使う。
- View
- GtkTreeViewを使う。
今回はキャプチャしたパケットを人間が読める形のデータに変換してGtkListStoreやGtkTreeStoreに保存します。そうして作成した各ModelをGtkTreeViewに紐付けることでウィンドウに表示します。このように一旦ModelとViewを紐付けてしまえば、以降キャプチャしたパケットを都度変換して各Modelに放り込んでいくだけパケットの情報が表示されます。
ここまでで作成・編集したファイルは以下になります。
.
├── Cargo.toml
├── src
| ├── main.rs
| └── win.rs
└── ui
└── win.ui
プロジェクトのルートディレクトリでcargo runで実行するとウィンドウが表示されます。
パケットをキャプチャする
UIができたので、実際にパケットをキャプチャする部分を実装していきます。
パケットキャプチャにはtcpdumpやWireSharkなどでも使われているpcapライブラリを使います。Ubuntuの場合、以下のようにaptでlibpcapをインストールしておきます。
# libpcapのバージョンは環境に応じて変更。自分の環境では0.8を指定。
sudo apt install libpcap0.8 libpcap-dev
そしてpcapのクレートを使うのでCargo.tomlの[dependencies]に追加しておきます。
...
[dependencies]
...
pcap = "0.7.0"
...
コードを編集する前に、パケットデータの取得から表示までの流れについて説明しておきます。
pcapライブラリでパケットをキャプチャする際、パケットを受信するまでの間パケット待ち状態でスレッドがブロックします。つまりメインスレッドでパケット待ちをするとウィンドウの操作ができなくなりアプリ自体がフリーズしてしまいます。このような状況を避ける為にパケットキャプチャをする処理をメインスレッドとは別のスレッド(キャプチャスレッドと呼ぶことにします)で実行します。キャプチャスレッドでキャプチャしたパケットデータはスレッド間のチャネルを使ったメッセージパッシングでメインスレッドに渡すことにします。また、メインスレッドからキャプチャスレッドへのキャプチャ開始・停止の指示もチャネルを使ってすることにします。纏めると以下のような流れになります。
メインスレッド キャプチャスレッド
|| キャプチャ開始指示 ||
|| ------------------> ||
|| ||
|| キャプチャ開始報告 ||
|| <------------------ ||
|| ||
|| パケットデータ ||
|| <------------------ ||
|| パケットデータ ||
|| <------------------ ||
|| ・ ||
|| ・ ||
|| ・ ||
|| キャプチャ停止指示 ||
|| ------------------> ||
|| ||
|| キャプチャ停止報告 ||
|| <------------------ ||
パケットキャプチャの処理を追加したwin.rsのコードは以下のようになります。
extern crate gtk;
extern crate gio;
extern crate pcap; //pcapのクレートを使用
use std::path::Path;
use std::thread; //スレッドを使う
use std::sync::mpsc; //Multi-Producer,Single-Consumer FIFO Queueをスレッド間コミュニケーションで使う
use gio::{
SimpleActionExt, ActionMapExt
};
use gtk::{
WindowExt, ComboBoxTextExt,
};
//スレッド間コミュニケーションで使う制御用メッセージを定義
enum Ctrl {
StartCapture(pcap::Capture<pcap::Active>), //キャプチャ開始を指示するメッセージ
StopCapture, //キャプチャ停止を指示するメッセージ
CaptureStarted, //キャプチャが開始したことを報告するメッセージ
CaptureStopped, //キャプチャが停止したことを報告するメッセージ
}
fn string_to_dev(s: String) -> Option<pcap::Capture<pcap::Inactive>> {
if let Ok(mut l) = pcap::Device::list() { //このホストが持っているNICのリストを取得する
//取得したリストから指定されたNICを探しそのpcapハンドルを返す
if let Some(i) = l.iter().position(|ref d| d.name == s) {
if let Ok(cap) = pcap::Capture::from_device(l.remove(i)) {
//プロミスキャスモードにして、パケット受信待ち時間を300msに指定しておく
return Some(cap.promisc(true).timeout(300));
}
}
}
return None;
}
fn init_action(win: >k::ApplicationWindow, builder: >k::Builder) {
use self::Ctrl::{StartCapture, StopCapture, CaptureStarted, CaptureStopped};
let start_capture_action = gio::SimpleAction::new("start-capture", None);
let stop_capture_action = gio::SimpleAction::new("stop-capture", None);
stop_capture_action.set_enabled(false);
let (main_tx, cap_rx) = mpsc::channel(); //キャプチャ開始・停止指示用チャネル
let (start_cap_tx, start_main_rx) = mpsc::channel(); //キャプチャ開始報告用チャネル
let (stop_cap_tx, stop_main_rx) = mpsc::channel(); //キャプチャ停止報告用チャネル
{
let stop_capture_action = stop_capture_action.clone();
let if_combo: gtk::ComboBoxText = builder.get_object("if-combobox").unwrap();
let main_tx = mpsc::Sender::clone(&main_tx);
start_capture_action.connect_activate(move |act, _| {
if let Some(if_name) = if_combo.get_active_text() { //コンボボックスで選択されているNIC名を取得
if let Ok(cap) = string_to_dev(if_name).unwrap().open() { //選択されたNICのpcapハンドラ取得
//キャプチャスレッドへpcapハンドラと共にキャプチャ開始指示のメッセージを送信
main_tx.send(StartCapture(cap)).unwrap();
//キャプチャスレッドよりキャプチャ開始の報告メッセージを受け取ったら
//スタートアクション(ボタン)を無効、ストップアクション(ボタン)を有効にする
if let Ok(CaptureStarted) = start_main_rx.recv() {
act.set_enabled(false);
stop_capture_action.set_enabled(true);
}
}
}
});
}
{
let start_capture_action = start_capture_action.clone();
stop_capture_action.connect_activate(move |act, _| {
main_tx.send(StopCapture).unwrap(); //キャプチャスレッドへキャプチャストップのメッセージを送信
//キャプチャスレッドよりキャプチャ停止の報告メッセージを受け取ったら
//スタートアクション(ボタン)を有効、ストップアクション(ボタン)を無効にする
if let Ok(CaptureStopped) = stop_main_rx.recv() {
act.set_enabled(false);
start_capture_action.set_enabled(true);
}
});
}
let (pkt_tx, pkt_rx) = mpsc::channel(); //パケットデータ送受信用チャネル
//キャプチャスレッドを生成
thread::spawn(move || {
let mut n: u32; //キャプチャしたパケットの番号
while let Ok(msg) = cap_rx.recv() { //メインスレッドからの指示待ち
if let StartCapture(mut cap) = msg { //キャプチャ開始指示の場合
n= 1;
start_cap_tx.send(CaptureStarted).unwrap(); //キャプチャ開始の報告メッセージをメインスレッドに送信
//キャプチャループ
loop {
if let Ok(pkt) = cap.next() { //pcapハンドラからパケットを取得
//メインスレッドへパケットデータを送信
pkt_tx.send((n, pkt.header.clone(), pkt.data.to_vec())).unwrap();
n+=1;
//メインスレッドからキャプチャ停止指示を受信していたらキャプチャ停止
if let Ok(StopCapture) = cap_rx.try_recv() {
break;
}
} else { //パケット受信待ち(300ms)がタイムアウトした場合
//メインスレッドからキャプチャ停止指示を受信していたらキャプチャ停止
if let Ok(StopCapture) = cap_rx.try_recv() {
break;
}
}
}
stop_cap_tx.send(CaptureStopped).unwrap(); //メインスレッドへキャプチャ停止の報告を送信
}
}
});
//メインスレッドでキャプチャスレッドから送信されてくるパケットを待ち受ける
gtk::timeout_add(300, move || { //パケットが送られてきていない場合は300ms間をおいて再度受信チェックする
while let Ok((n, hdr, data)) = pkt_rx.try_recv() {
println!("received packet let: {}", hdr.len); //標準出力に受信したパケットのサイズを表示
}
gtk::Continue(true) //この処理を繰り返し実行する(falseを指定するとtimeoutの処理は無効にされて実行されなくなる)
});
win.add_action(&start_capture_action);
win.add_action(&stop_capture_action);
}
pub fn create(app: >k::Application) -> gtk::ApplicationWindow {
let builder = gtk::Builder::new_from_file(Path::new("./ui/win.ui"));
let win: gtk::ApplicationWindow = builder.get_object("window").unwrap();
win.set_application(Some(app));
//このホストが持っているNICのリストを選択肢としてコンボボックスに設定する
if let Ok(if_list) = pcap::Device::list() {
let if_combo: gtk::ComboBoxText = builder.get_object("if-combobox").unwrap();
if_list.iter().for_each(|d| if_combo.append(None, &d.name));
}
init_action(&win, &builder);
win
}
ウィンドウを作成するcreate関数の中では、コンボボックスにNICのリストを表示する初期化処理を追加しています。そのあとに実行されるinit_action()関数内では、キャプチャスタート・ストップのハンドラに、キャプチャスレッドへキャプチャ開始・停止を指示するメッセージの送信処理を追加しています。更に、キャプチャスレッドを生成(thread::spawn())し、メインスレッドでのパケットデータ待ちの処理(gtk::timeout_add())を開始しています。
NICを操作するためスーパーユーザの権限が必要となるので、sudo cargo runで実行します。
pcapについても触れておきます。cap.next()はキャプチャしたパケットデータをPacket構造体で返します。Packet構造体は、受信時間やパケットのサイズを保持するheader: &PacketHeaderフィールドと、パケット全体のバイナリデータであるdata: &[u8]フィールドを持ちます。キャプチャスレッドではこのheaderと、dataをVec<u8>型に変換したものをメインスレッドへ渡しています。
sudo実行時にcargoへのパスが通っていない場合は、事前に下記の通りsudoersファイルを編集しておきます。
Defaults secure_path="/usr/local/sbin:/usr/local/bin:/usr/sbin:/usr/bin:/sbin:/bin:/snap/bin"
↓ secure_pathをコメントアウト
# Defaults secure_path="/usr/local/sbin:/usr/local/bin:/usr/sbin:/usr/bin:/sbin:/bin:/snap/bin"
env_keepに環境変数PATHを追加
Defaults env_keep += "PATH"
これでsudo cargo runを実行して動作を確認できます。
コンボボックスからキャプチャしたいNICを選んでキャプチャスタートボタンをクリックすると、パケットを受信するたびに標準出力にキャプチャしたパケットのサイズが表示されます。キャプチャストップボタンでキャプチャが停止することも確認できます。
パケットをツリー表示する
パケットをキャプチャできるようになったので、GtkTreeViewを使ってパケットデータを表示します。
先ほど軽く説明しましたが、GtkTreeVeiwはMVCパターンのViewに対応するウィジェットとなります。Viewには表示するデータとしてModelを紐付ける必要があります。今回表示したいデータは「キャプチャしたパケットの一覧」と「各パケットの詳細」の2つになります。それぞれ以下のようなデータ構造にします。
- キャプチャしたパケットの一覧
| No.| Time | Source | Destination | Protocol | Length | Info |
|:--:|:-------------------:|:-------------:|:-------------:|:--------:|:------:|:------------:|
| 1 | 2017-12-23 16:01:20 | 192.168.0.1 | 192.168.0.250 | ICMP | 98 | Echo request |
| 2 | 2017-12-23 16:01:21 | 192.168.0.250 | 192.168.0.1 | ICMP | 98 | Echo reply |
| 3 | 2017-12-23 16:01:22 | 192.168.0.1 | 192.168.0.250 | ICMP | 98 | Echo request |
. . . . . . . .
- 各パケットの詳細
├── Ethernet
| ├── Destination: XX:XX:XX:XX:XX:XX
| ├── Source: XX:XX:XX:XX:XX:XX
| └── Type: 0x0800
├── Internet Protocol V4
| ├── Time to live: 64
| ├── Protocol: 6
| ├── Source: XXX.XXX.XXX.XXX
| └── Destination: XXX.XXX.XXX.XXX
├── Transmission Control Protocol
| ├── Source Port: 35000
. .
「キャプチャしたパケットの一覧」は7つのカラムを持つデータのリストで、「各パケットの詳細」は各レイヤーのプロトコル情報のツリーになっています。このようなデータ構造を保持できるModelがGTK+のビルトインウィジェットにあります。リストはGtkListStore、ツリーはGtkTreeStoreになります。これらModelオブジェクトをGtkTreeViewに紐付けると、リストはテーブル表示に、ツリーは折り畳みできるツリー表示にすることができます。
それでは、UIファイルwin.uiにGtkTreeViewを構成していきます。
...
<object class="GtkTreeView" id="list_view">
<property name="visible">True</property>
<!-- Modelとしてid=list-store(GtkListStore)のオブジェクトを紐付ける -->
<property name="model">list-store</property>
<!-- childとして各カラムを定義していく -->
<child>
<!-- カラムの情報はGtkTreeViewColumnに設定する -->
<object class="GtkTreeViewColumn" id="number-column">
<!-- テーブルのカラムヘッダーに表示する文字列を指定 -->
<property name="title">No.</property>
<child>
<!-- GtkCellRendererTextを使って、Modelのデータをこのカラムのセルにテキストで表示する -->
<object class="GtkCellRendererText" id="number-renderer" />
<attributes>
<!-- Modelのカラム番号0のデータをこのカラムにマッピングする -->
<attribute name="text">0</attribute>
</attributes>
</child>
</object>
</child>
<!-- 他のカラムも同様に定義していく -->
<child>
<object class="GtkTreeViewColumn" id="time-column">
<property name="title">Time</property>
<child>
<object class="GtkCellRendererText" id="time-renderer" />
<attributes>
<attribute name="text">1</attribute>
</attributes>
</child>
</object>
</child>
<child>
<object class="GtkTreeViewColumn" id="src-column">
<property name="title">Source</property>
<child>
<object class="GtkCellRendererText" id="src-renderer" />
<attributes>
<attribute name="text">2</attribute>
</attributes>
</child>
</object>
</child>
<child>
<object class="GtkTreeViewColumn" id="dst-column">
<property name="title">Destination</property>
<child>
<object class="GtkCellRendererText" id="dst-renderer" />
<attributes>
<attribute name="text">3</attribute>
</attributes>
</child>
</object>
</child>
<child>
<object class="GtkTreeViewColumn" id="proto-column">
<property name="title">Protocol</property>
<child>
<object class="GtkCellRendererText" id="proto-renderer" />
<attributes>
<attribute name="text">4</attribute>
</attributes>
</child>
</object>
</child>
<child>
<object class="GtkTreeViewColumn" id="len-column">
<property name="title">Length</property>
<child>
<object class="GtkCellRendererText" id="len-renderer" />
<attributes>
<attribute name="text">5</attribute>
</attributes>
</child>
</object>
</child>
<child>
<object class="GtkTreeViewColumn" id="info-column">
<property name="title">Info</property>
<child>
<object class="GtkCellRendererText" id="info-renderer" />
<attributes>
<attribute name="text">6</attribute>
</attributes>
</child>
</object>
</child>
<!-- GtkTreeViewで表示されている特定データ(行)を選択したときに生成されるヘルパーオブジェクトを定義 -->
<child internal-child="selection">
<!-- 選択されたデータ(行)に対応するModelのデータをGtkTreeSelectionオブジェクトとして返すようにする -->
<object class="GtkTreeSelection" id="selection">
</object>
</child>
</object>
...
<object class="GtkTreeView" id="detail_view">
<property name="visible">True</property>
<!-- Modelとしてid=detail-store(GtkTreeStore)のオブジェクトを紐付ける -->
<property name="model">detail-store</property>
<child>
<object class="GtkTreeViewColumn" id="detail-column">
<property name="title">Detail</property>
<child>
<object class="GtkCellRendererText" id="detail-renderer" />
<attributes>
<attribute name="text">0</attribute>
</attributes>
</child>
</object>
</child>
</object>
...
<!-- list-store(GtkListStore)のデータ構造を定義 -->
<object class="GtkListStore" id="list-store">
<!-- カラムとカラムのデータ型を定義 -->
<columns>
<column type="guint" /> <!-- No. -->
<column type="gchararray" /> <!-- Time -->
<column type="gchararray" /> <!-- Source -->
<column type="gchararray" /> <!-- Destination -->
<column type="gchararray" /> <!-- Protocol -->
<column type="guint" /> <!-- Length -->
<column type="gchararray" /> <!-- Info -->
<column type="gchararray" /> <!-- TreeData ※後述-->
</columns>
</object>
<!-- detail-strore(GtkTreeStore)のデータ構造を定義 -->
<object class="GtkTreeStore" id="detail-store">
<columns>
<column type="gchararray" /> <!-- Detail -->
</columns>
</object>
<object class="GtkImage" id="start-capture-image">
...
GtkTreeViewにModelを紐付けるにはmodelプロパティにGtkTreeModelインターフェイスを実装したGtkListStoreやGtkTreeStoreを設定します。GtkTreeViewのカラムの情報(カラムヘッダやModelのどのカラムと紐付けるか等)はGtkTreeViewColumnにより設定します。また、カラムのセルにどのようにModelのデータを表示するかはGtkCellRenderer***という名前のレンダラーで設定します。今回、データは全てテキストで表示するためGtkCellRendererTextを使っています。他のレンダラーとしてGtkCellRendererPixbuffは画像を表示するために使います。
Modelの定義として、GtkListStoreやGtkTreeStoreについても各カラムの型を記述しています。<column>タグの記載順にModelのカラム番号として0から番号がアサインされますので、GtkTreeViewで紐付けるModelのカラム番号を指定する際にはこの番号を使います。
ここで一旦、アプリの挙動を一連の操作の流れに沿って説明しておきます。
今回は以下のよう流れで各Modelにデータを挿入することでパケットの情報を表示させます。
- パケットキャプチャを開始する。
- パケットの受信都度、キャプチャしたパケットデータを解析してユーザが読める表現に変換する。
- 変換したデータをModelである
list-store(GtkListStore)の1エントリとして追加する。 - ウィンドウ上半分の領域(パケットリスト)に、追加したパケットデータが表示される。
- ユーザがパケットリストの適当な行をクリックして選択する。
- 選択したパケットデータに対応する詳細情報を
detail-store(GtkTreeStore)に設定する。 - パケットの詳細情報がウィンドウ下半分の領域(詳細ツリー)に表示される。
各処理について具体的にどのようにするか説明していきます。
まず、2については各カラムのデータをそれぞれ以下のようにして適切なデータ型に変換します。
- Time
- Packet構造体のheader(PacketHeader構造体)フィールドのts(timeval構造体)フィールドを時間表現文字列に変換
- Source
- Packet構造体のdata(&[u8])フィールドを解析して送信元IPアドレスを抜き出し文字列に変換
- Destination
- Packet構造体のdata(&[u8])フィールドを解析して宛先IPアドレスを抜き出し文字列に変換
- Protocol
- Packet構造体のdata(&[u8])フィールドを解析して宛先Port番号を抜き出し対応するプロトコル名文字列に変換
- Length
- Packet構造体のheader(PacketHeader構造体)フィールドのlen(u32型)フィールドの値をそのまま使う
- Info
- Packet構造体のdata(&[u8])フィールドを解析してパケットの要約を文字列にする
次に3では、2で生成したデータをGtkListStoreの1エントリとして追加します。
そして、6でパケットリストから選択したエントリに対応するパケットの詳細情報を木構造で表示させます。これを実現するためには、パケットリストのエントリとパケットの詳細情報を関連付ける必要があります。いくつか方法は考えられますが、今回はシンプルにlist-store(GtkListStore)の1カラムとしてパケットの詳細情報を持たせることにします。選択されたエントリからこのパケット詳細情報を取り出して詳細ツリーに表示させるわけですから、パケット詳細情報自体も木構造であった方が処理しやすくなります。そこで、list-store(GtkListStore)のパケット詳細情報カラムに持たせるデータは、木構造を表現する以下のような構造体にしようかと考えました。
struct PacketTree<'a> {
label: String,
value: String,
child: &'a PacketTree<'a>,
next: &'a PacketTree<'a>,
}
しかし、Gtk-rsでは基本的に、GtkListStoreのカラムに設定できるデータの型はu32などのプリミティブ型やStringであり、ユーザ定義型のデータを設定するには更にコードを追加する必要がありそうなことがわかりました。2 これは大変そうなので、別の方法をとることにしました。木構造を表現できればよいので木構造を表現する文字列をStringで持たせることにしました。木構造を表現できる文字列表現としてはJSONやXMLがメジャーだと思いますが、今回のような単純な木構造を表現するにはもっとシンプルな形式が良いと考えS式を採用することにしました。パケット詳細情報は以下のようなS式として保持することにします。
<パケット詳細情報> ::= (<詳細情報> <childノード> <nextノード>)
<詳細情報> ::= (<label> <value>)
<childノード> ::= <パケット詳細情報> | ()
<nextノード> ::= <パケット詳細情報> | ()
<label> ::= "ラベル文字列"
<value> ::= "値文字列"
これにより、上記2においてlist-store(GtkListStore)のカラムとして以下を追加します。
- Data
- Packet構造体のdata(&[u8])フィールドを解析してパケット詳細情報を表すS式の文字列にする
以上でキャプチャしたパケットデータをどのようにGtkTreeViewに表示させるかが明らかになってきたかと思います。
それでは、上記2のパケットデータを解析して変換する部分を実装していきます。
解析対象であるPacket構造体のdataフィールドは、パケットのバイナリデータがそのまま入っていて&[u8]型でアクセスできます。このバイナリデータを各プロトコルのヘッダ構造に沿ってバイト単位で切り出し、その値に応じた(ユーザが読める)文字列表現に変換していきます。WireSharkではこの解析処理を実行する部分をDissectorと呼んでいます。TCP/IPを使った通信のパケットの場合、解析の流れは①Ethernet DissectorでEthernetヘッダを解析、②IP DissectorでEthernetペイロードのIPヘッダを解析、③TCP DissectorでIPペイロードのTCPヘッダを解析、...という流れになります。変換後の文字列表現については、例えばIPヘッダの送信元IPアドレスは、最終的にSource: 192.168.0.1のようにラベルと値を「:」で区切った形式にしたいので、ツリーデータのノードは(("Source" "192.168.0.1") <child> <next>)というS式になります。
以下、win.rsの変更部分になります。
...
use disctr::{
PacketInfo, dissect
};
...
fn init_action(win: >k::ApplicationWindow, builder: >k::Builder/) {
...
gtk::timeout_add(300, move || {
while let Ok((n, hdr, data)) = pkt_rx.try_recv() {
//dissect関数によりパケットデータを解析し結果をS式(String)で受け取る
//またパケットリストに表示する情報が記録されているPacketInfo構造体も併せて受け取る
let (tree, pinfo) = dissect(n, hdr, data/*, disct_tbl.clone(), write_proc*/);
//解析結果のS式を標準出力に出力する
println!("received packet: {}", tree);
}
gtk::Continue(true)
});
...
}
そして、Dissector(dissect関数)は新規ファイルdisctr.rsに記述します。
use pcap;
use std::io::Cursor;
//バイトオーダーを考慮した読み込みをする為Crate byteorderを使う
use byteorder::{ReadBytesExt, BigEndian};
//時間の日時表示をする為Crate timeを使用(std::timeとは別物)
use time::{Timespec};
//各種プロトコルのタイプを表す定数を定義
const ETHERTYPE_IPV4: u16 = 0x0800;
const IPPROTO_ICMP: u8 = 1;
const IPPROTO_TCP: u8 = 6;
const IPPROTO_UDP: u8 = 17;
const ICMP_ECHO_REPLY: u8 = 0;
const ICMP_DST_UNREACH: u8 = 3;
const ICMP_ECHO_REQUEST: u8 = 8;
const ICMP_NET_UNREACH: u8 = 0;
const ICMP_HOST_UNREACH: u8 = 1;
const ICMP_PROTO_UNREACH: u8 = 2;
const ICMP_PORT_UNREACH: u8 = 3;
const ICMP_FRAG_NEED: u8 = 4;
const ICMP_SRC_RT_FAIL: u8 = 5;
//パケットリストに表示する情報を保持する構造体
# [derive(Debug)]
pub struct PacketInfo {
pub num: u32,
pub time: Timespec,
pub len: u32,
pub net_src: Option<String>,
pub net_dst: Option<String>,
pub src_port: Option<u16>,
pub dst_port: Option<u16>,
pub proto: Option<String>,
pub info: Option<String>,
}
//TCP Dissector
fn dissect_tcp(data: &[u8], mut pinfo: PacketInfo) -> (String, PacketInfo) {
let src_port;
let dst_port;
let mut rdr = Cursor::new(&data[0..4]); //先頭4バイトのリーダー
src_port = rdr.read_u16::<BigEndian>().unwrap(); //先頭2バイトをビッグエンディアンとして読み込み(送信元ポート番号)
dst_port = rdr.read_u16::<BigEndian>().unwrap(); //2バイト目から2バイト分を同様に読み込み(宛先ポート番号)
let tcp_val = format!("TCP {} -> {}", src_port, dst_port);
//TCPヘッダの情報を表すS式(String)を生成
let tcp_tree = format!("((\"Transmission Control Protocol\" \"Src Port: {}, Dst Port: {}\") \
((\"Source Port\" \"{}\") () \
((\"Destination Port\" \"{}\") () ()))\
())",
src_port, dst_port, src_port, dst_port);
pinfo.info = Some(tcp_val); //パケットリストのInfoカラムに表示する文字列を設定
pinfo.src_port = Some(src_port); //今回パケットリストでは使わないが一応保存しておく
pinfo.dst_port = Some(dst_port); //今回パケットリストでは使わないが一応保存しておく
(tcp_tree, pinfo) //TCPヘッダを表すS式(String)とPacketInfo構造体を返す
}
//UDP Dissector
fn dissect_udp(data: &[u8], mut pinfo: PacketInfo) -> (String, PacketInfo) {
let src_port;
let dst_port;
let mut rdr = Cursor::new(&data[0..4]);
src_port = rdr.read_u16::<BigEndian>().unwrap();
dst_port = rdr.read_u16::<BigEndian>().unwrap();
let udp_val = format!("UDP {} -> {}", src_port, dst_port);
let udp_tree = format!("((\"User Datagram Protocol\" \"Src Port: {}, Dst Port: {}\") \
((\"Source Port\" \"{}\") () \
((\"Destination Port\" \"{}\") () ()))\
())",
src_port, dst_port, src_port, dst_port);
pinfo.info = Some(udp_val);
pinfo.src_port = Some(src_port);
pinfo.dst_port = Some(dst_port);
(udp_tree, pinfo)
}
//ICMPのタイプとコードを解析して返すヘルパー関数(一部だけ実装)
fn icmp_type_and_code(typ: u8, cod: u8) -> (String, String) {
match typ {
ICMP_ECHO_REPLY => (String::from("Echo Reply(0)"), cod.to_string()),
ICMP_DST_UNREACH => {
let t = String::from("Destination Unreachable(3)");
match cod {
ICMP_NET_UNREACH => (t, String::from("net unreachable(0)")),
ICMP_HOST_UNREACH => (t, String::from("host unreachable(1)")),
ICMP_PROTO_UNREACH => (t, String::from("protocol unreachable(2)")),
ICMP_PORT_UNREACH => (t, String::from("port unreachable(3)")),
ICMP_FRAG_NEED => (t, String::from("fragmentation needed and DF set(4)")),
ICMP_SRC_RT_FAIL => (t, String::from("source route failed(5)")),
_ => (t, String::from("unknown code")),
}
},
ICMP_ECHO_REQUEST => (String::from("Echo Request(8)"), cod.to_string()),
_ => (String::from("Not implemented yet"), String::from("Sorry")),
}
}
//ICMP Dissector
fn dissect_icmp(data: &[u8], mut pinfo: PacketInfo) -> (String, PacketInfo) {
//先頭1バイト目がタイプ、2バイト目がコードなので解析する
let (type_val, code_val) = icmp_type_and_code(data[0], data[1]);
let icmp_val = format!("ICMP {}, {}", type_val, code_val);
let icmp_tree = format!("((\"Internet Control Message Protocol\" \"icmp\") \
((\"Type\" \"{}\") () \
((\"Code\" \"{}\") () \
((\"Data\" \"...\") () ())))\
())",
type_val, code_val);
pinfo.info = Some(icmp_val);
(icmp_tree, pinfo)
}
//バイト列からIPアドレス形式の文字列を出力するヘルパー関数
fn ipaddr_str(bytes: &[u8]) -> String {
format!("{}.{}.{}.{}", bytes[0], bytes[1], bytes[2], bytes[3])
}
//IP Dissector
fn dissect_ip(data: &mut [u8], mut pinfo: PacketInfo) -> (String, PacketInfo) {
let ttl_val = data[8];
let src_val = ipaddr_str(&data[12..16]);
let dst_val = ipaddr_str(&data[16..20]);
let ip_val = format!("IP {} -> {}", src_val, dst_val);
let payload;
let proto_val = match data[9] { //9バイト目のプロトコル番号に応じて上位プロトコルを解析する
IPPROTO_TCP => {
let (pl, inf) = dissect_tcp(&data[20..], pinfo);
payload = pl;
pinfo = inf;
String::from("TCP")
},
IPPROTO_UDP => {
let (pl, inf) = dissect_udp(&data[20..], pinfo);
payload = pl;
pinfo = inf;
String::from("UDP")
},
IPPROTO_ICMP => {
let (pl, inf) = dissect_icmp(&data[20..], pinfo);
payload = pl;
pinfo = inf;
String::from("ICMP")
},
n => {
payload = String::from("UNKNODWN");
n.to_string()
},
};
pinfo.net_src = Some(src_val.clone());
pinfo.net_dst = Some(dst_val.clone());
pinfo.proto = Some(proto_val.clone());
if pinfo.info.is_none() { pinfo.info = Some(ip_val.clone()); }
let ip_tree = format!("((\"Internet Protocol v4\" \"{}\") \
((\"Time to live\" \"{}\") () \
((\"Protocol\" \"{}\") () \
((\"Source\" \"{}\") () \
((\"Destination\" \"{}\") () ())))) \
{})",
ip_val, ttl_val, proto_val, src_val, dst_val, payload);
(ip_tree, pinfo)
}
//バイト列からMACアドレス形式の文字列を出力するヘルパー関数
fn hwaddr_str(bytes: &[u8]) -> String {
format!("{:02x}:{:02x}:{:02x}:{:02x}:{:02x}:{:02x}",
bytes[0], bytes[1], bytes[2], bytes[3], bytes[4], bytes[5])
}
fn dissect_ethernet(data: &mut [u8], mut pinfo: PacketInfo) -> (String, PacketInfo) {
let dst_val = hwaddr_str(&data[0..6]);
let src_val = hwaddr_str(&data[6..12]);
let eth_val = format!("Ethernet {} -> {}", src_val, dst_val);
let typ;
{
let mut rdr = Cursor::new(&data[12..14]); //12バイト目にある2バイトが上位プロトコル番号
typ = rdr.read_u16::<BigEndian>().unwrap();
}
let payload;
let type_val = match typ { //先ほど切り出した番号に応じて上位プロトコルを解析
ETHERTYPE_IPV4 => {
let (pl, inf) = dissect_ip(&mut data[14..], pinfo);
payload = pl;
pinfo = inf;
String::from("IPv4")
},
n => {
payload = String::from("UNKNODWN");
n.to_string()
},
};
if pinfo.net_src.is_none() { pinfo.net_src = Some(src_val.clone()); }
if pinfo.net_dst.is_none() { pinfo.net_dst = Some(dst_val.clone()); }
if pinfo.info.is_none() { pinfo.info = Some(eth_val.clone()); }
let eth_tree = format!("((\"Ethernet\" \"{}\") \
((\"Destination\" \"{}\") () \
((\"Source\" \"{}\") () \
((\"Type\" \"{}\") () ()))) \
{})",
eth_val, dst_val, src_val, type_val, payload);
(eth_tree, pinfo)
}
//Dissectorのエントリーポイント
pub fn dissect(n: u32, hdr: pcap::PacketHeader, mut data: Vec<u8>) -> (String, PacketInfo) {
let pinfo = PacketInfo {
num: n,
time: Timespec::new(hdr.ts.tv_sec, (hdr.ts.tv_usec * 1000) as i32), //PacketHeaderからTimespecを生成
len: hdr.len,
//以下フィールドは各Dissectorにて設定する
net_src: None, net_dst: None,
src_port: None, dst_port: None,
proto: None, info: None,
};
//Ethernetヘッダから解析を始める
dissect_ethernet(&mut data, pinfo)
}
main.rsにもクレートの参照と新規に作成したdisctr.rsへの参照を追加しておきます。
...
extern crate byteorder;
extern crate time;
...
mod disctr;
...
Cargo.tomlへのクレート指定も忘れずに追加。
[dependencies]
...
byteorder = "1.2.1"
time = "0.1.38"
...
これで再度実行すると、今度は標準出力にパケットの詳細情報を表すS式が出力されるようになります。
パケット詳細情報(S式)を生成できるようになったので、GtkTreeViewへ表示させるよう変更していきます。
まず、パケット受信都度パケット情報を出力するパケットリストの表示方法を説明します。パケットリストはModelのGtkListStoreにエントリを追加していきます。GtkListStoreへのエントリ追加は、①GtkListStoreにデータを設定する空のエントリを追加し、②追加した空のエントリに挿入したいデータの値を設定する、という流れになります。①で空のエントリを追加した際に、そのエントリを指すイテレータが生成されるので、②ではそのイテレータを使ってエントリを特定し値を設定します。以下イメージになります。
①空のエントリを末尾に追加 (gtk::ListStore::append())
| No.| Time | Source | Destination | Protocol | Length | Info |
|:--:|:-------------------:|:-------------:|:-------------:|:--------:|:------:|:------------:|
| 1 | 2017-12-23 16:01:20 | 192.168.0.1 | 192.168.0.250 | ICMP | 98 | Echo request |
| 2 | 2017-12-23 16:01:21 | 192.168.0.250 | 192.168.0.1 | ICMP | 98 | Echo reply |
| <---- NEW ENTRY ----> | <== iterator
②iteratorが指すエントリに値を設定 (gtk::ListStore::set(iterator, <カラムリスト>, <値リスト>))
| No.| Time | Source | Destination | Protocol | Length | Info |
|:--:|:-------------------:|:-------------:|:-------------:|:--------:|:------:|:------------:|
| 1 | 2017-12-23 16:01:20 | 192.168.0.1 | 192.168.0.250 | ICMP | 98 | Echo request |
| 2 | 2017-12-23 16:01:21 | 192.168.0.250 | 192.168.0.1 | ICMP | 98 | Echo reply |
| 3 | 2017-12-23 16:01:22 | 192.168.0.1 | 192.168.0.250 | ICMP | 98 | Echo request | <== iterator
一方、パケット詳細情報はパケットリストから特定の行をクリックして選択されるたびにGtkListStoreの対象エントリのDATAカラムからS式(String)を取り出し、そのS式をパースしてGtkTreeStoreにエントリを追加していきます。GtkTreeStoreへのエントリの追加もGtkListStoreと同様にイテレータを取得して値を設定しますが、空のエントリの追加方法が少々異なります。リスト構造の場合は単純に末尾に追加すればよいのですが、木構造の場合は特定のノードの子ノードに追加するという指定の仕方をします。以下イメージになります。
①空のエントリを[Internet Protocol V4]ノードの子ノードとしてエントリを追加 (gtk::TreeStore::append(parent_iterator))
├── Ethernet
| ├── Destination: XX:XX:XX:XX:XX:XX
| ├── Source: XX:XX:XX:XX:XX:XX
| └── Type: 0x0800
├── Internet Protocol V4 <== parent_iterator
| ├── Time to live: 64
| ├── Protocol: 6
| ├── Source: XXX.XXX.XXX.XXX
| └── [ <---- NEW ENTRY ----> ] <== iterator
├── Transmission Control Protocol
| ├── Source Port: 35000
②iteratorが指すエントリに値を設定 (gtk::TreeStore::set(iterator, <カラムリスト>, <値リスト>))
├── Ethernet
| ├── Destination: XX:XX:XX:XX:XX:XX
| ├── Source: XX:XX:XX:XX:XX:XX
| └── Type: 0x0800
├── Internet Protocol V4 <== parent_iterator
| ├── Time to live: 64
| ├── Protocol: 6
| ├── Source: XXX.XXX.XXX.XXX
| └── Destination: XXX.XXX.XXX.XXX <== iterator
├── Transmission Control Protocol
| ├── Source Port: 35000
S式を文字列としてパースしながら上記のようにエントリ追加をしていくとコードが煩雑になりますので、S式の文字列をいったんS式を表す構造体に変換してからGtkTreeStoreにエントリを追加していきます。S式をパースして構造体を生成する部分はsexpクレートを使います。
...
use gtk::{
...
ListStoreExt, TreeModelExt,
ListStoreExtManual, TreeViewExt,
TreeStoreExt, TreeStoreExtManual,
TreeSelectionExt, Cast
};
use time;
//S式をパースするCrateを使う
use sexp;
use sexp::{Sexp, Atom};
...
const NUMBER_COLUMN: u32 = 0;
const TIME_COLUMN: u32 = 1;
const SRC_COLUMN: u32 = 2;
const DST_COLUMN: u32 = 3;
const PROTO_COLUMN: u32 = 4;
const LEN_COLUMN: u32 = 5;
const INFO_COLUMN: u32 = 6;
const DATA_COLUMN: u32 = 7;
const DETAIL_COLUMN: u32 = 0;
...
//PacketInfoのデータとS式(String)をGtkListStoreの新しいエントリとして追加する
fn output_packet(tree: String, pinfo: PacketInfo, store: gtk::TreeModel) {
let store = store.downcast::<gtk::ListStore>().ok().unwrap();
//GtkListStoreの末尾に新しいエントリを追加
let itr = store.append();
let time = time::strftime("%F %T", &time::at(pinfo.time)).unwrap();
//追加したエントリに情報を設定する
store.set(&itr,
&[NUMBER_COLUMN, TIME_COLUMN, SRC_COLUMN, DST_COLUMN, PROTO_COLUMN,
LEN_COLUMN, INFO_COLUMN, DATA_COLUMN],
&[&pinfo.num, &time, &pinfo.net_src, &pinfo.net_dst, &pinfo.proto,
&pinfo.len, &pinfo.info, &tree]);
}
...
fn init_action(win: >k::ApplicationWindow, builder: >k::Builder) {
...
{
...
let lst_store: gtk::ListStore = builder.get_object("list-store").unwrap();
start_capture_action.connect_activate(move |act, _| {
//スタートボタンを押すたびにパケットリストをクリアしてからキャプチャを開始するようにする
lst_store.clear();
...
}
...
let lst_v: gtk::TreeView = builder.get_object("list_view").unwrap();
let store = lst_v.get_model().unwrap(); //GtkListStoreを取得
gtk::timeout_add(300, move || {
while let Ok((n, hdr, data)) = pkt_rx.try_recv() {
let (tree, pinfo) = dissect(n, hdr, data);
output_packet(tree, pinfo, store.clone()); //パケットリストにキャプチャした情報を表示させる
}
gtk::Continue(true)
});
...
}
//S式(Sexp)からノードのラベルと値をパースして"ラベル: 値"の文字列を返す
fn parse_lbl_val(sxp: &Sexp) -> String {
if let &Sexp::List(ref kv_lst) = sxp {
if let &Sexp::Atom(ref k) = &kv_lst[0] {
if let &Atom::S(ref lbl_str) = k {
if let Sexp::Atom(ref v) = kv_lst[1] {
if let &Atom::S(ref val_str) = v {
return format!("{}: {}", lbl_str, val_str);
}
}
}
}
}
String::from("** Parse Error **")
}
//S式(Sexp)で構成されたパケットの木構造をパースしてパケット詳細情報(GtkTreeStore)に設定する
fn set_detail_tree(sxp: &Sexp, store: gtk::TreeStore, parent_itr: Option<>k::TreeIter>) {
if let &Sexp::List(ref lst) = sxp {
if lst.len() != 3 { return; }
let itr = store.append(parent_itr);
let disp_str = parse_lbl_val(&lst[0]);
store.set(&itr, &[DETAIL_COLUMN], &[&disp_str]);
set_detail_tree(&lst[1], store.clone(), Some(&itr));
set_detail_tree(&lst[2], store, parent_itr);
}
}
//S式(String)をパースしてSexp構造体に変換し、パケット詳細情報(GtkTreeStore)へ表示させる
fn set_detail_pane(store: gtk::TreeStore, tree: String) {
store.clear();
match sexp::parse(&tree) {
Ok(sxp) => set_detail_tree(&sxp, store, None),
Err(e) => println!("Error: {}", e),
}
}
//パケットリストのエントリをクリックして選択した際に発生するGtkTreeSelectionオブジェクトの
//changedシグナルに対応するハンドラでパケット詳細情報にパケット情報を設定する
fn init_list_view(builder: >k::Builder) {
let select: gtk::TreeSelection = builder.get_object("selection").unwrap();
let dtl_store: gtk::TreeStore = builder.get_object("detail-store").unwrap();
select.connect_changed(move |slct| {
if let Some((model, itr)) = slct.get_selected() {
let data = model.get_value(&itr, DATA_COLUMN as i32);
if let Some(tree) = data.get::<String>() {
set_detail_pane(dtl_store.clone(), tree);
}
}
});
}
pub fn create(app: >k::Application) -> gtk::ApplicationWindow {
...
init_list_view(&builder); //パケットリストのエントリをクリックしたときのハンドラを設定する
init_action(&win, &builder);
win
}
...
main.rsとCargo.tomlにもクレートを指定。
...
extern crate sexp;
...
...
[dependencies]
...
sexp = "1.1.4"
...
以上でキャプチャしたパケットがウィンドウ内に表示されるようになっていますので、試しにキャプチャを開始してPingを打って動作を確認します。
ここまでで解析できるプロトコルは非常に限られていますが、後は気合でDissectorを書いていけば解析できるプロトコルを増やしていけます。ですが、単調な作業なので今回はここでひと区切りにしたいと思います。
ただ、TCP/UDPの上位プロトコルはともかくARPくらいは実装したいと思います。
WireSharkではユーザがLuaを使って独自にDissectorを実装することができます。この機能により、ある組織内で独自に開発したプロトコルを解析したい場合や、新しいプロトコルでWireShark自体がまだ対応していない場合、ユーザが自らそのプロトコルのDissectorをLuaで書くことで解析できるようになります。
そこで、本アプリでも同様に、ユーザが作成したスクリプトでDissectorを書くことができるようにします。そして、試しにARPのDissectorをスクリプトで書いて解析できるようにします。
スクリプト言語でアプリの機能を拡張する
やり方としては、Rustからパケットデータをスクリプト言語で定義したDissector関数に渡して解析し、解析結果をRustで書いた部分で受け取り、以降のパケット表示はこれまでと同様に処理します。この機能拡張のためにアプリケーションに他の言語処理系を埋め込む形になります。埋め込む言語処理系は、Foreign Function Interface(FFI)を持つものであれば何でも良いのですが、例えばWireSharkではLuaを使っています。Luaは軽量・高速な言語処理系を持っているので組み込みに適した言語となっていますが、同じだとつまらない3ので別の言語にします。Dissectorを書くだけの用途なので、シンプルな言語仕様が良く、DissectorはS式を出力することになるのでLisp系言語から処理系を選ぶことにしました。結果、組み込みの実績等も考慮してGNU guileを組み込むことにしました。guileはSchemeの処理系で、Gnu cashやGNU makeなどにも組み込まれています。そして、何よりもSchemeの言語仕様がとてもシンプルなので今回の用途に適していると思います。
ARPのDissector関数はSchemeでは以下のような関数にします。
(use-modules (rnrs bytevectors))
(use-modules (system foreign))
(define (dissect-arp bv pinfo)
;PacketInfoオブジェクトのprotoフィールドに"ARP"を設定
(set-proto pinfo "ARP")
;パケット詳細情報を表すS式を構築し、Dissectorの解析結果として返す
(list
(list
"Address Resolution Protocol"
(number->string (bytevector-u16-ref bv 6 (endianness big))))
(list
(list "Source Protocol Address"
(inet-ntop AF_INET (bytevector-u32-ref bv 14 (endianness big))))
'()
(list
(list "Destination Protocol Address"
(inet-ntop AF_INET (bytevector-u32-ref bv 24 (endianness big)))) '() '()))
'()))
;定義したDissector関数をDissectorTableに登録する
;Ethernetの上位プロトコルタイプ番号0x0806(=ARP)に対応するDissectorとして登録
(register-dissector 'net #x0806 dissect-arp)
では、早速アプリに組み込んでいきます。
まずは事前にguileをインストールする必要があります。Ubuntuの場合は以下でインストールできます。
sudo apt install guile-2.0-dev
そしてguileのクレートもインストールするのですが、guileのFFIだけ使うのでguile-sysというクレートを使用します。また、RustとC関数の間で値をやり取りするためには型の変換等の処理が必要になるので、libcというクレートも使用します。
...
[dependencies]
...
libc = "0.2.34"
guile-sys = "0.1.1"
...
guile-sysはCの関数への単純なインターフェイスを提供しているだけですので、これらの関数を使うときは常にunsafeを指定する必要があります。以下、guileを組み込むのための変更部分になります。(本来必須の値の型チェックやエラー処理は省略しています)
...
extern crate libc;
extern crate guile_sys;
...
use std::rc::Rc;
use std::cell::RefCell;
use std::ffi::CStr;
use std::ffi::CString;
use libc::c_void;
use guile_sys::{
SCM, scm_c_define_gsubr, scm_from_pointer,
scm_c_define, scm_with_guile, scm_c_primitive_load
};
use disctr::{
DissectorTable, set_dissector, set_info,
set_proto,
};
...
unsafe extern "C" fn init_guile(dissector_tbl: *mut c_void) -> *mut c_void {
//rustのset_dissector関数をguileのset-dissector関数として登録
//guileのオブジェクトは全てSCM型で扱う
let prc = set_dissector as *mut fn(SCM, SCM, SCM, SCM) -> SCM as *mut c_void;
scm_c_define_gsubr(CStr::from_bytes_with_nul(b"set-dissector\0").unwrap().as_ptr(), 4, 0, 0, prc);
let prc = set_proto as *mut fn(SCM, SCM) -> SCM as *mut c_void;
scm_c_define_gsubr(CStr::from_bytes_with_nul(b"set-proto\0").unwrap().as_ptr(), 2, 0, 0, prc);
let prc = set_info as *mut fn(SCM, SCM) -> SCM as *mut c_void;
scm_c_define_gsubr(CStr::from_bytes_with_nul(b"set-info\0").unwrap().as_ptr(), 2, 0, 0, prc);
//rustのDissectorTableオブジェクトをguileのシンボルdissector-tableにバインドする(guileのglobalから参照できるようにする)
let dsctr_tbl = scm_from_pointer(dissector_tbl, None);
scm_c_define(CStr::from_bytes_with_nul(b"dissector-table\0").unwrap().as_ptr(), dsctr_tbl);
dissector_tbl
}
fn run(args: Args) {
match gtk::Application::new("com.github.koji-m.wire_shake", gio::APPLICATION_HANDLES_OPEN) {
Ok(app) => {
...
//guileで定義するDissectorを登録するDissctorTableを用意する
let mut disct_tbl = DissectorTable::new();
unsafe {
//guileを初期化する。init_guile()が実行されて各種関数などが定義される。
scm_with_guile(Some(init_guile), &mut disct_tbl as *mut _ as *mut c_void);
//dissector.scmがロードされてARP Dissectorが登録される
scm_c_primitive_load(CString::new("src/dissector.scm").unwrap().as_ptr());
}
let disct_tbl = Rc::new(RefCell::new(disct_tbl));
{
app.connect_activate(move |app| {
let w = win::create(app, disct_tbl.clone());
...
};
}
...
...
use std::rc::Rc;
use std::cell::RefCell;
use std::ffi::CString;
use guile_sys::{
scm_variable_ref, scm_c_lookup,
};
use disctr::{
...
DissectorTable
};
...
fn init_action(win: >k::ApplicationWindow, builder: >k::Builder, disct_tbl: Rc<RefCell<DissectorTable>>) {
...
let write_proc;
unsafe {
//パケット解析後に生成されたguileのオブジェクトを文字列に変換する際に指定する関数writeへの参照を取得しておく
write_proc = scm_variable_ref(scm_c_lookup(CString::new("write").unwrap().as_ptr()));
}
gtk::timeout_add(300, move || {
while let Ok((n, hdr, data)) = pkt_rx.try_recv() {
let (tree, pinfo) = dissect(n, hdr, data, disct_tbl.clone(), write_proc);
...
}
...
pub fn create(app: >k::Application, disct_tbl: Rc<RefCell<DissectorTable>>) -> gtk::ApplicationWindow {
...
init_action(&win, &builder, disct_tbl);
win
}
...
use std::collections::HashMap;
use std::rc::Rc;
use std::cell::RefCell;
use std::ffi::CString;
use libc::c_void;
use guile_sys::{
SCM, scm_to_pointer, scm_symbol_to_string, scm_to_locale_string,
scm_to_uint16, scm_to_uint8, scm_from_pointer,
scm_pointer_to_bytevector, scm_from_int32,
scm_from_utf8_symbol, scm_call_2, scm_object_to_string
};
...
//guileで定義されたDissector関数を登録する構造体
pub struct DissectorTable {
net_dissectors: HashMap<u16, SCM>, //ネットワーク層のDissectorテーブル
transport_dissectors: HashMap<u8, SCM>, //トランスポート層のDissectorテーブル
tcp_dissectors: HashMap<u8, SCM>, //TCPの上位プロトコルのDissectorテーブル
udp_dissectors: HashMap<u8, SCM>, //UDPの上位プロトコルのDissectorテーブル
}
impl DissectorTable {
pub fn new() -> Self {
DissectorTable {
net_dissectors: HashMap::new(),
transport_dissectors: HashMap::new(),
tcp_dissectors: HashMap::new(),
udp_dissectors: HashMap::new(),
}
}
fn net(&self, type_num: u16) -> Option<&SCM> {
self.net_dissectors.get(&type_num)
}
fn set_net(&mut self, type_num: u16, disct_proc: SCM) {
self.net_dissectors.insert(type_num, disct_proc);
}
fn transport(&self, num: u8) -> Option<&SCM> {
self.transport_dissectors.get(&num)
}
#[allow(dead_code)]
fn set_transport(&mut self, num: u8, disct_proc: SCM) {
self.transport_dissectors.insert(num, disct_proc);
}
#[allow(dead_code)]
fn tcp(&self, port_num: u8) -> Option<&SCM> {
self.tcp_dissectors.get(&port_num)
}
fn set_tcp(&mut self, port_num: u8, disct_proc: SCM) {
self.tcp_dissectors.insert(port_num, disct_proc);
}
#[allow(dead_code)]
fn udp(&self, port_num: u8) -> Option<&SCM> {
self.udp_dissectors.get(&port_num)
}
fn set_udp(&mut self, port_num: u8, disct_proc: SCM) {
self.udp_dissectors.insert(port_num, disct_proc);
}
}
//guileの中で定義したDissector関数をDissectorTableに登録する関数
pub extern "C" fn set_dissector(tbl: SCM, tbl_type: SCM, num: SCM, prc: SCM) -> SCM{
unsafe {
let tbl_ptr = scm_to_pointer(tbl) as *mut DissectorTable;
let tbl = tbl_ptr.as_mut().unwrap();
let tbl_type = scm_symbol_to_string(tbl_type);
let tbl_type: &str = &CString::from_raw(scm_to_locale_string(tbl_type)).into_string().unwrap();
match tbl_type {
"net" => {
let num = scm_to_uint16(num) as u16;
tbl.set_net(num, prc);
},
"tcp" => {
let num = scm_to_uint8(num) as u8;
tbl.set_tcp(num, prc);
},
"udp" => {
let num = scm_to_uint8(num) as u8;
tbl.set_udp(num, prc);
},
_ => {
println!("dissector registration error");
}
}
}
tbl
}
//guileで定義するDissector関数の中でPacketInfo構造体のprotoフィールドに値を設定する為の関数
pub extern "C" fn set_proto(pinfo: SCM, proto: SCM) -> SCM{
{
unsafe {
let pinfo = scm_to_pointer(pinfo) as *mut PacketInfo;
let pinfo = pinfo.as_mut().unwrap();
let proto = CString::from_raw(scm_to_locale_string(proto)).into_string().unwrap();
pinfo.proto = Some(proto);
}
}
pinfo
}
//guileで定義するDissector関数の中でPacketInfo構造体のinfoフィールドに値を設定する為の関数
pub extern "C" fn set_info(pinfo: SCM, info: SCM) -> SCM{
{
unsafe {
let pinfo = scm_to_pointer(pinfo) as *mut PacketInfo;
let pinfo = pinfo.as_mut().unwrap();
let info = CString::from_raw(scm_to_locale_string(info)).into_string().unwrap();
pinfo.info = Some(info);
}
}
pinfo
}
//&[u8]型のデータをguileのBytevectorオブジェクトに変換する関数
fn to_bytevector(bytes: &mut [u8]) -> SCM {
let v_ptr = bytes.as_mut_ptr() as *mut c_void;
unsafe {
let scm_ptr = scm_from_pointer(v_ptr, None);
let cstr = CString::new("u8").unwrap();
scm_pointer_to_bytevector(scm_ptr,
scm_from_int32(bytes.len() as i32),
scm_from_int32(0),
scm_from_utf8_symbol(cstr.as_ptr()))
}
}
...
fn dissect_ip(data: &mut [u8], mut pinfo: PacketInfo, disct_tbl: Rc<RefCell<DissectorTable>>, write_proc: SCM) -> (String, PacketInfo) {
...
let proto_val = match data[9] {
...
//rustで定義されていないプロトコルの場合、DissectorTableに登録されていればそのDissectorで解析する
n => {
//guileで定義されたDisector関数を取得
if let Some(dsctr) = disct_tbl.borrow().transport(n) {
unsafe {
let pinfo_ptr = scm_from_pointer(&mut pinfo as *mut _ as *mut c_void, None);
//引数としてパケットデータ(Bytevector)とPacketInfo構造体への参照を渡してDissector関数(guile関数)を実行
let res = scm_call_2(*dsctr,
to_bytevector(&mut data[20..]),
pinfo_ptr);
//解析の結果(guileオブジェクト)をguileの文字列オブジェクトに変換し、更に文字列への生ポインタに変換する
let res = scm_to_locale_string(scm_object_to_string(res, write_proc));
//文字列への生ポインタをrustのStringに変換
payload = CString::from_raw(res).into_string().unwrap();
}
} else {
payload = String::from("UNKNODWN");
}
n.to_string()
}
};
}
...
fn dissect_ethernet(data: &mut [u8], mut pinfo: PacketInfo, disct_tbl: Rc<RefCell<DissectorTable>>, write_proc: SCM) -> (String, PacketInfo) {
...
let type_val = match typ {
ETHERTYPE_IPV4 => {
let (pl, inf) = dissect_ip(&mut data[14..], pinfo, disct_tbl, write_proc);
...
},
n => {
if let Some(dsctr) = disct_tbl.borrow().net(n) {
unsafe {
let pinfo_ptr = scm_from_pointer(&mut pinfo as *mut _ as *mut c_void, None);
let res = scm_call_2(*dsctr,
to_bytevector(&mut data[14..]),
pinfo_ptr);
let res = scm_to_locale_string(scm_object_to_string(res, write_proc));
payload = CString::from_raw(res).into_string().unwrap();
}
} else {
payload = String::from("UNKNODWN");
}
n.to_string()
},
};
...
}
pub fn dissect(n: u32, hdr: pcap::PacketHeader, mut data: Vec<u8>, disct_tbl: Rc<RefCell<DissectorTable>>, write_proc: SCM) -> (String, PacketInfo) {
...
dissect_ethernet(&mut data, pinfo, disct_tbl, write_proc)
}
main.rsでは、guileを使う準備としてscm_with_guile()でguileの環境を初期化しています。このとき、引数として渡した関数init_guile()が実行されます。init_guile()では、rustで定義した関数をguileの中から呼べるように登録したり、rustで生成した構造体をguileのグローバルスコープから参照できるシンボルにバインドしています。
scm_call_2(<guileで定義したDissector関数>, <解析対象のパケットデータ>, <PacketInfo構造体>)が、guileで定義したDissector関数をrustから呼ぶ部分となります。
最後に、先ほどARP Dissectorを定義したdissector.scmに、Dissector関数を登録するための関数register-dissectorを定義しておきます。
(define (register-dissector tbl num dsctr)
;rustで定義したset_dissector関数をguileから呼び出す
(set-dissector dissector-table tbl num dsctr))
以上で、guileで定義したARP DissectorによりARPが解析されることが確認できます。試しに存在しないIPアドレスにpingを打って確認してみて下さい。
最後に
今回作成したコードはこちらにあげておきます。Makefileやアイコンイメージ、その他 アプリ配布時に必要なファイルも作成してあります。これらの作成方法は前の記事を参考にして頂ければと思います。