1. AlphaFold2をコードで理解する
AlphaFold2(以下AlphaFold)とはGoogle DeepMindが開発したタンパク質構造予測モデルで、アミノ酸配列からタンパク質の立体構造を予測します。2021年に発表されたHighly accurate protein structure prediction with AlphaFoldでアルゴリズムが説明されていて、ソースコードも公開されています。
アルゴリズムの概要を理解することを目的とした記事はいくつか既にあるので、この記事ではPyTorchで各ブロックを簡易的に実装し、どのような処理が行われているかをコードベースで理解することを目的とします。
1.2 AlphaFoldアルゴリズム概要
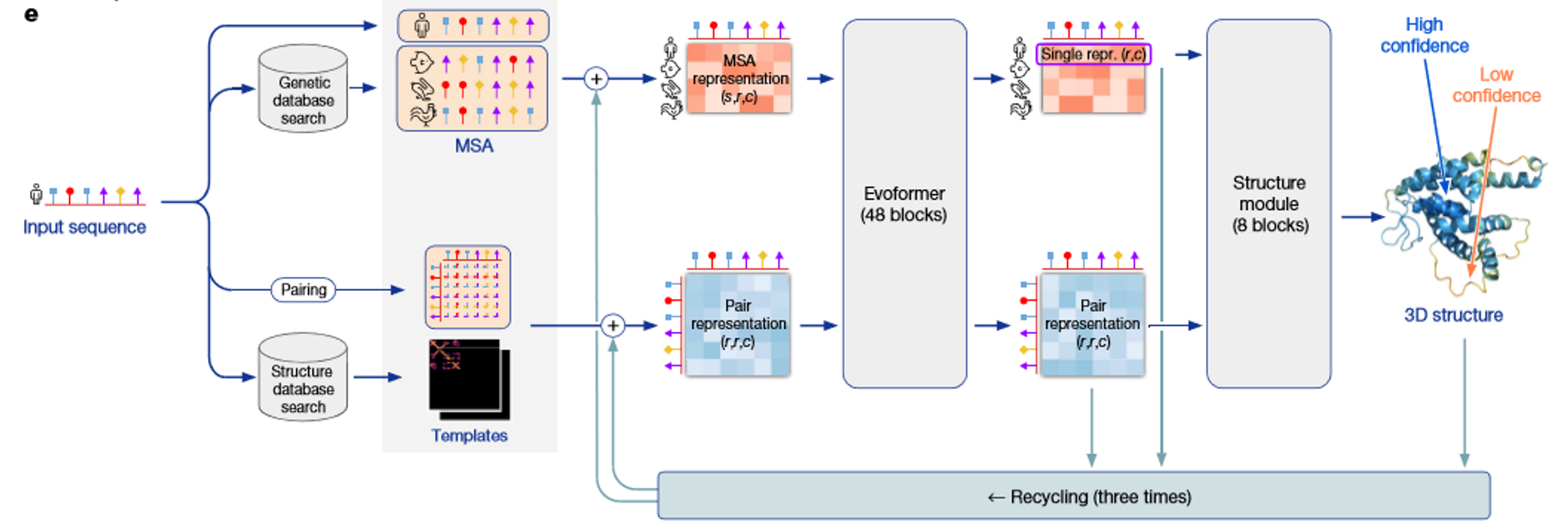
AlphaFoldではMSA(Multiple Sequene Alignmet)表現という入力アミノ酸配列に似ている配列を探してきて並べたものをもとにした特徴量と、ペア表現という入力配列の各残基間の関係性を表現するような特徴量の2つを使って特徴抽出します。
MSA表現、ペア表現をEvoformerブロックと呼ばれるモジュールに通して洗練し、その結果をStructure Moduleと呼ばれるモジュールに通して立体構造の座標情報を出力します。最終的に5種類の誤差関数を使って正解となる立体構造との誤差を最小化するように学習を行います。
1.3 実装内容
あくまで理解を目的としているため、本物のAlphaFoldのアルゴリズムからは以下の点は省略して実装しました。
- MSA取得部分の処理
- 学習時MSA表現にマスクをかける処理
- Extra MSA処理
- 出力結果を再度ネットワークに入力し直すRecycling処理
- 側鎖の座標予測
- 誤差関数
PyTorchによる実装は既にあるため、そちらも参考にしつつ本記事の実装に上記を追加することで全体を自分で実装することは可能だと思います。
アルゴリズムは大きくわけると以下3ブロックになるのでそれぞれについて説名していきます。
- MSA表現、ペア表現の埋め込み
- Evoformerブロック
- Struture Module
2. Input Embedding
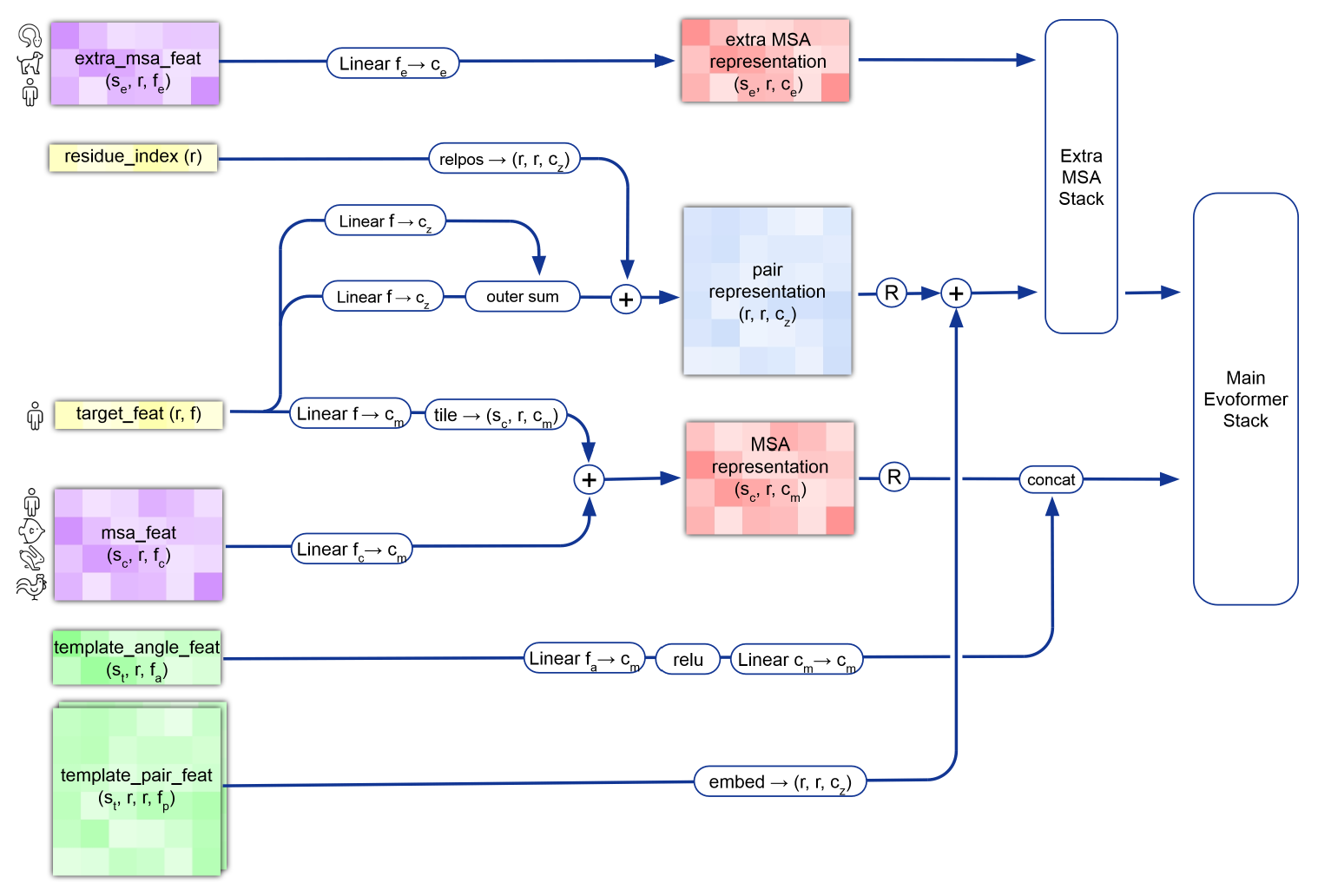
入力配列とMSA表現からEvoformerブロックの入力となるMSA表現、ペア表現を作成します。Recycling処理やテンプレートなどからの入力も同時にありますが簡単のため本実装では省略します。


最初に必要なライブラリをインポートしておきます
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
from dataclasses import dataclass
from einops import rearrange, repeat
入力埋め込みモジュールです。
class InputEmbedder(nn.Module):
"""
Algorithm3: Embeddings for initial representations
"""
def __init__(self, channel_size_feat, channel_size_msa, channel_size_pair, sequence_size, sequence_num):
super().__init__()
self.to_a = nn.Linear(channel_size_feat, channel_size_pair)
self.to_b = nn.Linear(channel_size_feat, channel_size_pair)
self.to_m1 = nn.Linear(channel_size_feat, channel_size_msa)
self.to_m2 = nn.Linear(channel_size_feat, channel_size_msa)
self.pos_proj = nn.Linear(65, channel_size_pair)
self.sequence_size = sequence_size
self.sequence_num = sequence_num
def forward(self, target_feat, residue_index, msa_feat):
a = self.to_a(target_feat)
b = self.to_b(target_feat)
a = repeat(a, 'b s c -> b r s c', r=self.sequence_size)
b = repeat(b, 'b s c -> b s r c', r=self.sequence_size)
z = a + b
z += self.relpos(residue_index)
target_feat = repeat(target_feat, 'b r c -> b n r c', n=self.sequence_num)
m = self.to_m1(msa_feat) + self.to_m2(target_feat)
return m, z
def relpos(self, residue_index, vbins=(torch.arange(65)-32)):
"""
Algorithm4: Relative position enccoding
"""
d_left = repeat(residue_index, 'b r -> b i r', i=self.sequence_size)
d_right = repeat(residue_index, 'b r -> b r i', i=self.sequence_size)
d = d_left - d_right
p = self.one_hot(d, vbins)
p = p.to(torch.float32)
p = self.pos_proj(p)
return p
def one_hot(self, x, vbins):
"""
Algorithm5: One-hot ecoding with nearest bin
"""
bin_size = vbins.shape[0]
b, r1, r2 = x.shape
x = repeat(x, 'b r1 r2 -> b r1 r2 d', d=bin_size)
vbins = repeat(vbins, 'd -> b r1 r2 d', b=b, r1=r1, r2=r2)
index = torch.argmin(torch.abs(x - vbins), dim=-1)
index = index.flatten()
p = torch.zeros_like(x, dtype=x.dtype)
p = rearrange(p, 'b r1 r2 v -> (b r1 r2) v')
p[index] = 1
p = rearrange(p, '(b r1 r2) v -> b r1 r2 v', r1=self.sequence_size, r2=self.sequence_size)
return p
試しにこのブロックに入力してみるため、まず定数を整理するため以下のconfigを作ります。
@dataclass(frozen=True)
class Config:
batch_size:int = 2 #バッチサイズ
sequence_size:int = 100 #アミノ酸残基数(数字は適当)
sequence_num:int = 7 #MSAで取ってくる配列数+1(+1は入力配列の分)
channel_size_feat: int = 23 #入力MSAのチャンネルサイズ(アミノ酸20種類+不明(1)+ギャップ(1)+マスク(1)=23)
channel_size_msa:int = 10 #MSA表現チャンネルサイズ(数字は適当)
channel_size_pair:int = 10 #ペア表現チャンネルサイズ(数字は適当)
入力配列に対するMSAは取得してきたものとして、以下のように疑似的に入力配列、MSA、残基インデックス配列を用意しておきます。
config = Config()
residue_index = repeat(torch.arange(config.sequence_size), 's -> b s', b=config.batch_size)
msa_feat = torch.randn(
config.batch_size,
config.sequence_num,
config.sequence_size,
config.channel_size_feat
)
target_feat = torch.randn(
config.batch_size,
config.sequence_size,
config.channel_size_feat
)
これらをInputEmbedderに入力するとMSA表現、ペア表現に対する最初の埋め込みを得ます。
embed = InputEmbedder(config.channel_size_feat, config.channel_size_msa, config.channel_size_pair, config.sequence_size, config.sequence_num)
print(f"{target_feat.shape=}")
print(f"{residue_index.shape=}")
print(f"{msa_feat.shape=}")
print()
msa_repr, pair_repr = embed(target_feat, residue_index, msa_feat)
print(f"{msa_repr.shape=}")
print(f"{pair_repr.shape=}")
#出力結果
target_feat.shape=torch.Size([2, 100, 23])
residue_index.shape=torch.Size([2, 100])
msa_feat.shape=torch.Size([2, 7, 100, 23])
msa_repr.shape=torch.Size([2, 7, 100, 10])
pair_repr.shape=torch.Size([2, 100, 100, 10])
3. Evoformer
Evoformerブロックは下図のようにMSA表現を処理する部分(図の上段)とペア表現を処理する部分(図の下段)に分かれており、それぞれについてみていきます。
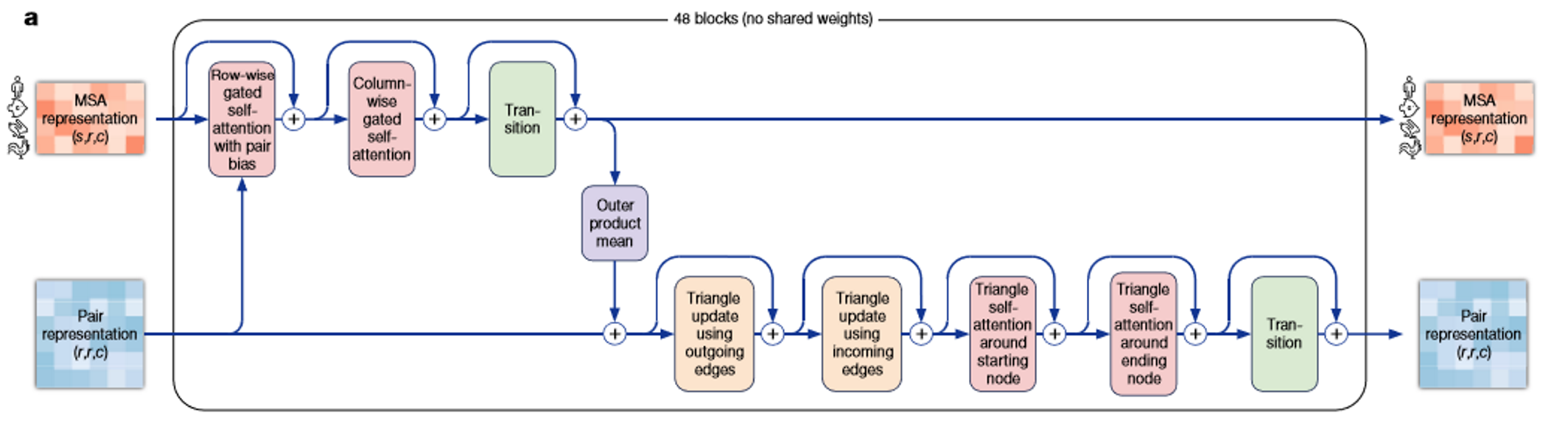
3.1 Process for MSA representation
3.1.1 MSARowWiseAttentionWithPairBias
まずMSA表現の行方向にアテンションをとって特徴抽出します。
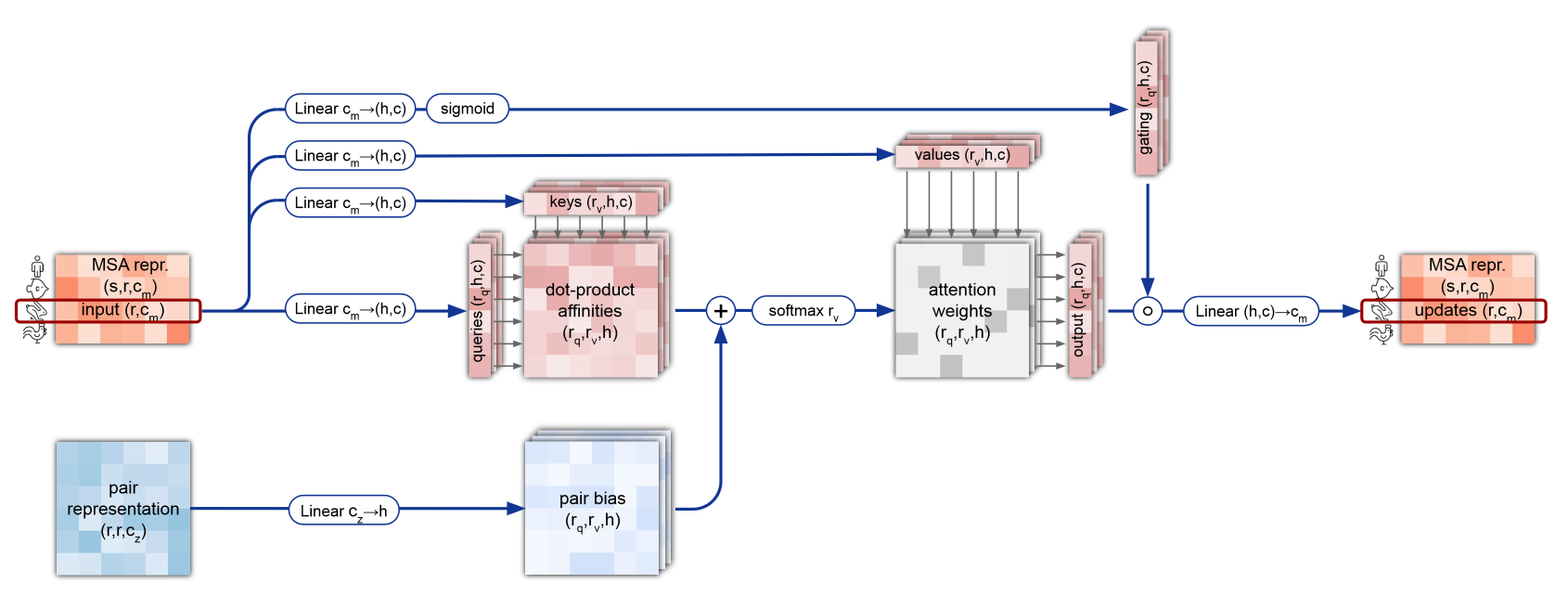
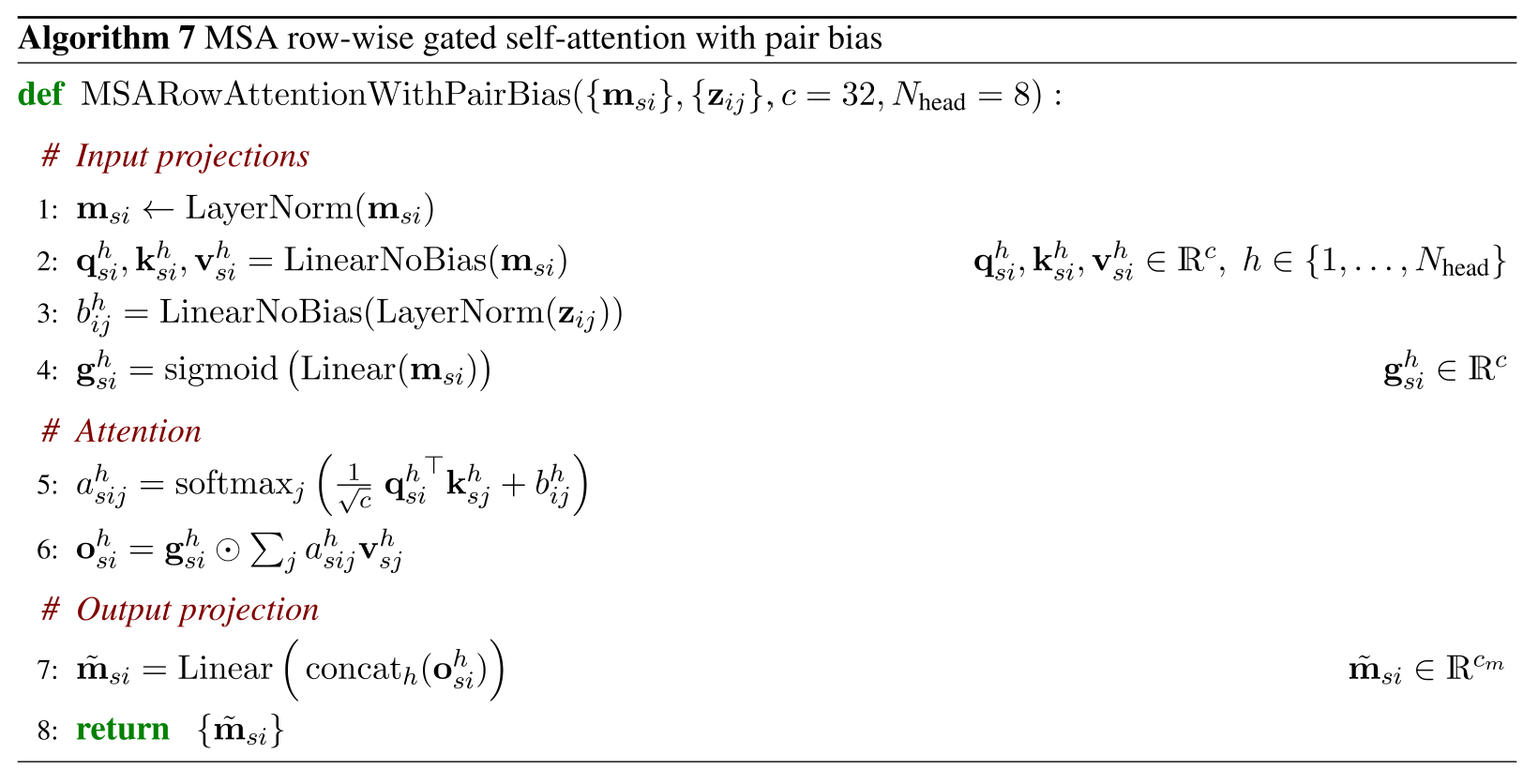
class MSARowWiseAttentionWithPairBias(nn.Module):
"""
Algorithm7: MSA row-wise gated self-attetion with pair bias
"""
def __init__(self, sequence_num, sequence_size, channel_size_msa, channel_size_pair, hidden_channel=32, nhead=8):
super().__init__()
self.layernorm = nn.LayerNorm(sequence_size)
self.to_q = nn.Linear(channel_size_msa, nhead*hidden_channel, bias=False)
self.to_k = nn.Linear(channel_size_msa, nhead*hidden_channel, bias=False)
self.to_v = nn.Linear(channel_size_msa, nhead*hidden_channel, bias=False)
self.to_bias = nn.Linear(channel_size_pair, nhead)
self.to_g = nn.Linear(channel_size_msa, nhead*hidden_channel)
self.last_layer = nn.Linear(nhead*hidden_channel, channel_size_msa)
self.nhead = nhead
self.hidden_channel = hidden_channel
self.sequence_size = sequence_size
self.sigmoid = nn.Sigmoid()
self.softmax = nn.Softmax(dim=3)
self.scale = 1 / (hidden_channel ** 0.5)
def forward(self, msa_repr, pair_repr):
#Input Projecction
x = rearrange(msa_repr, 'b s r c -> b c s r')
x = self.layernorm(x)
x = rearrange(x, 'b c s r -> b s r c')
tbatch = x.shape[1]
x = rearrange(x, 'b h w c -> (b h) w c') #here should be changed in column-wise attention
q = self.to_q(x)
k = self.to_k(x)
v = self.to_v(x)
q, k, v = map(lambda t: rearrange(t, 'b n (h d) -> b h n d', h = self.nhead), (q, k, v))
bias = self.to_bias(pair_repr)
bias = rearrange(bias, 'b i j h -> b h i j')
bias = repeat(bias, 'b i j h -> (a b) i j h', a=tbatch)
g = self.sigmoid(self.to_g(x))
g = rearrange(g, 'b i (h d) -> b h i d', d = self.hidden_channel)
#Attention
dots = torch.einsum('b h i d, b h j d -> b h i j', q, k)
attn = self.softmax(self.scale * dots + bias)
out = torch.einsum('b h i j, b h j d -> b h i d', attn, v)
out = g * out
#Output projetion
out = rearrange(out, '(b h) n w d -> b h w n d', h=tbatch)
out = torch.concat([out[:,:,:,i,:] for i in range(out.shape[3])], dim=-1) #out.shape = (b,h,w,n*d)
out = self.last_layer(out) #out.shape = (b,h,w,c)
return out
3.1.2 MSAColumnWiseAttention
次にMSA表現の列方向にアテンションをとって特徴抽出します。
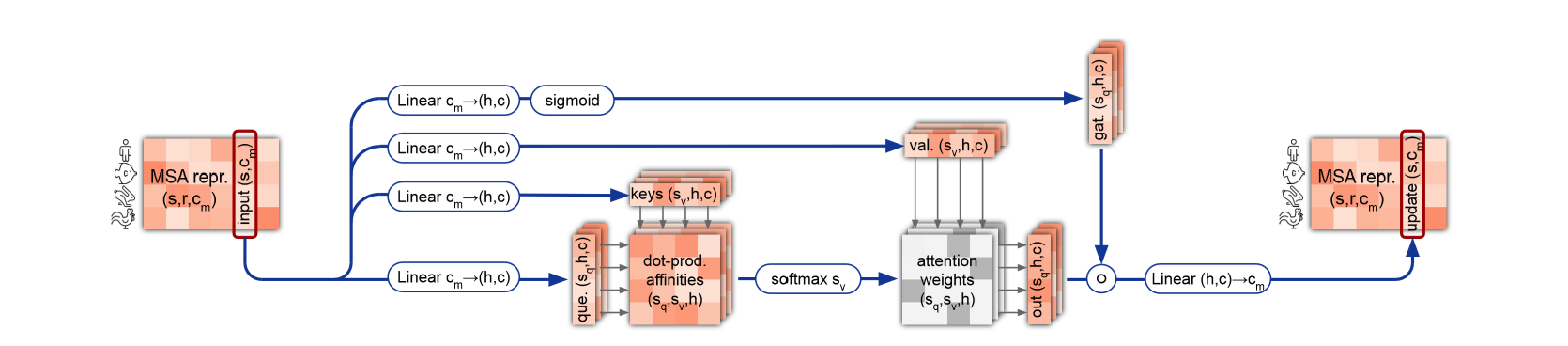

class MSAColumnWiseAttention(nn.Module):
"""
Algorithm8: MSA column-wise gated self-attention
"""
def __init__(self, sequence_num, sequence_size, channel_size_msa, channel_size_pair, hidden_channel=32, nhead=8):
super().__init__()
self.layernorm = nn.LayerNorm(sequence_num)
self.to_q = nn.Linear(channel_size_msa, nhead*hidden_channel, bias=False)
self.to_k = nn.Linear(channel_size_msa, nhead*hidden_channel, bias=False)
self.to_v = nn.Linear(channel_size_msa, nhead*hidden_channel, bias=False)
self.to_bias = nn.Linear(channel_size_pair, nhead)
self.to_g = nn.Linear(channel_size_msa, nhead*hidden_channel)
self.last_layer = nn.Linear(nhead*hidden_channel, channel_size_msa)
self.nhead = nhead
self.hidden_channel = hidden_channel
self.sequence_size = sequence_size
self.sigmoid = nn.Sigmoid()
self.softmax = nn.Softmax(dim=3)
self.scale = 1 / (hidden_channel ** 0.5)
def forward(self, msa_repr):
#Input Projecction
msa_repr = rearrange(msa_repr, 'b s r c -> b r s c')
x = rearrange(msa_repr, 'b s r c -> b c s r')
x = self.layernorm(x)
x = rearrange(x, 'b c s r -> b s r c')
tbatch = x.shape[1]
x = rearrange(x, 'b h w c -> (b h) w c') #here should be changed in column-wise attention
q = self.to_q(x)
k = self.to_k(x)
v = self.to_v(x)
q, k, v = map(lambda t: rearrange(t, 'b n (h d) -> b h n d', h = self.nhead), (q, k, v))
g = self.sigmoid(self.to_g(x))
g = rearrange(g, 'b i (h d) -> b h i d', d = self.hidden_channel)
#Attention
dots = torch.einsum('b h i d, b h j d -> b h i j', q, k)
attn = self.softmax(self.scale * dots)
out = torch.einsum('b h i j, b h j d -> b h i d', attn, v)
out = g * out
#Output projetion
out = rearrange(out, '(b h) n w d -> b h w n d', h=tbatch)
out = torch.concat([out[:,:,:,i,:] for i in range(out.shape[3])], dim=-1) #out.shape = (b,h,w,n*d)
out = self.last_layer(out) #out.shape = (b,h,w,c)
out = rearrange(out, 'b h w c -> b w h c')
return out
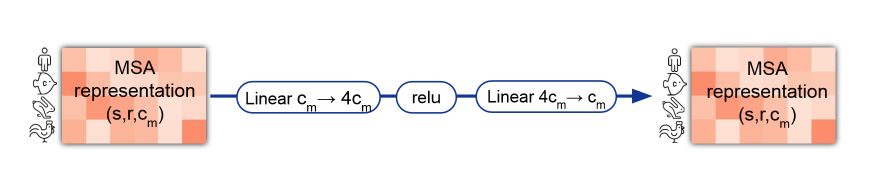
3.1.3 Transition
class Trasition(nn.Module):
"""
Algorithm9: Transition layer in the MSA stack
"""
def __init__(self, channel_size_msa, n=4):
super().__init__()
self.norm = nn.LayerNorm(channel_size_msa)
self.linear1 = nn.Linear(channel_size_msa, n*channel_size_msa)
self.relu = nn.ReLU()
self.linear2 = nn.Linear(n*channel_size_msa, channel_size_msa)
def forward(self, msa_repr):
x = self.norm(msa_repr)
x = self.linear1(x)
x = self.relu(x)
x = self.linear2(x)
return x
3.2 Process for Pair represetation
ペア表現の方の処理は大きく以下お3つが必要で、下2つはそれぞれoutgoingとincoming、startingとendingの2種類ありますが似ているので2種類ずつまとめて実装します。
- OuterProductMean
- TriangularMultiplicativeUpdate
- TriangularGatedSelfAttention
3.2.1 OuterProductMean
MSA表現からの情報を受け取るため、MSA表現各列同士のテンソル積をとってペア表現の形状に変形します。
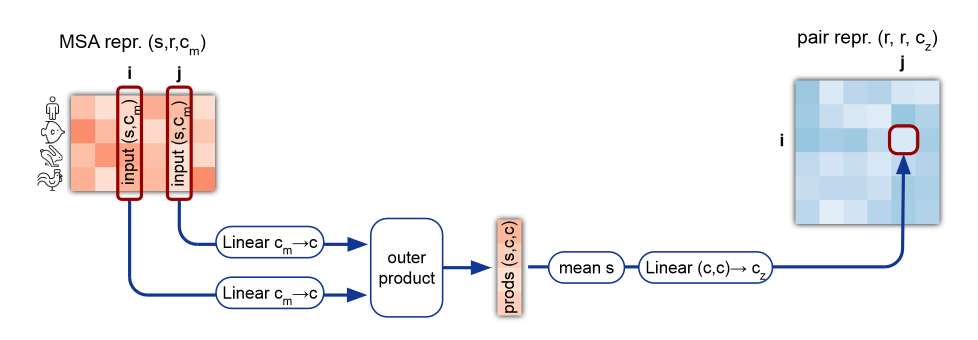
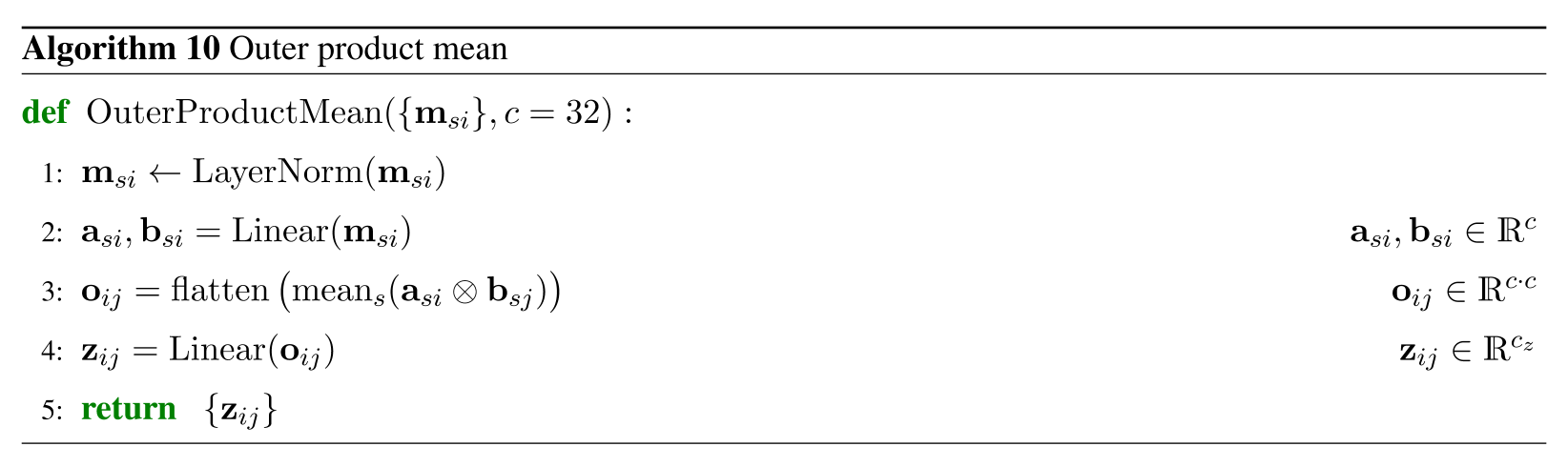
class OuterProductMean(nn.Module):
"""
Algorithm10: Outer product mean
"""
def __init__(self, sequence_num, sequence_size, channel_size_msa, channel_size_pair, hidden_channel=32):
super().__init__()
self.norm = nn.LayerNorm(channel_size_msa)
self.left_proj = nn.Linear(channel_size_msa, hidden_channel)
self.right_proj = nn.Linear(channel_size_msa, hidden_channel)
self.out_proj = nn.Linear(hidden_channel**2, channel_size_pair)
self.sequence_size = sequence_size
def forward(self, msa_repr):
x = rearrange(msa_repr, 'b s r c -> (b r) s c')
x = self.norm(x)
left = self.left_proj(x) #left.shape = (b,s,d)
right = self.right_proj(x)
left = repeat(left, '(b r) s d -> b r s d', r=self.sequence_size)
right = repeat(right, '(b r) s d -> b r s d', r=self.sequence_size)
outer = rearrange(left, 'b r s d -> b r () s d') * rearrange(right, 'b r s d -> b () r s d')
outer = rearrange(outer, 'b a c s d -> b a c s d ()') * rearrange(outer, 'b a c s d -> b a c s () d')
outer = outer.mean(dim=3)
outer = rearrange(outer, 'b i j d e -> b i j (d e)')
z = self.out_proj(outer)
return z
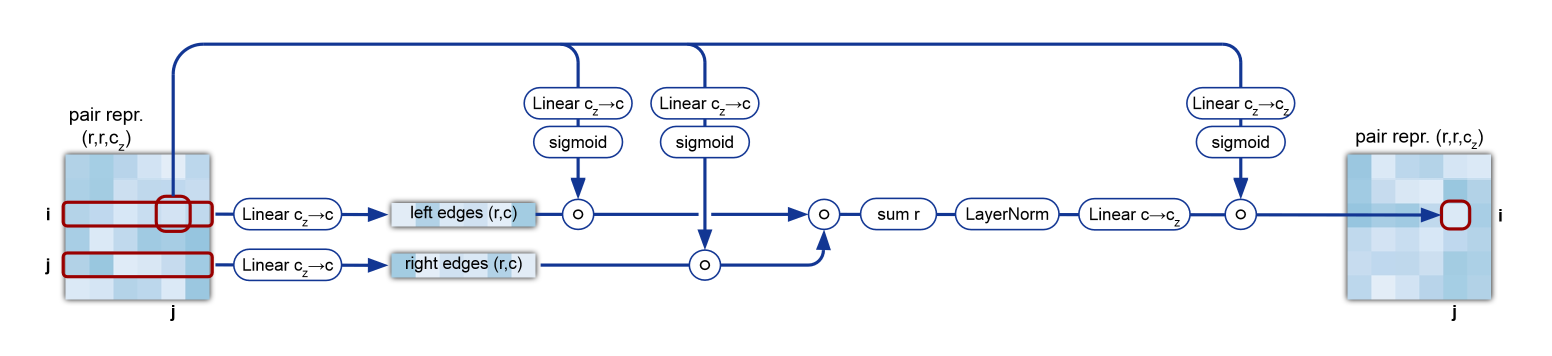
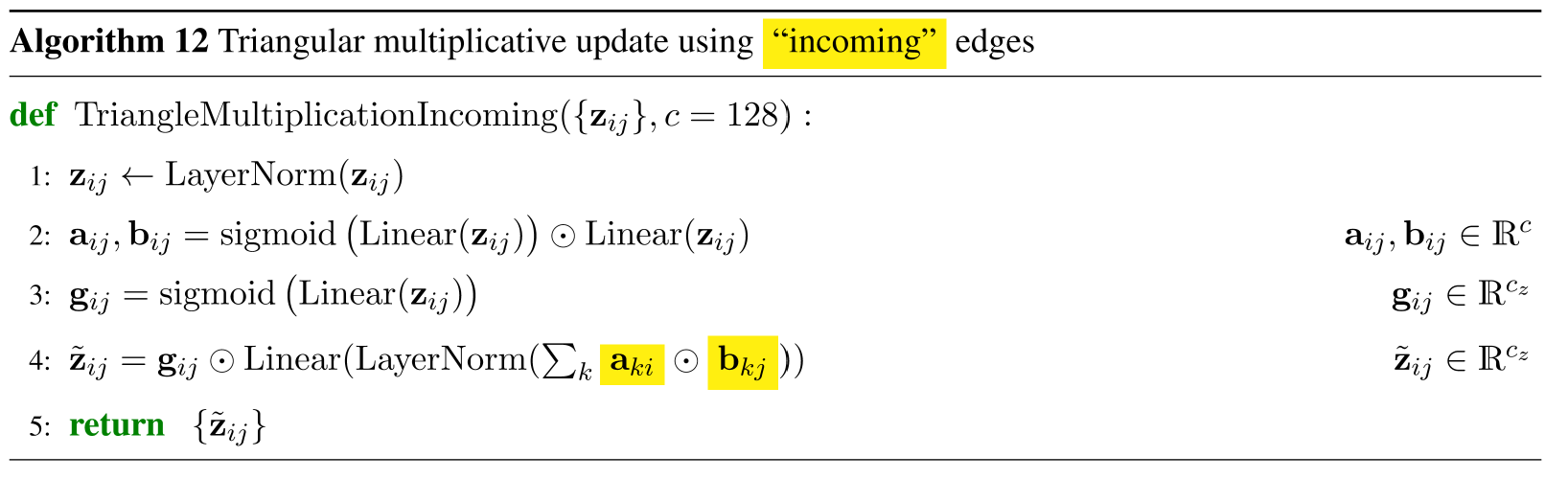
3.2.2 TriangularMultiplicativeUpdate
各残基間の関係性を学習するため、ペア表現の2ノードijから伸びる任意のノードへの情報からijの特徴量を更新します。これがoutgoingの場合です。incomingでは逆に任意のノードから伸びるijへの枝からの更新を受けます。
文章で書くとよくわからず、理解が未だに曖昧な点ですがコードにすると(設計の意図はともかく)どんな処理をしているかは理解できます。outgoingとincomingは2種類まとめて実装します。
class TriangularMultiplicativeUpdate(nn.Module):
"""
Algorithm 11: Triangular multiplicative update using 'outgoing' edges
Algorithm 12: Triangular multiplicative update using 'incoming' edges
"""
def __init__(self, channel_size_pair, hidden_channel=128, mode='outgoing'):
super().__init__()
self.norm = nn.LayerNorm(channel_size_pair)
self.to_g1 = nn.Linear(channel_size_pair, hidden_channel)
self.to_g2 = nn.Linear(channel_size_pair, hidden_channel)
self.to_g3 = nn.Linear(channel_size_pair, channel_size_pair)
self.left_proj = nn.Linear(channel_size_pair, hidden_channel)
self.right_proj = nn.Linear(channel_size_pair, hidden_channel)
self.norm2 = nn.LayerNorm(channel_size_pair)
self.out_proj = nn.Linear(hidden_channel, channel_size_pair)
self.sigmoid = nn.Sigmoid()
assert mode in ['outgoing', 'incoming'], 'mode must be either "outgoing" or "incoming"'
self.mode = mode
def forward(self, pair_repr):
z = self.norm(pair_repr)
g1 = self.sigmoid(self.to_g1(z))
g2 = self.sigmoid(self.to_g2(z))
left = g1 * self.left_proj(z)
right = g2 * self.right_proj(z)
if self.mode == 'outgoing':
x = torch.einsum('b i k d, b j k d -> b i j d', left, right)
elif self.mode == 'incoming':
x = torch.einsum('b k i d, b k j d -> b i j d', left, right)
x = self.sigmoid(self.to_g3(z)) * self.norm2(self.out_proj(x))
return x
3.2.3 TriangularGatedSelfAttention
TriangularMultiplicativeUpdateをもう少し複雑にしたような処理で、ペア表現の行方向と列方向にアテンションをとります。こちらもstarting nodeを基準とする場合とending nodeを基準とする場合で2種類ありますがまとめて実装します。
class TriangularGatedSelfAttention(nn.Module):
"""
Algorithm 13: Triangular gated self-attetion around starting node
Algorithm 14: Triangular gated self-attetion around ending node
"""
def __init__(self, channel_size_pair, sequence_size, hidden_channel=32, nhead=4, around='starting'):
super().__init__()
self.norm = nn.LayerNorm(channel_size_pair)
self.to_q = nn.Linear(channel_size_pair, nhead*hidden_channel, bias=False)
self.to_k = nn.Linear(channel_size_pair, nhead*hidden_channel, bias=False)
self.to_v = nn.Linear(channel_size_pair, nhead*hidden_channel, bias=False)
self.to_bias = nn.Linear(channel_size_pair, nhead, bias=False)
self.to_g = nn.Linear(channel_size_pair, nhead*hidden_channel)
self.out_proj = nn.Linear(nhead*hidden_channel, channel_size_pair)
self.sigmoid = nn.Sigmoid()
self.softmax = nn.Softmax(dim=4)
assert around in ['starting', 'ending'], 'around must be either "starting" or "ending"'
self.around = around
self.nhead = nhead
self.sequence_size = sequence_size
self.scale = 1 / (hidden_channel**0.5)
def forward(self, pair_repr):
#Input Projections
z = self.norm(pair_repr)
q, k, v = self.to_q(z), self.to_k(z), self.to_v(z)
q, k, v = map(lambda t: rearrange(t, 'b h w (n d) -> b n h w d', n = self.nhead), (q, k, v))
bias = self.to_bias(z) #bias.shape = (b, h, w, n)
bias = rearrange(bias, 'b h w n -> b n h w')
if self.around=='starting':
bias = repeat(bias, 'b n h w -> b n k h w', k=self.sequence_size)
elif self.around=='ending':
bias = repeat(bias, 'b n h w -> b n h k w', k=self.sequence_size)
g = self.sigmoid(self.to_g(z))
g = rearrange(g, 'b h w (n d) -> b n h w d', n=self.nhead)
#Attetion
if self.around == 'starting':
dots = self.scale * torch.einsum('b n i j d, b n i k d -> b n i j k', q, k) + bias
elif self.around == 'ending':
dots = self.scale * torch.einsum('b n i j d, b n k j d -> b n i j k', q, k) + bias
dots = self.softmax(dots)
if self.around == 'starting':
out = g * torch.einsum('b n i j k, b n i j d -> b n i j d', dots, v)
elif self.around == 'ending':
out = g * torch.einsum('b n i j k, b n k j d -> b n i j d', dots, v)
out = rearrange(out, 'b n i j d -> b i j (n d)')
#Outer Projection
z = self.out_proj(out)
return z
3.3 Evoformerブロックの処理全体
ここまで実装したことをもとにEvoformerブロック全体を実装します。
入力としてMSA表現、ペア表現をとり、更新されたMSA表現、ペア表現、ターゲット配列を出力します。

class EvoformerBlock(nn.Module):
"""
Algorithm6: Evoformer stack
"""
def __init__(self, sequence_num, sequence_size, channel_size_msa, channel_size_pair, depth=5):
super().__init__()
self.msa_row = MSARowWiseAttentionWithPairBias(
sequence_num,
sequence_size,
channel_size_msa,
channel_size_pair
)
self.msa_column = MSAColumnWiseAttention(
sequence_num,
sequence_size,
channel_size_msa,
channel_size_pair
)
self.trans_msa = Trasition(
channel_size_msa,
)
self.outer_prod = OuterProductMean(
sequence_num,
sequence_size,
channel_size_msa,
channel_size_pair,
)
self.outgoing = TriangularMultiplicativeUpdate(
channel_size_pair,
mode='outgoing'
)
self.incoming = TriangularMultiplicativeUpdate(
channel_size_pair,
mode='incoming'
)
self.starting = TriangularGatedSelfAttention(
channel_size_pair,
sequence_size,
around='starting'
)
self.ending = TriangularGatedSelfAttention(
channel_size_pair,
sequence_size,
around='ending'
)
self.trans_pair = Trasition(
channel_size_pair,
)
self.depth = depth
self.dropout15 = nn.Dropout(p=0.15)
self.dropout25 = nn.Dropout(p=0.25)
self.to_s = nn.Linear(channel_size_msa, channel_size_msa)
def forward(self, msa_repr, pair_repr):
x = msa_repr
z = pair_repr
for i in range(self.depth):
#MSA stack
x += self.dropout15(self.msa_row(x, z))
x += self.msa_column(x)
x += self.trans_msa(x)
#Communication
z += self.outer_prod(x)
#Pair stack
z += self.dropout25(self.outgoing(z))
z += self.dropout25(self.incoming(z))
z += self.dropout25(self.starting(z))
z += self.dropout25(self.ending(z))
z += self.trans_pair(z)
#Extract the sigle represetation
s = self.to_s(x[:,0,:,:])
return x, z, s
3.3.1 入出力形状確認
ここまでの実装を簡易的に確認するため、乱数で生成したmsa_reprとpair_reprを入力してみてデータの形状を確認します。
evoformer = EvoformerBlock(config.sequence_num, config.sequence_size, config.channel_size_msa, config.channel_size_pair)
msa_repr, pair_reppr, targe_seq = evoformer(msa_repr, pair_repr)
print(f"{msa_repr.shape=}")
print(f"{pair_repr.shape=}")
print(f"{target_seq.shape=}")
#出力結果
msa_repr.shape=torch.Size([2, 7, 100, 10])
pair_repr.shape=torch.Size([2, 100, 100, 10])
target_seq.shape=torch.Size([2, 100, 10])
4. Structure Module
いよいよMSA表現、ペア表現から構造予測を行うモジュールです。ターゲット配列、ペア表現、主鎖の位置を入力にとって回転行列と並進ベクトルを予測、主鎖の位置を更新します。さらにそれをもとに側鎖の位置も決定します。
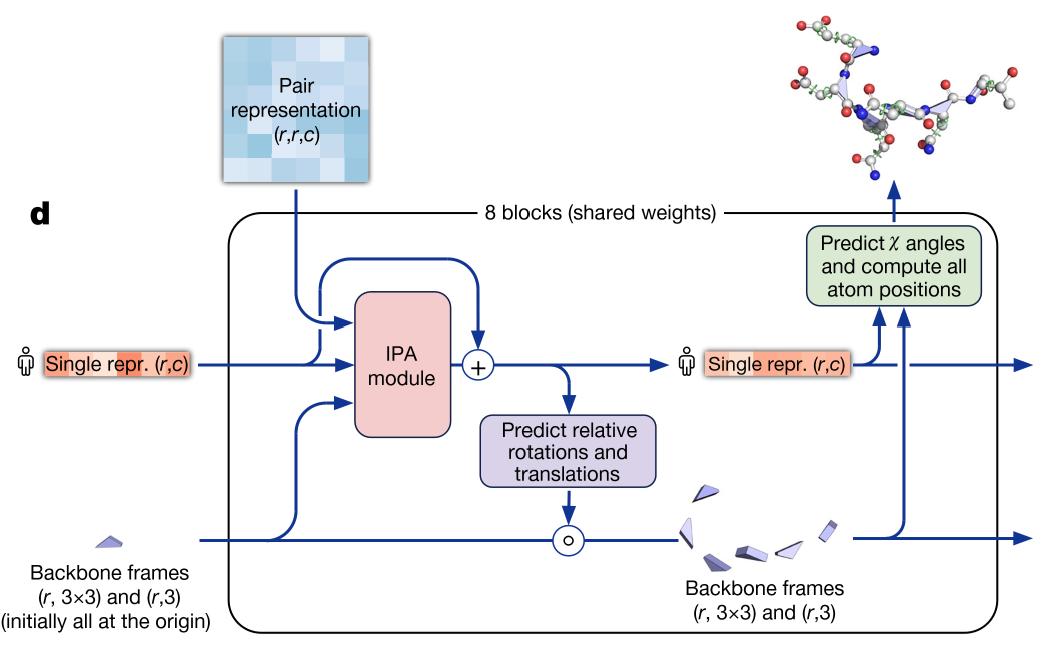
本記事では簡単のため以下は省略しました。
- IPAモジュール(既存パッケージから流用)
- テンプレート構造の入力
- 側鎖構造の予測(出力は主鎖のみにとどめる)
4.1 インポート
必要なパッケージをインポートします。
from invariant_point_attention import IPABlock
import torch.nn.functional as F
4.2 Structure Module実装
論文の図の通りに実装します。quaternionから回転行列を作る関数やquaternionを合成する処理は既存パッケージの実装をもとに利用しました。
def quaternion_to_matrix(quaternions: torch.Tensor) -> torch.Tensor:
"""
Convert rotations given as quaternions to rotation matrices.
Args:
quaternions: quaternions with real part first,
as tensor of shape (..., 4).
Returns:
Rotation matrices as tensor of shape (..., 3, 3).
"""
r, i, j, k = torch.unbind(quaternions, -1)
# pyre-fixme[58]: `/` is not supported for operand types `float` and `Tensor`.
two_s = 2.0 / (quaternions * quaternions).sum(-1)
o = torch.stack(
(
1 - two_s * (j * j + k * k),
two_s * (i * j - k * r),
two_s * (i * k + j * r),
two_s * (i * j + k * r),
1 - two_s * (i * i + k * k),
two_s * (j * k - i * r),
two_s * (i * k - j * r),
two_s * (j * k + i * r),
1 - two_s * (i * i + j * j),
),
-1,
)
return o.reshape(quaternions.shape[:-1] + (3, 3))
def quaternion_raw_multiply(a: torch.Tensor, b: torch.Tensor) -> torch.Tensor:
"""
Multiply two quaternions.
Usual torch rules for broadcasting apply.
Args:
a: Quaternions as tensor of shape (..., 4), real part first.
b: Quaternions as tensor of shape (..., 4), real part first.
Returns:
The product of a and b, a tensor of quaternions shape (..., 4).
"""
aw, ax, ay, az = torch.unbind(a, -1)
bw, bx, by, bz = torch.unbind(b, -1)
ow = aw * bw - ax * bx - ay * by - az * bz
ox = aw * bx + ax * bw + ay * bz - az * by
oy = aw * by - ax * bz + ay * bw + az * bx
oz = aw * bz + ax * by - ay * bx + az * bw
return torch.stack((ow, ox, oy, oz), -1)
class StructureModule(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, channel_size_msa, heads=8, scalar_key_dim=16, scalar_value_dim=16, point_key_dim=4, point_value_dim=4):
super().__init__()
self.ipa_block = IPABlock(
dim = channel_size_msa,
heads = heads,
scalar_key_dim = scalar_key_dim,
scalar_value_dim = scalar_value_dim,
)
self.out_proj = nn.Linear(channel_size_msa, 6)
def forward(self, target_seq, pair_repr, translations, quaternions):
rotations = quaternion_to_matrix(quaternions)
single_repr = self.ipa_block(
target_seq,
pairwise_repr = pair_repr,
rotations = rotations,
translations = translations,
)
# update quaternion and translation
updates = self.out_proj(single_repr)
quaternion_update, translation_update = updates.chunk(2, dim=-1)
quaternion_update = F.pad(quaternion_update, (1, 0), value = 1.)
quaternions = quaternion_raw_multiply(quaternions, quaternion_update)
translations = translations + torch.einsum('b n c, b n c r -> b n r', translation_update, rotations)
return translations, quaternions
4.3 Backbone構造予測
実装したStructure ModuleをもとにBackboneの構造予測を簡易的に行います。テンプレートやRecycligを省略しているので最初のtranslationは乱数で初期化しています。
ここらへんは本物から簡単化しすぎて解釈を間違えてるところがあるかもしれません。
class PredictStructure(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, channel_size_msa, depth=2):
super().__init__()
self.structure_module = StructureModule(channel_size_msa)
self.depth = depth
self.to_points = nn.Linear(channel_size_msa, 3)
def forward(self, msa_repr, pair_repr):
b, _, n, _ = msa_repr.shape
translations = torch.randn(b, n, 3)
quaternions = repeat(torch.tensor([1., 0., 0., 0.]), 'd -> b n d', b = b, n = n)
single_repr = msa_repr[:,0,:,:]
for i in range(self.depth):
translations, quaternions = self.structure_module(single_repr, pair_repr, translations, quaternions)
points_local = self.to_points(single_repr)
rotations = quaternion_to_matrix(quaternions)
coords = torch.einsum('b n c, b n c d -> b n d', points_local, rotations) + translations
return coords
4.4 入出力形状確認
実装したStructure ModuleにMSA表現とペア表現を入力してみて、出力として座標を取り出してみます。
predict = PredictStructure(config.channel_size_msa)
print(f"{msa_repr.shape=}")
print(f"{pair_repr.shape=}")
print()
coords = predict(msa_repr, pair_repr)
print(f"{coords.shape=}")
#出力結果
msa_repr.shape=torch.Size([2, 7, 100, 10])
pair_repr.shape=torch.Size([2, 100, 100, 10])
coords.shape=torch.Size([2, 100, 3])
5. まとめ
以上AlphaFoldの各モジュールをPyTorchで実装してみました。最初に説明したように実際にはMSAのマスクやExtra MSA、誤差関数、側鎖予測など省略した処理が多々あるので全部実装するにはまだまだ足りないですが、アルゴリズムをシンプルなコードで理解する上では参考になると思います。