A - I'm a teapot
文字列の最後の3文字がteaか判定する問題です。
substringを使用しましょう。
C++
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define rep(i,n) for(int i=0; i<(n); ++i)
#define repx(i,x,n) for(int i=x; i<(n); ++i)
#define fixed_setprecision(n) fixed << setprecision((n))
#define execution_time(ti) printf("Execution Time: %.4lf sec\n", 1.0 * (clock() - ti) / CLOCKS_PER_SEC);
#define pai 3.1415926535897932384
#define NUM_MAX 2e18
#define NUM_MIN -1e9
using namespace std;
using ll = long long;
using P = pair<int,int>;
template<class T> inline bool chmax(T& a, T b){ if(a<b){ a=b; return 1; } return 0; }
template<class T> inline bool chmin(T& a, T b){ if(a>b){ a=b; return 1; } return 0; }
int main() {
int n;
cin >> n;
string s;
cin >> s;
if(s.length() > 2 && s.substr(n-3, 3) == "tea"){
cout << "Yes" << endl;
}else{
cout << "No" << endl;
}
return 0;
}
B - You're a teapot
問題文を理解するのが難しい問題です。
n <= 100の制約により、3重ループの全探索を行いましょう。
2点間を決める2重ループ。
tを求める3重目のループ。
と分けて考えると実装しやすいです。
C++
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define rep(i,n) for(int i=0; i<(n); ++i)
#define repx(i,x,n) for(int i=x; i<(n); ++i)
#define fixed_setprecision(n) fixed << setprecision((n))
#define execution_time(ti) printf("Execution Time: %.4lf sec\n", 1.0 * (clock() - ti) / CLOCKS_PER_SEC);
#define pai 3.1415926535897932384
#define NUM_MAX 2e18
#define NUM_MIN -1e9
using namespace std;
using ll = long long;
using P = pair<int,int>;
template<class T> inline bool chmax(T& a, T b){ if(a<b){ a=b; return 1; } return 0; }
template<class T> inline bool chmin(T& a, T b){ if(a>b){ a=b; return 1; } return 0; }
int main() {
string s;
cin >> s;
int n = s.length();
double ans = 0;
rep(i, n){
rep(j, n){
if(s[i] == 't' && s[j] == 't'){
int cnt = 0;
for(int k = i; k <= j; k++){
if(s[k] == 't') cnt++;
}
if(j - (i - 1) >= 3){
ans = max(ans, ((double)cnt - 2.0) / ((double)abs(j - (i - 1)) - 2.0));
}
}
}
}
cout << fixed_setprecision(10) << ans << endl;
return 0;
}
C - Flush
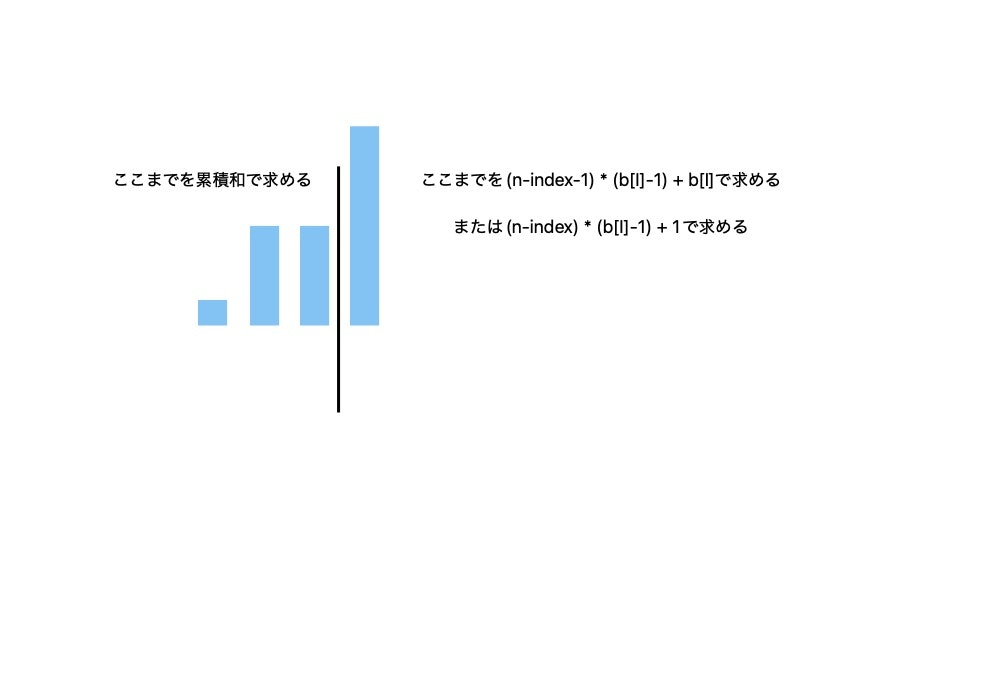
累積和の問題です。
私はコンテスト中の考察が足らなくて累積和、二分探索で解きました。
サンプル1の入力で考察します。
図で書くとこのような形になります。
nとqで2重ループにするとTLEになります。
O((N+Q)logN)のイメージで解きました。
C++
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define rep(i,n) for(int i=0; i<(n); ++i)
#define repx(i,x,n) for(int i=x; i<(n); ++i)
#define fixed_setprecision(n) fixed << setprecision((n))
#define execution_time(ti) printf("Execution Time: %.4lf sec\n", 1.0 * (clock() - ti) / CLOCKS_PER_SEC);
#define pai 3.1415926535897932384
#define NUM_MAX 2e18
#define NUM_MIN -1e9
using namespace std;
using ll = long long;
using P = pair<int,int>;
template<class T> inline bool chmax(T& a, T b){ if(a<b){ a=b; return 1; } return 0; }
template<class T> inline bool chmin(T& a, T b){ if(a>b){ a=b; return 1; } return 0; }
int main() {
ll n, q;
cin >> n >> q;
vector<ll> a(n), aa(n+1);
rep(i, n) cin >> a[i];
vector<ll> b(q);
rep(i, q) cin >> b[i];
sort(a.begin(), a.end());
rep(i, n) aa[i+1] = aa[i] + a[i];
rep(i, q){
if(b[i] == 1){
cout << 1 << endl;
continue;
}
int index = lower_bound(a.begin(), a.end(), b[i]) - a.begin();
if(index < n){
cout << aa[index] + (n - index - 1) * (b[i] - 1) + b[i] << endl;
}else{
cout << -1 << endl;
}
}
return 0;
}
O(N+Q)
こちらが正攻法の回答になります。
すぬけさんのコードは綺麗だな。
C++
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define rep(i,n) for(int i=0; i<(n); ++i)
#define repx(i,x,n) for(int i=x; i<(n); ++i)
#define fixed_setprecision(n) fixed << setprecision((n))
#define execution_time(ti) printf("Execution Time: %.4lf sec\n", 1.0 * (clock() - ti) / CLOCKS_PER_SEC);
#define pai 3.1415926535897932384
#define NUM_MAX 2e18
#define NUM_MIN -1e9
using namespace std;
using ll = long long;
using P = pair<int,int>;
template<class T> inline bool chmax(T& a, T b){ if(a<b){ a=b; return 1; } return 0; }
template<class T> inline bool chmin(T& a, T b){ if(a>b){ a=b; return 1; } return 0; }
int main() {
ll n, q;
cin >> n >> q;
vector<ll> a(n), aa(1000000+1), bb(1000000+1);
rep(i, n) cin >> a[i];
vector<ll> b(q);
rep(i, q) cin >> b[i];
sort(a.begin(), a.end());
rep(i, n) aa[a[i]] += a[i];
rep(i, n) bb[a[i]]++;
rep(i, 1000000){
aa[i+1] = aa[i+1] + aa[i];
bb[i+1] = bb[i+1] + bb[i];
}
rep(i, q){
if(b[i] == 1){
cout << 1 << endl;
continue;
}
ll ans = aa[b[i]-1] + (n - bb[b[i]-1]) * (b[i]-1) + 1;
if(bb[b[i]-1] == n){
cout << -1 << endl;
}else{
cout << ans << endl;
}
}
return 0;
}
D - XNOR Operation
dpの問題です。
漸化式は、
C++
rep(i, n){
if(t[i] == '0'){
dp[i+1][0] = dp[i][1] + 1;
dp[i+1][1] = dp[i][0];
}else{
dp[i+1][0] = dp[i][0];
dp[i+1][1] = dp[i][1] + 1;
}
ans += dp[i+1][1];
}
Sに残った唯一の文字を1にすることができるか、
という問題なので
C++
ans += dp[i+1][1];
で取り出しています。
C++
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define rep(i,n) for(int i=0; i<(n); ++i)
#define repx(i,x,n) for(int i=x; i<(n); ++i)
#define fixed_setprecision(n) fixed << setprecision((n))
#define execution_time(ti) printf("Execution Time: %.4lf sec\n", 1.0 * (clock() - ti) / CLOCKS_PER_SEC);
#define pai 3.1415926535897932384
#define NUM_MAX 2e18
#define NUM_MIN -1e9
using namespace std;
using ll = long long;
using P = pair<int,int>;
template<class T> inline bool chmax(T& a, T b){ if(a<b){ a=b; return 1; } return 0; }
template<class T> inline bool chmin(T& a, T b){ if(a>b){ a=b; return 1; } return 0; }
int main() {
ll n;
cin >> n;
string t;
cin >> t;
ll ans = 0;
vector<vector<ll>> dp(n+1, vector<ll>(2, 0));
rep(i, n){
if(t[i] == '0'){
dp[i+1][0] = dp[i][1] + 1;
dp[i+1][1] = dp[i][0];
}else{
dp[i+1][0] = dp[i][0];
dp[i+1][1] = dp[i][1] + 1;
}
ans += dp[i+1][1];
}
cout << ans << endl;
return 0;
}