前説
AI (Deep Learning)の流行とともにPythonの人気が上がっていますね。
Pythonで画像を表示・描き込み・保存するGUIアプリケーションを以前から作っていたもコードなどを整理して作ってみました。自分の理解を整理するためにも、その仕組みを書いてみます。
使ったものはQt for Python(PySide2)というライブラリです。
Qtは元々C++で開発されており、同一のソースコードからWindows, Mac, Linuxなどの様々なOSで動作するクロスプラットフォームなアプリケーションが開発できます。
PythonからQtを利用するにはQt for PythonかPyQtがありますが、作成したアプリのライセンスの縛りがそれほどないQt for Pythonを使いました。
GUIアプリケーション作りではオブジェクト指向について把握していると理解しやすいです。画像を描画するときにいくつもオブジェクトが出てきて、それぞれの役割や関係がわかりづらいところが初心者に辛く感じるところですが、きれいな形でなくても動くものができてくると理解が進みます。(経験談)
なので、作りたいイメージがあったら諦めずに色々試行錯誤してみてください。この記事がそのときの一助にでもなれば幸いです。
アプリの全体像
アプリの全体像は下図のようになります。
Layoutというウィンドウなどのサイズに合わせて自動的に置いた部品(Widget)を整列する機能を持つもので画面構成を管理しています。

QVBoxLayout()が縦方向に整列させ、QHBoxLayout()が横方向に整列させます。
その他に名称とその値のような組にしたいときにQFormLayout()を使います。
使用例は以下のようになります。
self.main_layout = QVBoxLayout()
# 画像表示領域をセット
self.graphics_view = QGraphicsView()
self.upper_layout.addWidget(self.graphics_view)
# メインレイアウトに画面上部のレイアウトを入れ子にする
self.upper_layout = QHBoxLayout()
self.main_layout.addLayout(self.upper_layout)
メインウィンドウの作成
メインウィンドウとしてQMainWindowを継承したclass MainWindow(QMainWIndow)を作ります。この中に様々な機能を持たせた部品(Widget)を配置し、それを押したときなどの動作を記述していきます。
ここで初期化のなかで、self.mainWidget = QWidget(self)のように宣言しておかないとLayoutを設定していけませんでした。
アプリケーションの起動のためのコードは、以下のようになります。
class MainWindow(QMainWindow):
def __init__(self):
# 以下、色々な処理を記述
if __name__ == '__main__':
app = QApplication(sys.argv)
window = MainWindow()
window.show()
sys.exit(app.exec_())
メニューバーの作成
メインウィンドウにメニューバー(アプリケーションの上部の選択項目)を作るにはコンストラクタ(def init() )のなかで宣言します。
メニューバーを作り、その中に「File」というメニューを作成するには下のようにします。
class MainWindow(QMainWindow):
def __init__(self):
self.main_menu = self.menuBar()
self.file_menu = self.main_menu.addMenu('File')
「File」メニューに「File Open」という項目を作りたい場合は下のようにします。
# Set "Original Image Open" menu
self.org_img_open_button = QAction(self.style().standardIcon(getattr(QStyle, 'SP_FileDialogStart')), 'Open Orginal Image', self)
self.org_img_open_button.setShortcut('Ctrl+O')
self.org_img_open_button.triggered.connect(self.open_org_img_dialog)
self.file_menu.addAction(self.org_img_open_button)
1行目でこの項目が選択された時に機能するQAction()として設定し、アイコンを標準のものから選び、表示される名称を'Open Orginal Image'としています。
2行目でCtrl+Oのショートカットキーでこの項目を選択できるように設定しています。
3行目はこの項目が選択されたときの動作を設定する関数とつなげています。ここは次の節で説明します。
4行目でこの項目をfile_menuに登録しています。
部品へのアクションを受け取る仕組み
Qtではユーザーからの操作とそれに対応するコンピュータのリアクションをSignalとSlotと呼ばれる方法で実施しています。
ユーザーがメニューのボタン、マウスをドラッグするなどの操作をするとSignalを発します。そして、各シグナルを受け取るように定義したSlotで対応する処理を実行します。
具体的には、メニューバーの項目を選択したときの動作は下のように書きます。
# メニューバー -> ファイル -> 'Original Image Open'が選択されたとき、
# triggeredシグナルを発信する。そのシグナルはopen_org_img_dialog関数に接続される。
self.org_img_open_button = QAction(self.style().standardIcon(getattr(QStyle, 'SP_FileDialogStart')), 'Open Orginal Image', self)
self.org_img_open_button.triggered.connect(self.open_org_img_dialog)
# メニューバー -> ファイル -> 'Original Image Open'が選択されたとき発信されるシグナルを受け取るSlotとなる関数
def open_org_img_dialog(self):
options = QFileDialog.Options()
org_img_default_path = self.app_setting["SoftwareSetting"]["file_path"]["org_img_dir"]
self.org_img_file_path, selected_filter = QFileDialog.getOpenFileName(self, 'Select original image', org_img_default_path, 'Image files(*.jpg *jpeg *.png)', options=options)
org_img_dir_path, org_img_file = os.path.split(self.org_img_file_path)
org_img_bare_name, org_img_ext = os.path.splitext(org_img_file)
self.org_img_path_label.setText(self.org_img_file_path)
後で説明するカラーバーからマウスクリックで色を選択したとき、その選択色を表示用の描画領域に四角形で描画して、ユーザーにわかりやすく表示しようとします。
このとき、カラーバーと選択色描画領域のオブジェクト間で作用する必要が出てきます。そのとき親となるメインウィンドウを介してSignalとSlotをつなげる必要が出てきます。その場合に選択色描画領域に載せる描画アイテムを管理するクラスで独自のSignalを定義し、クリックしたところのカラー情報を持つSignalを発信(emit)するようにしています。
具体的には、下のようなコードになります。
# Class for graphics contents of tools on main window
class GraphicsSceneForTools(QGraphicsScene):
# Define custom signal
img_info = Signal(QColor)
def mousePressEvent(self, event):
# For check program action
pos = event.scenePos()
x = pos.x()
y = pos.y()
# 画像編集ツールバーでカーソルかペンが選ばれていたらクリックした場所のカラー情報(QColor)を持つSignalをだす
if self.mode == 'cursor' or self.mode == 'pen':
self.pix_rgb = self.img_content.pixelColor(x, y)
self.img_info.emit(self.pix_rgb)
# メインウィンドウ側で選択されたカラー情報のSignalに対応するSlotを定義する
class MainWindow(QMainWindow):
# カラーバー用の描画アイテム管理オブジェクト
self.color_bar_scene = GraphicsSceneForTools()
# カラー情報を発信したSignalを受け取るSlotとなる関数と接続する
self.color_bar_scene.img_info.connect(self.set_selected_color)
画像表示の仕組み
画像表示にはいくつかのWidgetを連携させます。
下図のような関係になっており、MainWindowに描画領域オブジェクトであるQGraphicsViewを用意し、その中に描画オブジェクトを保持・管理するQGraphicsSceneを配置し、QGraphicsSceneにラインや円などの描画や画像を加えていきます。
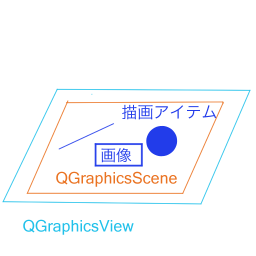
メインの描画領域に設定するQGraphicsSceneにはカーソルのツールを選んでいるときは表示されている画像の画素情報をステータスバーに表示し、ペンや消しゴムのツールを選んでいるときは画像の上のレイヤーにお絵描きをするようにします。そのような自分で設定した機能を追加するためQGraphicSceneを継承したGraphicsSceneを以下のように作成します。
初期化init関数において、親である描画領域のQGraphicsViewとそのさらに親であるMainWindowを設定することで、このGraphicsSceneの各アイテムで得た情報を描画領域やウィンドウに渡せるようにします。
正直、最初はQGraphicsViewとQGraphicsSceneがよく分からないけど分かれていてなんか複雑でコンテンツへのアクセスや制御が面倒!と思いました。
これは描画する対象コンテンツは変わらなくても、視点を変えて見える範囲(描画できる範囲)で描画するという複雑な要求にも応えられる設計にしているためと思われます。例えば、描画するコンテンツが描画エリアより大きいときにスクロールバーで視点を変えながら表示する、3Dオブジェクトを視点を変えながら表示するといったことが考えられます。
class GraphicsSceneForMainView(QGraphicsScene):
def __init__(self, parent=None, window=None, mode='cursor'):
QGraphicsScene.__init__(self, parent)
# Set parent view area
self.parent = parent
# Set grand parent window
self.window = window
# Set action mode
self.mode = mode
# mouse move pixels
self.points = []
# added line items
self.line_items = []
self.lines = []
# added line's pen attribute
self.pens = []
def set_mode(self, mode):
self.mode = mode
def set_img_contents(self, img_contents):
# image data of Graphics Scene's contents
self.img_contents = img_contents
def clear_contents(self):
self.points.clear()
self.line_items.clear()
self.lines.clear()
self.pens.clear()
self.img_contents = None
def mousePressEvent(self, event):
# For check program action
pos = event.scenePos()
x = pos.x()
y = pos.y()
if self.mode == 'cursor':
# Get items on cursor
message = '(x, y)=({x}, {y}) '.format(x=int(x), y=int(y))
for img in self.img_contents:
# Get pixel value
pix_val = img.pixel(x, y)
pix_rgb = QColor(pix_val).getRgb()
message += '(R, G, B) = {RGB} '.format(RGB=pix_rgb[:3])
# show scene status on parent's widgets status bar
self.window.statusBar().showMessage(message)
QGraphicsViewのドキュメントへのリンク
QGraphicsSceneのドキュメントへのリンク
画像オブジェクト
QGraphicsSceneに画像を配置するには、QPixmapという形式にして、QGraphicsScene.addItem(QPixmap)とします。ただし、QPixmap形式だと各画素の情報を取得したり、書き換えたりすることができないため、QImage形式で保持しておいて、それをQPixmapに変換して描画させます。画像ファイルからQImageを作成し、それをQPixmapにして、QGraphicsSceneに加えるには以下のようなコードとなります。
# selfはMainWindowをさす
self.scene = GraphicsSceneForMainView(self.graphics_view, self)
self.org_qimg = QImage(self.org_img_file_path)
self.org_pixmap = QPixmap.fromImage(self.org_qimg)
scene.addItem(self.org_pixmap)
空の各8bit(256階調)RGBA(Aは透過度)のQImageを作るには、以下のようなコードとなります。
self.layer_qimg = QImage(self.org_img_width, self.org_img_height, QImage.Format_RGBA8888)
QImageのドキュメントへのリンク
QPixmapのドキュメントへのリンク
カラーバーの設定
こちらの記事を参考にさせていただき、ペンの色を選択するカラーバーをヒートマップ調(低温の青色から高温の赤色まで滑らかに変化)で作ってみました。
カラーバーをセットするオブジェクトは「部品へのアクションを受け取る仕組み」の説明で一部記載しましたがQGraphicsSceneを継承したGraphicsSceneForToolsというクラスを作り、それを使っています。それによりその上でマウスクリックなどすることで、そのオブジェクトから押された位置に応じたSignalを発するようにし、そのオブジェクトを配置した親オブジェクトのMainWindow(正確にはMainWindow->QGraphicsView->GraphicsSceneForTools)でSignalに受け取るSlot関数を用意することで、ユーザーがカラーバーから選んだ色で選択色表示領域を塗りつぶして、わかりやすく表示します。
新たに用意したクラスGraphicsSceneForTools(QGraphicsScene)では、img_info = Signal(QColor)としてQColor(色情報)を持ったSignalを用意し、def mousePressEvent(self, event)のおいてマウスクリックをされたときにセットされている描画アイテム(ここではカラーバー)のクリックされた座標位置の色(self.pix_rgb)を持たせたSignal信号をself.img_info.emit(self.pix_rgb)として出すようにしています。
MainWindow側では、self.color_bar_scene.img_info.connect(self.set_selected_color)として、GraphicsSceneForToolsオブジェクトが該当するSignalを発したとき、受け取り側のSlot関数としてset_selected_color()を用意します。
具体的には以下のようなコードになります。
class MainWindow(QMainWindow):
# Set color bar
self.color_bar_width = 64
self.color_bar_height = 256
self.color_bar_view = QGraphicsView()
self.color_bar_view.setFixedSize(self.color_bar_width+3, self.color_bar_height+3)
self.color_bar_scene = GraphicsSceneForTools()
# カラーバーをセットする。
# カラーバーの元となる色変化データはself.colormap_dataに入っている。
# 作成方法はソースコードもしくは参考記事を参照してください。
self.color_bar_img = QImage(self.color_bar_width, self.color_bar_height, QImage.Format_RGB888)
for i in range(self.color_bar_height):
# Set drawing pen for colormap
ii = round(i * (1000/256))
color = QColor(self.colormap_data[ii][0], self.colormap_data[ii][1], self.colormap_data[ii][2])
pen = QPen(color, 1, Qt.SolidLine, \
Qt.SquareCap, Qt.RoundJoin)
self.color_bar_scene.addLine(0, self.color_bar_height - i-1, self.color_bar_width, self.color_bar_height - i-1, pen=pen)
for j in range(self.color_bar_width):
self.color_bar_img.setPixelColor(j, self.color_bar_height-i-1, color)
self.color_bar_scene.set_img_content(self.color_bar_img)
self.color_bar_view.setScene(self.color_bar_scene)
# Connect signal to slot of color_bar_scene
self.color_bar_scene.img_info.connect(self.set_selected_color)
# Slot of color bar clicked for selection color
def set_selected_color(self, color):
# Delete existng image item
self.select_color_scene.removeItem(self.select_color_rect)
self.draw_color = color
brush = QBrush(self.draw_color)
self.select_color_rect = self.select_color_scene.addRect(QRect(0, 0, self.select_color_view_size, self.select_color_view_size), \
brush=brush)
self.select_color_view.setScene(self.select_color_scene)
# Class for graphics contents of tools on main window
class GraphicsSceneForTools(QGraphicsScene):
# Define custom signal
img_info = Signal(QColor)
def __init__(self, parent=None, window=None):
QGraphicsScene.__init__(self, parent)
# Set parent view area
self.parent = parent
# Set grand parent window
self.window = window
self.mode = 'cursor'
def set_mode(self, mode):
self.mode = mode
def set_img_content(self, img_content):
# image data of Graphics Scene's contents
self.img_content = img_content
def mousePressEvent(self, event):
# For check program action
pos = event.scenePos()
x = pos.x()
y = pos.y()
if self.mode == 'cursor' or self.mode == 'pen':
self.pix_rgb = self.img_content.pixelColor(x, y)
self.img_info.emit(self.pix_rgb)
描画した内容を反映して、ファイルとして保存
上述した内容で、ペンや消しゴムのツールを選んでお絵描きすることができるようになります。原画像を表示し、自分のお絵描きした結果はその上の別レイヤーに描くようにしています。
さらに自分の描いた内容を保存するには、マウスドラッグによる描画内容を画像として書き出す必要があります。ユーザーのマウスドラッグによる描画内容は、軌跡である線の集まりとして保存されています。線は始点と終点、ペンの属性(色、サイズ)を持ちます。なので、線の集まりから順次、始点と終点をもとに画像上で通過する座標を計算し、書き出し用の画像に反映する処理を行います。
# 描画領域に配置するアイテムを管理するクラス
class GraphicsSceneForMainView(QGraphicsScene):
# ペンか消しゴムが選択され、マウスドラッグで描画されるとき
def mouseMoveEvent(self, event):
# For check program action
pos = event.scenePos()
x = pos.x()
y = pos.y()
if self.mode == 'pen' or self.mode == 'eraser':
if x >= 0 and x < self.width() and y >= 0 and y < self.height():
if len(self.points) != 0:
draw_color = self.window.draw_color
# Set transparenc value
draw_color.setAlpha(self.window.layer_alpha)
draw_size = self.window.draw_tool_size
pen = QPen(draw_color, draw_size, Qt.SolidLine, Qt.RoundCap, Qt.RoundJoin)
self.lines_items.append(self.addLine(QLineF(self.points[-1].x(), self.points[-1].y(), x, y), pen=pen))
# 後で画像として保存するときのために、描き込まれた線の位置とそのときのペンの属性(色、サイズ)を保存しておく
self.lines.append(self.lines_items[-1].line())
self.pens.append(pen)
self.points.append(pos)
# Main Window components
class MainWindow(QMainWindow):
# ユーザーの描き込みを画像に反映する処理
# マウスドラッグにより描き込まれた内容は始点と終点を持つ線情報の集まりとなっている
def make_layer_image(self):
for i, line in enumerate(self.scene.lines):
pen = self.scene.pens[i]
pen_size = int(pen.width())
pen_color = pen.color()
# start pixel of line
x1 = int(line.x1())
y1 = int(line.y1())
# end pixel of line
x2 = int(line.x2())
y2 = int(line.y2())
dx = int(line.dx())
dy = int(line.dy())
# When only 1pixl line
if dx <= 1 and dy <= 1:
draw_pix_x1_s = max(x1 - int(pen_size/2), 0)
draw_pix_x1_e = min(x1 + int(pen_size/2), self.org_img_width-1)
draw_pix_y1_s = max(y1 - int(pen_size/2), 0)
draw_pix_y1_e = min(y1 + int(pen_size/2), self.org_img_height-1)
# for Pen's size
for y in range(draw_pix_y1_s, draw_pix_y1_e):
for x in range(draw_pix_x1_s, draw_pix_x1_e):
self.layer_qimg.setPixelColor(x, y, pen_color)
draw_pix_x2_s = max(x2 - int(pen_size/2), 0)
draw_pix_x2_e = min(x2 + int(pen_size/2), self.org_img_width-1)
draw_pix_y2_s = max(y2 - int(pen_size/2), 0)
draw_pix_y2_e = min(y2 + int(pen_size/2), self.org_img_height-1)
# for Pen's size
for y in range(draw_pix_y2_s, draw_pix_y2_e):
for x in range(draw_pix_x2_s, draw_pix_x2_e):
self.layer_qimg.setPixelColor(x, y, pen_color)
else:
# For avoid devide by 0
if dx == 0:
for y in range(y1, y2+1):
draw_pix_y_s = y - int(pen_size/2)
draw_pix_y_e = y + int(pen_size/2)
# for Pen's size
for yy in range(draw_pix_y_s, draw_pix_y_e):
self.layer_qimg.setPixelColor(x1, yy, pen_color)
else:
grad = dy/dx
# Choose coordinates with small slope not to skip pixels
if grad >= 1.0:
for x in range(dx):
y = y1 + int(grad * x + 0.5)
draw_pix_x_s = max(x1 + x - int(pen_size/2), 0)
draw_pix_x_e = min(x1 + x + int(pen_size/2), self.org_img_width-1)
draw_pix_y_s = max(y - int(pen_size/2), 0)
draw_pix_y_e = min(y + int(pen_size/2), self.org_img_height-1)
# for Pen's size
for yy in range(draw_pix_y_s, draw_pix_y_e+1):
for xx in range(draw_pix_x_s, draw_pix_x_e+1):
self.layer_qimg.setPixelColor(xx, yy, pen_color)
else:
for y in range(dy):
x = x1 + int(1/grad * y + 0.5)
draw_pix_y_s = max(y1 + y - int(pen_size/2), 0)
draw_pix_y_e = min(y1 + y + int(pen_size/2), self.org_img_height-1)
draw_pix_x_s = max(x - int(pen_size/2), 0)
draw_pix_x_e = min(x + int(pen_size/2), self.org_img_width-1)
# for Pen's size
for yy in range(draw_pix_y_s, draw_pix_y_e+1):
for xx in range(draw_pix_x_s, draw_pix_x_e+1):
self.layer_qimg.setPixelColor(xx, yy, pen_color)
Fileメニューに'Save Layer Image'を追加し、それを選択したときに、ユーザーが描き込んだ画像を保存する処理を行うようにする。
具体的には以下のようなコードになり、上記で説明したmake_layer_image()で描画を反映したQImage画像を作成する処理を実行し、保存用のファイルダイアログを開き、入力された画像ファイル名で保存します。
# Main Window components
class MainWindow(QMainWindow):
def __init__(self):
# Set "Save layer image" menu
self.layer_img_save_button = QAction(self.style().standardIcon(getattr(QStyle, 'SP_FileDialogEnd')), 'Save Layer Image', self)
self.layer_img_save_button.setShortcut('Ctrl+S')
self.layer_img_save_button.triggered.connect(self.save_layer_image)
self.file_menu.addAction(self.layer_img_save_button)
# Slot function of save layer image button clicked
def save_layer_image(self):
self.make_layer_image()
layer_img_default_path = self.app_setting["SoftwareSetting"]["file_path"]["layer_img_dir"]
options = QFileDialog.Options()
file_name, selected_filete = QFileDialog.getSaveFileName(self, 'Save layer image', layer_img_default_path, \
'image files(*.png, *jpg)', options=options)
self.layer_qimg.save(file_name)
ret = QMessageBox(self, 'Success', 'layer image is saved successfully', QMessageBox.Ok)
GUIでのWidget(部品)配置
QtにはQt DesignerというGUI画面上で作りたいアプリケーションの画面でボタンなどのパーツを配置するツールも付いています。
慣れないうちはどんな部品(Widget)があるかなどイメージしやすいため、これを使って外観を作ってみるとわかりやすいかもしれません。
ソースコード
作成したアプリのソースコードを以下の場所に掲載します。
アプリのソースコードのページ