MySQL 8.0のJSON型を使うと、リレーショナルデータベースにもっと柔軟性を持たせることができます。Google Colabで実際に動かしながら学んでみました。
注意事項
- Google Colabの制限: ランタイムがリセットされると、インストールしたMySQLとすべてのデータが消失します
- 本格的な開発: 永続化が必要な場合は、AWS RDS、Google Cloud SQL等のマネージドデータベースサービスを使用してください
- JSONカラムの制限: MySQL 8.0.13より前のバージョンでは、JSONカラムにNULL以外のデフォルト値を設定できません
環境準備
# MySQL 8.0インストールと起動
!apt update && apt install mysql-server -y
!service mysql start
!mysql -u root -e "ALTER USER 'root'@'localhost' IDENTIFIED WITH mysql_native_password BY 'password';"
# バージョン確認
!mysql -u root -p'password' -e "SELECT VERSION();"
# PyMySQLライブラリのインストールと接続設定
!pip install pymysql
import pymysql
import json
# データベース接続
connection = pymysql.connect(host='localhost', user='root', password='password', charset='utf8mb4')
with connection.cursor() as cursor:
# データベースとテーブル作成
cursor.execute("CREATE DATABASE IF NOT EXISTS json_demo")
cursor.execute("USE json_demo")
cursor.execute("""
CREATE TABLE users (
id INT AUTO_INCREMENT PRIMARY KEY,
username VARCHAR(50),
profile JSON
)
""")
connection.commit()
print("✅ データベースセットアップ完了")
connection.close()
基本操作
データ挿入
# データベース接続
connection = pymysql.connect(host='localhost', user='root', password='password', database='json_demo', charset='utf8mb4')
# JSONデータの挿入
user_data = {
'name': '田中太郎',
'age': 28,
'skills': ['Python', 'MySQL'],
'address': {'city': '東京都'}
}
with connection.cursor() as cursor:
cursor.execute("""
INSERT INTO users (username, profile) VALUES (%s, %s)
""", ('tanaka', json.dumps(user_data, ensure_ascii=False)))
connection.commit()
print("✅ ユーザーデータを挿入しました")
connection.close()
データ取得
# データベース接続
connection = pymysql.connect(host='localhost', user='root', password='password', database='json_demo', charset='utf8mb4')
# JSONから値を抽出
with connection.cursor() as cursor:
cursor.execute("""
SELECT
username,
JSON_EXTRACT(profile, '$.name') as name,
JSON_EXTRACT(profile, '$.age') as age,
JSON_EXTRACT(profile, '$.skills[0]') as first_skill
FROM users
""")
results = cursor.fetchall()
for row in results:
print(f"ユーザー: {row[0]}, 名前: {row[1]}, 年齢: {row[2]}, スキル: {row[3]}")
connection.close()
データ更新
# データベース接続
connection = pymysql.connect(host='localhost', user='root', password='password', database='json_demo', charset='utf8mb4')
# JSONデータの更新
with connection.cursor() as cursor:
cursor.execute("""
UPDATE users
SET profile = JSON_SET(profile, '$.age', 29, '$.department', 'エンジニア')
WHERE username = 'tanaka'
""")
connection.commit()
# 更新確認
cursor.execute("SELECT username, profile FROM users WHERE username = 'tanaka'")
result = cursor.fetchone()
print(f"更新後: {result[0]} - {result[1]}")
connection.close()
実用例:商品管理
# データベース接続
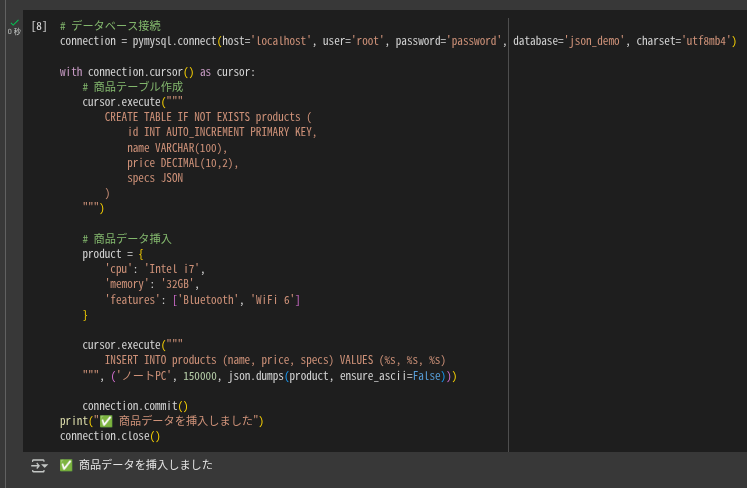
connection = pymysql.connect(host='localhost', user='root', password='password', database='json_demo', charset='utf8mb4')
with connection.cursor() as cursor:
# 商品テーブル作成
cursor.execute("""
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS products (
id INT AUTO_INCREMENT PRIMARY KEY,
name VARCHAR(100),
price DECIMAL(10,2),
specs JSON
)
""")
# 商品データ挿入
product = {
'cpu': 'Intel i7',
'memory': '32GB',
'features': ['Bluetooth', 'WiFi 6']
}
cursor.execute("""
INSERT INTO products (name, price, specs) VALUES (%s, %s, %s)
""", ('ノートPC', 150000, json.dumps(product, ensure_ascii=False)))
connection.commit()
print("✅ 商品データを挿入しました")
connection.close()
検索とフィルタリング
# データベース接続
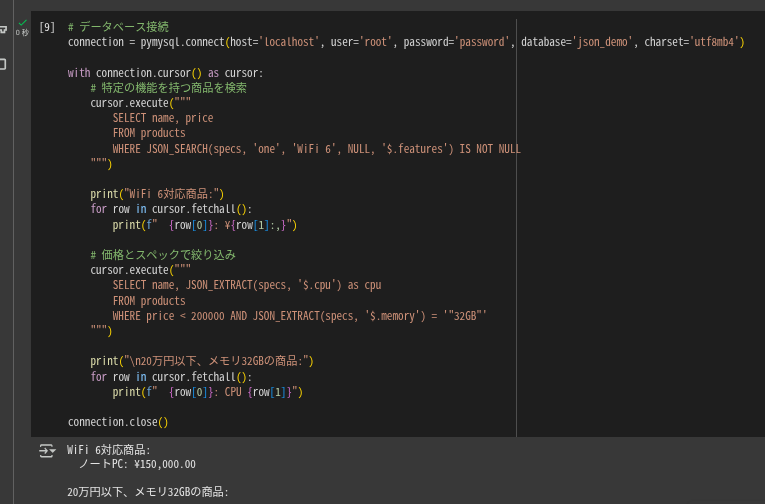
connection = pymysql.connect(host='localhost', user='root', password='password', database='json_demo', charset='utf8mb4')
with connection.cursor() as cursor:
# 特定の機能を持つ商品を検索
cursor.execute("""
SELECT name, price
FROM products
WHERE JSON_SEARCH(specs, 'one', 'WiFi 6', NULL, '$.features') IS NOT NULL
""")
print("WiFi 6対応商品:")
for row in cursor.fetchall():
print(f" {row[0]}: ¥{row[1]:,}")
# 価格とスペックで絞り込み
cursor.execute("""
SELECT name, JSON_EXTRACT(specs, '$.cpu') as cpu
FROM products
WHERE price < 200000 AND JSON_EXTRACT(specs, '$.memory') = '"32GB"'
""")
print("\n20万円以下、メモリ32GBの商品:")
for row in cursor.fetchall():
print(f" {row[0]}: CPU {row[1]}")
connection.close()
よく使うJSON関数
-
JSON_EXTRACT(json, path)- 値を取得 -
JSON_SET(json, path, value)- 値を設定・更新 -
JSON_INSERT(json, path, value)- 新しい値を挿入 -
JSON_REMOVE(json, path)- 値を削除 -
JSON_SEARCH(json, 'one', value)- 値を検索
まとめ
JSON型は、設定情報やAPIレスポンス、ログデータの保存など、柔軟な構造が求められる場面で便利です。特にスキーマが頻繁に変わるデータには適しています。一方で、厳密な型管理や複雑なリレーションが必要な場合は、従来のリレーショナル設計の方が適しています。
参考情報