Powershellで.NETを扱う
C#の記事を参考にしてPowershellで.Netを扱いたい場合の覚え書きです。
環境
PS /workspaces> $PSVersionTable.PSVersion
Major Minor Patch PreReleaseLabel BuildLabel
----- ----- ----- --------------- ----------
7 0 2
実行エンジン… .NET Core 3.1.5
参考:v7.0.2 Release of Powershell
入門
その前に:インテリセンス(補完)機能
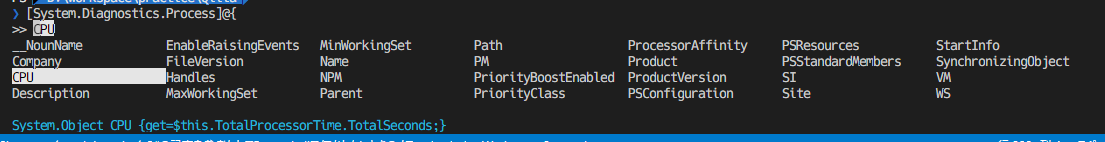
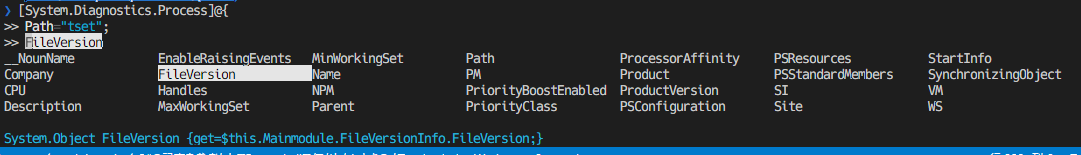
Powershellのコマンド名はとにかく長い。そして、.NETのクラスの名前空間なども長い。
ただし、インテリセンス(補完)機能は割と強力。
名前空間が分からないクラスを探すときなども便利。
もちろんコマンドレットでもインテリセンスを使える。
Windowsの場合はCtrl+Spacebarで最初から使用可能。
Linuxの場合はデフォルトでは設定されてないので$profile等に設定コマンドを記述して使えるようにする。
# 基本的にコマンドが割り当てられてないキーなら何処でも良い。
Set-PSReadLineKeyHandler -Chord Alt+q -Function MenuComplete
※この記事はPowershellの補完機能を前提にしています。
Get-Member
数値
PS /workspaces> 17 | gm # Get-Memberのエイリアス
実行結果
TypeName: System.Int32
Name MemberType Definition
---- ---------- ----------
CompareTo Method int CompareTo(System.Object value), int CompareTo(int value), int IComparable.CompareTo(System.Object obj), int IComparable[int].CompareTo(int other)
Equals Method bool Equals(System.Object obj), bool Equals(int obj), bool IEquatable[int].Equals(int other)
GetHashCode Method int GetHashCode()
GetType Method type GetType()
GetTypeCode Method System.TypeCode GetTypeCode(), System.TypeCode IConvertible.GetTypeCode()
ToBoolean Method bool IConvertible.ToBoolean(System.IFormatProvider provider)
ToByte Method byte IConvertible.ToByte(System.IFormatProvider provider)
ToChar Method char IConvertible.ToChar(System.IFormatProvider provider)
ToDateTime Method datetime IConvertible.ToDateTime(System.IFormatProvider provider)
ToDecimal Method decimal IConvertible.ToDecimal(System.IFormatProvider provider)
ToDouble Method double IConvertible.ToDouble(System.IFormatProvider provider)
ToInt16 Method short IConvertible.ToInt16(System.IFormatProvider provider)
ToInt32 Method int IConvertible.ToInt32(System.IFormatProvider provider)
ToInt64 Method long IConvertible.ToInt64(System.IFormatProvider provider)
ToSByte Method sbyte IConvertible.ToSByte(System.IFormatProvider provider)
ToSingle Method float IConvertible.ToSingle(System.IFormatProvider provider)
ToString Method string ToString(), string ToString(string format), string ToString(System.IFormatProvider provider), string ToString(string format, System.IFormatProvider provider), stri…
ToType Method System.Object IConvertible.ToType(type conversionType, System.IFormatProvider provider)
ToUInt16 Method ushort IConvertible.ToUInt16(System.IFormatProvider provider)
ToUInt32 Method uint IConvertible.ToUInt32(System.IFormatProvider provider)
ToUInt64 Method ulong IConvertible.ToUInt64(System.IFormatProvider provider)
TryFormat Method bool TryFormat(System.Span[char] destination, [ref] int charsWritten, System.ReadOnlySpan[char] format, System.IFormatProvider provider)
文字列
PS /workspaces> 'Foo' | gm
実行結果
TypeName: System.Int32
Name MemberType Definition
---- ---------- ----------
CompareTo Method int CompareTo(System.Object value), int CompareTo(int value), int IComparable.CompareTo(System.Object obj), int IComparable[int].CompareTo(int other)
Equals Method bool Equals(System.Object obj), bool Equals(int obj), bool IEquatable[int].Equals(int other)
GetHashCode Method int GetHashCode()
GetType Method type GetType()
GetTypeCode Method System.TypeCode GetTypeCode(), System.TypeCode IConvertible.GetTypeCode()
ToBoolean Method bool IConvertible.ToBoolean(System.IFormatProvider provider)
ToByte Method byte IConvertible.ToByte(System.IFormatProvider provider)
ToChar Method char IConvertible.ToChar(System.IFormatProvider provider)
ToDateTime Method datetime IConvertible.ToDateTime(System.IFormatProvider provider)
ToDecimal Method decimal IConvertible.ToDecimal(System.IFormatProvider provider)
ToDouble Method double IConvertible.ToDouble(System.IFormatProvider provider)
ToInt16 Method short IConvertible.ToInt16(System.IFormatProvider provider)
ToInt32 Method int IConvertible.ToInt32(System.IFormatProvider provider)
ToInt64 Method long IConvertible.ToInt64(System.IFormatProvider provider)
ToSByte Method sbyte IConvertible.ToSByte(System.IFormatProvider provider)
ToSingle Method float IConvertible.ToSingle(System.IFormatProvider provider)
ToString Method string ToString(), string ToString(string format), string ToString(System.IFormatProvider provider), string ToString(string format, System.IFormatProvider provider), stri…
ToType Method System.Object IConvertible.ToType(type conversionType, System.IFormatProvider provider)
ToUInt16 Method ushort IConvertible.ToUInt16(System.IFormatProvider provider)
ToUInt32 Method uint IConvertible.ToUInt32(System.IFormatProvider provider)
ToUInt64 Method ulong IConvertible.ToUInt64(System.IFormatProvider provider)
TryFormat Method bool TryFormat(System.Span[char] destination, [ref] int charsWritten, System.ReadOnlySpan[char] format, System.IFormatProvider provider)
メソッド実行
PS /workspaces> 'Foo'.ToUpper()
FOO
キャスト
幾つか方法がある。
PS /workspaces> 'Foo' -as [char[]]
F
o
o
PS /workspaces> [char[]]'Foo'
F
o
o
多段キャスト
この場合はas演算子を使った方がわかりやすい気がする。
PS /workspaces> [int[]][char[]]'Foo'
70
111
111
PS /workspaces> 'Foo' -as [char[]] -as [int[]]
70
111
111
組み合わせる
※Foreach()はコレクションで使用可能なPowershell固有の特殊メソッド。
他にはClear()やWhere()がある。
Powershell7では差が縮まったがForeach-Objectよりもパフォーマンスに優れる。
配列について知りたかったことのすべて
Methods of arrays
PS /workspaces> 'Foo' -as [char[]] -as [Byte[]] | ForEach-Object {$_ + 10 -as [char]} | Join-String
Pyy
PS /workspaces> ('Foo' -as [char[]] -as [Byte[]]).ForEach{$_ + 10 -as [char]} -join ''
Pyy
オブジェクトを生成する方法
Powershellでオブジェクトを扱う方法は幾つもある。
公式の解説はこちら。
About Object Creation
この記事で扱うのは以下の通り。
- 静的メソッド
new()でクラスのコンストラクタを実行する - 連想配列からキャストする
-
New-Objectを使う
この記事では詳しく扱わないがSystem.ActivatorのCreateInstance()を使う方法もある。
PS > $list=[System.Activator]::CreateInstance([System.Collections.Generic.List[int]])
PS > $list.Count
0
PS > $list.AddRange([int[]]@(1..10))
PS > $list[4..7]
5
6
7
8
PS > $list=[System.Activator]::CreateInstance([System.Collections.Generic.List[int]], [int[]]@(1..5))
PS > $list
1
2
3
4
5
静的メソッドnew()でコンストラクタを呼び出す
Powershell5以降、クラスのコンストラクタは静的メソッドnew()で呼び出せる。
C#のnewに相当する。コンストラクタ有無はGetConstructors().Countで確認可能。
PS > [string].GetConstructors().Count
9
PS > [string]::new
OverloadDefinitions
-------------------
string new(char[] value)
string new(char[] value, int startIndex, int length)
string new(System.Char*, System.Private.CoreLib, Version=4.0.0.0, Culture=neutral, PublicKeyToken=7cec85d7bea7798e value)
string new(System.Char*, System.Private.CoreLib, Version=4.0.0.0, Culture=neutral, PublicKeyToken=7cec85d7bea7798e value, int startIndex, int length)
string new(System.SByte*, System.Private.CoreLib, Version=4.0.0.0, Culture=neutral, PublicKeyToken=7cec85d7bea7798e value)
string new(System.SByte*, System.Private.CoreLib, Version=4.0.0.0, Culture=neutral, PublicKeyToken=7cec85d7bea7798e value, int startIndex, int length)
string new(System.SByte*, System.Private.CoreLib, Version=4.0.0.0, Culture=neutral, PublicKeyToken=7cec85d7bea7798e value, int startIndex, int length, System.Text.Encoding enc)
string new(char c, int count)
string new(System.ReadOnlySpan[char] value)
そのため、new()のPSMethodのNameプロパティは.NET IL (中間言語)のコンストラクタメソッドである.ctorとなっている。
PS > [string]::new | Get-Member
TypeName: System.Management.Automation.PSMethod
Name MemberType Definition
---- ---------- ----------
Copy Method System.Management.Automation.PSMemberInfo Copy()
Equals Method bool Equals(System.Object obj)
GetHashCode Method int GetHashCode()
GetType Method type GetType()
Invoke Method System.Object Invoke(Params System.Object[] arguments)
ToString Method string ToString()
IsInstance Property bool IsInstance {get;}
MemberType Property System.Management.Automation.PSMemberTypes MemberType {get;}
Name Property string Name {get;}
OverloadDefinitions Property System.Collections.ObjectModel.Collection[string] OverloadDefinitions {get;}
TypeNameOfValue Property string TypeNameOfValue {get;}
Value Property System.Object Value {get;set;}
PS > [string]::new.name
.ctor
※通常、メソッド名とNameプロパティは一致している。
PS > [string]::Compare.name
Compare
PS > [string]::Concat.name
Concat
暗黙の型変換があるのでメソッドの引数はある程度柔軟に記述出来る。
PS > 'Bar'.GetType()
IsPublic IsSerial Name BaseType
-------- -------- ---- --------
True True String System.Object
PS > [char[]]'Bar'
B
a
r
PS > [string]::new([char[]]'Bar')
Bar
PS > [string]::new('Bar')
Bar
連想配列からキャストする方法
引数なしコンストラクタがある場合、連想配列からインスタンスを生成出来る。
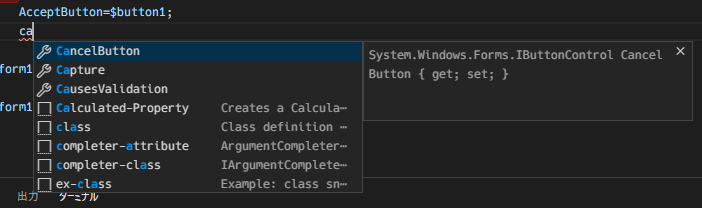
この方法を使うとそのクラスのプロパティを補完入力できる。
プロパティを複数設定する場合は改行するか;で区切る。
改行だけでも動作はするが、補完入力は;で区切る時のみ有効になる。
New-Objectを使う方法
次のような場面で使用する。
- Comobjectを扱う場合...面倒な部分をラップしてくれる。
- 引数ありコンストラクタとプロパティの設定を同時に行う場合
# @を書き忘れるとエラーになる
PS ❯ $WshShell = New-Object -ComObject WScript.Shell -Property {CurrentDirectory="D:\"}
New-Object: Cannot bind parameter 'Property'. Cannot convert the "CurrentDirectory="D:\"" value of type "System.Management.Automation.ScriptBlock" to type "System.Collections.IDictionary".
⨯ PS ❯ $WshShell = New-Object -ComObject WScript.Shell -Property @{CurrentDirectory="D:\"}
PS ❯ $WshShell.CurrentDirectory
D:\
usingについて
公式ドキュメント:about_Using - PowerShell | Microsoft Docs
Powershellのusingは3つの使い方がある。
using namespace <.NET-namespace> # 指定したnamecpaceを省略出来るようになる
using module <module-name> # Powershellモジュールで定義されたクラスを利用出来るようにする
using assembly <.NET-assembly-path> # 指定したアセンブリのクラスを継承したクラスを作成するために使う
using assemblyはclass構文で使われる。
Genericクラスの書き方
PS > using namespace System.Collections.Generic
PS > $list=[List[int]]::new()
PS > $list.add(12)
PS > $list
12
PS > $dic=[Dictionary[string,System.Diagnostics.Process]]::new()
PS > $dic.Count
0
PS > Get-Process | ForEach-Object {$dic.TryAdd($_.ProcessName,$_) > $null}
PS > $dic.Count
140
(7月13日(月)修正)Genericメソッドで型引数を指定する方法
Powershellは構文として型引数を設定したGenericメソッドの実行をサポートしていないのでMethodInfo.MakeGenericMethod(Type[])を利用する。
参考
MethodInfo.MakeGenericMethod(Type[]) メソッド (System.Reflection) | Microsoft Docs
vors/GenericMethods.ps1
PS > $OfTypeInt=[System.Linq.Enumerable].GetMethods().where{$_.IsGenericMethod -and $_.name -eq 'Oftype'}.MakeGenericMethod([int])
PS > $OfTypeInt.Invoke($null,(,@(1,2,'a')))
1
2
PS > $OfTypeInt.Invoke($null,@(1,2,'a'))
MethodInvocationException: Exception calling "Invoke" with "2" argument(s): "Parameter count mismatch."
ただし、厳密に型を合わせることにより、型引数の設定は省略が出来る。
Powershellではサポートしていないので ...
ぢつは、厳密に型を合わせれば、呼べなくもない
`Powershell
using namespace System.Linq$a0 = 1..5
$fn = { param($x) $x * 10 }[Enumerable]::Select($a0, $fn -as [Func[object, object]])
`
公式ドキュメントの関連箇所(推定)
型引数は省略することもできます。コンパイラが推定します。 次は、前の呼び出しと同じように Swap を呼び出します。
ジェネリック メソッド - C# プログラミング ガイド | Microsoft Docs
実践~MSDNの記事を利用する~
お題はFormの記事のサンプルコード
Form クラス (System.Windows.Forms) | Microsoft Docs
その1:そのままPowershellに置き換える
new()とusing namespaceでほぼ公式通りに記述することが可能。
using namespace System.Drawing
using namespace System.Windows.Forms
Add-Type -AssemblyName System.Windows.Forms
# コンストラクタ
# Form作成
$form1 = [Form]::new()
# ボタン作成
$button1 = [Button]::new()
$button2 = [Button]::new()
# ボタンの設定
# サンプルコードとの違い…DialogResultは明示的に設定
$button1.Text = "OK"
$button1.DialogResult=[DialogResult]::OK
$button1.Location = [Point]::new(10, 10)
$button2.Text = "Cancel"
$button2.DialogResult=[DialogResult]::Cancel
$button2.Location = [Point]::new(
$button1.Left,
$button1.Height + $button1.Top + 10
)
# Formの設定
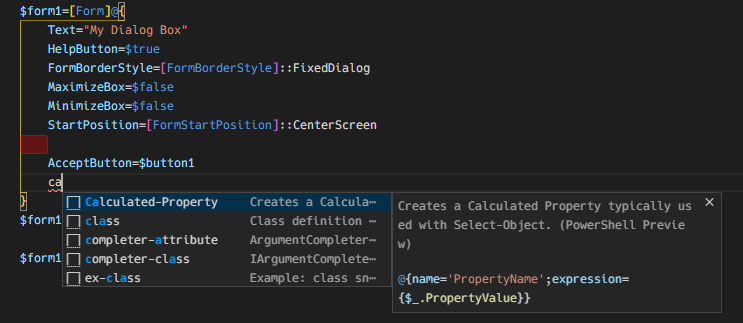
$form1.Text="My Dialog Box"
$form1.HelpButton =$true
$form1.FormBorderStyle=[FormBorderStyle]::FixedDialog
$form1.MaximizeBox=$false
$form1.MinimizeBox=$false
# 生成したボタンを設定
$form1.AcceptButton=$button1
$form1.CancelButton=$button2
# 表示位置
$form1.StartPosition=[FormStartPosition]::CenterScreen
# 合体
$form1.Controls.Add($button1)
$form1.Controls.Add($button2)
# 表示
$form1.ShowDialog()
その2:Powershellで書きやすいように書く
連想配列を使ったオブジェクト生成を利用するとプロパティ設定をまとめやすい。
AddRange()が使える場合は書き換えを検討する。
using namespace System.Drawing
using namespace System.Windows.Forms
Add-Type -AssemblyName System.Windows.Forms
$button1=[Button]@{
Text="OK";
DialogResult=[DialogResult]::OK;
Location=[Point]::new(10,20);
}
$button2=[Button]@{
Text="Cancel";
DialogResult=[DialogResult]::Cancel;
Location=[Point]@{
X=$button1.Left;
Y=$button1.Height + $button1.Top + 10;
};
}
$form1=[Form]@{
Text="My Dialog Box";
HelpButton=$true;
FormBorderStyle=[FormBorderStyle]::FixedDialog;
MaximizeBox=$false;
MinimizeBox=$false;
StartPosition=[FormStartPosition]::CenterScreen;
AcceptButton=$button1;
CancelButton=$button2;
}
$form1.Controls.AddRange(@($button1,$button2))
$form1.ShowDialog()
インテリセンスが効かなくなるが;が無くても動作する。
using namespace System.Drawing
using namespace System.Windows.Forms
Add-Type -AssemblyName System.Windows.Forms
$button1=[Button]@{
Text="OK"
DialogResult=[DialogResult]::OK
Location=[Point]::new(10,20)
}
$button2=[Button]@{
Text="Cancel"
DialogResult=[DialogResult]::Cancel
Location=[Point]@{
X=$button1.Left
Y=$button1.Height + $button1.Top + 10
}
}
$form1=[Form]@{
Text="My Dialog Box"
HelpButton=$true
FormBorderStyle=[FormBorderStyle]::FixedDialog
MaximizeBox=$false
MinimizeBox=$false
StartPosition=[FormStartPosition]::CenterScreen
AcceptButton=$button1
CancelButton=$button2
}
$form1.Controls.AddRange(@($button1,$button2))
$form1.ShowDialog()
Powershellだと難しいこと
次のような場合は再現は難しくなったり面倒になったりする。
IL、リフレクションを使えば大体のことは出来るが手間がかかる。
- ラムダ式…Powershellにはラムダ式はないため。なお、Linqは静的メソッドで利用可能。
- 自動生成コードが仕事をしている場合。WPFなどが該当。裏で自動生成されている箇所も手動で処理する必要がある。そういう部分をラップするのもPowershellモジュールの役目。
参考
High Performance PowerShell with LINQ
PowershellでLinqするためのレシピ。個人的にSum()をよく使う。(Measure-Objectよりも簡潔に書けるから)
終わりに
- Powershellの生命線は補完機能だと思っている。
- 機会があったら
Register-ArgumentCompleterについて掘り下げてみたい。
公式ドキュメント:Register-ArgumentCompleter (Microsoft.PowerShell.Core) - PowerShell | Microsoft Docs
次回があったら書きたいこと
イベント、BackgroundJobといった非同期の処理。
鍵を握るのは[scriptblock]と型変換。
※他の有力候補
- VScodeでPowershellの開発コンテナを立ち上げる
- VScodeでPowershellのハイブリッドモジュールを作成する
- PowershellとWPFとXAML、あとバインド