はじめに
機能が豊富なPostgreSQLは、FDW(外部データラッパ)やテーブルパーティショニング機能の充実で益々便利になってきました。これまでデータベースは単体で使う事が普通だったと思いますが、これからはスケールアウト用途で複数のデータベースを同時に使う機会も増えてくるかもしれません。
データベースを安定運用するには統計情報の確認が欠かせませんが、複数のデータベースを扱うようになると個々の値をチェックするだけでなく、データベース間の統計値を比較してバランスをとる必要が出てきますので、統計情報のバランスがパッと見分かると嬉しいですよね。
そこで、PostgreSQLの統計データをグラフ化してみようと思います。
データの可視化には(色々な意味で最近ハマっている)Nuxt.jsを使ってみました。
なお、PostgreSQLのモニタリング手法やツールの導入を真面目に検討されている方は、公式サイトのwiki をご覧ください。
このテーマで書き始めた所、少々長くなってしまいましたので、目的別に章を4つに分けました。
1.環境構築編(この章です)
2.バックエンド編
3.フロントエンド編
4.単体テスト編
興味のある章をお選びください。
環境構築 事始め
普段はLinuxを使っているのですが、今回はWindows上で環境構築にチャレンジしてみました。
まずは、npm をインストールします。
・Node.js の公式サイト https://nodejs.org/ja/
続いて、後から色々便利なのでyarnもインストールします。
・yarn の公式サイト https://yarnpkg.com/ja/
エディタとしてVisual Studio Code (VSCode)をインストールします。
・VSCode の公式サイト https://code.visualstudio.com/
データベース(PostgreSQL)環境構築
(リモート環境のPostgreSQLを使う場合は「Nuxt環境構築」の章までスキップしてください)
Windows用のPostgreSQLのインストーラは、EnterpriseDB社のサイトからダウンロード出来ます。
https://www.postgresql.org/download/windows/
インストーラを起動してメッセージに従ってインストールしてください。
(今回は2019年12月時点で最新のバージョン12をインストールしました。)
pg_stat_statementsモジュール設定
"postgresql.conf"ファイルに'shared_preload_libraries'で'pg_stat_statements'を読み込むように設定を追加します。postgresql.confファイルは、デフォルトだと"C:\Program Files\PostgreSQL[version]\data"の下にあると思います。
(設定後、postgreSQLの再起動が必要です)
# - Shared Library Preloading -
shared_preload_libraries = 'pg_stat_statements'
pg_stat_statements.max = 10000
pg_stat_statements.track = all
DB作成
PostgreSQLのインストール時に同梱されているpgAdmin4を使ってデータベースを作ってみます。
"Servers" >"PostgreSQL 12" > "Databases"を右クリックして"Create" > "Database..."を選択します。
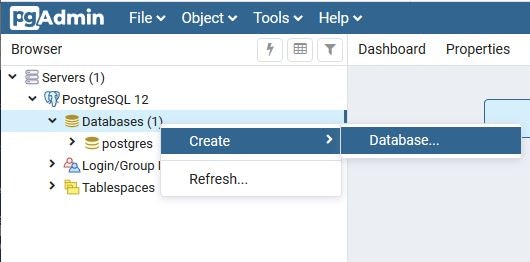
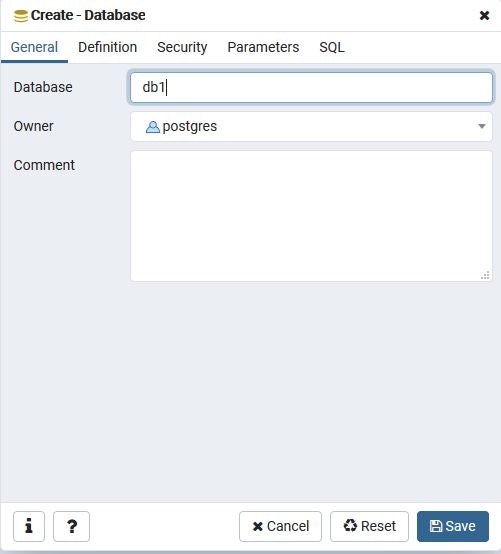
DB名を編集してデータベースを作成します。
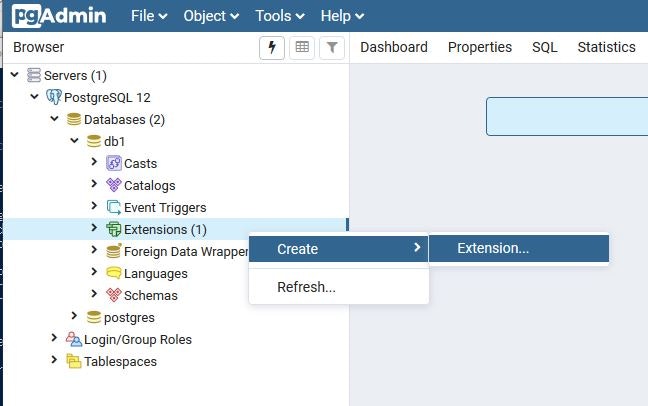
Extension登録
作成したデータベースの"Extensions"を右クリックして"Create" > "Extension..."を選択します。
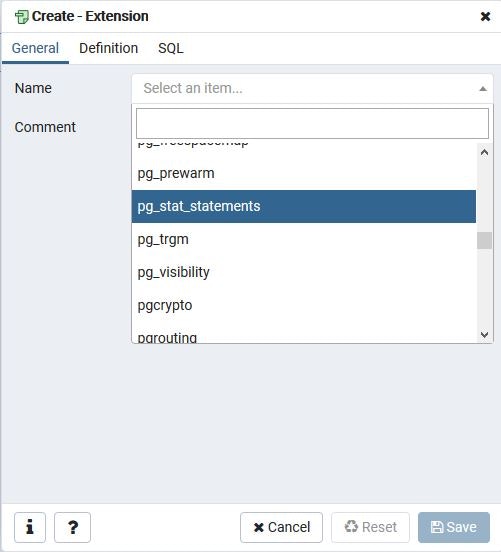
"Name"のプルダウンから"pg_stat_statements"を選択し、Extensionを登録します。
SQLでExtensionを登録する場合は、以下のSQLを実行します。
CREATE EXTENSION pg_stat_statements;
Nuxt環境構築
作業フォルダに移動して、PowerShellで npx create-nuxt-app プロジェクト名 というコマンドを叩きます。
(ここでは例としてpgmonというプロジェクト名を使っています)
> npx create-nuxt-app pgmon
環境構築時に色々聞いてきますが、以下を選択しました。
| 質問事項 | 選択 |
|---|---|
| Choose the package manager | Yarn |
| Choose UI framework | Vuetify.js |
| Choose custom server framework | Express |
| Choose Nuxt.js modules | Axios |
| Choose linting tools | ESLint |
| Choose test framework | Jest |
| Choose rendering mode | Universal (SSR) |
| Choose development tools | jsconfig.json |
プロジェクト名で指定したフォルダが出来ていますので、プロジェクトフォルダに降ります(ここ大事)。
続いて、今回の開発に必要なモジュールをインストールします。
> yarn add vue-context
> yarn add @nuxtjs/axios
> yarn add compression
> yarn add path
> yarn add cors
> yarn add pg pg-hstore
> yarn add -D nyc
> yarn add vue-i18n
> yarn add apexcharts vue-apexcharts
> yarn add eslint-config-prettier eslint-loader eslint-plugin-vue
> yarn add mocha supertest
以下のコマンドで環境をビルドして成功すればOKです。
> yarn run build
バックエンドサーバ(Express)環境設定
起動スクリプトがどうなっているかをpackage.jsonで確認します。
"scripts": {
"dev": "cross-env NODE_ENV=development nodemon server/index.js --watch server",
"build": "nuxt build",
"start": "cross-env NODE_ENV=production node server/index.js",
"generate": "nuxt generate",
"lint": "eslint --ext .js,.vue --ignore-path .gitignore .",
"test": "jest"
},
この例では"server/index.js"から起動されている事が分かります。
デフォルトの"server/index.js"にはフロントエンド側しか書かれていないので、バックエンド側(Express)の起動を追加します。
まず、"nuxt.config.js"にフロントエンドとバックエンドの待ち受けポート等の設定を追加します。
module.exports = {
mode: 'universal',
frontend: {
host: '0.0.0.0',
port: '8080'
},
backend: {
host: '0.0.0.0',
port: '3000'
},
env: {
apiUrl: 'http://localhost:3000'
},
(以下略)
次に、"server/index.js"にバックエンド側(Express)の起動を追加します。
const express = require('express')
const consola = require('consola')
const { Nuxt, Builder } = require('nuxt')
const compression = require('compression')
const cors = require('cors')
// Import and Set Nuxt.js options
const config = require('../nuxt.config.js')
config.dev = process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production'
// Init Nuxt.js
const nuxt = new Nuxt(config)
// Backend startup script
async function backend() {
const app = express()
app.use(compression({
threshold: 0,
level: 9,
memLevel: 9
}))
app.use(express.json())
app.use(express.urlencoded({ extended: false }))
app.use(cors())
const { host, port } = nuxt.options.backend
var http = require('http')
app.set('port', port)
var server = http.createServer(app)
server.listen(port, host)
consola.ready({
message: `Backend listening on ${host}:${port}`,
badge: true
})
}
backend() // start backend script
多言語対応(i18n)の設定
"lang"フォルダの下に日本語定義ファイル(ja.json)と英語定義ファイル(en.json)を用意し、"nuxt.config.js"に"nuxt-i18n"の設定を追加します。
modules: [
'@nuxtjs/axios',
[
'nuxt-i18n',
{
locales: [
{
code: 'en',
iso: 'en',
file: 'en.json'
},
{
code: 'ja',
iso: 'ja',
file: 'ja.json'
}
],
defaultLocale: 'ja',
lazy: true,
langDir: 'lang/'
}
]
],
日本語設定ファイル(ja.json)はこんな感じです。
{
"label": {
"otherError": "エラー",
"pageNotFound": "ページはありません",
"pgbmon": "Pg バランスモニター"
},
"button": {},
"tooltip": {
"menu": "メニュー"
},
"message": {
"otherError": "エラーが発生しました",
"pageNotFound": "指定のページはありません"
}
}
"layout/error.vue"を多言語化すると、こんな感じです。
<template>
<v-app dark>
<h1 v-if="error.statusCode === 404">
{{ $t('label.pageNotFound') }}
</h1>
<h1 v-else>
{{ $t('label.otherError') }}
</h1>
<NuxtLink to="/">
{{ $t('label.homePage') }}
</NuxtLink>
</v-app>
</template>
<script>
export default {
(省略)
data () {
const $t = this.$t.bind(this)
return {
pageNotFound: $t('message.pageNotFound'),
otherError: $t('message.otherError')
}
}
}
</script>
コード検証ツール(ESLint)の設定
Nuxt環境構築時にESLintはインストールされていますが、Expressのコードやテストコード用に".eslintrc.js"に設定値を追加します。
"env": {
"browser": true,
"es6": true,
"node": true,
"jest": true
},
"extends": [
"@nuxtjs",
"plugin:nuxt/recommended"
],
"globals": {
"Atomics": "readonly",
"SharedArrayBuffer": "readonly"
},
"parserOptions": {
"parser": "babel-eslint",
"ecmaVersion": 2018,
"sourceType": "module"
},
"plugins": [
"vue"
],
"rules": {
"no-unused-vars": ["error", { "args": "none" }],
"func-call-spacing": ["error", "never"],
"no-multi-spaces": 0,
"no-var": 0,
"nuxt/no-cjs-in-config": "off",
"vue/singleline-html-element-content-newline": 0,
"vue/max-attributes-per-line": 0,
"object-shorthand": 0,
"quote-props": ["error", "as-needed"]
}
package.jsonに以下の記述が無ければ追加してください。
"scripts": {
(省略)
"lint": "eslint --ext .js,.vue --ignore-path .gitignore .",
"lintfix": "eslint --fix --ext .js,.vue --ignore-path .gitignore ."
},
テストツール(mocha,supertest)の設定
Nuxt環境構築時にJestがインストールされていますが、バックエンドのExpressのテストはsupertest+mochaが便利なので、"package.json"のスクリプトに設定を追加します。
"scripts": {
(省略)
"test": "jest ./test/store/statistics.spec.js",
"nyc": "nyc mocha --timeout 20000 ./test/routers/*.spec.js",
},
(省略)
"jest": {
"transform": {
"^.+\\.(js)$": "babel-jest",
".*\\.(vue)$": "vue-jest"
},
"moduleNameMapper": {
"^@/(.*)$": "<rootDir>/$1",
"^~/(.*)$": "<rootDir>/$1"
},
"moduleFileExtensions": [
"js",
"vue"
],
"collectCoverageFrom": [
"<rootDIr>/**/*.{js,vue}"
]
},
"babel": {
"presets": [
[
"@babel/preset-env",
{
"targets": {
"node": "current"
}
}
]
]
},
"nyc": {
"check-coverage": true,
"sourceMap": true,
"instrument": true,
"exclude": [
".nuxt",
"app.js",
"*.js",
"*.sh",
"*.json",
"bin",
"config",
"coverage",
"log",
"middleware",
"migrations",
"node_modules",
"plugins",
"public",
"seeders",
"store",
"server/*.js",
"test",
"pgmon/.nuxt"
],
"reporter": [
"html",
"text"
],
"require": [],
"extension": [
".js"
],
"cache": true,
"all": true,
"report-dir": "./coverage"
}
さらに"nuxt.config.js"に設定を追加します。
build: {
extend (config, ctx) {
if (ctx.isDev && ctx.isClient) {
config.module.rules.push({
enforce: "pre",
test: /\.(js|vue)$/,
loader: "eslint-loader",
exclude: /(node_modules)/
})
}
}
}
server環境構築
"server"の下に"models"フォルダと"routers"フォルダを作成し、"config.js"ファイルを作成します。
config.jsにはバックエンドが接続するデータベースの情報を記述します。
exports.dbConf = [
{
host: 'localhost',
database: 'db1',
port: 5432,
user: 'postgres',
password: 'xxxxxxxx',
max: 20,
idleTimeoutMillis: 30000,
connectionTimeoutMillis: 2000
},
{
host: 'localhost',
database: 'db2',
port: 5432,
user: 'postgres',
password: 'xxxxxxxx',
max: 20,
idleTimeoutMillis: 30000,
connectionTimeoutMillis: 2000
},
{
host: 'localhost',
database: 'db3',
port: 5432,
user: 'postgres',
password: 'xxxxxxxx',
max: 20,
idleTimeoutMillis: 30000,
connectionTimeoutMillis: 2000
}
]
"server/models/index.js"にconfig.jsで設定したDBに接続するプログラムを書きます。
const dbConf = require('../config.js').dbConf
const { Pool } = require('pg')
const dbNum = dbConf.length
var pool = []
for (let i = 0; i < dbNum; i ++) {
pool[i] = new Pool(dbConf[i])
}
module.exports = { pool, dbConf }
まとめ
Windows環境にPostgreSQLサーバとNuxt環境を構築しました。
次はPostgreSQLの統計情報をAPIとして取得できるようにバックエンドを作ります。
>>PostgreSQLの統計情報を可視化(バックエンド編)