注意(2022年10月12日追記)
この記事は2021年4月に投稿したものであり、古い内容が含まれています。2022年10月に以下の記事を投稿しましたので参照してください。
・『ZynqMP 向け Ubuntu22.04で Lima を動かしてみた(DRM Lima 編)』@Qiita
はじめに
Lima とは Mali-400/450 用のオープンソースなグラフィックドライバです。筆者は Lima を Ultra96/Ultra96-V2 向け Ubuntu 20.04 で試験的に動かしてみました。動かすのに少々苦労したので、その方法を何回かに分けて説明します。
- 概要編
- DRM Lima 編(この記事)
- DRI Lima 編
- 共有バッファ編
- ストライド問題編
- インストール編
- Ubuntu Desktop ビルド編
この記事では DRM Lima を Linux Kernel に組み込む方法を説明します。
なお、現時点(2021年4月)では、Ubuntu 20.04 の gnome-shell が動作するところまで確認していますが、すべてのアプリケーションで動作を確認したわけでは無いことに注意してください。
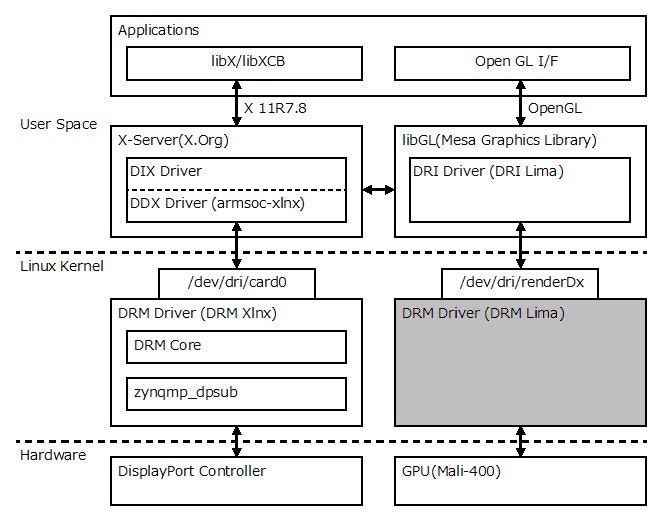
DRM Lima とは
DRM Lima はMali-400/450 を制御するための Linux カーネルの DRM(Direct Rendering Manager) ドライバです。DRM ドライバは DRI(Direct Rendering Infrastructure) の Linuxカーネル部分のコンポーネントです。
Fig.1 DRM Lima
DRM Lima のビルド
Kernel への組み込み
Linux Kernel 5.2 からはメインラインに DRM Lima が組み込まれています。ドライバのソースコードは drivers/gpu/drm/lima にあります。
linux-xlnx v2020.2 は Linux Kernel 5.4 をベースにしているので、DRM Lima が追加されています。しかしUltra96/Ultra96-V2 用に提供されているカーネルコンフィギュレーションファイル(xilinx_zynqmp_defconfig) では DRM Lima が組み込まれません。arch/arm64/configs/xilinx_zynqmp_defconfig に CONFIG_DRM_LIMA=y または CONFIG_DRM_LIMA=m を追加するか、 make menuconfig で Device Drivers > Graphics support > LIMA (DRM support for ARM Mali 400/450 GPU) を選択してください。
Device Tree の設定
linux-xlnx v2020.2 の zynqmp 用の Device Tree には次の記述があります。
:
(中略)
:
gpu: gpu@fd4b0000 {
status = "disabled";
compatible = "arm,mali-400", "arm,mali-utgard";
reg = <0x0 0xfd4b0000 0x0 0x10000>;
interrupt-parent = <&gic>;
interrupts = <0 132 4>, <0 132 4>, <0 132 4>, <0 132 4>, <0 132 4>, <0 132 4>;
interrupt-names = "IRQGP", "IRQGPMMU", "IRQPP0", "IRQPPMMU0", "IRQPP1", "IRQPPMMU1";
clock-names = "gpu", "gpu_pp0", "gpu_pp1";
power-domains = <&zynqmp_firmware PD_GPU>;
};
:
(後略)
また、Ultra96 用の Device Tree には次の記述があります。
/dts-v1/;
#include "zynqmp.dtsi"
:
(中略)
:
&gpu {
status = "okay";
};
:
(後略)
このことから、Ultra96 では GPU は有効になっているはずです。しかし、このままでは DRM Lima は動きません。実は、上で紹介した Device Tree は、DRM Lima 用ではなく Mali Driver 用だからです。
Device Tree を DRM Lima に対応させるためには、 gpu ノードのinterrupt-names プロパティとclock-names プロパティの値を変更する必要があります。
interrupt-names プロパティ
Mali Driver と DRM Lima では割り込みの名前が異なります。DRM Lima では interrupt-names プロパティを次のようにします。
interrupts = <0 132 4>, <0 132 4>, <0 132 4>, <0 132 4>, <0 132 4>, <0 132 4>;
interrupt-names = "gp", "gpmmu", "pp0", "ppmmu0", "pp1", "ppmmu1";
;
clock-names プロパティ
Mali Driver と DRM Lima とでは想定してるクロックが異なります。Mali Driver が想定しているクロックは "gpu"、"gpu_pp0"、"gpu_pp1" の3つですが、Lima が想定しているクロックは "bus"、"core" の二つです。
このように名前が異なるだけでなく、想定しているクロックの種類が異なるため、単純にクロックの名前を変えるだけでは「通常は」上手くいきません。「通常なら」 DRM Lima のソースコードレベルで変更が必要です。
しかし、ZynqMP に関しては少しトリッキーですが Device Tree を修正するだけで動かすことが可能です。具体的には次のように "gpu_pp0" を "core" に、"gpu_pp1" を "bus" に変更します。
clock-names = "gpu", "core", "bus";
DRM Lima はまず "bus" の名前を持つクロックを有効にします。しかしこの Device Tree では実質的には "gpu_pp1" のクロックが有効になります。続いて "core" の名前を持つクロックを有効にします。しかし実質的には "gpu_pp0" のクロックが有効になります。
じゃあ "gpu" クロックはどうなるのか? という疑問がわきますが、ZynqMP の場合は問題ありません。というのも ZynqMP では "gpu_pp0"、"gpu_pp1"、"gpu" は階層構造になっていて、"gpu" -> "gpu_pp0"、"gpu" -> "gpu_pp1" のように "gpu" クロック出力は "gpu_pp0" クロックの入力および "gpu_pp1" クロックの入力に接続されています。Linux Kernel のクロックドライバは、あるクロックを有効にしたときに階層にさかのぼって有効にします。したがって、"gpu_pp0" クロックを有効にした時点で "gpu" クロックも有効になります。
DRM Lima の起動
DRM Lima を組み込んだ Linux Kernel を起動すると次のようなログがコンソール(or dmesg)にでます。
shell$ dmesg
:
(中略)
:
[ 7.269921] lima fd4b0000.gpu: IRQ pmu not found
[ 7.274750] lima fd4b0000.gpu: IRQ ppmmu2 not found
[ 7.279683] lima fd4b0000.gpu: IRQ ppmmu3 not found
[ 7.284718] lima fd4b0000.gpu: gp - mali400 version major 1 minor 1
[ 7.291112] lima fd4b0000.gpu: pp0 - mali400 version major 1 minor 1
[ 7.297575] lima fd4b0000.gpu: pp1 - mali400 version major 1 minor 1
[ 7.304059] lima fd4b0000.gpu: IRQ pp2 not found
[ 7.308708] lima fd4b0000.gpu: IRQ pp3 not found
[ 7.313368] lima fd4b0000.gpu: l2 cache 64K, 4-way, 64byte cache line, 128bit external bus
[ 7.330325] lima fd4b0000.gpu: bus rate = 499999995
[ 7.335463] lima fd4b0000.gpu: mod rate = 499999995
[ 7.360178] [drm] Initialized lima 1.0.0 20190217 for fd4b0000.gpu on minor 1
:
(後略)
また、/dev/dri の下に renderD128 が出来ます。
shell$ ls -la /dev/dri
total 0
drwxr-xr-x 3 root root 120 Feb 14 2019 .
drwxr-xr-x 14 root root 13820 Feb 14 2019 ..
drwxr-xr-x 2 root root 100 Feb 14 2019 by-path
crw-rw---- 1 root video 226, 0 Feb 14 2019 card0
crw-rw---- 1 root video 226, 1 Feb 14 2019 card1
crw-rw---- 1 root render 226, 128 Feb 14 2019 renderD128
DRM Lima の問題点
DRM Lima を組み込んだ linux-xlnx v2020.2 を動かしてみましたが、現時点では次の二つの問題が生じました。
- zocl と共存できない
- 再起動に失敗する
zocl と共存できない
zocl は XRT(Xilinx Runtime) のカーネルモジュールです。zocl および XRT に関しては以下の記事を参照してください。
DRM Lima を組み込んだ状態で zocl を組み込むと、zocl のデバイスファイルが /dev/dri/renderD129 になります(renderD128 はすでに lima driver が使っている)。この状態で例えば [ZynqMP-XRT-Example-1-Ultra96] のサンプルプログラムを起動しようとすると次のようにデバイスが見つからないと言われます。
shell$ ./streaming_lap_filter5.exe streaming_lap_filter5.xclbin
Using FPGA binary file specfied through the command line: streaming_lap_filter5.xclbin
XRT build version: 2.6.0
Build hash: 7104cc336e010e3e0755264ff832d811ff605e2c
Build date: 2020-03-24 21:07:36
Git branch: 2019.2_Ultra96
PID: 610
UID: 1000
[Tue Jun 23 10:12:10 2020]
HOST: debian-fpga
EXE: /home/fpga/examples/ZynqMP-FPGA-XRT-Example-1-Ultra96/streaming_lap_filter5.exe
[XRT] ERROR: No devices found
../src/krnl_streaming_lap_host3.cpp:71 Error calling err = cl::Platform::get(&platforms), error code is: -1
どうやら /dev/dri/renderD128 が zocl に割り当てられてないとうまく動かないようです。試しに lima driver を rmmod してから zocl をロードして /dev/dri/renderD128 を zocl に割り当てると正常に動作しました。
再起動に失敗する
一度 DRM Lima を rmmod してから modprobe で再起動しようとすると、次のようなログがでて再起動に失敗します。
shell$ dmesg
:
(中略)
:
[ 1758.651570] lima fd4b0000.gpu: IRQ pmu not found
[ 1758.656223] lima fd4b0000.gpu: mmu gpmmu dte write test fail
[ 1758.662084] lima: probe of fd4b0000.gpu failed with error -5
この件に関しては現在保留中です。