巡回セールスマン問題とは
セールスマンが複数の地点を巡回するとします。ある地点から出発し,全ての地点を訪問して,出発地点に戻る場合,どのような順番でそれぞれの地点を回るのが最短経路であるかを探し出す、という問題です。
この問題を、遺伝的アルゴリズムで解いてみました。
遺伝的アルゴリズムとは
Wikipediaから引用。
遺伝的アルゴリズム(いでんてき-、英語:genetic algorithm、略称:GA)とは、1975年にミシガン大学のジョン・H・ホランド(John Henry Holland)によって提案された近似解を探索するメタヒューリスティックアルゴリズムである。人工生命同様、偶然の要素でコンピューターの制御を左右する。4つの主要な進化的アルゴリズムの一つであり、その中でも最も一般的に使用されている。
詳細な説明は、Wikipedaiを読んでいただくとして、ここで採用したアルゴリズムの流れを簡単に説明します。
- N固体を用意し、現世代のリストに入れる。
- 評価関数を適用し、上位X個を次世代のリストへ入れる。(淘汰)
- 交叉によりY個の子孫を作り、次世代リストに入れる (交叉は後述)
- 突然変異により子孫をつくり、次世代リストに入れる このとき、次世代の固体がN個になるように調節する。
- 次世代の固体を、現世代のリストに移し変え、2-4をG世代繰り返す。
- もっとも評価の良い個体を「解」とする。
これだけを読めばそれほど複雑なことをやっているわけではないことがわかると思います。
問題は、交叉や突然変異をどのように実装するのかということです。
これらを効率よく行うには、巡回する都市の経路データの表現形式が課題となってきます。
遺伝的アルゴリズムで巡回セールスマン問題解く
例えば、それぞれの都市をA,B,C,D,Eという5つの都市があったとします。
それぞれの都市の位置は、(x,y)という座標で表せますが、それをそのまま配列等に格納したのでは、いろいろと厄介なコードを書かなくてはなりません。
そこで、基準となるルートを設定し、未訪問都市の何番目にあたるかを整数のリストで表すこととします。
この経路表現を順序表現、一方、元のABCDEとう経路表現をここではパス表現と言うこととします。
参照: https://www.ite.or.jp/contents/keywords/FILE-20160413113035.pdf
例えば、基準経路 ABCDEに対して、経路 ACEDBを、順序表現で表すと [01210]となります。
最初の 0 ですが、最初訪問する都市が未訪問都市リストの0番目(A)にあたることを表しています。
次に訪れるのは、(このとき、未訪問都市リストからAは除去されている)1番目の都市 C です。
そして、次に訪れるのは、未訪問都市リストの2番目の都市の E となります。
4番目に訪れる都市は、1番目の D。最後は、未訪問都市リストの0番目の都市の B となります。
このような表現をとることで、遺伝的アルゴリズムの交叉が簡単に行えるようになります。
交叉とは、2つの固体(経路)から新しい子孫(経路)を残す方法のひとつです。ある点を選び、その後ろの経路を入れ替えるという操作でこれを実現します。
例えば、固体X [01010],固体Y [01210] で考えると3番目以降(0から開始)を入れ替えると [01010], [01210] という固体ができます。
これを元の経路に直してみると、ACBED, ACEDB という経路となります。
こうしてできた経路は、必ず正しい経路となります。同じ都市が重複するようなことは起こりえません。
ここでは、一点交叉の例を示しましたが、このプログラムでは、2点交叉と一様交叉といった交叉も採用しています。
突然変異については、いったんパス表現に戻してから、2つの都市の入れ替えなどを行っています。
実行例
以下に、実行例を示します。
なお、当記事の最後にCodePenのページを貼り付けていますので、実際に動かしてみることができます。
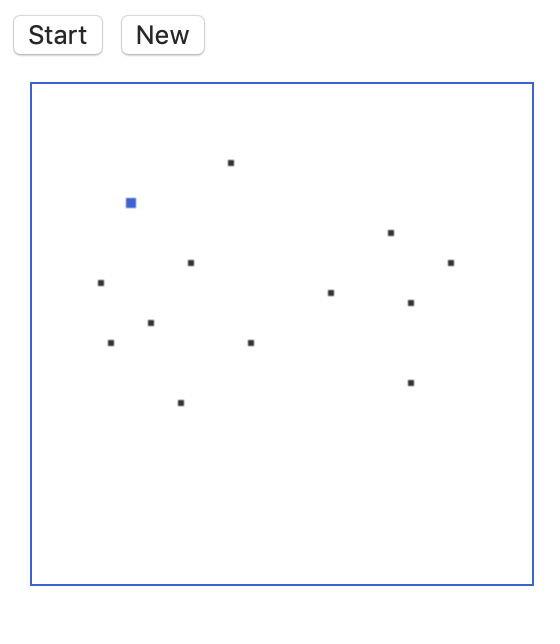
■初期状態
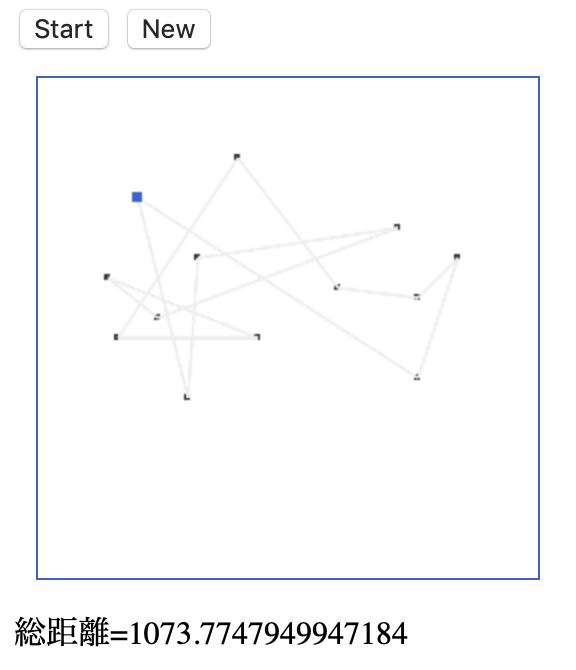
■実行途中
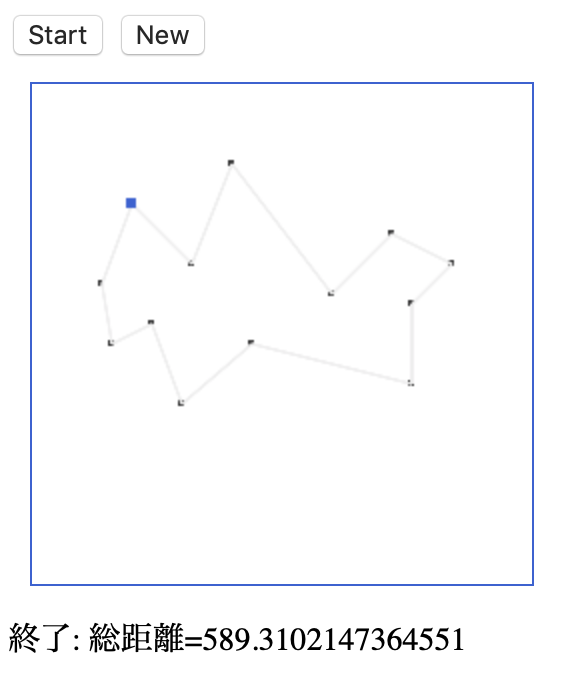
■実行終了
なお、作成したプログラムは、もう少しチューニングが必要なようで、(都市の数が多いと)最適解が得られないこともあります。
僕はこの手の専門家ではないし、十分な検証時間をとることもできないので、どこをどう改良したらよいのかまでは、検討できていません。
この手のアルゴリズムは、最善手を求めるのではなく、ある時間内に、できるだけ良い手を探し出すのが目的ですから、これでも目的は達成できてると考えることもできますが...
興味のある人は、ぜひこのプログラムを改良してみてください。
プログラムコード
以下、html と JavaScriptのソースコードを掲載します。
tsp.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<title>GA</title>
<style>
canvas {
border: solid 1px #3661d6;
margin: 11px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div>
<input id="startButton" type="button" value="Start" >
<input id="newButton" type="button" value="New" >
</div>
<div>
<canvas id="mycanvas"></canvas>
</div>
<div id="status"></div>
<script type="module">
import { main } from './program.js';
main();
</script>
</body>
</html>
program.js
import { MyCanvas } from './canvas.js';
import { PathGenerator } from './pathGenerator.js';
import { TravelingSalesmanProblem } from './travelingSalesmanProblem.js';
import { Gene } from './gene.js';
import { getRandom } from './getRandom.js';
Array.prototype.insert = function ( index, item ) {
this.splice( index, 0, item );
};
Array.prototype.shuffle = function () {
for (let i = this.length - 1; i > 0; i--) {
const j = getRandom(1, i + 1);
[this[i], this[j]] = [this[j], this[i]];
}
return this;
};
Array.prototype.removeAt = function (index) {
this.splice(index,1);
};
Array.prototype.swap = function (i, j) {
let temp = this[i];
this[i] = this[j];
this[j] = temp;
};
export class Program {
constructor(width, height) {
this._canvas = new MyCanvas('mycanvas', width, height);
// 求める答え
this._ans = null;
// 位置を保持したリスト
// 初期の位置を設定する
this._path = PathGenerator.makeInitialPath();
this.paint(this._ans);
this.prevans = null;
}
run() {
document.getElementById('startButton')
.addEventListener('click', () => this.start(), false);
document.getElementById('newButton')
.addEventListener('click', () => this.newState(), false);
};
start() {
Gene.setOrigin(this._path);
let tsp = new TravelingSalesmanProblem();
tsp.OnChanged = (tsp, best) => {
this._ans = best;
this.paint(this._ans);
};
tsp.initialize(this._path);
let path = tsp.evaluate()[0];
this.paint(path);
this._ans = tsp.solve().then(() => {
this.paint(this._ans, true);
});
};
newState() {
this._ans = null;
this._path = PathGenerator.makeRandom(this._canvas.width, this._canvas.height);
this.paint(this._ans);
};
// 描画 (初期状態の描画 と 途中の状態の描画)
paint(ans, end=false) {
if (ans != null) {
if (ans.encode()[0] !== 0)
console.log("error");
var list = ans.decode();
this._canvas.clearAll();
for (var p of this._path) {
this._canvas.drawPoint(p.X, p.Y, '#333', 3);
}
for (let ix = 0; ix < list.length -1; ix++) {
let p1 = list[ix];
let p2 = list[ix+1]
this._canvas.drawLine(p1.X, p1.Y, p2.X, p2.Y, '#eee', 1);
}
let p1 = list[list.length -1];
let p2 = list[0]
this._canvas.drawLine(p1.X, p1.Y, p2.X, p2.Y, '#eee', 1);
this._canvas.drawPoint(this._path[0].X, this._path[0].Y, '#3661d6', 5);
this.prevans = list;
let div = document.querySelector('#status');
if (end) {
div.textContent = '終了: 総距離=' + ans.getScore();
} else {
div.textContent = '総距離=' + ans.getScore();
}
} else {
this._canvas.clearAll();
for (var p of this._path) {
this._canvas.drawPoint(p.X, p.Y, '#333', 3);
}
this._canvas.drawPoint(this._path[0].X, this._path[0].Y, '#3661d6', 5);
}
}
}
export function main() {
window.onload = function() {
var program = new Program(250, 250);
program.run();
};
}
pathGenerator.js
import { Point } from './point.js';
import { getRandom } from './getRandom.js';
export class PathGenerator {
static makeInitialPath() {
var path = [];
path.push(new Point(50, 60));
path.push(new Point(75, 160));
path.push(new Point(80, 90));
path.push(new Point(180, 75));
path.push(new Point(60, 120));
path.push(new Point(35, 100));
path.push(new Point(110, 130));
path.push(new Point(40, 130));
path.push(new Point(100, 40));
path.push(new Point(150, 105));
path.push(new Point(190, 110));
path.push(new Point(210, 90));
path.push(new Point(190, 150));
return path;
}
static makeRandom(width, height) {
var path = [];
let count = getRandom(7, 11);
for (let i = 0; i < count; i++) {
let x = getRandom(15, width-15);
let y = getRandom(15, height-15);
path.push(new Point(x, y));
}
return path;
}
}
point.js
export class Point {
constructor(x, y) {
this.X = x;
this.Y = y;
}
// 等しいか
equals(other) {
return this.X === other.X && this.Y === other.Y;
}
}
getRandom.js
// min以上 から max未満の乱数を得る (整数)
export function getRandom(min, max) {
return Math.floor(Math.random() * (max - min) + min);
}
travelingSalesmanProblem.js
import { Point } from './point.js';
import { Gene } from './gene.js';
import { getRandom } from './getRandom.js';
const NumOfPopulation = 50;
const NumOfSurvival = 10;
var NumOfMutation = 5;
var NumOfCróssing = NumOfPopulation - NumOfSurvival - NumOfMutation;
const LimitOfNoEvolution = 1000;
// 遺伝的アルゴリズムで巡回セールスマン問題を解く
export class TravelingSalesmanProblem {
constructor () {
// 現世代 個体群
this._population1 = [];
this._population2 = [];
// 個体数
this._mutateRate = 10;
this.OnChanged = null;
this.minscore = Number.MAX_SAFE_INTEGER;
this.bestGene = null;
this.betterGene = null;
this.count = 0;
}
// 初期化
initialize(original) {
// original が仮の巡回ルートとする
this._population1.push(new Gene(original));
// 適当にシャッフルして他の巡回ルートも作成する
for (let i = 1; i < NumOfPopulation; i++) {
this._population1.push(new Gene(original.shuffle()));
}
}
async solve() {
if (this.OnChanged != null) {
this.OnChanged(this, this._population1[0]);
}
// 次世代の 個体群を用意
this.minscore = Number.MAX_SAFE_INTEGER;
this.bestGene = null;
this.betterGene = null;
this.count = 0;
// 安定するまで繰り返す LimitOfNoEvolution回繰り返してもスコアが更新されなければ安定したと判定
while (this.count < LimitOfNoEvolution) {
await this.next();
}
return this.bestGene;
}
next() {
return new Promise( resolve => {
setTimeout(() => {
this.count++;
this._population1 = this.evaluate();
// 現世代で最も良い遺伝子を記憶する
this.betterGene = this._population1[0];
// その評価関数を呼び出し、scoreに入れる
let score = this.betterGene.getScore();
if (score < this.minscore) {
// 現世代でスコアが良くなっていれば下記の処理をする
// 世代が上がっても進化しないこともあり得る。
this.count = 0;
this.minscore = score;
this.bestGene = this.betterGene.clone();
if (this.OnChanged != null) {
this.OnChanged(this, this.bestGene);
}
}
if (this.count % 20 === 19) {
// なかなか進化しない場合は、新しい種を入れる必要がある。
// 変異率を変えることで対応
this._mutateRate++;
// 上位のいくつかを削除する
this._population1.splice(4,5);
}
// 選択・淘汰
this._population2 = this.take(this._population1, NumOfSurvival);
// 交叉(自分よりも良い子孫だけが登録される)
let children = this.take(this.bearByCrossover(), NumOfCróssing);
this._population2 = this._population2.concat(children);
// 突然変異 (自分よりも良い子孫だけが登録される)
let children2 = this.take(this.bearByMutate(), NumOfMutation);
this._population2 = this._population2.concat(children2);
// 不足分を補う
// ここでは、無条件に変異させたものを登録することで、良い子孫ができることを期待
let shortage = NumOfPopulation - this._population2.length;
for (let i = 0; i < shortage; i++) {
var gene = this._population2[i];
this._population2.push(gene.bean());
}
this._population1 = this._population2;
resolve();
}, 0);
});
}
// 評価をし、良い順に並び替える。
evaluate() {
var sorted = this._population1.slice()
.sort(g => g.getScore())
.filter((g, i, self) => self.findIndex(e => e.equals(g)) === i);
return sorted;
}
take(sequence, n) {
let result = [];
let i = 0;
for (let item of sequence) {
if (++i > n)
return result;
result.push(item);
}
return result;
}
// 子孫を残す (交叉)
*bearByCrossover() {
let count = this._population1.length;
for (let index1 = 0; index1 < 10; index1++) { // できるだけ良い遺伝子と交叉させるため
for (let i = 0; i < NumOfPopulation; i++) {
let index2 = getRandom(index1+1, count);
let g1 = this._population1[index1];
let g2 = this._population1[index2];
if (getRandom(0, 2) === 0) {
for (var x of g1.crossover2(g2))
yield x;
} else {
for (var x of g1.crossover(g2))
yield x;
}
}
}
}
// 子孫を残す (変異)
*bearByMutate() {
for (let p of this._population1) {
for (var x of p.mutate())
yield x;
}
}
}
gene.js
import { Point } from './point.js';
import { getRandom } from './getRandom.js';
export class Gene {
// コンストラクタ (route: Point[])
constructor (route) {
this._size = 0;
this._codes = [];
if (route.length === 0) {
// route: int[]
let codes = route;
this._size = codes.length;
this._codes = codes.slice(); // clone()
} else if (route[0].X === undefined) {
let codes = route;
this._size = codes.length;
this._codes = codes.slice(); // clone()
} else {
// route: Point[]
this._size = route.length;
this._codes = this._encode(route);
}
};
// 最初の位置を記憶しておく。Encode、Decodeするのに必要。
static setOrigin(original) {
Gene.original = original.slice();
}
// 複製する
clone() {
return new Gene(this.encode());
}
// 順序表現に変換する route: Point[]
_encode(route) {
let codes = [];
let temp = Gene.original.slice();
for (let i = 0; i < this._size; i++) {
let n = temp.findIndex(x => x.equals(route[i]));
temp.removeAt(n);
codes.push(n);
}
return codes.slice();
}
// 順序表現に変換する
encode() {
return this._codes;
}
// 順序表現をPointのリストに戻す
decode() {
let route = [];
let temp = Gene.original.slice();
for (let code of this._codes) {
route.push(temp[code]);
temp.removeAt(code);
}
return route;
}
// 評価
getScore() {
let score = 0;
let route = this.decode();
for (let i = 0; i < route.length; i++) {
let a = route[i];
let b = (i == route.length - 1)
? route[0]
: route[i + 1];
score += this.getDistance(a, b);
}
return score;
}
// 距離を求める
getDistance(a, b) {
return Math.sqrt(Math.abs(a.X - b.X) * Math.abs(a.X - b.X) + Math.abs(a.Y - b.Y) * Math.abs(a.Y - b.Y));
}
// 変異 パスの値を変更する
// 改善されなければ、返さない
*mutate() {
let val = this.getScore();
let array = this.encode().slice();
for (let i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
let seed = getRandom(1, array.length - 3);
for (let j = 0; j < seed; j++) {
let ix = getRandom(1, this._size - 1);
array[ix] = getRandom(0, array.length - ix);
}
let newGene = new Gene(array);
if (val > newGene.getScore())
yield newGene;
}
}
// 交叉
*crossover2(spouse) {
// 2点交叉
let gene1 = this.encode();
let gene2 = spouse.encode();
let ix1 = getRandom(1, this._size - 1);
let temp = gene1[ix1];
gene1[ix1] = gene2[ix1];
gene2[ix1] = temp;
let ix2 = getRandom(ix1+1, this._size);
temp = gene1[ix2];
gene1[ix2] = gene2[ix2];
gene2[ix2] = temp;
let child = new Gene(gene1);
if (child.getScore() < this.getScore())
yield child;
let child2 = new Gene(gene2);
if (child2.getScore() < spouse.getScore())
yield child2;
}
*crossover(spouse) {
let score = Math.min(this.getScore(), spouse.getScore());
// 一様交叉
let temp1 = this.encode();
let temp2 = spouse.encode();
for (let i = 1; i < this._size - 1; i++) {
if (getRandom(0, 2) == 0) {
let temp = temp1[i];
temp1[i] = temp2[i];
temp2[i] = temp;
}
}
let child = new Gene(temp1);
if (child.getScore() < score)
yield child;
child = new Gene(temp2);
if (child.getScore() < score)
yield child;
}
// 無条件に子孫を残す ここではSlideを採用
bean() {
return new Gene(this.slide(this.decode()));
}
// 等しいか
equals(other) {
if (this == null)
return false;
if (this.encode == null)
return false;
if (other == null)
return false;
if (other.encode == null)
return false;
var obj1 = this.encode();
let obj2 = other.encode();
for (let i = 0; i < obj1.length; i++) {
if (obj1[i] !== obj2[i]) {
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
// ランダムに選んだ2つの間を反転させる。
reverse(list) {
let ix1 = getRandom(1, this._size - 1);
let ix2 = getRandom(ix1 + 1, this._size);
let array = [];
for (let i = 0; i < ix1; i++)
array.push(list[i]);
for (let i = ix2; i >= ix1; i--)
array.push(list[i]);
for (let i = ix2 + 1; i < list.length; i++)
array.push(list[i]);
return array;
}
// ランダムに選んだ値の位置を変更する。
slide(list) {
let ix1 = getRandom(1, this._size - 2);
let ix2 = getRandom(ix1+1, this._size - 1);
let temp = list.slice();
let pt = temp[ix1];
temp.removeAt(ix1);
temp.insert(ix2, pt);
return temp;
}
// 2つのPointを入れ替える
swap(list) {
let child = list.slice();
let ix1 = getRandom(1, this._size);
let ix2 = getRandom(1, this._size);
let temp = child[ix1];
child[ix1] = child[ix2];
child[ix2] = temp;
return child;
}
// デバッグ用
toString() {
let s = _codes.map(n => n.toString()).join(',');
let s2 = this.decode().map(n => n.X.toString()).join(',');
return s + " - " + s2 + " - " + this.getScore().toString();
}
}
board.js
import { Cell } from './cell.js';
// Cellを管理する
export class Board {
// コンストラクタ
constructor(w, h) {
this.width = w;
this.height = h;
this.map = new Array((this.width) * (this.height));
this.clearAll();
this.onChange = {};
}
// Location から Indexを求める
toIndex(x, y) {
return x + y * (this.width);
};
// IndexからLocationを求める
toLocation(index) {
return { x: index % (this.width), y: Math.floor(index / (this.width)) };
};
// 盤上のすべての位置(index)を列挙する
getAllIndexes() {
var list = [];
for (var y = 0; y < this.height; y++) {
for (var x = 0; x < this.width; x++) {
list.push(this.toIndex(x, y));
}
}
return list;
};
// 全てのCellをクリアする
clearAll() {
this.getAllIndexes().forEach(ix => {
this.map[ix] = new Cell();
});
};
// 反転する
reverse(index) {
var cell = this.map[index];
cell.toggle();
this.onChange(index, cell);
};
// 位置の補正 はみ出たらぐるっと回る
corectIndex(x, y) {
x = (x < 0) ? this.width - 1 : x;
y = (y < 0) ? this.height - 1 : y;
x = (x >= this.width) ? 0 : x;
y = (y >= this.height) ? 0 : y;
return this.toIndex(x,y);
// { this.ToIndex(x % (this.width + 1), y % (this.height + 1));
};
// 周りの生存者の数を数える
countAround(index) {
var location = this.toLocation(index);
var arounds = [
{ x: location.x-1, y: location.y-1 },
{ x: location.x-1, y: location.y },
{ x: location.x-1, y: location.y+1 },
{ x: location.x, y: location.y-1 },
{ x: location.x, y: location.y+1 },
{ x: location.x+1, y: location.y-1 },
{ x: location.x+1, y: location.y },
{ x: location.x+1, y: location.y+1 },
];
return arounds
.map(loc => this.corectIndex(loc.x, loc.y))
.filter(ix => this.map[ix].IsAlive)
.length;
};
// 生死を決める
survive() {
var count = 0;
this.getAllIndexes().forEach(ix => {
var cell = this.map[ix];
if (cell.survive(this.countAround(ix)))
count++;
});
if (count > 0) {
this.getAllIndexes().forEach(ix => {
var cell = this.map[ix];
if (cell.nextStage()) {
this.onChange(ix, cell);
}
});
}
return count;
};
}
canvas.js
export class MyCanvas {
constructor (id, width, height) {
this.canvas = document.getElementById(id);
this.ctx = this.canvas.getContext('2d');
if (width)
this.ctx.canvas.width = width;
if (height)
this.ctx.canvas.height = height;
this.width = this.ctx.canvas.width;
this.height = this.ctx.canvas.height;
// ユーザが定義するイベントハンドラ
this.onClick = null;
//let self = this;
this.canvas.onclick = (e) => {
let x = e.clientX - this.canvas.offsetLeft;
let y = e.clientY - this.canvas.offsetTop;
if (this.onClick)
this.onClick(x, y);
};
}
// 線
drawLine(x1, y1, x2, y2, color = null, width = 1) {
this.ctx.save();
if (color != null)
this.ctx.strokeStyle = color;
this.ctx.lineWidth = width;
this.ctx.beginPath();
this.ctx.moveTo(x1, y1);
this.ctx.lineTo(x2, y2);
this.ctx.closePath();
this.ctx.stroke();
this.ctx.restore();
}
drawPoint(x1, y1, color, size = 3) {
this.ctx.save();
this.ctx.beginPath();
this.ctx.fillStyle = color;
this.ctx.fillRect(x1 - Math.ceil(size/2), y1-Math.ceil(size/2), size, size);
this.ctx.restore();
}
// すべてをクリア
clearAll() {
this.ctx.clearRect(0, 0, this.width, this.height);
}
}
CodePenのページを埋め込む
CodePenのページを埋め込んでみました。
なお、このプログラムはCodePenの制限で無限ループと判定されてしまい(絶対に、無限ループはしないのですが)、実行が途中で止まう場合があるようです。
最後まで動作を確認したい場合は、掲載したコードを手元の環境で動作させてください。