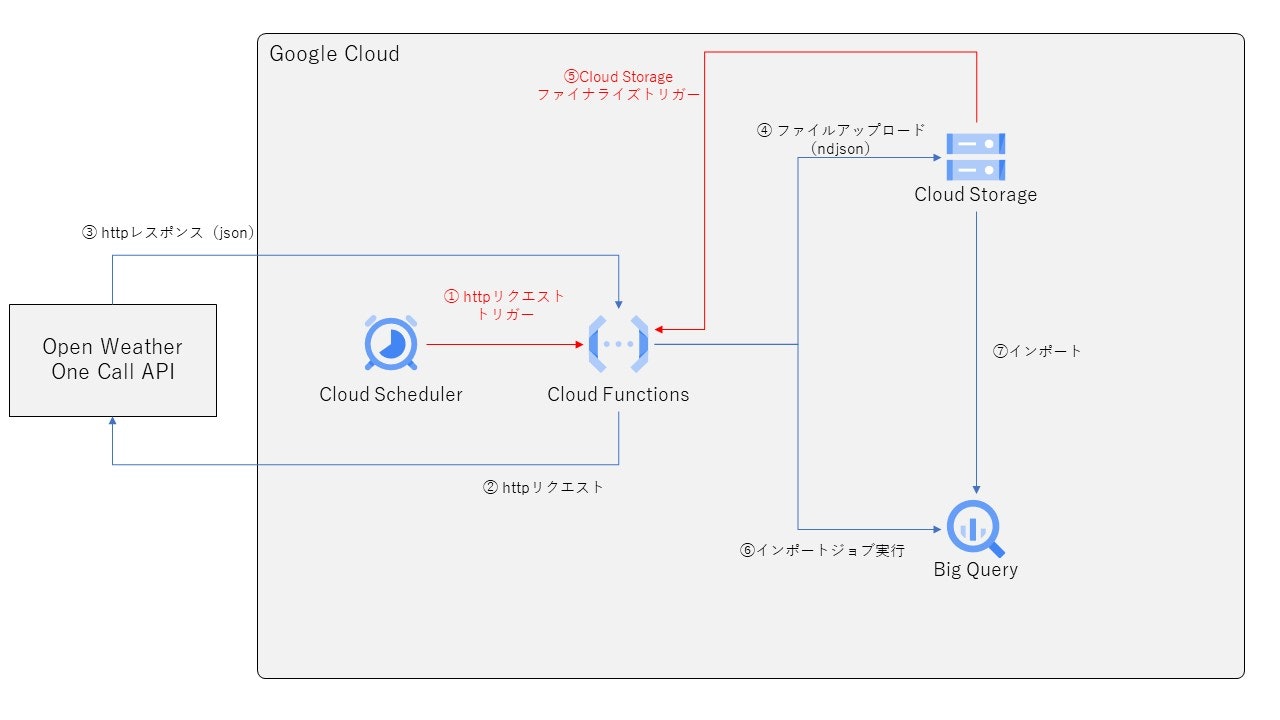
データ可視化や分析をする上で練習用データが欲しかったので、勉強も兼ねて無料で利用できるOpenWeatherで天気情報の収集~蓄積を実装しました。
処理概要
- Cloud SchedulerでCloud FunctionsのトリガーURLにHTTPリクエストを投げる
- Cloud FunctionsでOpen Weather One Call APIにHTTPリクエストを投げ、レスポンスとしてjson形式の天気情報を受け取る
- json形式の天気情報をndjson形式でCloud Storageに格納する
- Cloud Storageにndjson形式のファイルが作成(ファイナライズ)されたら、Cloud Functionsでそのイベントを検知し、BigQueryにインポートする
次にそれぞれの細かい実装部分について、個別に見ていこうと思います。
Cloud Schedulerで処理を起動
今回は情報の収集~蓄積まで、すべてCloud Functionsが実施しています。ですがCloud Functionsは、自身で処理の起動を行うことができません。なので、外部から処理の開始を促してあげる必要があります。開始方法は、以下の2つがあります。
- Cloud FunctionsがHTTPリクエストを受け付ける
- Cloud Functionsがクラウド上で発生する特定のイベントを検知する
情報収集の処理は、HTTPリクエストで起動するタイプのCloud Functionsを用意したので、とある時刻になったらCloud FunctionsのトリガーURLにHTTPリクエストを送るCloud Schedulerを設定しました。設定内容は以下の通りです。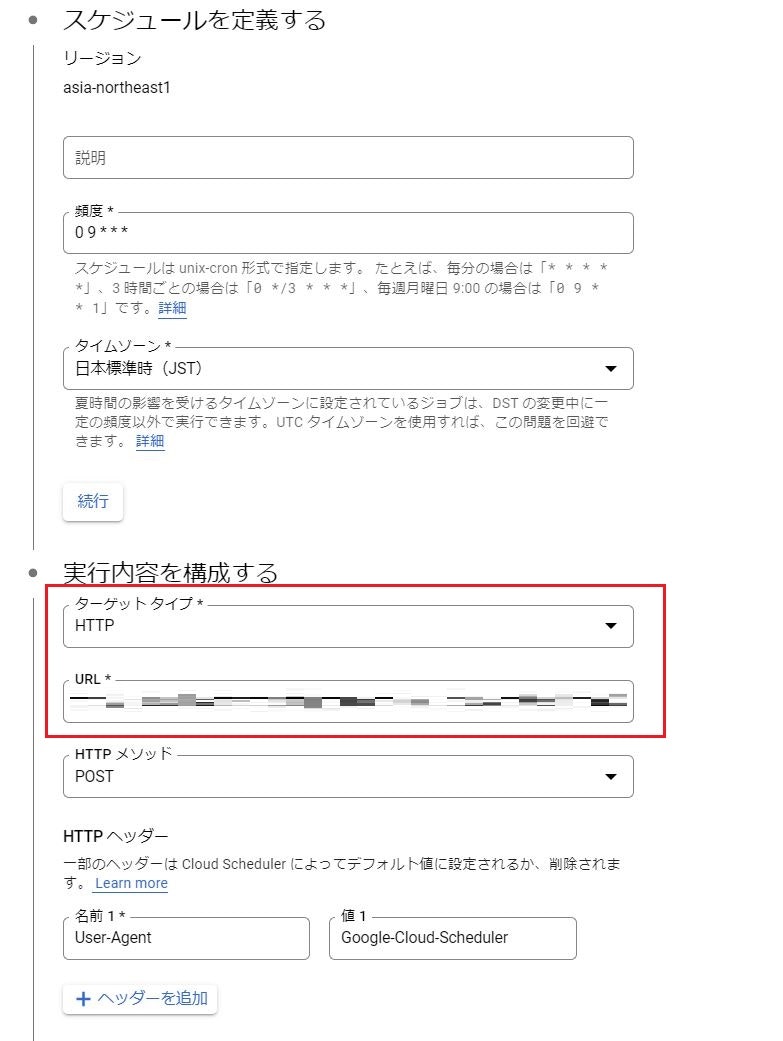
「頻度」の欄に実行したいスケジュールを記載します。指定方法はLinuxのcrontabと同じです。Googleのドキュメントにもcronジョブスケジュールの構成なるものがあるので、分からない人は確認してみてください。赤枠部分がCloud Functions(HTTP関数)で大切な設定であり、URL欄にCloud FunctionsのトリガーURLを記載します。
また、Cloud FunctionsはHTTPをトリガーとする場合、デフォルトで接続元の認証が行われます。以下がCloud Functionsを起動するための認証設定です。

サービスアカウント部分に関数の起動権限があるサービスアカウントを指定してあげてください。Cloud Functionsの認証については、ここに詳しく記載されているので、確認してみてください。
Cloud Functionsで天気情報を取得
ここからは、天気情報を取得しているプログラムを実際に見ていきましょう。ランタイムはPython3.9を選択しています。
ソースコード
from datetime import datetime, date
import json
import requests
from google.cloud import bigquery
from google.cloud import storage
target_url = "https://api.openweathermap.org/data/2.5/onecall"
gcs_bucket = "jsonファイルを配置したいバケット名を記載"
class OpenWeatherManager(object):
def __init__(self):
with open("open-weather-api.json", "r") as api_token_file:
api_token_json = json.load(api_token_file)
self.__api_token = api_token_json["api_token"]
# OpenWeatherからjson形式で天気情報を取得
# 取得対象:current, daily, hourly
def oneCall(self):
with open("target-city.json", "r") as target_city_file:
target_cities = json.load(target_city_file)
oneCallData = []
for target_city in target_cities:
city_name = target_city["city_name"]
latitude = target_city["latitude"]
longitude = target_city["longitude"]
params = {
"lat":latitude,
"lon":longitude,
"appid":self.__api_token,
"exclude":"minutely,alerts",
"units":"metric",
"mode":"json",
"lang":"ja"
}
response = requests.get(target_url, params=params)
oneCallData.append({
"city_name":city_name,
"weather_info":response.json()
})
return oneCallData
def unix2Datetime(self, unix_time):
return datetime.fromtimestamp(unix_time).strftime("%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S")
# 取得した情報からcurrentの情報を整形
def currentDump(self, current_data):
current_data["dt"] = self.unix2Datetime(current_data["dt"])
current_data["sunrise"] = self.unix2Datetime(current_data["sunrise"])
current_data["sunset"] = self.unix2Datetime(current_data["sunset"])
if "wind_gust" not in current_data.keys():
current_data["wind_gust"] = 0.0
if "rain" not in current_data.keys():
current_data["rain_1h"] = 0.0
else:
current_data["rain_1h"] = current_data["rain"]["1h"]
del current_data["rain"]
if "snow" not in current_data.keys():
current_data["snow_1h"] = 0.0
else:
current_data["snow_1h"] = current_data["snow"]["1h"]
del current_data["snow"]
weather_data_dict = current_data["weather"][0]
for weather_data_key in weather_data_dict.keys():
new_key = "weather_" + weather_data_key
current_data[new_key] = weather_data_dict[weather_data_key]
del current_data["weather"]
parse_data = json.dumps(current_data)
return parse_data
# 取得した情報からhourlyの情報を整形
def hourlyDump(self, hourly_data):
parse_data = ""
for hourly_row in hourly_data:
hourly_row["dt"] = self.unix2Datetime(hourly_row["dt"])
if "wind_gust" not in hourly_row.keys():
hourly_row["wind_gust"] = 0.0
if "rain" not in hourly_row.keys():
hourly_row["rain_1h"] = 0.0
else:
hourly_row["rain_1h"] = hourly_row["rain"]["1h"]
del hourly_row["rain"]
if "snow" not in hourly_row.keys():
hourly_row["snow_1h"] = 0.0
else:
hourly_row["snow_1h"] = hourly_row["snow"]["1h"]
del hourly_row["snow"]
hourly_weather = hourly_row["weather"][0]
for hourly_weather_key in hourly_weather.keys():
new_key = "weather_" + hourly_weather_key
hourly_row[new_key] = hourly_weather[hourly_weather_key]
del hourly_row["weather"]
parse_row = json.dumps(hourly_row)
parse_data += (parse_row + "\n")
return parse_data
# 取得した情報からdailyの情報を整形
def dailyDump(self, daily_data):
parse_data = ""
for daily_row in daily_data:
daily_row["dt"] = self.unix2Datetime(daily_row["dt"])
daily_row["sunrise"] = self.unix2Datetime(daily_row["sunrise"])
daily_row["sunset"] = self.unix2Datetime(daily_row["sunset"])
daily_row["moonrise"] = self.unix2Datetime(daily_row["moonrise"])
daily_row["moonset"] = self.unix2Datetime(daily_row["moonset"])
if "wind_gust" not in daily_row.keys():
daily_row["wind_gust"] = 0.0
if "rain" not in daily_row.keys():
daily_row["rain"] = 0.0
if "snow" not in daily_row.keys():
daily_row["snow"] = 0.0
daily_temp_data = daily_row["temp"]
for daily_temp_key in daily_temp_data.keys():
new_temp_key = "temp_" + daily_temp_key
daily_row[new_temp_key] = daily_temp_data[daily_temp_key]
del daily_row["temp"]
daily_feels_data = daily_row["feels_like"]
for daily_feels_key in daily_feels_data.keys():
new_feels_key = "feels_like_" + daily_feels_key
daily_row[new_feels_key] = daily_feels_data[daily_feels_key]
del daily_row["feels_like"]
daily_weather_data = daily_row["weather"][0]
for daily_weather_key in daily_weather_data.keys():
new_weather_key = "weather_" + daily_weather_key
daily_row[new_weather_key] = daily_weather_data[daily_weather_key]
del daily_row["weather"]
parse_row = json.dumps(daily_row)
parse_data += (parse_row + "\n")
return parse_data
# 取得した情報をGCS上にndjson形式で書き込む
def toJson(self, oneCallData):
storage_client = storage.Client()
target_bucket = storage_client.bucket(gcs_bucket)
for city_data in oneCallData:
city_name = city_data["city_name"]
for weather_data_key in city_data["weather_info"].keys():
if weather_data_key == "current":
current_data = city_data["weather_info"][weather_data_key]
parse_data_str = self.currentDump(current_data)
target_blob = target_bucket.blob(
"current_{}_{}.json".format(
city_name,
date.today().strftime('%Y%m%d')
)
)
target_blob.upload_from_string(parse_data_str)
elif weather_data_key == "hourly":
hourly_data = city_data["weather_info"][weather_data_key]
parse_data_str = self.hourlyDump(hourly_data)
target_blob = target_bucket.blob(
"hourly_{}_{}.json".format(
city_name,
date.today().strftime('%Y%m%d')
)
)
target_blob.upload_from_string(parse_data_str)
elif weather_data_key == "daily":
daily_data = city_data["weather_info"][weather_data_key]
parse_data_str = self.dailyDump(daily_data)
target_blob = target_bucket.blob(
"daily_{}_{}.json".format(
city_name,
date.today().strftime('%Y%m%d')
)
)
target_blob.upload_from_string(parse_data_str)
def getInfo(request):
owm = OpenWeatherManager()
oneCallData = owm.oneCall()
owm.toJson(oneCallData)
return "OK"
天気情報取得、Cloud Storageへのデータ格納の実装は、以下のページを参考にしました。
天気情報はいくつか種類がありますが、今回はcurrent、hourly、dailyの3種類の取得しています。
GCSへアップロードしたファイルはndjson形式としたのですが、これはBigQueryが通常のjson形式でのインポートを提供していないためです。Cloud Storageからjsonファイルをインポートする場合の制限事項は、ここに記載があるので確認してみてください。
APIキーファイル
このファイルには、OpenWeatherのAPIキーを記載しています。別にこれは必須ではなく、環境変数にセットするでも全然いいと思います。OpenWeatherのWebページからAPIキーを発行できます。(事前にアカウント作成が必要)
{
"api_token":"ここに発行したAPIキーを張り付けてください"
}
天気情報取得対象ファイル
このファイルには、天気情報を取得したい都市の名前、緯度、経度情報を記載してください。私はGoogle Mapで緯度、経度を調べました。
[
{
"city_name":"都市名1",
"latitude":"緯度情報1",
"longitude":"経度情報1"
},
{
"city_name":"都市名2",
"latitude":"緯度情報2",
"longitude":"経度情報2"
},
{
必要であればこれ以降も記載...
}
]
プログラム利用モジュール
このファイルには、プログラムが利用している外部モジュールを記載しておきます。
google-cloud-bigquery
google-cloud-storage
requests
Cloud Functionsの設定
Cloud Functionsは、基本的に上に記載した4ファイルを配置していただければよいです。HTTPトリガーで実行するので、そこだけ間違えないようにします。
赤枠部分がトリガーURLで、Cloud Schedulerに設定するものとなります。
このままで情報取得は可能なのですが、取得した情報の時刻が9時間ずれてしまいます。なんで、ランタイム環境変数に東京のタイムゾーンの設定を入れていおきます。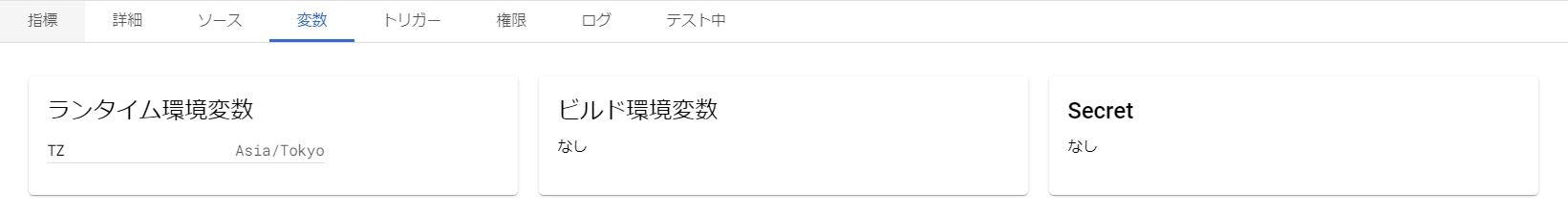
注意事項
先程記載した通り、Cloud Functionsはデフォルトで起動元の認証を行いますが、省略することも可能です。Cloud Functionsでの認証を省略した場合、サービスアカウントの設定は不要となりますが、不特定多数の人が処理を起動できることになってしまうのでやめた方がいいでしょう。
Cloud FunctionsでBigQueryへのインポート
次に格納したndjsonファイルをBigQueryにインポートする処理を見ていきます。
ソースコード
from google.cloud import storage
from google.cloud import bigquery
def importJson2bq(event, context):
"""Triggered by a change to a Cloud Storage bucket.
Args:
event (dict): Event payload.
context (google.cloud.functions.Context): Metadata for the event.
"""
file = event
table_id = "weather_data." + file["name"].split(".")[0]
client = bigquery.Client()
job_config = bigquery.LoadJobConfig(
autodetect=True,
source_format=bigquery.SourceFormat.NEWLINE_DELIMITED_JSON
)
uri = "gs://ファイルを格納したバケット名を記載/" + file["name"]
load_job = client.load_table_from(
uri, table_id, job_config=job_config
)
load_job.result()
destination_table = client.get_table(table_id)
return "Loaded {} table".format(destination_table.name)
変数uriにndjsonファイルを格納したバケット名を記載してください。BigQueryへのインポート処理の実装は、ここのページを参考にしました。
プログラム利用モジュール
このファイルは先ほどとほぼ同じです。requestsは不要なので、記載を削除しています。
google-cloud-bigquery
google-cloud-storage
Cloud Functionsの設定
BigQueryへインポートする処理のポイントは、Cloud Storageにファイルが作成されたら処理を開始するという点です。設定は以下の感じで指定します。

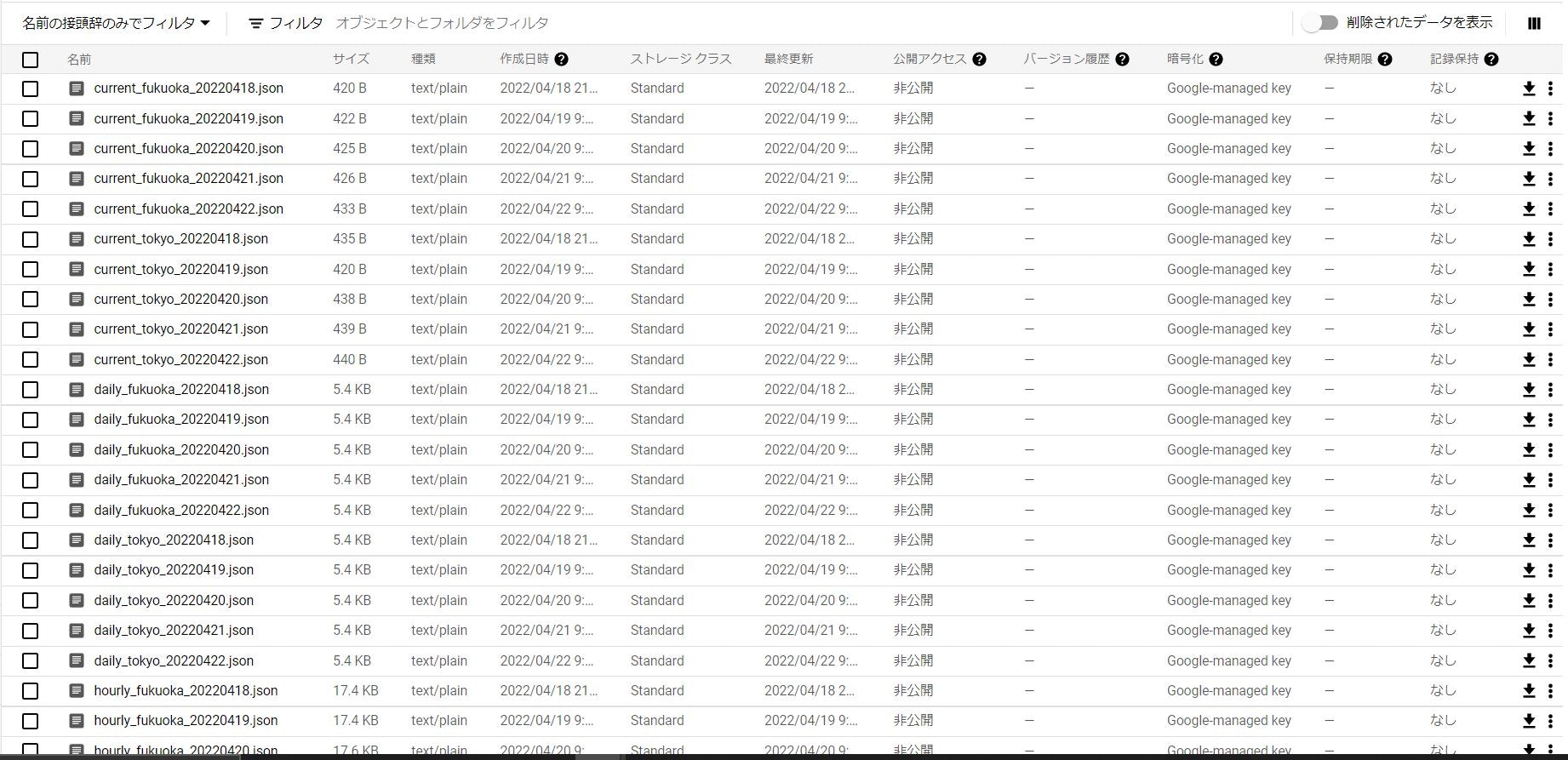
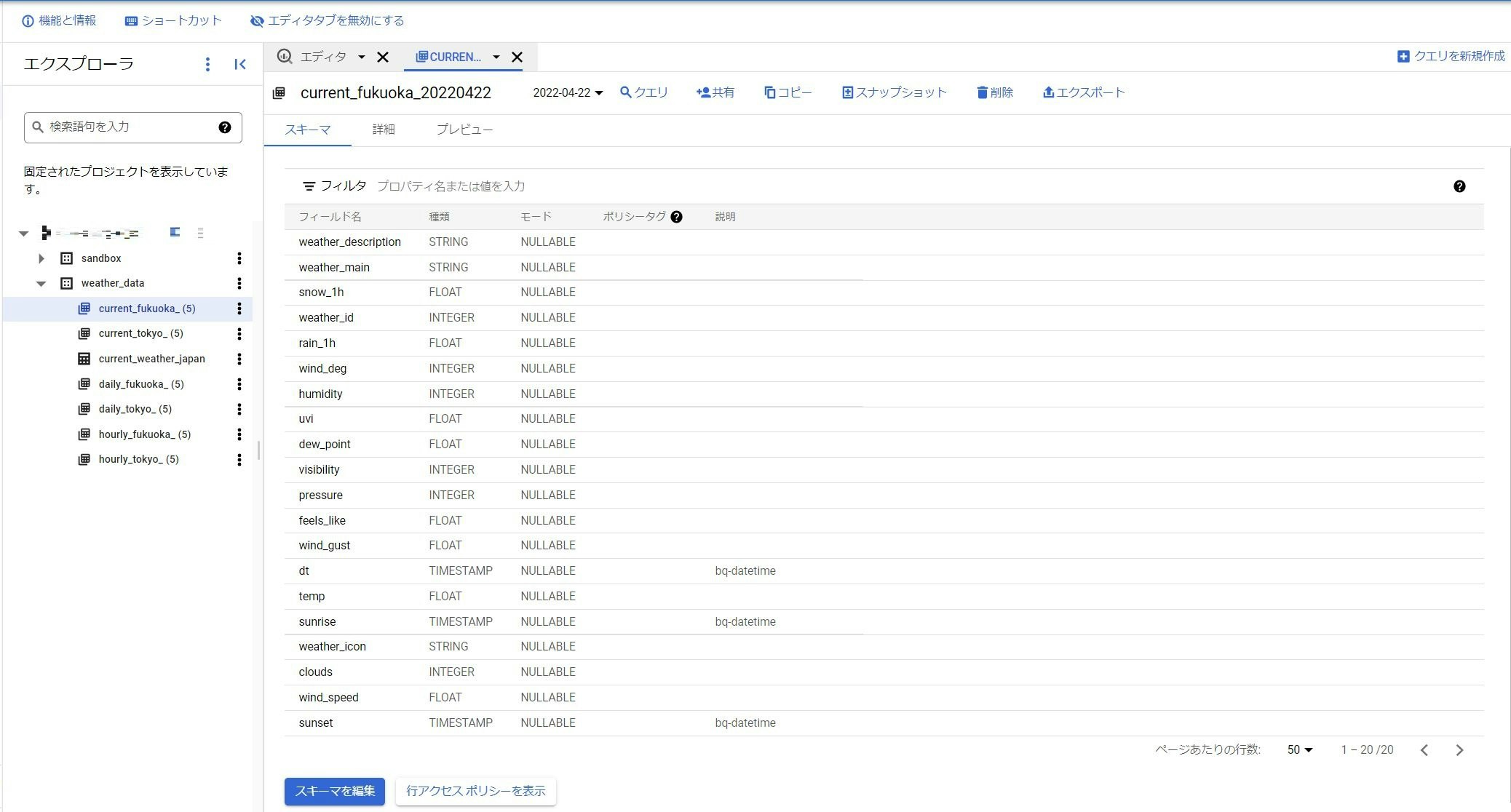
実行結果
結果はこんな感じです。
Cloud Storage
Big Query
最後に
なんとかデータの取得~蓄積まで実装できました。ただCloud Functionsのみで実装すると、システム運用の観点から見るとイマイチですね。次は、Cloud Composerとか使ってワークフロー化してみようかな。