はじめに
Terraformは、IaCの領域で広く使われているツールの一つです。しかし、Terraformのコードは時として冗長になりがちで、メンテナンスに苦労するケースも見受けられます。その解決策の1つとして、CDK for Terraform(以下、CDKTF)には、以前から関心を持っていました。
この記事では、公式チュートリアルを実践し、CDKTFによるAWSリソースのライフサイクル管理、すなわち、リソースの作成、変更、および破棄を試してみた結果を紹介します。
AWS CDKとは
AWS Cloud Development Kit(以下、AWS CDK)はAWSが2018年に初めて公開した、IaCのフレームワークです。
AWS CDKは、TypeScript、Python、GO、Java、C#といった一般的なプログラミング言語でAWSリソースのプロビジョニングと構成が可能です。AWS CDKはAWS CloudFormationのテンプレートを生成し、それをデプロイする形で動作します。
CDKTFとは
AWS CDKの成功を受けて、HashiCorpとAWSはCDK for Terraform(以下、CDKTF)の共同開発を開始し、2020年に初めて公開しました。
このツールはTerraformのリソースを抽象化し、AWS CDKと同様にTypeScript、Python、GO、Java、C#といったプログラミング言語を用いて、Terraformリソースをより直感的に、かつ効率的に記述することが可能になります。簡潔に言えば、AWS CDKがコードを用いてCloudFormationの構成ファイルを生成するのと同様に、CDKTFはコードからTerraformの構成ファイルを生成します。
CDKTFはTerraformプロバイダーをそのまま使用するため、Terraformがサポートしているリソースは基本的に全てサポートされます。これにより、既存のTerraformコードからCDKTFへの移行が容易になっています。
Terraformとは
Terraformは、HashiCorpによって開発された、IaCを実現するツールです。AWS、GCP、Azureなど、多くのクラウドプロバイダーをサポートしており、HCL(HashiCorp Configuration Language)と呼ばれる独自の言語で設定を記述します。
Terraformはplan、apply、destroyといったコマンドでインフラストラクチャーのライフサイクルを管理します。この一連の流れは、CDKTFにも引き継がれています。
検証に利用した環境とコード
検証に利用した環境を記載します。
lsb_release -a
No LSB modules are available.
Distributor ID: Ubuntu
Description: Ubuntu 22.04.3 LTS
Release: 22.04
Codename: jammy
terraform --version
Terraform v1.5.6
on linux_amd64
node --version
v18.16.0
npm --version
9.5.1
検証に使ったコードは、こちらにあります。
CDKTFのセットアップ
公式ページを参考に、CDKTFをセットアップします。
npm install --global cdktf-cli@latest
cdktf --version #=> 0.19.0
チュートリアルの実践
ここからは、公式のチュートリアルを参考にしました。
AWSプロバイダーのバージョンなど、アップデートされていない箇所を適宜修正した上で実施しています。
CDKプロジェクトの初期化
作業ディレクトリを作成します。
mkdir sample
cd sample
プロジェクトを初期化します。
cdktf init --template="typescript" --providers="aws@~>5.0"
Welcome to CDK for Terraform!
By default, cdktf allows you to manage the state of your stacks using Terraform Cloud for free.
cdktf will request an API token for app.terraform.io using your browser.
If login is successful, cdktf will store the token in plain text in
the following file for use by subsequent Terraform commands:
/home/jhashimoto/.terraform.d/credentials.tfrc.json
Note: The local storage mode isn't recommended for storing the state of your stacks.
? Do you want to continue with Terraform Cloud remote state management? (Y/n)
ステートの管理にはTerraform Cloudの利用が推奨されていますが、今回は簡易的にローカルで管理することにします。
? Do you want to continue with Terraform Cloud remote state management? (Y/n) # nを入力
その他のオプションは、すべてデフォルトを受け入れます。
output
? Project Name sample
? Project Description A simple getting started project for cdktf.
? Do you want to start from an existing Terraform project? no
? Do you want to send crash reports to the CDKTF team? Refer to
https://developer.hashicorp.com/terraform/cdktf/create-and-deploy/configuration-file#enable-crash-reporting-for-the-cli for more information yes
added 2 packages, and audited 57 packages in 2s
7 packages are looking for funding
run `npm fund` for details
found 0 vulnerabilities
added 313 packages, and audited 370 packages in 18s
38 packages are looking for funding
run `npm fund` for details
found 0 vulnerabilities
========================================================================================================
Your CDKTF TypeScript project is ready!
cat help Print this message
Compile:
npm run get Import/update Terraform providers and modules (you should check-in this directory)
npm run compile Compile typescript code to javascript (or "npm run watch")
npm run watch Watch for changes and compile typescript in the background
npm run build Compile typescript
Synthesize:
cdktf synth [stack] Synthesize Terraform resources from stacks to cdktf.out/ (ready for 'terraform apply')
Diff:
cdktf diff [stack] Perform a diff (terraform plan) for the given stack
Deploy:
cdktf deploy [stack] Deploy the given stack
Destroy:
cdktf destroy [stack] Destroy the stack
Test:
npm run test Runs unit tests (edit __tests__/main-test.ts to add your own tests)
npm run test:watch Watches the tests and reruns them on change
Upgrades:
npm run upgrade Upgrade cdktf modules to latest version
npm run upgrade:next Upgrade cdktf modules to latest "@next" version (last commit)
Use Providers:
You can add prebuilt providers (if available) or locally generated ones using the add command:
cdktf provider add "aws@~>3.0" null kreuzwerker/docker
You can find all prebuilt providers on npm: https://www.npmjs.com/search?q=keywords:cdktf
You can also install these providers directly through npm:
npm install @cdktf/provider-aws
npm install @cdktf/provider-google
npm install @cdktf/provider-azurerm
npm install @cdktf/provider-docker
npm install @cdktf/provider-github
npm install @cdktf/provider-null
You can also build any module or provider locally. Learn more https://cdk.tf/modules-and-providers
========================================================================================================
[2023-10-21T17:11:36.610] [INFO] default - Checking whether pre-built provider exists for the following constraints:
provider: aws
version : ~>5.0
language: typescript
cdktf : 0.19.0
[2023-10-21T17:11:39.589] [INFO] default - Found pre-built provider.
Adding package @cdktf/provider-aws @ 18.0.1
[2023-10-21T17:11:39.594] [INFO] default - Installing package @cdktf/provider-aws @ 18.0.1 using npm.
[2023-10-21T17:11:46.542] [INFO] default - Package installed.
プロジェクトの初期化により、作成されたディレクトリとファイルを示します。
ls -1F
cdktf.json
help
jest.config.js
main.ts
node_modules/
package.json
package-lock.json
setup.js
__tests__/
tsconfig.json
Terraform構成ファイルを出力するCDKコードの記述
main.tsにコードを記述します。
AWSプロバイダーに資格情報を渡す方法は複数ありますが、今回は、プロファイルと環境変数AWS_PROFILEを使用します。
export AWS_PROFILE=<profile name>
import { Construct } from "constructs";
import { App, TerraformStack, TerraformOutput } from "cdktf";
import { AwsProvider } from "@cdktf/provider-aws/lib/provider";
import { Instance } from "@cdktf/provider-aws/lib/instance";
class MyStack extends TerraformStack {
constructor(scope: Construct, id: string) {
super(scope, id);
new AwsProvider(this, "AWS", {
region: "ap-northeast-1",
});
const ec2Instance = new Instance(this, "compute", {
ami: "ami-0d48337b7d3c86f62", // Amazon Linux 2023
instanceType: "t2.micro",
});
new TerraformOutput(this, "public_ip", {
value: ec2Instance.publicIp,
});
}
}
const app = new App();
new MyStack(app, "aws_instance");
app.synth();
Terraformの構成ファイルを合成してみる
デプロイの前に、Terraformの構成ファイルを合成してみます。尚、合成は、先述のチュートリアルの手順には含まれてなく、スキップしてもリソースのデプロイはできます。
"合成"(synthesize)とは、プログラミング言語で記述されたインフラコードを、特定のIaCツールが理解できる形式に変換するプロセスのことです。元はAWS CDKの用語で、CDKTFにも引き継がれています。
具体的には、合成のプロセスにより、AWS CDKの場合はCloudFormationテンプレートに、CDKTFの場合はTerraformが理解できるJSON形式に変換されます。
この合成されたファイルが実際にデプロイの際に使用されます。CDKTFではterraform applyコマンドが、合成されたJSON形式のTerraform構成ファイルを用いてリソースをデプロイします。
CDKTFのコードを合成するには、cdktf synthコマンドを実行します。これにより、*.tsファイルに記述されたリソースが、Terraformが解釈できるJSON形式で出力されます。
cdktf synth
Generated Terraform code for the stacks: aws_instance
合成されたJSONファイルは、cdktf.outディレクトリに出力されます。
{
"//": {
"metadata": {
"backend": "local",
"stackName": "aws_instance",
"version": "0.19.0"
},
"outputs": {
"aws_instance": {
"public_ip": "public_ip"
}
}
},
"output": {
"public_ip": {
"value": "${aws_instance.compute.public_ip}"
}
},
"provider": {
"aws": [
{
"profile": "<profile name>,
"region": "ap-northeast-1"
}
]
},
"resource": {
"aws_instance": {
"compute": {
"//": {
"metadata": {
"path": "aws_instance/compute",
"uniqueId": "compute"
}
},
"ami": "ami-0d48337b7d3c86f62",
"instance_type": "t2.micro"
}
}
},
"terraform": {
"backend": {
"local": {
"path": "<parent dir>/sample/terraform.aws_instance.tfstate"
}
},
"required_providers": {
"aws": {
"source": "aws",
"version": "5.22.0"
}
}
}
}
HCL形式での合成を期待したのですが、そのようなオプションはないようです。 ver 0.20でHCLの合成がサポートされました。
インフラストラクチャのプロビジョニング
main.tsに記述したリソースをデプロイします。
cdktf deploy
output
aws_instance Initializing the backend...
aws_instance Initializing provider plugins...
aws_instance - Reusing previous version of hashicorp/aws from the dependency lock file
aws_instance - Using previously-installed hashicorp/aws v5.22.0
Terraform has been successfully initialized!
aws_instance
You may now begin working with Terraform. Try running "terraform plan" to see
any changes that are required for your infrastructure. All Terraform commands
should now work.
If you ever set or change modules or backend configuration for Terraform,
rerun this command to reinitialize your working directory. If you forget, other
commands will detect it and remind you to do so if necessary.
aws_instance Terraform used the selected providers to generate the following execution plan.
Resource actions are indicated with the following symbols:
+ create
Terraform will perform the following actions:
aws_instance # aws_instance.compute (compute) will be created
+ resource "aws_instance" "compute" {
+ ami = "ami-0d48337b7d3c86f62"
+ arn = (known after apply)
+ associate_public_ip_address = (known after apply)
+ availability_zone = (known after apply)
+ cpu_core_count = (known after apply)
+ cpu_threads_per_core = (known after apply)
+ disable_api_stop = (known after apply)
+ disable_api_termination = (known after apply)
+ ebs_optimized = (known after apply)
+ get_password_data = false
+ host_id = (known after apply)
+ host_resource_group_arn = (known after apply)
+ iam_instance_profile = (known after apply)
+ id = (known after apply)
+ instance_initiated_shutdown_behavior = (known after apply)
+ instance_lifecycle = (known after apply)
+ instance_state = (known after apply)
+ instance_type = "t2.micro"
+ ipv6_address_count = (known after apply)
+ ipv6_addresses = (known after apply)
+ key_name = (known after apply)
+ monitoring = (known after apply)
+ outpost_arn = (known after apply)
+ password_data = (known after apply)
+ placement_group = (known after apply)
+ placement_partition_number = (known after apply)
+ primary_network_interface_id = (known after apply)
+ private_dns = (known after apply)
+ private_ip = (known after apply)
+ public_dns = (known after apply)
+ public_ip = (known after apply)
+ secondary_private_ips = (known after apply)
+ security_groups = (known after apply)
+ source_dest_check = true
+ spot_instance_request_id = (known after apply)
+ subnet_id = (known after apply)
+ tags_all = (known after apply)
+ tenancy = (known after apply)
+ user_data = (known after apply)
+ user_data_base64 = (known after apply)
+ user_data_replace_on_change = false
+ vpc_security_group_ids = (known after apply)
}
Plan: 1 to add, 0 to change, 0 to destroy.
Changes to Outputs:
+ public_ip = (known after apply)
Do you want to perform these actions?
Terraform will perform the actions described above.
Only 'yes' will be accepted to approve.
Please review the diff output above for aws_instance
❯ Approve Applies the changes outlined in the plan.
Dismiss
Stop
EC2インスタンスをデプロイするplanが出力されました。Approveを選択し、デプロイを実行します。
aws_instance Enter a value: yes
aws_instance
aws_instance aws_instance.compute (compute): Creating...
aws_instance aws_instance.compute (compute): Still creating... [10s elapsed]
aws_instance aws_instance.compute (compute): Still creating... [20s elapsed]
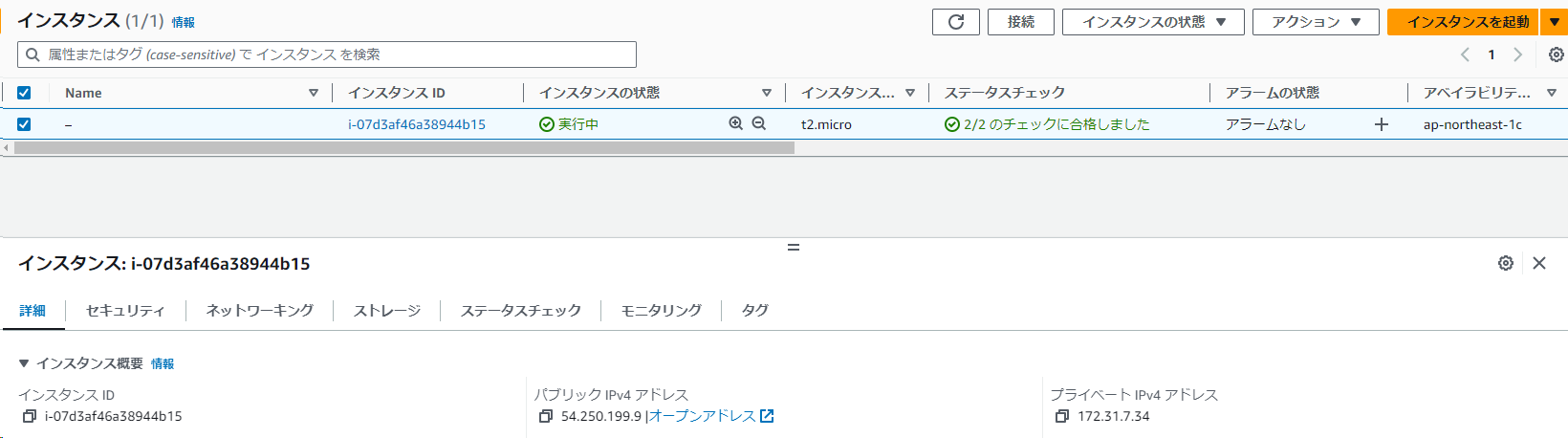
aws_instance aws_instance.compute (compute): Creation complete after 21s [id=i-07d3af46a38944b15]
aws_instance
Apply complete! Resources: 1 added, 0 changed, 0 destroyed.
Outputs:
aws_instance public_ip = "54.250.199.9"
aws_instance
public_ip = 54.250.199.9
マネージメントコンソールで、インスタンスが作成されたことを確認できます。
インフラストラクチャの変更
次に、インスタンスに名前タグを追加してみます。
main.tsを編集します。
import { Construct } from "constructs";
import { App, TerraformStack, TerraformOutput } from "cdktf";
import { AwsProvider } from "@cdktf/provider-aws/lib/provider";
import { Instance } from "@cdktf/provider-aws/lib/instance";
class MyStack extends TerraformStack {
constructor(scope: Construct, id: string) {
super(scope, id);
new AwsProvider(this, "AWS", {
region: "ap-northeast-1",
});
const ec2Instance = new Instance(this, "compute", {
ami: "ami-0d48337b7d3c86f62", // Amazon Linux 2023
instanceType: "t2.micro",
+ tags: {
+ Name: "CDKTF-Demo",
+ },
});
new TerraformOutput(this, "public_ip", {
value: ec2Instance.publicIp,
});
}
}
const app = new App();
new MyStack(app, "aws_instance");
app.synth();
デプロイ前に、コードの変更により生じる差分を確認します。
cdktf diff
output
aws_instance Initializing the backend...
aws_instance Initializing provider plugins...
aws_instance - Reusing previous version of hashicorp/aws from the dependency lock file
aws_instance - Using previously-installed hashicorp/aws v5.22.0
aws_instance Terraform has been successfully initialized!
You may now begin working with Terraform. Try running "terraform plan" to see
any changes that are required for your infrastructure. All Terraform commands
should now work.
If you ever set or change modules or backend configuration for Terraform,
rerun this command to reinitialize your working directory. If you forget, other
commands will detect it and remind you to do so if necessary.
aws_instance aws_instance.compute (compute): Refreshing state... [id=i-07d3af46a38944b15]
aws_instance Terraform used the selected providers to generate the following execution
plan. Resource actions are indicated with the following symbols:
~ update in-place
Terraform will perform the following actions:
aws_instance # aws_instance.compute (compute) will be updated in-place
~ resource "aws_instance" "compute" {
id = "i-07d3af46a38944b15"
~ tags = {
+ "Name" = "CDKTF-Demo"
}
~ tags_all = {
+ "Name" = "CDKTF-Demo"
}
# (30 unchanged attributes hidden)
# (8 unchanged blocks hidden)
}
Plan: 0 to add, 1 to change, 0 to destroy.
─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────
Saved the plan to: plan
To perform exactly these actions, run the following command to apply:
terraform apply "plan"
期待通りNameタグが追加されるplanが出力されたので、デプロイします。
cdktf deploy
output
aws_instance Initializing the backend...
aws_instance Initializing provider plugins...
aws_instance - Reusing previous version of hashicorp/aws from the dependency lock file
aws_instance - Using previously-installed hashicorp/aws v5.22.0
Terraform has been successfully initialized!
You may now begin working with Terraform. Try running "terraform plan" to see
any changes that are required for your infrastructure. All Terraform commands
should now work.
If you ever set or change modules or backend configuration for Terraform,
rerun this command to reinitialize your working directory. If you forget, other
commands will detect it and remind you to do so if necessary.
aws_instance aws_instance.compute (compute): Refreshing state... [id=i-07d3af46a38944b15]
aws_instance Terraform used the selected providers to generate the following execution plan.
Resource actions are indicated with the following symbols:
~ update in-place
Terraform will perform the following actions:
aws_instance # aws_instance.compute (compute) will be updated in-place
~ resource "aws_instance" "compute" {
id = "i-07d3af46a38944b15"
~ tags = {
+ "Name" = "CDKTF-Demo"
}
~ tags_all = {
+ "Name" = "CDKTF-Demo"
}
# (30 unchanged attributes hidden)
# (8 unchanged blocks hidden)
}
Plan: 0 to add, 1 to change, 0 to destroy.
Do you want to perform these actions?
Terraform will perform the actions described above.
Only 'yes' will be accepted to approve.
Please review the diff output above for aws_instance
❯ Approve Applies the changes outlined in the plan.
Dismiss
Stop
aws_instance Enter a value: yes
aws_instance
aws_instance aws_instance.compute (compute): Modifying... [id=i-07d3af46a38944b15]
aws_instance aws_instance.compute (compute): Modifications complete after 2s [id=i-07d3af46a38944b15]
aws_instance
Apply complete! Resources: 0 added, 1 changed, 0 destroyed.
Outputs:
aws_instance public_ip = "54.250.199.9"
aws_instance
public_ip = 54.250.199.9
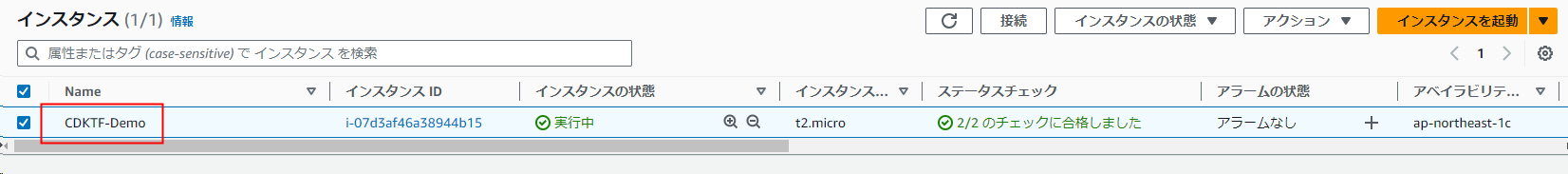
インスタンスに名前が設定されたことが確認できます。
インフラストラクチャのクリーンアップ
最後に、リソースを破棄します。
cdktf destroy
output
aws_instance Initializing the backend...
aws_instance Initializing provider plugins...
aws_instance - Reusing previous version of hashicorp/aws from the dependency lock file
aws_instance - Using previously-installed hashicorp/aws v5.22.0
Terraform has been successfully initialized!
You may now begin working with Terraform. Try running "terraform plan" to see
any changes that are required for your infrastructure. All Terraform commands
should now work.
If you ever set or change modules or backend configuration for Terraform,
rerun this command to reinitialize your working directory. If you forget, other
commands will detect it and remind you to do so if necessary.
aws_instance aws_instance.compute (compute): Refreshing state... [id=i-07d3af46a38944b15]
aws_instance Terraform used the selected providers to generate the following execution plan.
Resource actions are indicated with the following symbols:
- destroy
Terraform will perform the following actions:
aws_instance # aws_instance.compute (compute) will be destroyed
- resource "aws_instance" "compute" {
- ami = "ami-0d48337b7d3c86f62" -> null
- arn = "arn:aws:ec2:ap-northeast-1:xxxxxxxxxxxx:instance/i-07d3af46a38944b15" -> null
- associate_public_ip_address = true -> null
- availability_zone = "ap-northeast-1c" -> null
- cpu_core_count = 1 -> null
- cpu_threads_per_core = 1 -> null
- disable_api_stop = false -> null
- disable_api_termination = false -> null
- ebs_optimized = false -> null
- get_password_data = false -> null
- hibernation = false -> null
- id = "i-07d3af46a38944b15" -> null
- instance_initiated_shutdown_behavior = "stop" -> null
- instance_state = "running" -> null
- instance_type = "t2.micro" -> null
- ipv6_address_count = 0 -> null
- ipv6_addresses = [] -> null
- monitoring = false -> null
- placement_partition_number = 0 -> null
- primary_network_interface_id = "eni-0b586094ee0a5400e" -> null
- private_dns = "ip-172-31-7-34.ap-northeast-1.compute.internal" -> null
- private_ip = "172.31.7.34" -> null
- public_dns = "ec2-54-250-199-9.ap-northeast-1.compute.amazonaws.com" -> null
- public_ip = "54.250.199.9" -> null
- secondary_private_ips = [] -> null
- security_groups = [
- "default",
] -> null
- source_dest_check = true -> null
- subnet_id = "subnet-16868d4d" -> null
- tags = {
- "Name" = "CDKTF-Demo"
} -> null
- tags_all = {
- "Name" = "CDKTF-Demo"
} -> null
- tenancy = "default" -> null
- user_data_replace_on_change = false -> null
- vpc_security_group_ids = [
- "sg-51a8641b",
] -> null
- capacity_reservation_specification {
- capacity_reservation_preference = "open" -> null
}
- cpu_options {
- core_count = 1 -> null
- threads_per_core = 1 -> null
}
- credit_specification {
- cpu_credits = "standard" -> null
}
- enclave_options {
- enabled = false -> null
}
aws_instance - maintenance_options {
- auto_recovery = "default" -> null
}
- metadata_options {
- http_endpoint = "enabled" -> null
- http_protocol_ipv6 = "disabled" -> null
- http_put_response_hop_limit = 2 -> null
- http_tokens = "required" -> null
- instance_metadata_tags = "disabled" -> null
}
- private_dns_name_options {
- enable_resource_name_dns_a_record = false -> null
- enable_resource_name_dns_aaaa_record = false -> null
- hostname_type = "ip-name" -> null
}
- root_block_device {
- delete_on_termination = true -> null
- device_name = "/dev/xvda" -> null
- encrypted = false -> null
- iops = 3000 -> null
- tags = {} -> null
- throughput = 125 -> null
- volume_id = "vol-05dc60b6ed49344d3" -> null
- volume_size = 8 -> null
- volume_type = "gp3" -> null
}
}
Plan: 0 to add, 0 to change, 1 to destroy.
Changes to Outputs:
- public_ip = "54.250.199.9" -> null
Do you really want to destroy all resources?
Terraform will destroy all your managed infrastructure, as shown above.
There is no undo. Only 'yes' will be accepted to confirm.
Please review the diff output above for aws_instance
❯ Approve Applies the changes outlined in the plan.
Dismiss
Stop
aws_instance Enter a value: yes
aws_instance aws_instance.compute (compute): Destroying... [id=i-07d3af46a38944b15]
aws_instance aws_instance.compute (compute): Still destroying... [id=i-07d3af46a38944b15, 10s elapsed]
aws_instance aws_instance.compute (compute): Still destroying... [id=i-07d3af46a38944b15, 20s elapsed]
aws_instance aws_instance.compute (compute): Still destroying... [id=i-07d3af46a38944b15, 30s elapsed]
aws_instance aws_instance.compute (compute): Destruction complete after 30s
aws_instance
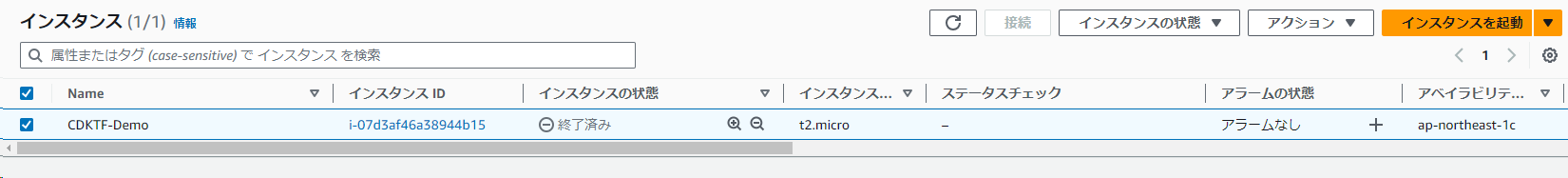
Destroy complete! Resources: 1 destroyed.
インスタンスが終了したことが確認できます。
参考: HCL形式のTerraform構成ファイル
参考までに、今回検証したCDKコードと同等のTerraform構成ファイルを載せておきます。CDKTFを利用しない場合は、このようにHCLでリソースを記述することになります。
terraform {
required_providers {
aws = {
source = "aws"
version = "5.22.0"
}
}
backend "local" {
path = "./terraform.aws_instance.tfstate"
}
}
provider "aws" {
region = "ap-northeast-1"
}
resource "aws_instance" "compute" {
ami = "ami-0d48337b7d3c86f62"
instance_type = "t2.micro"
tags = {
Name = "CDKTF-Demo"
}
}
output "public_ip" {
value = aws_instance.compute.public_ip
}
まとめ
CDKTFのチュートリアルを試してみて、CDKとTerraformの利用経験があれば、CDKTFへの移行は容易な印象を受けました。
CDKTFを利用すれば、Terraformの構成ファイルを直接記述することなく、リソースのライフサイクルを管理できるため、メンテナンスコストの低下が期待できます。
すでにTerraformを使用していて、さらなる効率化や再利用性を求めているのであれば、CDKTFは有力な選択肢になりそうです。