はじめに
Pythonのcollectionsモジュールは、リストや辞書を拡張した特殊なコンテナ型を提供します。適切に使い分けることで、コードの可読性とパフォーマンスを向上できます。
collectionsモジュールとは
from collections import (
namedtuple, # 名前付きタプル
deque, # 両端キュー
Counter, # カウンター
OrderedDict, # 順序付き辞書
defaultdict, # デフォルト値付き辞書
ChainMap, # 辞書のチェーン
UserDict, # 辞書のカスタマイズ用
UserList, # リストのカスタマイズ用
UserString, # 文字列のカスタマイズ用
)
各コンテナの特徴と用途
namedtuple - 名前でアクセスできるタプル
from collections import namedtuple
# 定義
Point = namedtuple('Point', ['x', 'y'])
p = Point(10, 20)
# 名前でアクセス
print(p.x, p.y) # 10 20
# インデックスでもOK
print(p[0], p[1]) # 10 20
用途: 構造化データ、CSVの行、座標、設定値
deque - 高速な両端操作
from collections import deque
d = deque([1, 2, 3])
# 両端に追加(O(1))
d.appendleft(0) # [0, 1, 2, 3]
d.append(4) # [0, 1, 2, 3, 4]
# 両端から削除(O(1))
d.popleft() # 0
d.pop() # 4
用途: キュー、スタック、履歴管理、スライディングウィンドウ
Counter - 要素のカウント
from collections import Counter
# カウント
c = Counter(['a', 'b', 'a', 'c', 'a'])
print(c) # Counter({'a': 3, 'b': 1, 'c': 1})
# 上位N件
print(c.most_common(2)) # [('a', 3), ('b', 1)]
用途: 頻度集計、ヒストグラム、単語カウント
OrderedDict - 順序を保持する辞書
from collections import OrderedDict
od = OrderedDict()
od['a'] = 1
od['b'] = 2
od['c'] = 3
# 順序が保証される
print(list(od.keys())) # ['a', 'b', 'c']
# 末尾に移動
od.move_to_end('a')
print(list(od.keys())) # ['b', 'c', 'a']
用途: LRUキャッシュ、順序が重要な設定、JSON出力の順序制御
defaultdict - 自動初期化される辞書
from collections import defaultdict
# リストとして初期化
d = defaultdict(list)
d['fruits'].append('apple')
d['fruits'].append('banana')
print(d) # {'fruits': ['apple', 'banana']}
# 整数として初期化(カウント用)
d = defaultdict(int)
d['a'] += 1
d['b'] += 1
print(d) # {'a': 1, 'b': 1}
用途: グルーピング、集計、ネスト辞書の構築
ChainMap - 複数辞書の仮想的な結合
from collections import ChainMap
defaults = {'color': 'red', 'size': 'medium'}
user_settings = {'color': 'blue'}
# 結合(user_settingsが優先)
config = ChainMap(user_settings, defaults)
print(config['color']) # blue
print(config['size']) # medium
用途: 設定の階層化、スコープ管理、環境変数のフォールバック
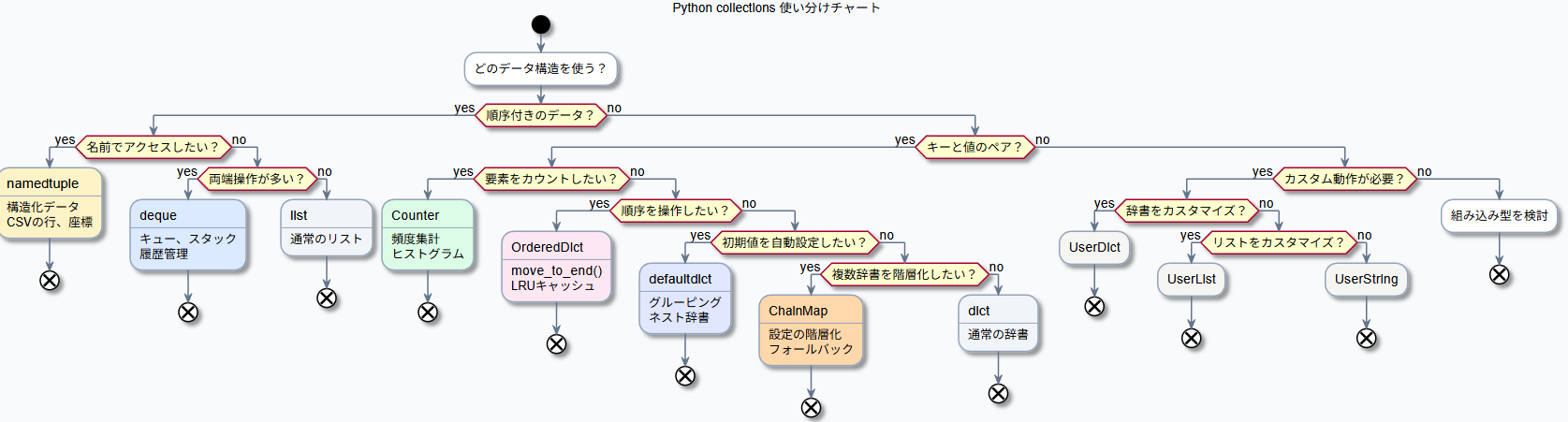
使い分けチャート
どのデータ構造を使う?
│
├─ 順序付きのデータ?
│ ├─ 名前でアクセスしたい → namedtuple
│ ├─ 両端操作が多い → deque
│ └─ 単純なリスト → list
│
├─ キーと値のペア?
│ ├─ 要素をカウントしたい → Counter
│ ├─ 順序を操作したい → OrderedDict
│ ├─ 初期値を自動設定したい → defaultdict
│ ├─ 複数辞書を階層化したい → ChainMap
│ └─ 単純な辞書 → dict
│
└─ カスタム動作が必要?
├─ 辞書をカスタマイズ → UserDict
├─ リストをカスタマイズ → UserList
└─ 文字列をカスタマイズ → UserString
パフォーマンス比較
| 操作 | list | deque |
|---|---|---|
末尾追加 append
|
O(1) | O(1) |
先頭追加 insert(0, x)
|
O(n) | O(1) |
末尾削除 pop()
|
O(1) | O(1) |
先頭削除 pop(0)
|
O(n) | O(1) |
| インデックスアクセス | O(1) | O(n) |
# リストの先頭追加は遅い
lst = list(range(100000))
lst.insert(0, -1) # 全要素をシフト
# dequeの先頭追加は速い
from collections import deque
dq = deque(range(100000))
dq.appendleft(-1) # O(1)
Python 3.7以降の変化
dict が順序を保持するように
Python 3.7以降、通常のdictも挿入順序を保持します。
# Python 3.7+
d = {}
d['a'] = 1
d['b'] = 2
d['c'] = 3
print(list(d.keys())) # ['a', 'b', 'c'] - 順序保持
OrderedDictを使う場面:
-
move_to_end()が必要 - 順序を考慮した
==比較が必要 - Python 3.6以前との互換性
実践例:設定管理
from collections import ChainMap, namedtuple
# デフォルト設定
defaults = {
'host': 'localhost',
'port': 8080,
'debug': False
}
# 環境別設定
production = {'debug': False, 'port': 80}
development = {'debug': True}
# 現在の環境設定を取得
def get_config(env='development'):
envs = {
'production': production,
'development': development
}
return ChainMap(envs.get(env, {}), defaults)
config = get_config('development')
print(f"Host: {config['host']}") # localhost
print(f"Port: {config['port']}") # 8080
print(f"Debug: {config['debug']}") # True
まとめ
| コンテナ | 主な用途 |
|---|---|
| namedtuple | 構造化データ、イミュータブルなレコード |
| deque | 両端操作、キュー、履歴 |
| Counter | カウント、頻度分析 |
| OrderedDict | 順序操作、LRUキャッシュ |
| defaultdict | グルーピング、自動初期化 |
| ChainMap | 設定の階層化 |
次回移行に機会があれば、それぞれ深掘りする予定。