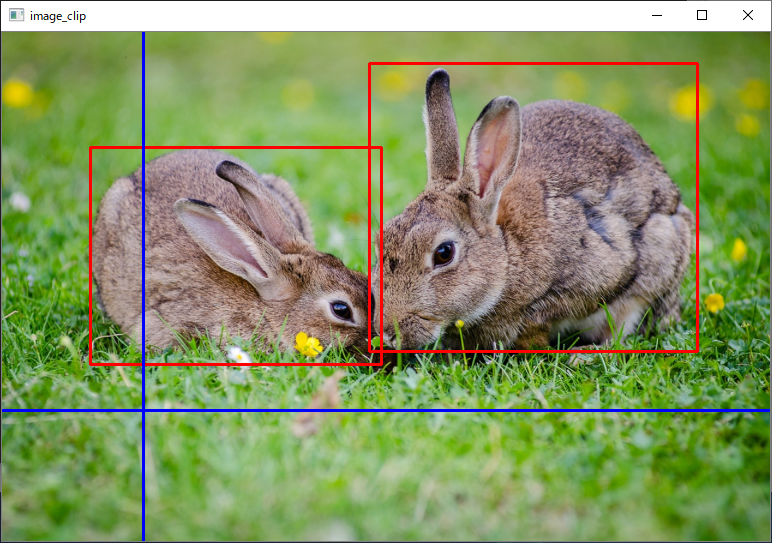
OpenCVで物体検出を自作するためには、訓練データとして大量の画像を切り出す必要があります。
そこで二つのツールを作成しました。
簡易的なGUIで画像の切り出しを行い、opencv_createsamples.exeにわたすファイルを生成します。
コードは下に載せました。
突貫工事で作ったので、バグが多々あるかもしれません。
使用方法
準備
以下のようなディレクトリ構成にします。
適当なディレクトリ/
├── images/
| ├── 画像ファイル1.png
| ├── 画像ファイル2.jpg
| | ︙
| └── 画像ファイルn.bmp
├── clipper.py
├── make_negative.py
├── opencv_createsamples.exe
├── opencv_traincascade.exe
└── (OpenCVのDLL類)
画像切り出し支援ツールの使用方法
- 左クリックのドラッグで、検出したい物体の範囲を選択
- 右クリックで、最後に選択した範囲の削除
- マウルホイールで画像の切り替え
- ESCキーか「Q」キーで終了
終了するとopencv_createsamples.exeに入力できるファイルpos.datが生成されます。
途中経過はファイルに保存されるので、終了しても作業を再開できます。
負例自動作成ツールの使用方法
画像切り出し支援ツールを使ってから、make_negative.pyを実行するだけです。
そうすると、ディレクトリnegativesに負例画像が生成され、bg.datに負例のリストが生成されます。
opencv_createsamples.exeの使用方法
とりあえず、下のコマンドを実行すれば大丈夫です。
opencv_createsamples.exe -info pos.dat -vec pos.vec
opencv_traincascade.exeの使用方法
opencv_traincascade.exe -data 出力ディレクトリ -vec pos.vec -bg bg.dat
コード
画像切り出し支援ツール
clipper.py
import cv2
import glob
import lzma
import os
import pickle
file_dir = './images'
state_file = './data'
output_file = './pos.dat'
display_size = 768
window_name = 'image_clip'
state = {}
mouse_position = [0, 0]
mouse_wheel = 0
crop_origin = None
crop_end = None
selecting = False
remove = False
def load_state():
global state
if os.path.exists(state_file):
with lzma.open(state_file, 'rb') as f:
state = pickle.load(f)
def save_state():
with lzma.open(state_file, 'wb') as f:
pickle.dump(state, f)
def output():
with open(output_file, 'w') as f:
for file_name, rects in state.items():
if len(rects) == 0:
continue
values = [os.path.abspath(file_name), str(len(rects))]
values += sum([[str(int(r)) for r in rect] for rect in rects], [])
f.write(' '.join(values) + '\n')
def mouse_callback(event, x, y, flags, param):
global mouse_position
global mouse_wheel
global crop_origin
global selecting
global crop_end
global remove
mouse_position = (x, y)
if event == cv2.EVENT_LBUTTONDOWN:
crop_origin = mouse_position
selecting = True
if event == cv2.EVENT_LBUTTONUP:
crop_end = mouse_position
selecting = False
if event == cv2.EVENT_RBUTTONDOWN:
remove = True
if event == cv2.EVENT_MOUSEWHEEL:
mouse_wheel = flags
def main():
global state
global mouse_wheel
global crop_origin
global crop_end
global remove
os.makedirs(file_dir, exist_ok=True)
image_files = glob.glob(os.path.join(file_dir, '*'))
if len(image_files) == 0:
print('imagesに画像を入れてください')
exit()
load_state()
cv2.namedWindow(window_name, cv2.WINDOW_AUTOSIZE)
cv2.setMouseCallback(window_name, mouse_callback)
image_counter = 0
for i in range(len(image_files)):
image_counter = i
if image_files[image_counter] not in state.keys():
break
while True:
if image_counter < 0:
image_counter = image_counter + len(image_files)
if image_counter >= len(image_files):
image_counter = image_counter - len(image_files)
save_state()
image_file = image_files[image_counter]
image = cv2.imread(image_file)
scale = display_size / max(image.shape[0], image.shape[1])
resized_image = cv2.resize(image,
dsize=None,
fx=scale,
fy=scale,
interpolation=cv2.INTER_AREA)
if image_file not in state:
state[image_file] = []
while True:
display_image = resized_image.copy()
for rect in state[image_file]:
left_top = (int(rect[0] * scale), int(rect[1] * scale))
right_bottom = (int((rect[0] + rect[2]) * scale), int((rect[1] + rect[3]) * scale))
display_image = cv2.rectangle(display_image,
left_top,
right_bottom,
(0, 0, 255),
2)
display_image = cv2.line(display_image,
(mouse_position[0], 0),
(mouse_position[0], display_image.shape[0]),
(255, 0, 0),
2)
display_image = cv2.line(display_image,
(0, mouse_position[1]),
(display_image.shape[1], mouse_position[1]),
(255, 0, 0),
2)
if selecting:
display_image = cv2.rectangle(display_image,
crop_origin,
mouse_position,
(0, 128, 255),
2)
cv2.imshow(window_name, display_image)
key = cv2.waitKey(10) & 0xFF
if crop_origin is not None and crop_end is not None:
rect_x = min(mouse_position[0], crop_origin[0])
rect_w = max(mouse_position[0], crop_origin[0]) - rect_x
rect_y = min(mouse_position[1], crop_origin[1])
rect_h = max(mouse_position[1], crop_origin[1]) - rect_y
new_rect = [rect_x / scale, rect_y / scale, rect_w / scale, rect_h / scale]
state[image_file].append(new_rect)
crop_origin = None
crop_end = None
if remove:
if len(state[image_file]) > 0:
state[image_file].pop(-1)
remove = False
if mouse_wheel != 0:
image_counter += 1 if mouse_wheel > 0 else -1
mouse_wheel = 0
break
if key == ord('q') or key == 27:
return
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
save_state()
output()
負例自動作成ツール
make_negative.py
import cv2
import glob
import lzma
import os
import pickle
import random
file_dir = './images'
output_dir = './negatives/'
output_list_file = './bg.dat'
state_file = './data'
def sample_start_point(width, height, positive_rects):
for i in range(100):
start_point = [random.randrange(width), random.randrange(height)]
for rect in positive_rects:
rect_left = rect[0]
rect_right = rect[0] + rect[2]
rect_top = rect[1]
rect_bottom = rect[1] + rect[3]
if ((rect_left <= start_point[0] and rect_right >= start_point[0]) and
(rect_top <= start_point[1] and rect_bottom >= start_point[1])):
break
else:
return start_point
return None
if __name__ == '__main__':
if not os.path.exists(state_file):
exit()
with lzma.open(state_file, 'rb') as f:
state = pickle.load(f)
image_counter = 0
for file_name, positive_rects in state.items():
if len(positive_rects) == 0:
continue
image = cv2.imread(file_name)
width = image.shape[1]
height = image.shape[0]
negative_rects = []
for i in range(1000):
start_point = sample_start_point(width, height, positive_rects)
if start_point is None:
continue
negative_rect = [start_point[0], start_point[1], start_point[0], start_point[1]]
min_x = 0
max_x = width
min_y = 0
max_y = height
directions = random.sample(['left', 'right', 'up', 'down'], 4)
for direction in directions:
for positive_rect in positive_rects:
positive_rect_left = positive_rect[0]
positive_rect_right = positive_rect[0] + positive_rect[2]
positive_rect_top = positive_rect[1]
positive_rect_bottom = positive_rect[1] + positive_rect[3]
if not (negative_rect[1] > positive_rect_bottom or
negative_rect[3] < positive_rect_top):
if direction == 'left':
if negative_rect[0] > positive_rect_right:
min_x = max(min_x, positive_rect_right)
if direction == 'right':
if negative_rect[2] < positive_rect_left:
max_x = min(max_x, positive_rect_left)
if not (negative_rect[0] > positive_rect_right or
negative_rect[2] < positive_rect_left):
if direction == 'up':
if negative_rect[1] > positive_rect_bottom:
min_y = max(min_y, positive_rect_bottom)
if direction == 'down':
if negative_rect[3] < positive_rect_top:
max_y = min(max_y, positive_rect_top)
if direction == 'left':
negative_rect[0] = min_x
if direction == 'right':
negative_rect[2] = max_x
if direction == 'up':
negative_rect[1] = min_y
if direction == 'down':
negative_rect[3] = max_y
if negative_rect[0] == negative_rect[2] or negative_rect[1] == negative_rect[3]:
continue
negative_rects.append(tuple([int(x) for x in negative_rect]))
negative_rects = set(negative_rects)
for negative_rect in negative_rects:
trimed_image = image[negative_rect[1]:negative_rect[3], negative_rect[0]:negative_rect[2], :]
os.makedirs(output_dir, exist_ok=True)
extention = os.path.splitext(file_name)[1]
output_file_path = os.path.join(output_dir, '{}{}'.format(image_counter, extention))
cv2.imwrite(output_file_path, trimed_image)
image_counter += 1
image_files = glob.glob(os.path.join(output_dir, '*'))
with open(output_list_file, 'w') as f:
for image_file in image_files:
f.write('{}\n'.format(os.path.abspath(image_file)))