Unityのバージョン
Unity 2019.4.16f1
背景
こちらの
SubclassSelector
を利用していて値が連動する挙動↓

原因としては、配列の要素を増やしたときに、SerializeReference属性を持つ変数の参照をそのまま複製していて
同じインスタンスを参照しているので値が連動してしまうのだろうという結論に至りました
そもそもSerializeReferenceが参照をMonoBehaviour内で共有するための物のようですし、当然の挙動ですね。
ただ、インスタンスの共有は行いたくない状況に遭遇し、面倒なのでコピーして代入しなおす事にしたのですが
managedReferenceValueにgetterが無く、コピー元を取得する事が出来ず、ちょっと調べてもこれと言って見つからなかったので書きました。
成果物
using System;
using System.Collections;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Text.RegularExpressions;
using System.Reflection;
using UnityEngine;
using UnityEditor;
public static class SerializedPropertyUtility
{
//ドットで分割させる時に邪魔なので空文字にしておく
private static readonly Regex ArrayData = new Regex(@"Array\.data\[\d{1,}\]", RegexOptions.Compiled);
private static readonly BindingFlags EveryInstanceField = BindingFlags.NonPublic | BindingFlags.Instance | BindingFlags.Public;
public static object GetManagedReferenceValue(SerializedProperty property)
{
if (property.propertyType != SerializedPropertyType.ManagedReference) { return null; }
property.serializedObject.ApplyModifiedProperties();
property.serializedObject.Update();
object targetObject = property.serializedObject.targetObject;
var pathHierarchy = ArrayData.Replace(property.propertyPath, string.Empty).Split('.');
EnqueueIndices(property);
foreach (var fieldName in pathHierarchy)
{
if (targetObject == null) { return null; }
var type = targetObject.GetType();
if (string.IsNullOrEmpty(fieldName))
{
if (type.IsArray)
{
var array = targetObject as Array;
targetObject = array.GetValue(Indices.Dequeue());
continue;
}
if (type.IsGenericType
&& type.GetGenericTypeDefinition() == typeof(List<>))
{
IList list = targetObject as IList;
targetObject = list[Indices.Dequeue()];
continue;
}
Debug.LogException(new InvalidOperationException("想定外の構造"));
return null;
}
targetObject = type.GetField(fieldName, EveryInstanceField).GetValue(targetObject);
}
return targetObject;
}
//クラスや変数名に数字が使われているケースを想定して数字一致ではなく[1]の様なケースに限定
private static readonly Regex ArrayIndex = new Regex(@"\[\d{1,}\]", RegexOptions.Compiled);
private static readonly char[] ArrayBrackets = new char[] { '[', ']' };
private static readonly Queue<int> Indices = new Queue<int>();
private static void EnqueueIndices(SerializedProperty property)
{
Indices.Clear();
var arrayIndcesMatch = ArrayIndex.Matches(property.propertyPath);
for (int i = 0; i < arrayIndcesMatch.Count; i++)
{
var pickedIndex = arrayIndcesMatch[i].Value.Trim(ArrayBrackets);
Indices.Enqueue(int.Parse(pickedIndex));
}
}
}
動くか確認
テストコード
void Test(SerializedProperty property)
{
var obj = SerializedPropertyUtility.GetManagedReferenceValue(property);
if (obj is TargetInterface target)
{
if (target.Value == 30)
{
target.Modify();
}
}
}
public class TopObject : MonoBehaviour
{
public SingleClass Class;
}
[Serializable]
public class SingleSerialized
{
public SerializedClass[] Array;
}
[Serializable]
public class SerializedClass
{
public List<ListedSerializedClass> List;
}
[Serializable]
public class ListedSerializedClass
{
[SerializeReference, SubclassSelector]
public ISingleInterface Single;
}
public interface ISingleInterface
{
List<IListInterface> Listed { get; }
}
[Serializable]
public class SingleClass : ISingleInterface
{
[SerializeReference, SubclassSelector]
private List<IListInterface> _Listed;
public List<IListInterface> Listed => _Listed;
}
public interface IListInterface
{
ArrayedInterface[] Array { get; }
}
[Serializable]
public class Listed : IListInterface
{
[SerializeReference, SubclassSelector]
private ArrayedInterface[] _Array;
public ArrayedInterface[] Array => _Array;
}
public interface ArrayedInterface
{
TargetInterface Target { get; }
}
[Serializable]
public class ArrayedClass : ArrayedInterface
{
[SerializeReference, SubclassSelector]
private TargetInterface _Target;
public TargetInterface Target => _Target;
}
public interface TargetInterface
{
int Value { get; }
void Modify();
}
[Serializable]
public class ModifyTarget : TargetInterface
{
[SerializeField]
private int _Value;
public int Value => _Value;
public void Modify()
{
_Value = int.MaxValue;
}
}
値が30になった時にInt.Maxを代入するようにしました
変な構造でも動いてるので概ね大丈夫そうです
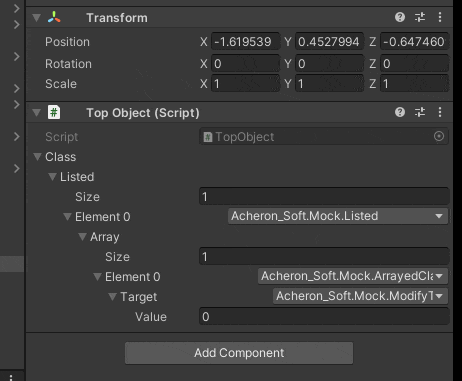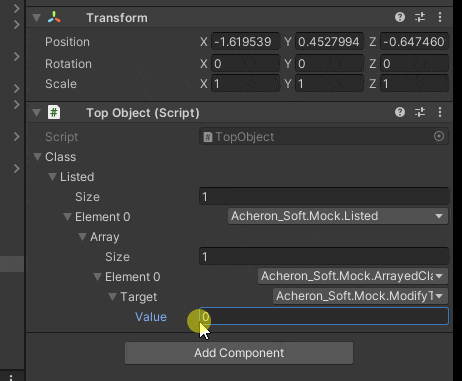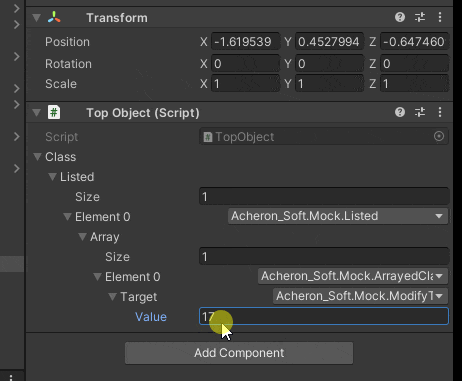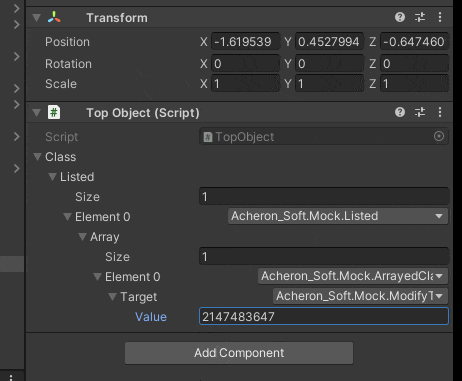
コードの流れをざっくり説明
仕組みとしてはSerializedPorperty.pathがそのまま 構造+リフレクションで必要な変数名 になっているので分解し
起点になってるSerializedPorperty.serializedObject.targetObject (MonobehaviourとかScriptableObject) から順に辿る形になってます
配列かListの場合のみ別の対応が必要で、パス内に存在するArray.data[0]から抜き出したIndexで要素を特定してさらに潜っていくという方法をとりました。