概要
HOG特徴量とSVMで物体検出をやってみたいと思います。よくある例は二値画像やマークなので、自然画像で試してみたいと思います。データは前回の記事と同じものを利用します。
前回の記事
データ
今回も丸太を検出してみようと思います。データはphotoACからダウンロードしました。推論対象画像はこの画像とこの画像のSサイズを使用し、学習用画像はこの画像のMサイズから正例と負例を10枚ずつトリミングしました。
推論対象画像1
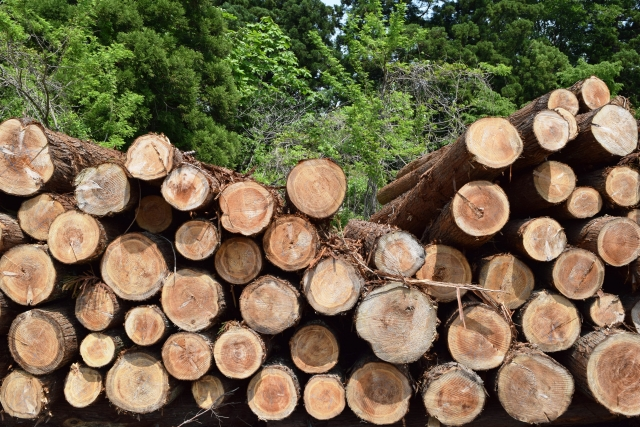

推論対象画像2
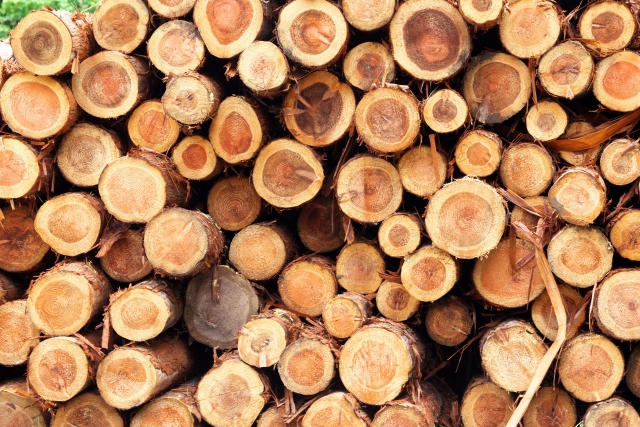

正例画像
負例画像

プログラム
下記のライブラリをインストールします。
pip install numpy
pip install matplotlib
pip install opencv-python
pip install scikit-learn
下記は物体検出を実行するコードです。
import json
from typing import Tuple
import cv2
import numpy as np
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
from sklearn.exceptions import NotFittedError
from sklearn.svm import SVC
def plot_box(img, boxes):
result_img = img.copy()
for box in boxes:
result_img = cv2.rectangle(
result_img,
pt1=box[:2],
pt2=box[2:],
color=(255, 0, 0),
thickness=2)
return result_img
def nms(boxes, scores, nms_thresh=0.5, top_k=200):
"""
boxes: np.array([[x1, y1, x2, y2],...])
"""
keep = []
if len(boxes) == 0:
return keep
x1 = boxes[:, 0]
y1 = boxes[:, 1]
x2 = boxes[:, 2]
y2 = boxes[:, 3]
area = (x2 - x1) * (y2 - y1)
idx = np.argsort(scores, axis=0)
idx = idx[-top_k:]
while len(idx) > 0:
last = len(idx)-1
i = idx[last] # index of current largest val
keep.append(i)
xx1 = np.maximum(x1[i], x1[idx[:last]])
yy1 = np.maximum(y1[i], y1[idx[:last]])
xx2 = np.minimum(x2[i], x2[idx[:last]])
yy2 = np.minimum(y2[i], y2[idx[:last]])
w = np.maximum(0, xx2 - xx1)
h = np.maximum(0, yy2 - yy1)
inter = w * h
union = area[idx[:last]] + area[i] - inter
iou = np.divide(
inter, union,
out=np.full_like(union.astype(np.float64), np.nan),
where=union != 0)
idx = np.delete(idx, np.concatenate(
([last], np.where(iou > nms_thresh)[0])))
return boxes[keep], scores[keep]
class SlidingWindow():
def __init__(
self,
window_size: Tuple[int, int],
step: Tuple[int, int] = (1, 1),
padding: Tuple[int, int] = (0, 0)
):
"""
window_size: (y, x)
"""
self.window_size = window_size
self.step = step
self.padding = padding
def coords(self, img_size):
"""
Return:
[(x1, y1, x2, y2), ...]
"""
rows, cols = img_size
window_size = self.window_size
step = self.step
padding = self.padding
i_idxs = np.arange(
padding[0], rows+padding[0]-window_size[0]+1, step[0])
j_idxs = np.arange(
padding[1], cols+padding[1]-window_size[1]+1, step[1])
ret = []
for i in i_idxs:
for j in j_idxs:
ret.append(
[int(j), int(i),
int(j+window_size[1]), int(i+window_size[0])]
)
return ret
def unpadding_coord(self, img_size, coords: list):
"""
coords: [(x1, y1, x2, y2),...]
Return:
[(x1, y1, x2, y2),...]
"""
rows, cols = img_size
padding = self.padding
ret = []
for i_coord in coords:
x1, y1, x2, y2 = list(map(int, i_coord))
x1_ = min(max(x1-padding[1], 0), cols)
y1_ = min(max(y1-padding[0], 0), rows)
x2_ = min(max(x2-padding[1], 0), cols)
y2_ = min(max(y2-padding[0], 0), rows)
area = (y2_ - y1_) * (x2_ - x1_)
if area <= 0:
x1_, y1_, x2_, y2_ = (-1, -1, -1, -1)
ret.append([x1_, y1_, x2_, y2_])
return ret
class HogDescriptor:
def __init__(
self,
win_size: Tuple[int, int] = (64, 64),
block_size: Tuple[int, int] = (16, 16),
block_stride: Tuple[int, int] = (8, 8),
cell_size: Tuple[int, int] = (8, 8),
nbins: int = 9,
):
self.win_size = win_size
self.block_size = block_size
self.block_stride = block_stride
self.cell_size = cell_size
self.nbins = nbins
self._hog = cv2.HOGDescriptor(
win_size,
block_size,
block_stride,
cell_size,
nbins
)
self.feature_dim = HogDescriptor.calc_feature_dim(
win_size, block_size, block_stride, nbins)
def get_feature_dim(self):
return self.feature_dim
def compute(self, imgs: list):
if not isinstance(imgs, list):
raise ValueError('imgs must be list of image array.')
X = []
for i_img in imgs:
descriptor = self._hog.compute(i_img)
descriptor = descriptor.ravel()
assert descriptor.shape[0] == self.feature_dim
X.append(descriptor)
X = np.array(X)
return X
@staticmethod
def calc_feature_dim(win_size, block_size, block_stride, nbins):
num_cell_per_block = block_size[0] / \
block_stride[0] * block_size[1]/block_stride[1]
num_h_block = (win_size[0] - block_size[0]) / block_stride[0] + 1
num_w_block = (win_size[1] - block_size[1]) / block_stride[1] + 1
num_block = num_h_block * num_w_block
return int(num_cell_per_block * num_block * nbins)
class HogSvmAdapter:
def __init__(
self,
hog: HogDescriptor,
clf: SVC,
window_size: Tuple[int, int],
scales: Tuple[float, ...] = (1.0,),
step: Tuple[int, int] = (1, 1),
padding: Tuple[int, int] = (0, 0),
):
self.hog = hog
self.clf = clf
self.window_size = window_size
self.scales = scales
self.padding = padding
self.step = step
self.sw_list = [
SlidingWindow(
window_size=[int(s*r)for s in window_size],
step=step,
padding=padding) for r in scales]
if clf.fit_status_ == 1:
raise NotFittedError('SVC instance is not fitted yet.')
def predict(
self,
img: np.ndarray,
threshold: float = 0.01,
nms_thresh: float = 0.1,
top_k: int = 0):
img_padded = np.pad(img, self.padding, mode='constant')
# スライディングウィンドウの座標で画像をクロップしHOG特徴量を計算
all_boxes, all_scores = [], []
for sw in self.sw_list:
coords = sw.coords(img_padded.shape[:2])
cropped_img_descriptor = []
cropped_imgs = []
for i_coord in coords:
x1, y1, x2, y2 = i_coord
cropped = img_padded[y1:y2, x1:x2]
cropped_resized = cv2.resize(cropped, (64, 64))
cropped_imgs.append(cropped_resized)
cropped_img_descriptor = self.hog.compute(cropped_imgs)
# クロップした画像に対してSVMで推論
scores = self.clf.decision_function(cropped_img_descriptor)
# 閾値でボックスをフィルター
unpad_coords = sw.unpadding_coord(img.shape[:2], coords)
boxes = np.array(unpad_coords)
boxes = boxes[scores > threshold]
scores = scores[scores > threshold]
all_boxes.append(boxes)
all_scores.append(scores)
all_boxes = np.concatenate(all_boxes, axis=0)
all_scores = np.concatenate(all_scores, axis=0)
# NMSを実行
boxes_detect_nms, scores_nms = nms(
all_boxes, all_scores, nms_thresh, top_k)
return boxes_detect_nms, scores_nms
def main():
# 学習画像読み込み
imgs, labels = [], []
for j in [0, 1]:
for i in range(1, 11):
img = cv2.imread(f'./train/{j}/{i:03d}.png', cv2.IMREAD_GRAYSCALE)
img = cv2.resize(img, (64, 64))
imgs.append(img)
labels.append(j)
# HOG特徴量を計算
params = {
'win_size': (64, 64), # (x, y)
'block_size': (16, 16),
'block_stride': (8, 8),
'cell_size': (8, 8),
'nbins': 9
}
hog = HogDescriptor(**params)
X_train = hog.compute(imgs)
y_train = np.array(labels)
# SVMを学習
clf = SVC(kernel='rbf', gamma=0.001, probability=True)
clf.fit(X_train, y_train)
hogsvm = HogSvmAdapter(
hog, clf,
window_size=params['win_size'][::-1],
scales=(1.0, 0.7, 0.8, 0.9, 1.1),
step=(8, 8),
padding=(32, 32)
)
# 推論対象画像読み込み
filenames = [
'./22456235_s.jpg',
'./25153855_s.jpg'
]
results, result_imgs = [], []
for i, fname in enumerate(filenames):
# 推論対象画像読み込み
img = cv2.imread(fname)
img_gray = cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
boxes, scores = hogsvm.predict(
img_gray, threshold=-1, nms_thresh=0.1, top_k=0)
# 検出結果を保存
for j, (box, score) in enumerate(zip(boxes, scores)):
detected_instance = {
'id': j+1,
'image_id': i+1,
'category_id': 1,
'iscrowd': 0,
'segmentation': []
}
x1, y1, x2, y2 = list(map(int, box))
detected_instance['bbox'] = [x1, y1, x2 - x1, y2 - y1]
detected_instance['area'] = (x2 - x1) * (y2 - y1)
detected_instance['score'] = float(score)
results.append(detected_instance)
result_img = plot_box(img, boxes)
result_img = cv2.cvtColor(result_img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)
result_imgs.append(result_img)
with open('./detections_coco.json', 'w') as f:
json.dump(results, f, indent=4)
# Boxを表示する
for result_img in result_imgs:
plt.imshow(result_img)
plt.show()
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
plot_box 関数は、画像に検出したボックスを描く関数です。
nms関数はNMS (Non-Maximum Suppression)を実行する関数です。スライディングウィンドウを使用して物体位置を特定するため、物体がある場所に複数のボックスを検出しやすいです。したがって、重複するボックスを排除することが必要となります。
SlidingWindowクラスはスライディングウィンドウの座標を出力するクラスです。
HogDescriptorクラスはcv2.HOGDescriptorをラップしており、画像のリストを受け取ってHOG特徴量を出力します。
HogSvmAdapterはHOG特徴量計算器とSVMの予測器のアダプターであり、画像を入力としてスライディングウィンドウを生成し、物体検出、NMSを実行します。
main関数ではSVMの学習と予測を行っています。ボックスの検出結果をCOCOフォーマットでファイルに出力しています。
検出結果
SVMの予測の確信度には分離境界面からの距離を使用しています。SVMのクラスにはメソッドpredict_probaも実装されていますが、このメソッドは分類結果と矛盾が生じる可能性があり($ \mathrm{argmax}(P(C|X))\neq C$)、使いにくいです。そこで、分離境界面からの距離を出力するdecision_functionを使用していますが、こちらの値は正規化等はされていないので、確信度の分布を見て閾値を適切に決定することが必要になります。
評価のコードは以前の記事で紹介しています。
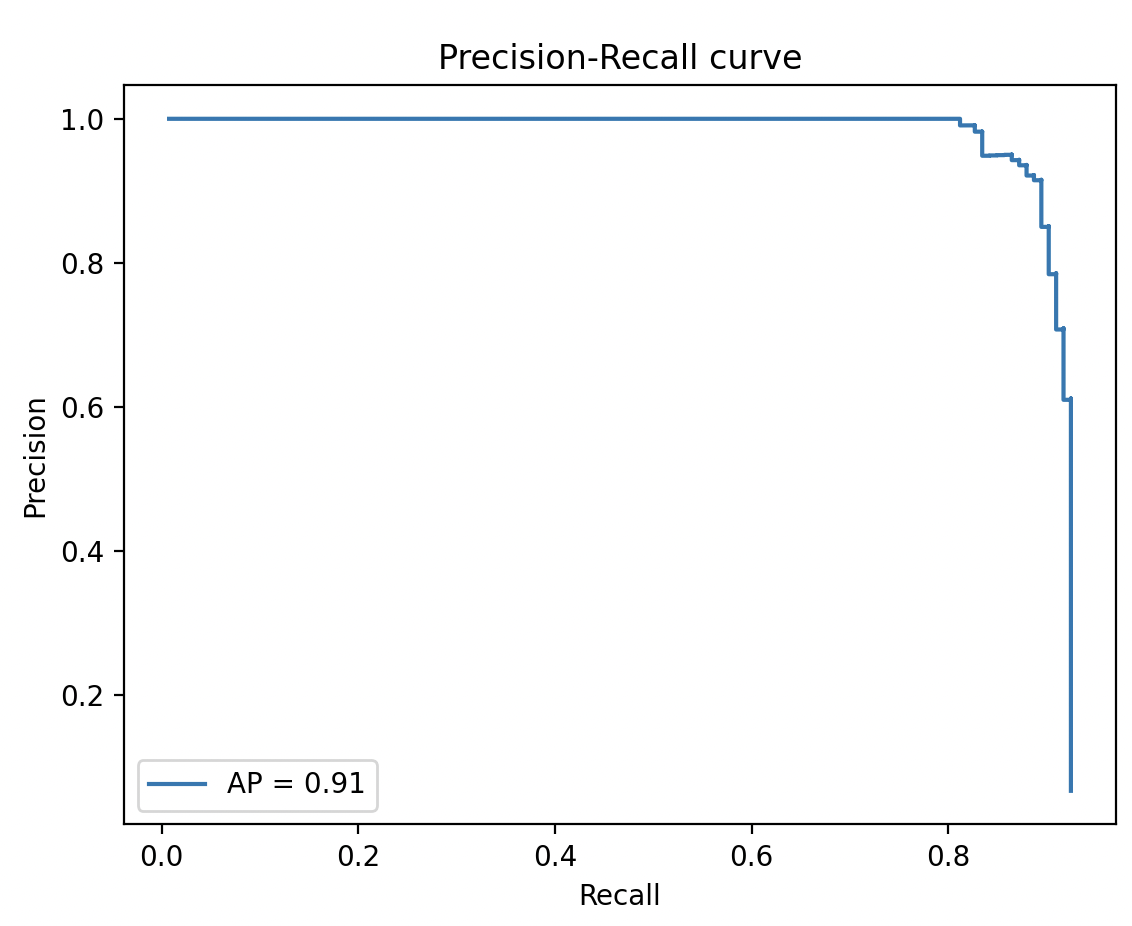
確信度の閾値を$-1$に設定し、予測を実行します。APは91.3となりました。下図はPrecision-Recall 曲線です。
| AP@IoU=0.5, nms=0.1, [tex: \mathrm{maxDets}=infty] |
|---|
| 91.3 |
*Precision-Recall 曲線
下記は確信度の閾値を0.01に設定したときの精度です。
| real_pos | real_neg | |
|---|---|---|
| pred_pos | tp = 119 | fp = 21 |
| pred_neg | fn = 14 | - |
| Precision@IoU=0.5,conf=0.01,nms=0.1 | Recall@IoU=0.5,conf=0.01,nms=0.1 |
|---|---|
| 85.0 | 89.5 |
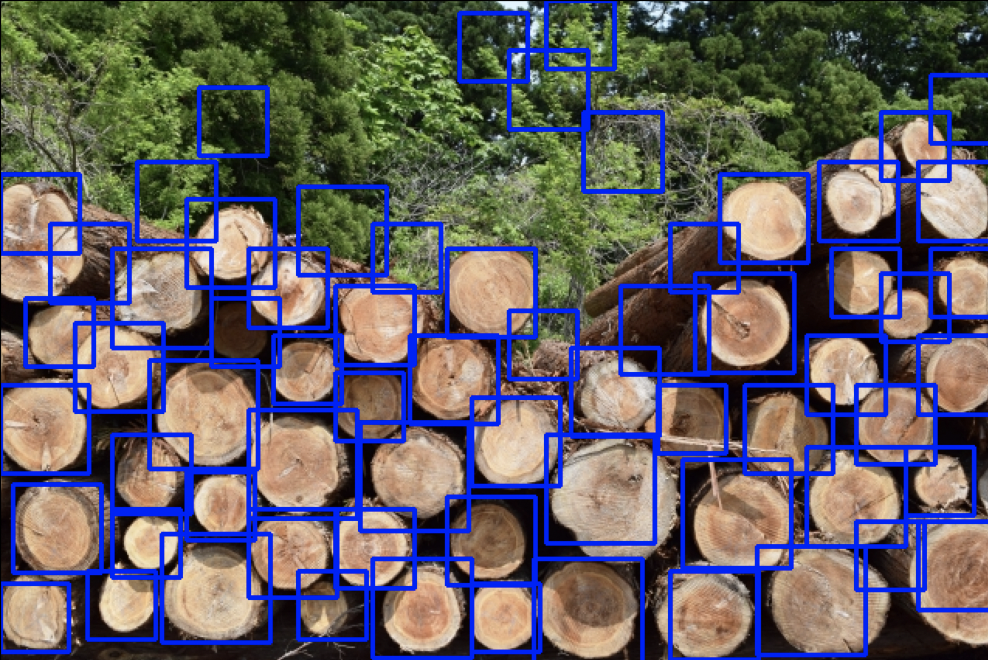
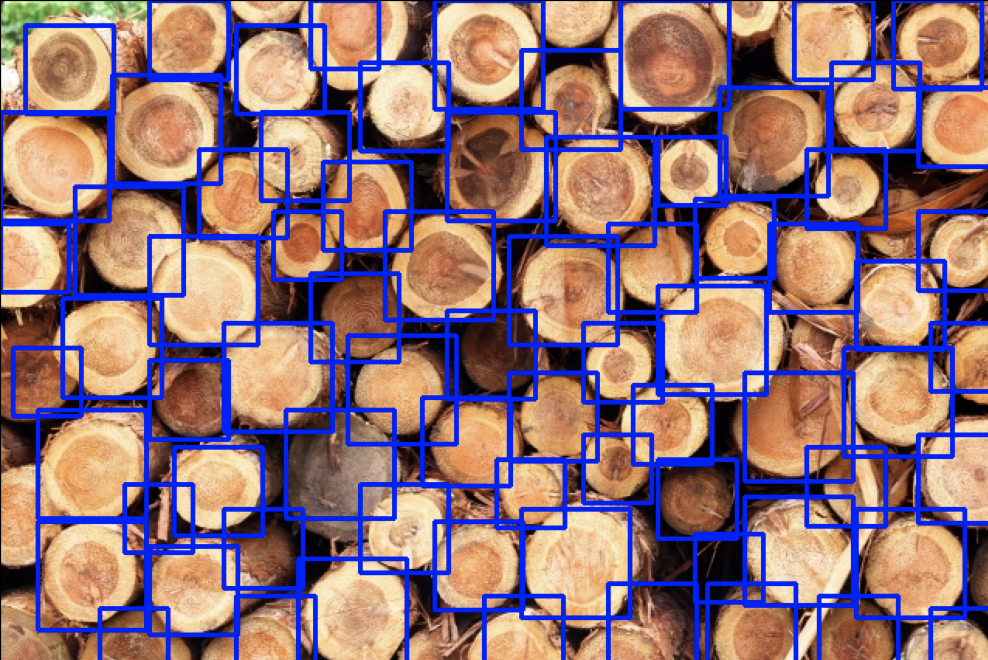
下図は検出結果です。
検出結果(画像1)

検出結果(画像2)

Reference