[Swift][NSOpenGLView]SwiftでNSOpenGLViewを使う
SwiftでCocoaアプリケーションを開発する際の、NSOpenGLView使用法についてメモ代わりにまとめました。
毎度のことですが、殴り書きご容赦ください。
私はObjective-Cの経験が無く、NSOpenGLViewのSwiftでの実装方法に四苦八苦しました。
NSOpenGLViewを使うメリットは、やはり描写の速さでしょうか。
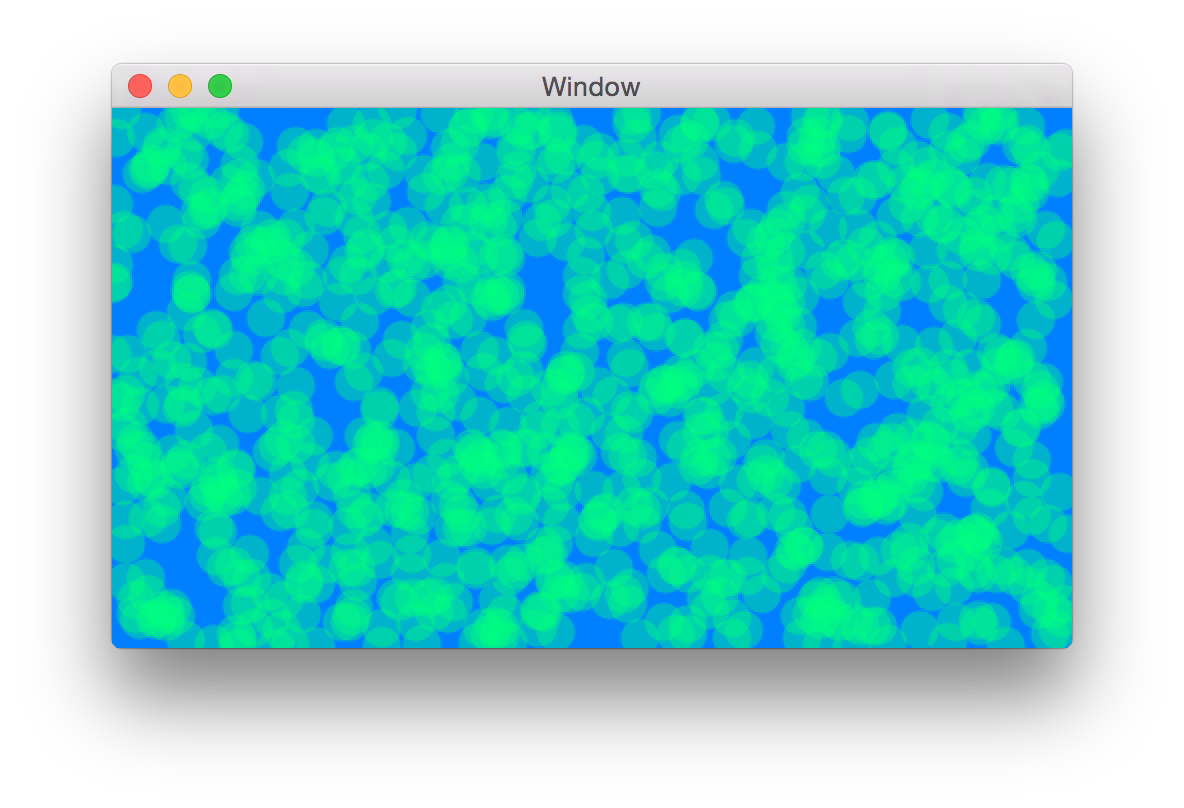
このサンプルコードでは1000個の点を描写しています。
ViewController
まずはViewControllerのコードです。
import Cocoa
class ViewController: NSViewController {
var OpenGLView:NSOpenGLView!
var OpenGLContents:OpenGLContentsDraw!
override func mouseDown(theEvent: NSEvent) {
self.OpenGLContents.updateScene()
}
override func viewDidLoad() {
super.viewDidLoad()
self.OpenGLView = NSOpenGLView(frame:CGRectMake(0,0,self.view.bounds.width,self.view.bounds.height))
self.OpenGLContents = OpenGLContentsDraw(frame:CGRectMake(0,0,self.view.bounds.width,self.view.bounds.height),PointSize:GLfloat(20.0))
self.OpenGLView.addSubview(self.OpenGLContents)
self.view.addSubview(self.OpenGLView)
// Do any additional setup after loading the view.
}
override var representedObject: AnyObject? {
didSet {
// Update the view, if already loaded.
}
}
}
今回は、stroyboardを使用せず、オブジェクトもコードで生成します。
**override func viewDisLoad()**は、viewのロードが完了した際に呼ばれる関数です。
ここで、NSOpenGLViewオブジェクトを生成します。生成方法は、window上の位置とオブジェクトのサイズをCGRectMakeで指定するのみです。
self.OpenGLView = NSOpenGLView(frame:CGRectMake(0,0,self.view.bounds.width,self.view.bounds.height))
実際にwindowに追加するには、以下のようにします。
self.view.addSubview(self.OpenGLView)
これで何も描写されていないNSOpenGLViewがWindow上に生成されるかと思います。
描写内容を生成し、NSOpenGLViewに描写するためにはcontentsを生成し、NSOpenGLViewに追加します。
ここで、新規ファイルを作成し、OpenGLContentsDraw.swiftをプロジェクトに追加します。
少し長いですが、以下のようにコードを書きます。
描写部分
import Foundation
import Cocoa
import OpenGL
import GLKit
import GLUT
class OpenGLContentsDraw:NSOpenGLView{
var width:GLsizei
var height:GLsizei
var PointSize:GLfloat
init?(frame:NSRect, PointSize:GLfloat) {
//set size of this view
self.width = GLsizei(frame.size.width)
self.height = GLsizei(frame.size.height)
self.PointSize = PointSize
//setup pixelFormatAttributes
let pixelFormatAttributes:[NSOpenGLPixelFormatAttribute] = [
UInt32(NSOpenGLPFAAccelerated),
UInt32(NSOpenGLPFADoubleBuffer),
UInt32(NSOpenGLPFADepthSize), UInt32(32),
UInt32(NSOpenGLPFAColorSize), UInt32(48),
UInt32(NSOpenGLPFAAlphaSize), UInt32(16),
UInt32(NSOpenGLPFAMultisample),
UInt32(NSOpenGLPFASampleBuffers), UInt32(1),
UInt32(NSOpenGLPFASamples), UInt32(4),
UInt32(NSOpenGLPFAMinimumPolicy),
UInt32(0)
]
let glPixelFormat = NSOpenGLPixelFormat(attributes:pixelFormatAttributes)
super.init(frame:frame,pixelFormat:glPixelFormat)
}
required init?(coder: NSCoder) {
fatalError("init(coder:) has not been implemented")
}
func updateScene(){
self.needsDisplay = true
self.update()
}
// draw something...
override func drawRect(dirtyRect:NSRect) {
Clear()
//draw something
//blend for PointSmooth
glBlendFunc(GLenum(GL_SRC_ALPHA), GLenum(GL_ONE_MINUS_SRC_ALPHA))
glEnable(GLenum(GL_BLEND))
glEnable(GLenum(GL_POINT_SMOOTH))
glPointSize(PointSize)
glColor4f(0.0, 1.0, 0.5,0.4)
for i in 0..<1000{
//generate random values
let x:GLfloat = GLfloat(arc4random_uniform(UInt32(self.width)))
let y:GLfloat = GLfloat(arc4random_uniform(UInt32(self.height)))
//draw
glBegin(GLenum(GL_POINTS))
glVertex2f(x, y)
glEnd()
}
glDisable(GLenum(GL_BLEND))
//flush
glFlush()
}
//when window is reshaped
override func reshape() {
glViewport(0,0,self.width,self.height)
glMatrixMode(GLenum(GL_PROJECTION))
glLoadIdentity()
glOrtho(0.0,GLdouble(width),0.0,GLdouble(height),-1.0,1.0);
glMatrixMode(GLenum(GL_MODELVIEW))
glLoadIdentity()
}
//clear buffer
func Clear()
{
glClearColor(0.0, 0.5, 1.0, 1.0)
glClear(GLenum(GL_COLOR_BUFFER_BIT) | GLenum(GL_DEPTH_BUFFER_BIT));
glViewport(0,0,width,height)
glMatrixMode(GLenum(GL_PROJECTION))
glLoadIdentity()
glOrtho(0.0,GLdouble(width),0.0,GLdouble(height),-1.0,1.0);
glMatrixMode(GLenum(GL_MODELVIEW))
glLoadIdentity()
}
}
上から順に説明すると、
init?(frame:NSRect, PointSize:GLfloat) {
//set size of this view
self.width = GLsizei(frame.size.width)
self.height = GLsizei(frame.size.height)
self.PointSize = PointSize
//setup pixelFormatAttributes
let pixelFormatAttributes:[NSOpenGLPixelFormatAttribute] = [
UInt32(NSOpenGLPFAAccelerated),
UInt32(NSOpenGLPFADoubleBuffer),
UInt32(NSOpenGLPFADepthSize), UInt32(32),
UInt32(NSOpenGLPFAColorSize), UInt32(48),
UInt32(NSOpenGLPFAAlphaSize), UInt32(16),
UInt32(NSOpenGLPFAMultisample),
UInt32(NSOpenGLPFASampleBuffers), UInt32(1),
UInt32(NSOpenGLPFASamples), UInt32(4),
UInt32(NSOpenGLPFAMinimumPolicy),
UInt32(0)
]
let glPixelFormat = NSOpenGLPixelFormat(attributes:pixelFormatAttributes)
super.init(frame:frame,pixelFormat:glPixelFormat)
}
required init?(coder: NSCoder) {
fatalError("init(coder:) has not been implemented")
}
初期化部分です。必須項目で、ここでNSOpenGLViewのpixelFormatを設定します。DoubleBufferやDepthtestなどなど
また、OpenGLDrawContentsに渡す引数もここで設定します。
上では、GLfloat型のPointSizeを渡しています。
この引数は、ViewControllerから渡すようになっています。
func updateScene(){
self.needsDisplay = true
self.update()
}
描写のアップデートを司る関数です。
NSOpenGLViewの描写をアップデートするために、update()が用意されていますが、これを単純に呼ぶだけでは描写は更新されません。
その前に、needsDisplayをtrueにする必要があります。
override func drawRect(dirtyRect:NSRect) {
//ここに描写内容を書く
}
drawRectはロード時、windowのreshape時、また、update()がコールされた時に実行されます。
OpenGLの描写内容はここで書きます。
//when window is reshaped
override func reshape() {
glViewport(0,0,self.width,self.height)
glMatrixMode(GLenum(GL_PROJECTION))
glLoadIdentity()
glOrtho(0.0,GLdouble(width),0.0,GLdouble(height),-1.0,1.0);
glMatrixMode(GLenum(GL_MODELVIEW))
glLoadIdentity()
}
windowがreshapeされた時に呼ばれます。
windowサイズが変更された時のため、glViewportをwindowサイズに合わせています。
これくらいでしょうか。
実装
ViewControllerに戻りまして、
OpenGLDrawContentsを生成し、NSOpenGLViewに追加するには以下のようにします。
OpenGLContentsDraw(frame:CGRectMake(0,0,self.view.bounds.width,self.view.bounds.height),
PointSize:GLfloat(20.0))
self.OpenGLView.addSubview(self.OpenGLContents)
アップデート
マウスで画面をクリックすると、描写をアップデートするようにしました。
override func mouseDown(theEvent: NSEvent) {
self.OpenGLContents.updateScene()
}
今回はテストのために、マウスダウンで描写を更新するようにしましたが、アニメーションを作る際は、NSTimerを使うようです。
参考