hpcmipsみたいな環境でインストーラを使わずにNetBSDをインストールする
NetBSD-hpcmipsとは?
NetBSD-hpcmipsは、MIPSベースのWindowsCEやPDAで動作するNetBSDです。NetBSDの特徴して、
様々なCPUアーキテクチャで動作する、というものがあり、こういったIntel系以外のCPUを搭載した
マシンへの対応が比較的容易になっています。
(という内容がNetBSDのWebサイトに書かれており、上記はその受け売りです...)
今日のNetBSD Advent Calendarでは、hpcmipsなマシンへのNetBSDインストール手順を紹介してみようと思います。
OSインストールの実際
NetBSD-amd64等では、インストールCDからOSをインストールできます。12/1の記事のように、基本的にはインストーラが提示してくる手順に従って進めるだけでOSをインストールできます。
しかしながら、PC(Intel系)以外のマシンではディスクの容量が少なくてインストーラが展開する配布ファイルを置くための空き容量の確保が難しかったり、そもそもCD-ROMドライブが接続できない等々、インストーラを利用する手間の方が大きい場合があります。
先に紹介したNetBSD-hpcmipsが動作するマシンも同様で、インストーラを動かすことも可能ですが、母艦となるPCからディスク(コンパクトフラッシュカード)のパーティション設定とNetBSD配布物の展開を行う方が結果的に楽だったりします。
手動でNetBSDをインストールする
コンパクトフラッシュカードを用意する
母艦となるPCにコンパクトフラッシュカード(以下「CF」)を接続します。dmesgや/var/log/messagesで確認すると、CFは/dev/wd1のようなデバイス名で見えます。
fdisk
まずはfdiskでパーティションテーブルを設定します。NetBSD-hpcmipsはWindowsCE上のhpcboot.exeというローダからNetBSDカーネルを読み込んで起動するので、MS-DOS領域(FAT)とNetBSD領域を作成します。
# fdisk -u /dev/wd1
fdisk: Cannot determine the number of heads
Disk: /dev/wd1d
NetBSD disklabel disk geometry:
cylinders: 993, heads: 16, sectors/track: 63 (1008 sectors/cylinder)
total sectors: 1000944
BIOS disk geometry:
cylinders: 993, heads: 16, sectors/track: 63 (1008 sectors/cylinder)
total sectors: 1000944
Partitions aligned to 1008 sector boundaries, offset 63
Do you want to change our idea of what BIOS thinks? [n]
Partition table:
0: <UNUSED>
1: <UNUSED>
2: <UNUSED>
3: <UNUSED>
Bootselector disabled.
No active partition.
Which partition do you want to change?: [none] 0
The data for partition 0 is:
<UNUSED>
sysid: [0..255 default: 169] 6
start: [0..993cyl default: 63, 0cyl, 0MB] 63
size: [0..993cyl default: 1000881, 993cyl, 489MB] 16224
bootmenu: []
Partition table:
0: Primary 'big' DOS, 16-bit FAT (> 32MB) (sysid 6)
start 63, size 16224 (8 MB, Cyls 0-16/2/33)
1: <UNUSED>
2: <UNUSED>
3: <UNUSED>
Bootselector disabled.
No active partition.
Which partition do you want to change?: [none] 1
The data for partition 1 is:
<UNUSED>
sysid: [0..255 default: 169]
start: [0..993cyl default: 16287, 16cyl, 8MB] 16287
size: [0..977cyl default: 984657, 977cyl, 481MB] 984657
bootmenu: []
Partition table:
0: Primary 'big' DOS, 16-bit FAT (> 32MB) (sysid 6)
start 63, size 16224 (8 MB, Cyls 0-16/2/33)
1: NetBSD (sysid 169)
start 16287, size 984657 (481 MB, Cyls 16/2/34-992)
PBR is not bootable: Bad magic number (0x0000)
2: <UNUSED>
3: <UNUSED>
Bootselector disabled.
No active partition.
Which partition do you want to change?: [none]
We haven't written the MBR back to disk yet. This is your last chance.
Partition table:
0: Primary 'big' DOS, 16-bit FAT (> 32MB) (sysid 6)
start 63, size 16224 (8 MB, Cyls 0-16/2/33)
1: NetBSD (sysid 169)
start 16287, size 984657 (481 MB, Cyls 16/2/34-992)
PBR is not bootable: Bad magic number (0x0000)
2: <UNUSED>
3: <UNUSED>
Bootselector disabled.
No active partition.
Should we write new partition table? [n] y
パーティション設定後のfdiskの出力は以下のようになります。MS-DOS領域に8MB、NetBSD領域に481MB割り当てています。
# fdisk /dev/wd1
Disk: /dev/wd1d
NetBSD disklabel disk geometry:
cylinders: 993, heads: 16, sectors/track: 63 (1008 sectors/cylinder)
total sectors: 1000944
BIOS disk geometry:
cylinders: 993, heads: 16, sectors/track: 63 (1008 sectors/cylinder)
total sectors: 1000944
Partitions aligned to 1008 sector boundaries, offset 63
Partition table:
0: Primary 'big' DOS, 16-bit FAT (> 32MB) (sysid 6)
start 63, size 16224 (8 MB, Cyls 0-16/2/33)
1: NetBSD (sysid 169)
start 16287, size 984657 (481 MB, Cyls 16/2/34-992)
PBR is not bootable: Bad magic number (0x0000)
2: <UNUSED>
3: <UNUSED>
Bootselector disabled.
No active partition.
disklabelの設定
次にdisklabelを設定します。fdiskはNetBSDで利用するUFSとMS-DOS領域を設定しますが、disklabelはNetBSD領域について、パーティション分割すると考えれば良いかもしれません。
(私もちゃんと理解しきれていないので、興味のある方は以下のNetBSD Documentationをご参照ください)
- 3.6. Disklabel partitions
今回の例では、安易にa:をUFS領域、b:をスワップデバイスとして割り当てています。
# disklabel -i /dev/wd1
Enter '?' for help
partition> P
6 partitions:
# size offset fstype [fsize bsize cpg/sgs]
c: 984657 16287 unused 0 0 # (Cyl. 16*- 992)
d: 1000944 0 unused 0 0 # (Cyl. 0 - 992)
e: 16224 63 unused 0 0 # (Cyl. 0*- 16*)
f: 984657 16287 unused 0 0 # (Cyl. 16*- 992)
partition>
partition> e
Filesystem type [?] [unused]: MSDOS
Start offset ('x' to start after partition 'x') [0.0625c, 63s, 0.03076171875M]: 63
Partition size ('$' for all remaining) [16.09523809523809489974155439995229244232c, 16224s, 7.921875M]: 16224
e: 16224 63 MSDOS # (Cyl. 0*- 16*)
partition>
partition> a
Filesystem type [?] [unused]: 4.2BSD
Start offset ('x' to start after partition 'x') [0c, 0s, 0M]: 16287
Partition size ('$' for all remaining) [0c, 0s, 0M]: 854865
a: 854865 16287 4.2BSD 0 0 0 # (Cyl. 16*- 864*)
partition> b
Filesystem type [?] [unused]: swap
Start offset ('x' to start after partition 'x') [0c, 0s, 0M]: 871152
Partition size ('$' for all remaining) [0c, 0s, 0M]: 129792
b: 129792 871152 swap # (Cyl. 864*- 992)
partition>
partition> P
6 partitions:
# size offset fstype [fsize bsize cpg/sgs]
a: 854865 16287 4.2BSD 0 0 0 # (Cyl. 16*- 864*)
b: 129792 871152 swap # (Cyl. 864*- 992)
c: 984657 16287 unused 0 0 # (Cyl. 16*- 992)
d: 1000944 0 unused 0 0 # (Cyl. 0 - 992)
e: 16224 63 MSDOS # (Cyl. 0*- 16*)
f: 984657 16287 unused 0 0 # (Cyl. 16*- 992)
partition>
partition> W
Label disk [n]? y
Label written
partition> Q
設定したdisklabelの内容を確認してみます。
# fdisk /dev/wd1
...
Partition table:
0: Primary 'big' DOS, 16-bit FAT (> 32MB) (sysid 6)
start 63, size 16224 (8 MB, Cyls 0-16/2/33)
1: NetBSD (sysid 169)
start 16287, size 984657 (481 MB, Cyls 16/2/34-992)
PBR is not bootable: Bad magic number (0x0000)
2: <UNUSED>
3: <UNUSED>
# disklabel /dev/wd1
...
6 partitions:
# size offset fstype [fsize bsize cpg/sgs]
a: 854865 16287 4.2BSD 0 0 0 # (Cyl. 16*- 864*)
b: 129792 871152 swap # (Cyl. 864*- 992)
c: 984657 16287 unused 0 0 # (Cyl. 16*- 992)
d: 1000944 0 unused 0 0 # (Cyl. 0 - 992)
e: 16224 63 MSDOS # (Cyl. 0*- 16*)
f: 984657 16287 unused 0 0 # (Cyl. 16*- 992)
newfsの実行
disklabelの設定が完了したので、ファイルシステムを構築します。Linuxではmkfsコマンドですが、BSD系ではnewfsコマンドを利用します。
UFSとFATの2つについてnewfsを実行します。
# newfs /dev/rwd1a
# newfs_msdos /dev/wd1e
ここまででインストーラでの作業における、ディスクのフォーマット(ファイルシステムの作成)まで完了した状態です。
NetBSD配布物の展開
ルートパーティションへのファイル展開
ここからはNetBSD配布物をファイルシステム上に展開していきます。といっても、CF上にファイルシステムを作成するところまで完了しているので、単に母艦となるPC上でCFをmountし、必要なファイルをtarで展開するだけです。
以下の手順でCFをmountします。/mntにはNetBSD-hpcmipsのCDをマウントしているので、CFのマウントポイントは/mnt2としています。
# mount /dev/wd1a /mnt2
# mount | grep wd1a
/dev/wd1a on /mnt2 type ffs (local)
配布物の展開
hpcmipsに限らず、NetBSDの配布物はCD-ROM内で以下のように格納されています。つまるところ、配布物はtar.gzで固められているだけなので、これを展開すれば良いだけです。
# cd /mnt/hpcmips/binary/sets/
# ls
MD5 games.tgz tests.tgz xfont.tgz
SHA512 kern-GENERIC.tgz text.tgz xserver.tgz
base.tgz kern-TX3912.tgz xbase.tgz
comp.tgz man.tgz xcomp.tgz
以下の手順で配布物を展開します。展開先を間違えないように注意してください。
# for i in kern-GENERIC.tgz base.tgz comp.tgz etc.tgz man.tgz misc.tgz text.tgz
do
tar zxvfp $i -C /mnt2
done
デバイスノードの作成
配布物の展開が完了したら、MAKEDEVスクリプトを実行してデバイスノードを作成します。
(これもインストーラが内部的に実行している手順です)
# cd /mnt2/dev
# ./MAKEDEV all
fstabの設定
次に/etc/fstabを編集し、ディスクのマウント情報を手で書き込みます。
# cat > /mnt2/etc/fstab
/dev/wd0a / ffs rw,noatime,nodevmtime 1 1
/dev/wd0b none swap sw,dp 0 0
kernfs /kern kernfs rw
procfs /proc procfs rw
rc.confの設定
/etc/rc.confを設定します。
# diff -u /mnt2/etc/rc.conf.
rc.conf.d/ rc.conf.orig
mnt2/etc/rc.conf.orig /mnt2/etc/rc.conf <
hayase# diff -u /mnt2/etc/rc.conf.orig /mnt2/etc/rc.conf
--- /mnt2/etc/rc.conf.orig 2014-06-17 10:14:12.000000000 +0900
+++ /mnt2/etc/rc.conf 2014-06-17 10:14:46.000000000 +0900
@@ -15,7 +15,11 @@
# If this is not set to YES, the system will drop into single-user mode.
#
-rc_configured=NO
+rc_configured=YES
# Add local overrides below
#
+wscons=YES
+postfix=NO
+sendmail=NO
+
CtrlとShiftキーの入れ替え
これはお好みで設定する内容ですが、wscons.confを設定することで、CtrlとShiftキーを入れ替えることができます。
(この設定を行う場合、/etc/rc.confで"wscons=YES"を入れておく必要がある点に注意してください)
# diff -u /mnt2/etc/wscons.conf.orig /mnt2/etc/wscons.conf
--- /mnt2/etc/wscons.conf.orig 2014-06-17 10:16:27.000000000 +0900
+++ /mnt2/etc/wscons.conf 2014-06-17 10:16:43.000000000 +0900
@@ -47,3 +47,7 @@
# Change keyboard repeat speed to faster settings.
#setvar wskbd repeat.del1 250
#setvar wskbd repeat.deln 30
+
+encoding us
+encoding us.swapctrlcaps
+
ここまでで配布物の展開と最低限必要な設定は完了なので、CFをunmountします。
# umount /mnt2
MSDOS領域へのファイル展開
残る作業は、MSDOS領域をmountして、hpcboot.exeをコピーします。
# mount /dev/wd1e /mnt2
# mount | grep wd1e
/dev/wd1e on /mnt2 type msdos (local)
# df -h | grep wd1e
/dev/wd1e 7.9M 0B 7.9M 0% /mnt2
# cp /mnt/hpcmips/installation/hpcboot.exe /mnt2/
hpcboot.exeコピーが完了したら、MSDOS領域をunmountします。
# umount /mnt2
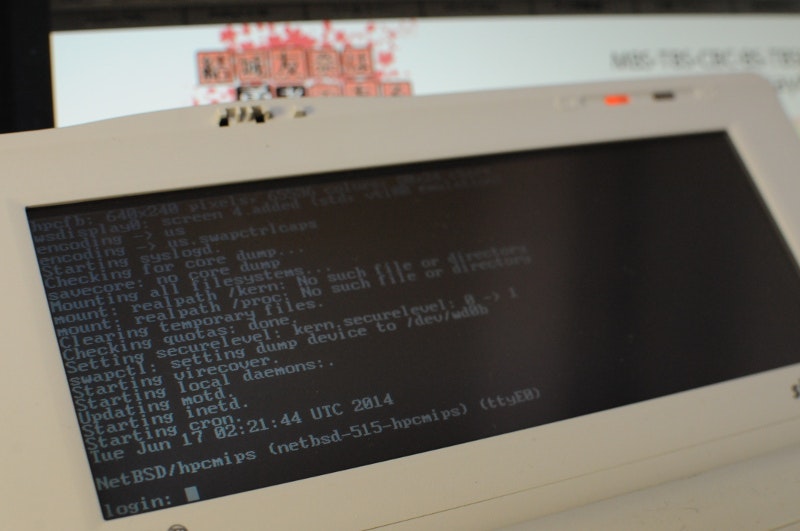
NetBSDの起動
WindowsCEからhpcboot.exeを実行し、(うまく行くと)以下のような感じでNetBSDが起動します。
まとめ
駆け足ではありますが、インストーラを使わずにNetBSD-hpcmipsをインストールする手順を紹介してみました。
明日はクロスコンパイルに関する記事を書こうと思います。お楽しみに!