Redux の Example 集の後半が結構読み応えがあったので、写経がてら面白かった箇所を書いていきます。
Redux Example
https://redux.js.org/introduction/examples
今回は Shopping Cart 。
この Example の肝は、API から取得したデータをそのまま store に保存するのではなく、「正規化」という方法をとって Redux が扱いやすい形状に変化させて store にデータを保存する箇所です。「正規化」という単語はデータベースの設計でよく出てくる単語ですが、JSON にも正規化が存在するようで勉強になりました。SQL 文を書くかのごとく、APIからのデータを JavaScript で扱います。
1. redux-devtools-extension をインストール
少し Example とコードを変更します。 Example ではミドルウェアに Redux-logger を利用していましたが、store の構成を把握することが難しいので redux-devtools-extension を yarn で install します。ソースコードは以下のとおりです。
// 省略
import thunk from 'redux-thunk';
import { composeWithDevTools } from 'redux-devtools-extension';
// 省略
const store = createStore(
reducer,
composeWithDevTools(applyMiddleware(...middleware))
);
//省略
2. products の store 構成を確認する
このアプリケーションは大きく分けて2つの store を持ちます。全商品を管理する「products」と、カート内の商品を管理する「cart」です。ここでは前者の内容から見ていきます。
API から取得した、全商品の商品情報はこのような 配列 の形式になっています。
[
{ "id": 1, "title": "iPad 4 Mini", "price": 500.01, "inventory": 2 },
{ "id": 2, "title": "H&M T-Shirt White", "price": 10.99, "inventory": 10 },
{ "id": 3, "title": "Charli XCX - Sucker CD", "price": 19.99, "inventory": 5 }
]
この形式だと、商品単体を参照する場合に都度 find 関数を使って抽出しなければならないので非効率です。配列の数が少ない場合はよいのですが、多くなってくるとパフォーマンスも下がってしまうと予想されます。
そこで、id をキーとしたハッシュに変換して byId という store にデータを保存します。
const byId = (state = {}, action) => {
switch (action.type) {
case RECEIVE_PRODUCTS:
return {
...state,
...action.products.reduce((obj, product) => {
obj[product.id] = product;
return obj;
}, {})
};
default:
const { productId } = action;
if (productId) {
return { ...state, [productId]: products(state[productId], action) };
}
return state;
}
};
reduce 関数をうまく使って配列からハッシュに変換しているのがわかります。
reduce 関数を試した結果。
https://jsfiddle.net/anton072/7faqbqhp/
こういうハッシュになりました。
{
"1": {
"id": 1,
"title": "iPad 4 Mini",
"price": 500.01,
"inventory": 2
},
"2": {
"id": 2,
"title": "H&M T-Shirt White",
"price": 10.99,
"inventory": 10
},
"3": {
"id": 3,
"title": "Charli XCX - Sucker CD",
"price": 19.99,
"inventory": 5
}
}
生成したハッシュと、元の配列ベースのデータの両方を store に保存するのは非効率です。なので、配列は ID だけを取得するデータに変換します。それが、store の visibleIds です。
const visibleIds = (state = [], action) => {
switch (action.type) {
case RECEIVE_PRODUCTS:
return action.products.map(product => product.id);
default:
return state;
}
};
さらに、なるほどな、と思ったのが、上記のデータから情報を抽出する関数が reducers/products.js に記述されている点です。
export const getProduct = (state, id) => state.byId[id];
export const getVisibleProducts = state =>
state.visibleIds.map(id => getProduct(state, id));
getProduct を使って、idベースで商品を抽出し、 getVisibleProductsを使って、元のAPIからのデータ同様の配列データを抽出できます。少しデータベースっぽい扱いができるようになりました。
2. cart の store 構成を確認する
続いて、cart の store を確認します。
const initialState = {
addedIds: [],
quantityById: {}
};
const cart = (state = initialState, action) => {
switch (action.type) {
case CHECKOUT_REQUEST:
return initialState;
case CHECKOUT_FAILURE:
return action.cart;
default:
return {
addedIds: addedIds(state.addedIds, action),
quantityById: quantityById(state.quantityById, action)
};
}
};
商品を cart に入れると、ADD_TO_CART アクションが発行されます。ここでは、default 句の内容が実行されます。ここも面白いなと思ったのが、reducer の中に reducer を入れ子にしている箇所です。addedIds と quantityById も reducer です。
チェックアウトをすると、cart の中身が初期化されます。initialState を返して初期化していますね。
const addedIds = (state = initialState.addedIds, action) => {
switch (action.type) {
case ADD_TO_CART:
if (state.indexOf(action.productId) !== -1) {
return state;
}
return [...state, action.productId];
default:
return state;
}
};
const quantityById = (state = initialState.quantityById, action) => {
switch (action.type) {
case ADD_TO_CART:
const { productId } = action;
return { ...state, [productId]: (state[productId] || 0) + 1 };
default:
return state;
}
};
addedIds はカート内にどの商品が入っているかの管理をします。重複はしません。quantityById は ID 単位で カートに商品がいくつ入っているかの管理をします。ここも 一覧と詳細を分けて管理しているのが興味深いです。何も考えないで作ると一個にまとめてしまいそうなところです。
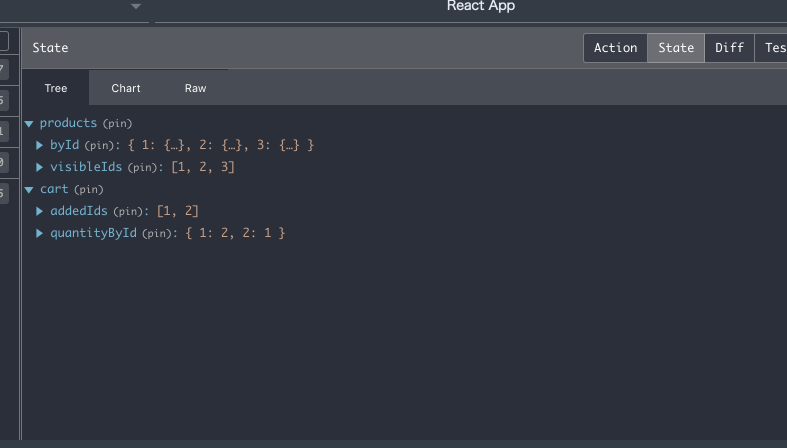
storeの状態
データの本体は byId に保存、それ以外の store はすべて ID で管理しているので、データの重複がなく、かなりスマートな構成になっているかと思います。
cart.js には products.js 同様、セレクト関数が2つ用意されています。セレクト関数は引数から store を参照しているのがポイントです。汎用性があります。
export const getQuantity = (state, productId) =>
state.quantityById[productId] || 0;
export const getAddedIds = state => state.addedIds;
3. productsデータとcartデータを組み合わせたデータを抽出する
reducers/index.js には products データと cart データを組み合わせたセレクト関数が実装されています。
const getAddedIds = state => fromCart.getAddedIds(state.cart);
const getQuantity = (state, id) => fromCart.getQuantity(state.cart, id);
const getProduct = (state, id) => fromProducts.getProduct(state.products, id);
export const getTotal = state => {
return getAddedIds(state)
.reduce((total, id) => {
return total + getProduct(state, id).price * getQuantity(state, id);
}, 0)
.toFixed(2);
};
export const getCartProducts = state => {
return getAddedIds(state).map(id => ({
...getProduct(state, id),
quantity: getQuantity(state, id)
}));
};
合計金額とカートの中の商品詳細を返す関数が定義してあります。おのおのの store にセレクト関数が定義してあるので処理がスマート。素敵です。
4. Action Creators
Action Creators については redux-thunk を上手くつかっているなという印象。
export const addToCart = productId => (dispatch, getState) => {
if (getState().products.byId[productId].inventory > 0) {
dispatch(addToCartUnsafe(productId));
}
};
export const checkout = products => (dispatch, getState) => {
const { cart } = getState();
dispatch({
type: types.CHECKOUT_REQUEST
});
shop.buyProducts(products, () => {
dispatch({
type: types.CHECKOUT_SUCCESS,
cart
});
});
};
redux-thunk を使うと Action Creator は関数を返すことができるようになります。
そして、関数の中でstateも参照できるので非同期処理などを Action Creator の中に押し込めます。処理がシンプルなので、自分は redux-saga より redux-thunk のほうが好きです。コードも追いやすい。
5. View
データ構造が完璧なので、View では特に何も必要ありません。ほぼ、レンダーしているだけです。強いてあげるなら、Cartのところの処理が興味深かったです。
const Cart = ({ products, total, onCheckoutClicked }) => {
const hasProducts = products.length > 0;
const nodes = hasProducts ? (
products.map(product => (
<Product
title={product.title}
price={product.price}
quantity={product.quantity}
key={product.id}
/>
))
) : (
<em>Please add some products to cart.</em>
);
return (
<div>
<h3>Your Cart</h3>
<div>{nodes}</div>
<p>Total: ${total}</p>
<button
onClick={onCheckoutClicked}
disabled={hasProducts ? '' : 'disabled'}
>
Checkout
</button>
</div>
);
};
処理を nodes という変数にまとめて、JSX はシンプルに。きれいなコードです。
React / Redux の成功の鍵はデータベース設計同様、いかに store のデータ構造を上手くつくるか、によるのかなーと思いました。勉強になりました!