はじめに
前回の「.NET6を使ってみた1」では、「.NET6」での新しいテンプレートでのコンソールアプリについて解説しましたが、今回はAzure Blobへのファイルアップロード/ダウンロードを実装していきたいと思います。また、アプリケーションの環境変数を外出しの設定ファイル(appsettings.json)から読込む方法も併せて解説していきます。
Nugetパッケージによるライブラリーのインストール
今回はAzure Blobストレージを利用するので、「Azure.Storage.Blobs」をNugetよりインストールします。また、「Microsoft.Extensions.Hosting」と「Microsoft.Extensions.Azure」も併せてインストールしておきます。
- Azure.Storage.Blobs
- Azure Blobへのアクセス
- Microsoft.Extensions.Hosting
- 環境変数を設定ファイルから読込み
- Microsoft.Extensions.Azure
- BlobServiceClientのDI
Nugetでのインストール
- Visual Studioでプロジェクトを右クリックし、「Nugetパッケージの管理」を選択します。
- 参照タブで「Azure.Storage.Blobs」を選択し、最新版のインストールを行います。
(同様にMicrosoft.Extensions.HostingとMicrosoft.Extensions.Azureも行います)

全てのインストールが完了するとcsprojファイルに以下が追加されます。
<ItemGroup>
<PackageReference Include="Azure.Storage.Blobs" Version="12.10.0" />
<PackageReference Include="Microsoft.Extensions.Azure" Version="1.1.1" />
<PackageReference Include="Microsoft.Extensions.Hosting" Version="6.0.0" />
</ItemGroup>
設定ファイルの読み込み(appsettings.json)
アプリケーションの環境変数を設定ファイルに定義し読込みます。今回はappsettings.json(名前は任意)というファイルから読込む例を解説していきます。
まずは、アプリケーションルートにappsettings.jsonを作成し、ファイルを右クリック、プロパティを選択し、「出力ディレクトリーにコピー」で「新しい場合はコピーする」を選択しておきます。
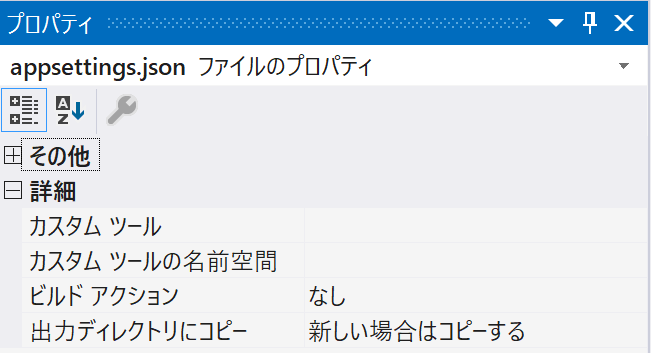
※ この設定を行わないと実行時にファイルが見つからないので注意です。
appsettings.jsonの設定値
appsettings.jsonファイルは以下のように設定しておきます。
{
"AzureBlobSettings": {
"AzureStorage": "Azure Storage Accountへの接続文字列",
"ContainerName": "コンテナ名"
"UploadFilePath": "アップロード対象のローカルファイルパス",
"DwonloadFileDir": "ダウンロードしたファイルを保存するローカルディレクトリパス"
}
}
appsettings.jsonの情報を格納するクラスを実装します。(属性名とプロパティ名は一致させる必要があります)
public class StorageOptions
{
public string AzureStorage { get; set; }
public string ContainerName { get; set; }
public string UploadFilePath { get; set; }
public string DwonloadFileDir { get; set; }
}
設定ファイルを読み込むために「Microsoft.Extensions.Hosting」を利用し、以下のよう実装します。
static IHostBuilder CreateHostBuilder(string[] args) =>
Host.CreateDefaultBuilder(args) // 既存の構成プロバイダをクリア
.ConfigureAppConfiguration((hostingContext, configuration) =>
{
// ソース(JSONファイルの内容などをクリア)
configuration.Sources.Clear();
// appsettings.jsonとappsettings.{Environment}.jsonをロード
IHostEnvironment env = hostingContext.HostingEnvironment;
configuration
.AddJsonFile("appsettings.json", optional: true, reloadOnChange: true)
.AddJsonFile($"appsettings.{env.EnvironmentName}.json", true, true);
}).ConfigureServices((context, services) => {
// StorageOptionsクラスに格納
var storageConfig = context.Configuration.GetSection("AzureBlobSettings");
services.Configure<StorageOptions>(storageConfig);
});
BlobServiceClientの追加
「Microsoft.Extensions.Azure」を利用し、BlobServiceClientをDI出来るように以下のコードを追加します。
static IHostBuilder CreateHostBuilder(string[] args) =>
Host.CreateDefaultBuilder(args)
.ConfigureAppConfiguration((hostingContext, configuration) =>
{
// ・・・
}).ConfigureServices((context, services) => {
// ・・・
services.AddAzureClients(azureBuilder =>
{
var storageOptions = new StorageOptions();
storageConfig.Bind(storageOptions);
azureBuilder.AddBlobServiceClient(storageOptions.AzureStorage);
});
});
BlobServiceClientを利用したアップロード/ダウンロード
実際のアップロードとダウンロードの処理を実装します。
// アップロード
static async Task UploadBlobAsync(BlobServiceClient blobServiceClient, StorageOptions options, string blobName)
{
// コンテナの取得
var containerClient = blobServiceClient.GetBlobContainerClient(options.ContainerName);
// コンテナの作成(存在しない場合のみ)
await containerClient.CreateIfNotExistsAsync();
// Blobの取得
var blobClient = containerClient.GetBlobClient(blobName);
// アップロード
await blobClient.UploadAsync(options.UploadFilePath, true);
}
// ダウンロード
static async Task DownloadBlobAsync(BlobServiceClient blobServiceClient, StorageOptions options, string blobName)
{
var downloadPath = $"{options.DwonloadFileDir}/{blobName}";
// コンテナの取得
var containerClient = blobServiceClient.GetBlobContainerClient(options.ContainerName);
// Blobの取得
var blobClient = containerClient.GetBlobClient(blobName);
// ダウンロード
await blobClient.DownloadToAsync(downloadPath);
}
DI対象のオブジェクトの取得
DI対象としたStorageOptionsとBlobServiceClientを取得します。(このコードを実装しなくても良いのですが、その実装方法は後述)
// appsettings.jsonの定義取得
var storageOptions = host.Services.GetRequiredService<IOptions<StorageOptions>>().Value;
// BlobServiceClient取得
var blobServiceClient = host.Services.GetRequiredService<BlobServiceClient>();
最後に、実行するコードを実装します。
IHost host = CreateHostBuilder(args).Build();
// BlobServiceClient取得
var blobServiceClient = host.Services.GetRequiredService<BlobServiceClient>();
// appsettings.jsonの定義取得
var storageOptions = host.Services.GetRequiredService<IOptions<StorageOptions>>().Value;
// Blob名
var blobName = "azure-blob-test.txt";
// Blobへのアップロード
await UploadBlobAsync(blobServiceClient, storageOptions, blobName);
// Blobからのダウンロード
await DownloadBlobAsync(blobServiceClient, storageOptions, blobName);
await host.RunAsync();
ここまでで環境変数を読込んで、Azure Blobへのファイルアップロード/ダウンロードが出来ました。
前述したようにStorageOptionsとBlobServiceClientのDIを任せられるように実装していきます。
まずは、Azure Blobへのアクセスを行うクラスを実装します。
この際、コンストラクタの引数にDI対象を定義すると、自動でインジェクションしてくれます。
public class AzureBlobService
{
private BlobServiceClient _BlobServiceClient;
private StorageOptions _Options;
// コンストラクタでインジェクション
public AzureBlobService(BlobServiceClient blobServiceClient, IOptions<StorageOptions> storageOptions)
{
this._BlobServiceClient = blobServiceClient;
this._Options = storageOptions.Value;
}
// アップロード
public async Task UploadBlobAsync(string blobName)
{
// コンテナの取得
var containerClient = this._BlobServiceClient.GetBlobContainerClient(this._Options.ContainerName);
// コンテナの作成(存在しない場合のみ)
await containerClient.CreateIfNotExistsAsync();
// Blobの取得
var blobClient = containerClient.GetBlobClient(blobName);
// アップロード
await blobClient.UploadAsync(this._Options.UploadFilePath, true);
}
// ダウンロード
public async Task DownloadBlobAsync(string blobName)
{
var downloadPath = $"{this._Options.DwonloadFileDir}/{blobName}";
// コンテナの取得
var containerClient = this._BlobServiceClient.GetBlobContainerClient(this._Options.ContainerName);
// Blobの取得
var blobClient = containerClient.GetBlobClient(blobName);
// ダウンロード
await blobClient.DownloadToAsync(downloadPath);
}
}
作成したクラスをDI対象とするために定義を追加します。
static IHostBuilder CreateHostBuilder(string[] args) =>
Host.CreateDefaultBuilder(args)
.ConfigureAppConfiguration((hostingContext, configuration) =>
{
// ・・・・
}).ConfigureServices((context, services) => {
// ・・・・
services.AddScoped<AzureBlobService>();
// ・・・・
});
最終的な実装
appsettings.json
{
"AzureBlobSettings": {
"AzureStorage": "Azure Storage Accountへの接続文字列",
"ContainerName": "コンテナ名"
"UploadFilePath": "アップロード対象のローカルファイルパス",
"DwonloadFileDir": "ダウンロードしたファイルを保存するローカルディレクトリパス"
}
}
Program.cs
using Azure.Storage.Blobs;
using Microsoft.Extensions.Azure;
using Microsoft.Extensions.Configuration;
using Microsoft.Extensions.DependencyInjection;
using Microsoft.Extensions.Hosting;
using Microsoft.Extensions.Options;
IHost host = CreateHostBuilder(args).Build();
var service = host.Services.GetRequiredService<AzureBlobService>();
// blob名
var blobName = "azure-blob-test.txt";
// Blobへのアップロード
await service.UploadBlobAsync(blobName);
// Blobからのダウンロード
await service.DownloadBlobAsync(blobName);
await host.RunAsync();
static IHostBuilder CreateHostBuilder(string[] args) =>
Host.CreateDefaultBuilder(args) // 既存の構成プロバイダをクリア
.ConfigureAppConfiguration((hostingContext, configuration) =>
{
// ソース(JSONファイルの内容などをクリア)
configuration.Sources.Clear();
// appsettings.jsonとappsettings.{Environment}.jsonをロード
IHostEnvironment env = hostingContext.HostingEnvironment;
configuration
.AddJsonFile("appsettings.json", optional: true, reloadOnChange: true)
.AddJsonFile($"appsettings.{env.EnvironmentName}.json", true, true);
}).ConfigureServices((context, services) => {
// StorageOptionsクラスに格納
var storageConfig = context.Configuration.GetSection("AzureBlobSettings");
services.Configure<StorageOptions>(storageConfig);
// AzureBlobServiceをDI対象へ
services.AddScoped<AzureBlobService>();
// BlobServiceClienをDI対象へ
services.AddAzureClients(azureBuilder =>
{
var storageOptions = new StorageOptions();
storageConfig.Bind(storageOptions);
azureBuilder.AddBlobServiceClient(storageOptions.AzureStorage);
});
});
public class StorageOptions
{
public string AzureStorage { get; set; }
public string ContainerName { get; set; }
public string UploadFilePath { get; set; }
public string DwonloadFileDir { get; set; }
}
public class AzureBlobService
{
private BlobServiceClient _BlobServiceClient;
private StorageOptions _Options;
// コンストラクタでインジェクション
public AzureBlobService(BlobServiceClient blobServiceClient, IOptions<StorageOptions> storageOptions)
{
this._BlobServiceClient = blobServiceClient;
this._Options = storageOptions.Value;
}
// アップロード
public async Task UploadBlobAsync(string blobName)
{
// コンテナの取得
var containerClient = this._BlobServiceClient.GetBlobContainerClient(this._Options.ContainerName);
// コンテナの作成(存在しない場合のみ)
await containerClient.CreateIfNotExistsAsync();
// Blobの取得
var blobClient = containerClient.GetBlobClient(blobName);
// アップロード
await blobClient.UploadAsync(this._Options.UploadFilePath, true);
}
// ダウンロード
public async Task DownloadBlobAsync(string blobName)
{
var downloadPath = $"{this._Options.DwonloadFileDir}/{blobName}";
// コンテナの取得
var containerClient = this._BlobServiceClient.GetBlobContainerClient(this._Options.ContainerName);
// Blobの取得
var blobClient = containerClient.GetBlobClient(blobName);
// ダウンロード
await blobClient.DownloadToAsync(downloadPath);
}
}
終わりに
今回は設定ファイル(appsettings.json)の読込みとBlobへのアクセスを実装しました。
基本的には、.NET Core 3.1から大きな変更は感じられませんでした。
次回はEntity FrameworkやAzure Functions/Web APIなどを試していきたいと思います。
