これは R Advent Calendar 2020 の 23日目の記事です。
簡単な自己紹介
- Who are you?: justInCase という insurTech(保険会社のスタートアップ) の共同創業者で Chief Analytics Officer (CAO) として日々の業務に邁進してます。
- What do you like?: 好きなRの関数は
bquote(R4.0でslice=TRUE追加された)、好きな python module はastです。
Python と R で何か理解しよう思った時には、だいたいこの二つのページからたどるようにしています。
- https://docs.python.org/3.9/c-api/index.html
- https://cran.r-project.org/doc/manuals/r-release/R-ints.html
この記事の目的
- R 3.5.0 からR言語内部に導入された ALTREP の機能ついて解説する。
- なおALTREPはオルト-レップの二音節で発音するっぽい。(オルトにアクセント)。
- ソースコードは執筆時点の R 4.0.3 (https://github.com/wch/r-source/blob/tags/R-4-0-3/src/main/altrep.c) をベースにするので、ALTREP が導入されった 3.5.0 時点と異なる可能性があるのでご注意下さい
なお、次の Reference を理解している方には、この記事を読んでも新しい情報はないです。あしからず。
Summary
- ALTREP は R言語内部で使われるC言語レベルでの効率的なベクトルを扱うデータ型
- R 3.5.0 から
sexpinfoの構造が 32 bit から 64 bit へ変更があり、altという1bit flagで判定される - (既存の)VECTOR 型は DATAPTR (ヘッダ)と VECTOR (実データ)が一体の密なオブジェクトだったが、 ALTREP ではヘッダと実データを分離したオブジェクトなので、object share でより効率的な処理が可能
- ALTREP VECTOR はメタデータとして、NAの有無、sortedの有無等がmethodで判定できるので、ALTREPに対応済みな関数では効率的な実行が可能
-
x <- 1:1000000などの連続したsequece vector は ALTREP による compact 表現として扱われ、メモリに実データが展開されない - R言語レベルでの syntax, semantics に変更はないので、R 3.5.0 以前のRコードもそのまま 3.5.0 で動き、実行速度向上に寄与する
- 自身のpackage開発においての ALTREP の使い方は https://github.com/ALTREP-examples/ を参考にすると良い
- なお、 ALTREP がフル活用されている package として爆速の
vroomがあり、 source を参考にするとなかな発見がある。 - Rcpp は ALTREP object を expand してしまうが cpp11 はその心配なし
- なお、 ALTREP がフル活用されている package として爆速の
以上。といいたいところだが、もう少し解説する。
事前準備
SEXPREC について R Internals 、または少し古いが日本語の RのオブジェクトのC実装 を読むと良い。
ALTREP オブジェクトについて
R 3.4.4 までは sxpinfo header が 32 bit だったが、 R 3.5.0 から 64 bit へ変更された。1 bit flag alt にて ALTREP object の判定がされる。
# define ALTREP(x) ((x)->sxpinfo.alt)
// R 3.4.4
struct sxpinfo_struct {
SEXPTYPE type : TYPE_BITS;/* ==> (FUNSXP == 99) %% 2^5 == 3 == CLOSXP
* -> warning: `type' is narrower than values
* of its type
* when SEXPTYPE was an enum */
unsigned int obj : 1;
unsigned int named : 2;
unsigned int gp : 16;
unsigned int mark : 1;
unsigned int debug : 1;
unsigned int trace : 1; /* functions and memory tracing */
unsigned int spare : 1; /* currently unused */
unsigned int gcgen : 1; /* old generation number */
unsigned int gccls : 3; /* node class */
}; /* Tot: 32 */
// R 3.5.0 over
struct sxpinfo_struct {
SEXPTYPE type : TYPE_BITS;
/* ==> (FUNSXP == 99) %% 2^5 == 3 == CLOSXP
* -> warning: `type' is narrower than values
* of its type
* when SEXPTYPE was an enum */
unsigned int scalar: 1;
unsigned int obj : 1;
unsigned int alt : 1;
unsigned int gp : 16;
unsigned int mark : 1;
unsigned int debug : 1;
unsigned int trace : 1; /* functions and memory tracing */
unsigned int spare : 1; /* used on closures and when REFCNT is defined */
unsigned int gcgen : 1; /* old generation number */
unsigned int gccls : 3; /* node class */
unsigned int named : NAMED_BITS;
unsigned int extra : 32 - NAMED_BITS;
}; /* Tot: 64 */
3.5 からは alt 以外に scalar が導入され、length 1 の vector を効率良く判定できるようになった(話題が逸れるので割愛)。
ALTREP 対応のために導入された関数(method)は、この辺眺めるとイメージつきます。
R 言語からの操作
# `Error: cannot allocate vector of size 74.5 Gb` が出るはずが、
# 私の動作環境ではdocker ごと落ちる
$ docker run --rm -it rocker/r-ver:3.4.4 R -q --vanilla
> x <- 1:1e10
[username@ ~]
$ docker run --rm -it rocker/r-ver:3.5.0 R -q --vanilla
# (.Machine$integer.max < 1e10) == TRUE なので `x` は integerではなくreal型
> install.packages("lobstr") # for check object size
> x <- 1:1e10
> print(object.size(x), unit="GB")
74.5 Gb
> lobstr::obj_size(x)
680 B # メモリ上のサイズ
> .Internal(inspect(x))
@55f4d8b07b28 14 REALSXP g0c0 [NAM(3)] 1 : 10000000000 (compact)
> .Internal(altrep_class(x))
[1] "compact_realseq" "base"
.Internal(altrep_class(x)) (内部的には do_altrep_class()) という隠し関数で ALTREP オブジェクトの判定がR言語側で可能。
R_compact_intrange
さて、 1:100000 のような sequence はどのように扱われるか。それは do_colon() -> seq_colon() -> R_compact_intrange() -> new_compact_intseq() or new_compact_realseq() -> R_new_altrep() を最終的に呼び出す。 data1 が REALSXP の要素数3のベクターであり、要素数、開始値、1 or -1 (inc or dec) が渡される
static SEXP new_compact_intseq(R_xlen_t n, int n1, int inc)
{
if (n == 1) return ScalarInteger(n1);
if (inc != 1 && inc != -1)
error("compact sequences with increment %d not supported yet", inc);
/* info used REALSXP to allow for long vectors */
SEXP info = allocVector(REALSXP, 3);
REAL0(info)[0] = (double) n;
REAL0(info)[1] = (double) n1;
REAL0(info)[2] = (double) inc;
SEXP ans = R_new_altrep(R_compact_intseq_class, info, R_NilValue);
# ifndef COMPACT_INTSEQ_MUTABLE
MARK_NOT_MUTABLE(ans); /* force duplicate on modify */
# endif
return ans;
}
SEXP R_new_altrep(R_altrep_class_t aclass, SEXP data1, SEXP data2)
{
SEXP sclass = R_SEXP(aclass);
int type = ALTREP_CLASS_BASE_TYPE(sclass);
SEXP ans = CONS(data1, data2);
SET_TYPEOF(ans, type);
SET_ALTREP_CLASS(ans, sclass);
return ans;
}
実行速度
メタデータ(およびそれを使うmethod)のおかげで、次の確認は実行速度ほぼゼロ。ただし min(...), max(...), min(...) に関してはメタデータでの判定がなされていないのか、実行に時間はかかる。
> system.time(print(anyNA(x)))
[1] FALSE
user system elapsed
0 0 0
> system.time(print(length(x)))
[1] 1e+10
user system elapsed
0 0 0
> system.time(print(is.unsorted(x)))
[1] FALSE
user system elapsed
0 0 0
> system.time(print(max(x)))
[1] 1e+10
user system elapsed
17.974 0.000 17.972
> system.time(print(min(x)))
[1] 1
user system elapsed
17.844 0.012 17.865
なお、compact 表現でメモリ上に展開されていなくても、 ALTREP に対応済みの関数は Get_region をC言語上で使うことで計算可能となっている。(100億要素(=1e+10)を舐めるので、たとえC言語上の実行でも時間はかかる)
> system.time(print(mean(x)))
[1] 5e+09
user system elapsed
31.250 0.026 31.379
また sbject の serialize の際も compact 表現は compact のまま保存される
> saveRDS(x, file="/tmp/x-74gb-compact.rds")
> system("ls -l /tmp/x-74gb-compact.rds")
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 103 Dec 13 01:53 /tmp/x-74gb-compact.rds
# 103 bytes
Memory Mapped
- 遅延ロード
- 複数プロセス間のメモリ共有(Apatch Arrow)
疲れより省略(詳しい方お願いします)。
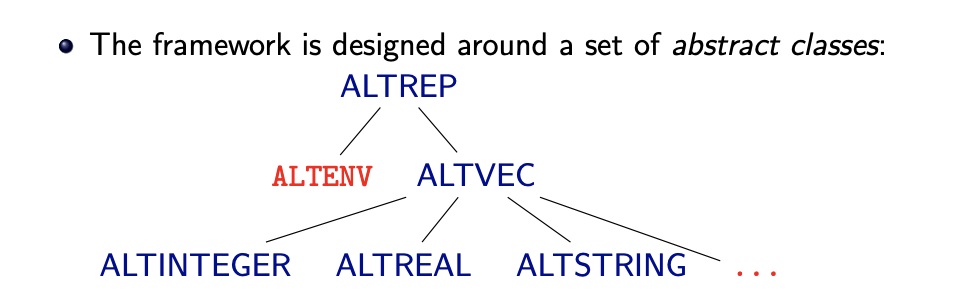
Classの構造について
source: slide 16 of Reference #2
説明に需要が無いと思われるので https://svn.r-project.org/R/branches/ALTREP/ALTREP.html#general_objects を読んでください。
package 開発者としてのALTREPの利用方法
Reference #3, #4, vroom package などを参考にしてください。(ここに書くには長すぎる)
なお Rcpp のVector型で受けると expand してしまう。 rcpp11 では compact のままである。この辺りの issue が open のまま議論されている。
# $ docker run --rm -it rocker/r-ver:4.0.3 R -q --vanilla
# install.packages("Rcpp")
x1 <- 1:100000
Rcpp::sourceCpp(code=r'|
# include "Rcpp.h"
using namespace Rcpp;
// [[Rcpp::export]]
Rcpp::IntegerVector identity_rcpp(Rcpp::IntegerVector x) {
return x;
}
|')
.Internal(inspect(x1))
# @7f95df94bb60 13 INTSXP g0c0 [REF(65535)] 1 : 100000 (compact)
invisible(identity_rcpp(x1))
.Internal(inspect(x1))
# @7f95df94bb60 13 INTSXP g0c0 [REF(65535)] 1 : 100000 (expanded)
# install.packages("cpp11")
cpp11::cpp_source(code = r'|
# include "cpp11/integers.hpp"
[[cpp11::register]]
cpp11::integers identity_cpp11(cpp11::integers x) {
return x;
}
|')
x2 <- 1:100000
.Internal(inspect(x2))
# @7f95df9497a8 13 INTSXP g0c0 [REF(65535)] 1 : 100000 (compact)
invisible(identity_cpp11(x2))
.Internal(inspect(x2))
# @7f95df9497a8 13 INTSXP g0c0 [REF(65535)] 1 : 100000 (compact)
以上。後半のグダグダ感は否めないが、1mmでもどなたかの理解の助けになったならば幸いです。こういうマニアックな話が好きな方、最近オフィスが茅場町に引っ越したのですが、ぜひ遊びに来てください。DMおまっちしております。
References
- https://svn.r-project.org/R/branches/ALTREP/ALTREP.html
- https://homepage.divms.uiowa.edu/~luke/talks/uiowa-2018.pdf
- https://purrple.cat/blog/2018/10/14/altrep-and-cpp/
- https://www.bioconductor.org/help/course-materials/2020/BiocDevelForum/17-ALTREP2.pdf
- https://speakerdeck.com/jimhester/cpp11-welding-r-and-c-plus-plus?slide=64
- https://github.com/wch/r-source/blob/tags/R-4-0-3/src/include/R_ext/Altrep.h
- https://github.com/wch/r-source/blob/tags/R-4-0-3/src/main/altrep.c