はじめに
以前、「機械学習の分類」で取り上げたアルゴリズムについて、その理論とpythonでの実装、scikit-learnを使った分析についてステップバイステップで学習していく。個人の学習用として書いてるので間違いなんかは大目に見て欲しいと思います。
前回、2クラス分類を多クラス分類に拡張しました。今回は実際にPythonで実装してみます。
参考にしたのは以下のサイト。ありがとうございます。
実装の方針
以前実装したロジスティック回帰を多クラスに拡張してみようと思います。方法は
- One-vs-Rest
- 多クラスソフトマックス
でやってみようと思います。
分類に使用するデータ
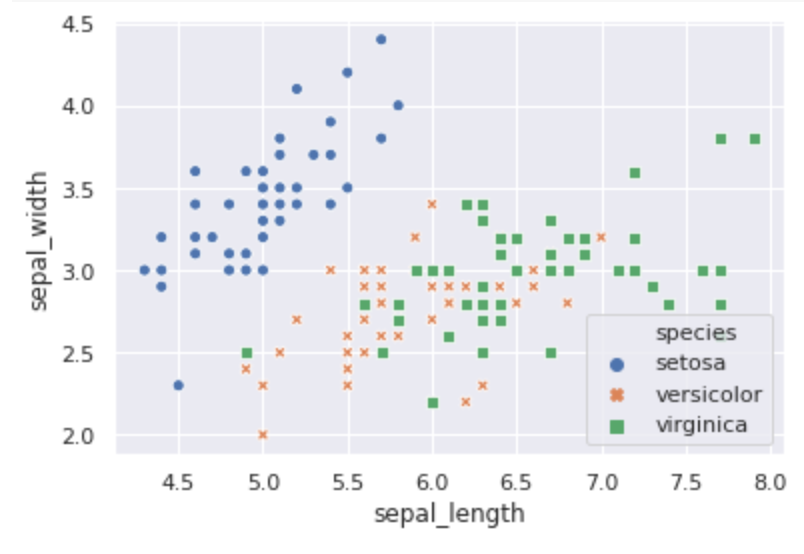
分類にはアヤメのデータを使います。4つの特徴量(sepal_length,sepal_width,petal_length,petal_width)を使い、3つのクラス(setosa,versicolor,virginica)に分類します。
以下、見やすくするためにsepal_lengthとsepal_widthを使って分類を実装していきます。
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import seaborn as sns
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
%matplotlib inline
from sklearn.datasets import load_iris
sns.set()
iris = sns.load_dataset("iris")
ax = sns.scatterplot(x=iris.sepal_length, y=iris.sepal_width,
hue=iris.species, style=iris.species)
One-vs-Rest
One-vs-Restは2クラス分類器をラベルのクラス分作って学習し、最後に一番もっともらしい値を使います。ロジスティック回帰は確率値を出力するので、確率が一番高い分類器の分類を採用します。
前回使ったロジスティック回帰のコードを少し変更したLogisticRegressionクラスを使います。どの値を採用するかを確率で決めるのでpredict_probaメソッドを作りました。
from scipy import optimize
class LogisticRegression:
def __init__(self):
self.w = None
def sigmoid(self, a):
return 1.0 / (1 + np.exp(-a))
def predict_proba(self, x):
x = np.hstack([1, x])
return self.sigmoid(self.w.T @ x)
def predict(self, x):
return 1 if self.predict_proba(x)>=0.5 else -1
def cross_entropy_loss(self, w, *args):
def safe_log(x, minval=0.0000000001):
return np.log(x.clip(min=minval))
t, x = args
loss = 0
for i in range(len(t)):
ti = 1 if t[i] > 0 else 0
h = self.sigmoid(w.T @ x[i])
loss += -ti*safe_log(h) - (1-ti)*safe_log(1-h)
return loss/len(t)
def grad_cross_entropy_loss(self, w, *args):
t, x = args
grad = np.zeros_like(w)
for i in range(len(t)):
ti = 1 if t[i] > 0 else 0
h = self.sigmoid(w.T @ x[i])
grad += (h - ti) * x[i]
return grad/len(t)
def fit(self, x, y):
w0 = np.ones(len(x[0])+1)
x = np.hstack([np.ones((len(x),1)), x])
self.w = optimize.fmin_cg(self.cross_entropy_loss, w0, fprime=self.grad_cross_entropy_loss, args=(y, x))
@property
def w_(self):
return self.w
One-vs-Restクラスを実装します。あとでアルゴリズムの比較に使うので、どれくらい正解しているかを計算するaccuracy_scoreメソッドも実装しました。
from sklearn.metrics import accuracy_score
class OneVsRest:
def __init__(self, classifier, labels):
self.classifier = classifier
self.labels = labels
self.classifiers = [classifier() for _ in range(len(self.labels))]
def fit(self, x, y):
y = np.array(y)
for i in range(len(self.labels)):
y_ = np.where(y==self.labels[i], 1, 0)
self.classifiers[i].fit(x, y_)
def predict(self, x):
probas = [self.classifiers[i].predict_proba(x) for i in range(len(self.labels))]
return np.argmax(probas)
def accuracy_score(self, x, y):
pred = [self.labels[self.predict(i)] for i in x]
acc = accuracy_score(y, pred)
return acc
実際に先ほどのデータを使って分類します。
model = OneVsRest(LogisticRegression, np.unique(iris.species))
x = iris[['sepal_length', 'sepal_width']].values
y = iris.species
model.fit(x, y)
print("accuracy_score: {}".format(model.accuracy_score(x,y)))
accuracy_score: 0.8066666666666666
正解率81%はあまり良くないですね。どう分類されたか可視化してみましょう。
可視化にはmatplotlibのcontourfメソッドを使います。格子点上の値がどれに分類されるかで着色します。
from matplotlib.colors import ListedColormap
x_min = iris.sepal_length.min()
x_max = iris.sepal_length.max()
y_min = iris.sepal_width.min()
y_max = iris.sepal_width.max()
x = np.linspace(x_min, x_max, 100)
y = np.linspace(y_min, y_max, 100)
data = []
for i in range(len(y)):
data.append([model.predict([x[j], y[i]]) for j in range(len(x))])
xx, yy = np.meshgrid(x, y)
cmap = ListedColormap(('blue', 'orange', 'green'))
plt.contourf(xx, yy, data, alpha=0.25, cmap=cmap)
ax = sns.scatterplot(x=iris.sepal_length, y=iris.sepal_width,
hue=iris.species, style=iris.species)
plt.show()

見てわかるように、setosaはちゃんと分類できていますが、残りの2クラスは混ざっているので正解率が少し低く出ているみたいです。とりあえずこんなもんでしょう。
マルチクラスソフトマックス
ロジスティック回帰でソフトマックス分類するためのLogisticRegressionMultiクラスを実装します。
評価するための誤差関数にクロスエントロピー誤差を利用し、最急勾配降下法を使ってパラメータを求めました。だいぶ適当に作りました、すみません
from sklearn.metrics import accuracy_score
class LogisticRegressionMulti:
def __init__(self, labels, n_iter=1000, eta=0.01):
self.w = None
self.labels = labels
self.n_iter = n_iter
self.eta = eta
self.loss = np.array([])
def softmax(self, a):
if a.ndim==1:
return np.exp(a)/np.sum(np.exp(a))
else:
return np.exp(a)/np.sum(np.exp(a), axis=1)[:, np.newaxis]
def cross_entropy_loss(self, w, *args):
x, y = args
def safe_log(x, minval=0.0000000001):
return np.log(x.clip(min=minval))
p = self.softmax(x @ w)
loss = -np.sum(y*safe_log(p))
return loss/len(x)
def grad_cross_entropy_loss(self, w, *args):
x, y = args
p = self.softmax(x @ w)
grad = -(x.T @ (y-p))
return grad/len(x)
def fit(self, x, y):
self.w = np.ones((len(x[0])+1, len(self.labels)))
x = np.hstack([np.ones((len(x),1)), x])
for i in range(self.n_iter):
self.loss = np.append(self.loss, self.cross_entropy_loss(self.w, x, y))
grad = self.grad_cross_entropy_loss(self.w, x, y)
self.w -= self.eta * grad
def predict(self, x):
x = np.hstack([1, x])
return np.argmax(self.softmax(x @ self.w))
def accuracy_score(self, x, y):
pred = [self.predict(i) for i in x]
y_ = np.argmax(y, axis=1)
acc = accuracy_score(y_, pred)
return acc
@property
def loss_(self):
return self.loss
LogisticRegressionMultiへの入力はOne-Hot-Encodingされたラベルを使います。これはPandasのget_dummiesを使うと簡単です。(作った後に思ったんですが、クラス内でget_dummies使えば良かったですね)
model = LogisticRegressionMulti(np.unique(iris.species), n_iter=10000, eta=0.1)
x = iris[['sepal_length', 'sepal_width']].values
y = pd.get_dummies(iris['species']).values
model.fit(x, y)
print("accuracy_score: {}".format(model.accuracy_score(x, y)))
accuracy_score: 0.8266666666666667
正解率83%くらいですね。誤差の履歴を見てみると収束しているようなので、こんなもんなのでしょう。

また、先ほどと同じようにどう分類されるかを着色してみます。

scikit-learnのロジスティック回帰と比較する
最後に、全ての特徴量を使い、今回作った分類器とscikit-learnのLogisticRegressionクラスを比較します。
| 手法 | accuracy_score |
|---|---|
| OneVsRest | 0.98 |
| LogisticRegressionMulti | 0.98 |
| sklearn LogisticRegression | 0.973 |
今回の実装でもアヤメの分類くらいなら悪くないスコアを出すことができてるみたいですね。
まとめ
ロジスティック回帰を使った多クラス分類を実装しました。ほかの分類器でも似たような考え方でいけるような気がします。特に、ニューラルネットワークではマルチクラスソフトマックスはよく使うやり方なので理論的な部分を理解するのは後々役に立つと思いました。