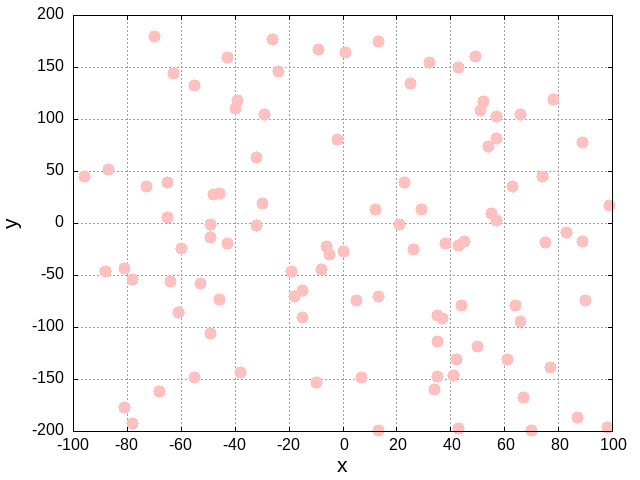
概要
- 2次元データ(x, y)をクラスタリングした
- クラスタ数は4つ
- (x, y)データは-100<=x<=100, -200<=y<=200の範囲でランダムな点を100個作成した
2D_data.csv
-49.00, -1.00
-53.00, -58.00
41.00, -146.00
99.00, 17.00
-32.00, -2.00
...
5.00, -74.00
90.00, -74.00
-73.00, 36.00
-24.00, 146.00
-70.00, 180.00
実装
main()
- フローチャート
- ソースコード
# main関数
def main():
# パラメータ初期設定
def initializeParameters():
# クラスタ数
clusterNum = 4
# データの変数の数
variablesNum = 2
return clusterNum, variablesNum
# パラメータ初期設定の関数ここまで
clusterNum, variablesNum = initializeParameters()
# 読み込むファイル名
filename = "00_2D_data.csv"
# データの読み込み
data = read_data(filename)
# クラスタリング実施
data, centroid = performClustering(data, clusterNum, variablesNum)
# クラスタリング後のデータの書き込み
filename2 = "02_afterClustering.csv"
write_data(data, filename2)
# 最終的に求まった重心を表示
print("-- finally calculated centroid --")
printCentroid(centroid, variablesNum)
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
- 変数の説明
- data...読み取った100個の(x, y)データを格納
- clusterNum...クラスタの個数
- variablesNum...データの次元. 今回は(x, y)なので2となる
- centroid...各クラスタの重心
performClustering(data, clusterNum, variablesNum)
- クラスタリングをする関数
- クラスタリング終了の条件
- それぞれのクラスタの重心の移動が小さくなる
- 一定回数クラスタの割り振りを繰り返す(重心の移動があっても強制終了する)
- クラスタリング終了の条件
- フローチャート
(分かりづらい...)
- ソースコード
performClustering(data, clusterNum, variablesNum)
# クラスタリングを実行する関数 the function performing clustering
def performClustering(data, clusterNum, variablesNum):
# 最初はランダムにクラスタリング->クラスタ番号を割り振る
data, centroid = firstRandomClustering(data, clusterNum, variablesNum)
# 各データの重心からの距離を格納する変数
deltaCentroid = 0.0
# クラスタリング開始 start clustering
# 重心の変化がほぼ0になるor各クラスタへの割り当てをrepeat回実施したら終了する
repeat = 20
print("== start clustering ==")
for cnt in range(repeat):
# 更新前の重心をコピーする
previousCentroid = copy.deepcopy(centroid)
# i番目のデータをいずれかのクラスタに分類
# classify data[i] into one of the clusters
for i in range(len(data)):
distance_min = 99999
provisionalClusterNumber = 99999
for j in range(0, clusterNum):
# 重心とデータの位置座標の距離を計算する
# calculate the distance between the centroid and the data coordinate
distance = calcDistance(data[i], centroid[j], variablesNum)
# データがどのクラスタの重心に一番近いかを判定する
# Determine which the cluster centroid the data is closest to
if distance < distance_min:
distance_min = distance
provisionalClusterNumber = j
# データと最も重心が近いクラスタの番号を代入する
# Input the cluster number whose centroid is closest to the data
data[i][variablesNum] = provisionalClusterNumber
# 各クラスタの(暫定的な)重心計算
# calculate the centroid of each cluster
centroid = calcCentroid(data, clusterNum, variablesNum, centroid)
# 重心がどれだけ変化したかを計算する
deltaCentroid = 0.0
for i in range(clusterNum):
deltaCentroid = deltaCentroid + calcDistance(previousCentroid[i], centroid[i], variablesNum)
print(f"{cnt+1:7d}th : change in centroid = {deltaCentroid:.8f}")
# 重心の移動の変化が小さければクラスタリングは終了とする
if deltaCentroid <= 1.0e-5:
print(f"{cnt+1:7d}th : finish calculating")
break
print("== finish clustering ==")
data.sort(key=lambda x: x[(variablesNum+1)-1])
return data, centroid
performClustering関数内で登場する関数一覧
firstRandomClustering(data, clusterNum, variablesNum)
- 内容
- ランダムにクラスタを割り振る
- その時点での重心を求める
- ソースコード
# 最初はランダムにクラスタリング->クラスタ番号を割り振る
def firstRandomClustering(data, clusterNum, variablesNum):
# i番目のデータのクラスタ番号をランダムに決定する
initialClusterNo = []
for i in range(len(data)):
initialClusterNo.append(random.randrange(0, clusterNum))
# dataに3列目に新たにクラスタ番号が追加される
# -> data[i] = [x, y, (クラスタ番号)]
for row, c in zip(data, initialClusterNo):
row.append(c)
# 各クラスタの重心の初期化
centroid = []
for i in range(clusterNum):
centroidEachCluster = [0.0 for _ in range(variablesNum)]
centroidEachCluster = centroidEachCluster + [i]
centroid.append(centroidEachCluster)
# 初期設定時点での各クラスタの重心を計算する
centroid = calcCentroid(data, clusterNum, variablesNum, centroid)
# ランダムにクラスタ番号を割り当てた初期のデータをファイルに書き込む
# write the initial data with randomly assigned to cluster numbers to a file
write_data(data, "01_beforeClustering.csv")
return data, centroid
calcCentroid(data, clusterNum, variablesNum, centroid)
# 各クラスタの重心を計算
def calcCentroid(data, clusterNum, variablesNum, centroid):
for i in range(clusterNum):
# 同じクラスタに属するサンプル数をカウントする変数
n = 0
# 同じクラスタに属するデータの各パラメータの平均値
Xmeans = [0.0] * variablesNum
# 同じクラスタに属するデータの各パラメータの合計
Xtotal = [0.0] * variablesNum
# 同じクラスタの所属するデータの各パラメータにおける平均を計算する
for j in range(len(data)):
if data[j][variablesNum] == i:
for k in range(variablesNum):
Xtotal[k] = Xtotal[k] + data[j][k]
n = n + 1
if n != 0:
for k in range(variablesNum):
Xmeans[k] = Xtotal[k]/n
# 算出した重心をそれ専用の配列に格納する
for j, row in enumerate(Xmeans):
if j == variablesNum:
centroid[i][j] = i
else:
centroid[i][j] = Xmeans[j]
return centroid
calcDistance(p1, p2, variablesNum)
# 2点間の距離を計算する
def calcDistance(p1, p2, variablesNum):
distance = 0.0
for i in range(variablesNum):
distance = distance + (p1[i] - p2[i])**2
distance = distance**0.5
return distance