背景・目的
最近、ECSのチュートリアルを行う機会がありました。その中でAWS Copilotを触る機会がありましたので整理します。
まとめ
下記に特徴をまとめます。
| 特徴 | 説明 |
|---|---|
| 概要 | ECS上のコンテナや環境にパッケージ化されたアプリケーションのデプロイと操作を直接行えるようにする包括的なツール NWやALBなどの関連リソースも作成する |
| Application | Service Envrionment,Pipeline等の概念をまとめるもの ServiceやデプロイされるEnvrionmentを1つのApplicationとして取りまとめる |
| Services | コンテナイメージをビルド、ECRへのPush、サービスのスケーラブル、セキュアな実行に必要なインフラのセットアップの一連の流れが、copilot で実現できる |
| Serviceのタイプ | 下記に大別される ・インターネットから接続可能なサービス ・Backendサービス ・Workerサービス |
| インターネットから接続可能なサービス | 下記に大別される ・Request-Driven Web Service ・Static Site ・Load Balanced Web Service |
| Request-Driven Web Service | AWS App Runner を利用する Service で、受け付けるトラフィックに応じてオートスケールし、トラフィックがない場合は設定された最低インスタンス数までスケールダウンする |
| Static Site | Amazon CloudFront で配信され、S3 でホスティングされた静的 Web サイト |
| Load Balanced Web Service | Application Load Balancer、Network Load Balancer、または両方をトラフィックの入り口として Fargate 上でタスクを実行する ECS サービス |
| Environments | サービスをデプロイする環境 |
コマンド一覧
| 概要 | コマンド |
|---|---|
| Applicationの作成 | copilot app init ${アプリケーション名} |
| Serviceの作成 | copilot svc init ${サービス名} |
| Serviceのデプロイ | copilot svc deploy --name ${サービス名} --env ${環境名} |
| Serviceの削除 | copilot svc delete --name ${サービス名} --env ${環境名} |
| Environmentの作成 | copilot env init ${環境名} |
概要
AWS Copilot CLI
Amazon ECS デベロッパーツールの概要を基に整理します。
AWS Copilot CLI (コマンドラインインターフェイス) は、Amazon ECS 上のコンテナや環境にパッケージ化されたアプリケーションのデプロイと操作をソースコードから直接行えるようにする包括的なツールです。AWS Copilot を使用すると、AWSと Amazon ECS 要素(Application Load Balancer、パブリックサブネット、タスク、サービス、クラスターなど)を理解しなくても、これらの操作を実行できます。AWSユーザーに代わって Copilot が作成するAWSリソースは、ロードバランサーウェブサービスやバックエンドサービスなどの独善的なサービスパターンから、コンテナ化されたアプリケーションが即時に本番稼働できる環境を提供します。AWS CodePipeline パイプラインを使用して、複数の環境、アカウント、またはリージョンにまたがってデプロイできます。それらのすべてが CLI 内で管理できます。AWS Copilot を使用して、ログの表示やサービスの健全性などのオペレータタスクを実行することもできます。AWSCopilot は、クラウドリソースの管理を容易にするオールインワンツールです。これにより、アプリケーションの開発と管理に集中できます。
包括的な AWS Copilot エンドツーエンドのデベロッパーワークフローを使用して、インフラストラクチャの AWS ベストプラクティスに準拠したコンテナアプリケーションを作成、リリース、運用します。
- Copilot CLIとは?
- ECS上のコンテナや環境にパッケージ化されたアプリケーションのデプロイと操作を直接行えるようにする包括的なツール
- NWやALBなどの関連リソースも作成する
Application
Applicationを基に整理します。
Application は、Service、Environment、Pipeline といった概念を取りまとめる概念です。あなたのアプリケーションがサービス1つですべてのことをやるものであるか、マイクロサービスの集まりであるかに関係なく、Copilot は Service やそれらがデプロイされる Environment を1つの Application として取りまとめます。
- Service Envrionment,Pipeline等の概念をまとめるもの
- ServiceやデプロイされるEnvrionmentを1つのApplicationとして取りまとめる
例を見ていきましょう。ここでは投票を受け付け、結果を集計する投票アプリを構築しようとしているとします。
- 投票を受け付ける。集計する投票アプリの例
投票の受け付けと結果の集計という2つのサービスを持つ投票アプリは、copilot init コマンド2回で構築できます。まず最初に copilot init を実行すると、この Service が所属することになる Application の名前を質問されます。ここでは投票システムを構築しようとしていますので、Application を "vote" 、そして投票を受け付ける Service を "collector" と名付けることにしましょう。2回目の init では、既存の "vote" Application に新しい Service を追加するために、今度は Service 名のみを質問されます。こちらは集計するサービスですので "aggregator" と名付けることにしましょう。
- 投票受付と集計の2つのサービスを持つ投票アプリでは、copilot initコマンド2回で構築可能
- はじめに、copilot initで、このServiceが所属することになるApplicationの名前を質問され、voteとして入力、受け付けるサービスをCollectとする
- 2回目は、既存のVote、Applicationに新しいServiceを使いするためにServiceのみ質問される。ここでaggregatorと名付ける
あなたの Application 設定(ここに複数の Service や Environment が所属します)は、AWS アカウントの中に保存されますので、あなた以外の開発者も "vote" アプリの開発に参加できます。これにより、例えばあなたが1つの Service 開発に取り組む一方で、チームメイトは別の Service 開発を進めることができます。

出典:AWS Copilot CLI > Concept > Applications
Services
Servicesを基に整理します
コンテナの素晴らしい特徴の1つは、コードを書き終わったらそれを簡単に docker run コマンドでローカル環境にて実行できることです。Copilot は、copilot init コマンドでこのコンテナの AWS 上での容易な実行を可能にします。コンテナイメージをビルド、Amazon ECR へのプッシュ、サービスのスケーラブルかつセキュアな実行に必要なインフラストラクチャのセットアップという一連の流れが Copilot によって簡単に実現できます。
Services
Servicesを基に整理します。
コンテナの素晴らしい特徴の1つは、コードを書き終わったらそれを簡単に docker run コマンドでローカル環境にて実行できることです。Copilot は、copilot init コマンドでこのコンテナの AWS 上での容易な実行を可能にします。コンテナイメージをビルド、Amazon ECR へのプッシュ、サービスのスケーラブルかつセキュアな実行に必要なインフラストラクチャのセットアップという一連の流れが Copilot によって簡単に実現できます。
- コンテナの特徴の一つは、docker runコマンドによりローカルで実行できること
- copilot initでこのコンテナのAWS上での実行を可能にする
- コンテナイメージをビルド、ECRへのPush、サービスのスケーラブル、セキュアな実行に必要なインフラのセットアップの一連の流れが、copilot で実現できる
Serviceタイプ
ここに辿り着くまでの間に、「Copilot は Service の実行に必要なインフラストラクチャリソースを自動的にセットアップする」といった説明をしてきました。では、Copilot はどのようにして必要なインフラストラクチャが何かを知るのでしょうか?
その秘密は、Service の作成時に Copilot が Service の タイプ を尋ねていることにあります。
- Serviceのタイプにより、必要なインフラが決まる
インターネットから接続可能なService
- "Request-Driven Web Service" - Service 実行環境として AWS App Runner サービスを作成します。
- "Static Site" - 静的 Web サイト用に専用の CloudFront ディストリビューションと S3 バケットをプロビジョニングします。
- "Load Balanced Web Service" - Service 実行環境として Appplication Load Balancer (ALB)、Network Load Balancer、またはその両方を作成し、セキュリティグループ、ECS サービス (Fargate) を利用します。
- 下記の3つに分かれる
- Request-Driven Web Service
- AWS App Runnerサービスを作成する
- Static Site
- CloudFrontとS3バケットを作成する
- Load Balanced Web Service
- ALB、NLBを作成し、SG、ECSを利用する
- Request-Driven Web Service
Load Balanced Web Service
Application Load Balancer、Network Load Balancer、または両方をトラフィックの入り口として Fargate 上でタスクを実行する ECS サービスです。 安定したリクエスト量が見込まれる場合、Service から VPC 内のリソースにアクセスする必要がある場合、あるいはより高度な設定の必要がある場合に適した HTTP または TCP サービスの選択肢です。
Application Load Balancer は Environment レベルのリソースであり、Environment 内の全ての Load Balanced Web Service で共有されることに注意しましょう。v1.32.0 では、Load Balanced Web Service の Manifest で指定することにより、既存の ALB を Service レベルでインポートできます。詳細については、こちらを確認してください。対照的に、 Network Load Balancer は Service レベルのリソースであり、 Service 間では共有されません。
- ALBは、Envrionment内のすべてのLoad Balanced Web Serviceで共有される
- NLBは Serviceレベルのリソースのため、Service間では共有されない

出典:AWS Copilot CLI > Concept > Services > Load Balanced Web Service
Backend Service
VPC 外部からアクセスさせる必要はないが、Application 内の他の Service からはアクセスできる必要があるという場合は、 Backend Service を 作りましょう。Copilot は AWS Fargate で実行される ECS サービスを作成しますが、インターネットに向けて開放されたエンドポイントを作成することはありません。なお、Backend Service で内部ロードバランサーを利用することもできます。内部ロードバランサーを利用する Backend Service について知りたい場合は、こちらを確認してください。
- VPCの外からアクセスは不要、他のServiceからアクセスできる必要がある場合
- 内部LBの作成ができる

出典:AWS Copilot CLI > Concept > Services > Backend Service
Worker Service
Worker Services は pub/sub アーキテクチャによる非同期のサービス間通信を実装できます。
アプリケーション内のマイクロサービスはイベントを Amazon SNS トピック に パブリッシュ でき、それを "Worker Service" がサブスクライバーとして受け取ることができます。
Worker Service は次の要素で構成されます。
- トピックにパブリッシュされた通知を処理する 1 つまたは複数の Amazon SQS キューと、失敗した通知を処理する デッドレターキュー
- SQS キューをポーリングし、メッセージを非同期で処理する権限を持つ AWS Fargate 上の Amazon ECS サービス
- Pub/Subアーキテクチャによる非同期サービス間通信を実装できる
- SNSトピックにPublishし、WorkerServiceがサブスクライバーとして受け取る
- 下記で構成される
- トピックにパブリッシュされた通知を1つ以上のSQSキューとDLQ
- SQSをポーリングし、メッセージを非同期で処理するFargate上のECSサービス

出典:AWS Copilot CLI > Concept > Services Worker Service>
Envrionments
Environmentsを基に整理します。
はじめて copilot init コマンドを実行すると、あわせて test Environment を作成するかを尋ねられます。この test Environment にはセキュアなネットワーク(e.g. VPC、サブネット、セキュリティグループ)を作成するために必要な AWS リソースや、複数の Service での共有を目的とした Application Load Balancer や ECS クラスタのようなリソースも含まれます。Service をこの test Environment にデプロイすると、この Service は test Environment のネットワークやリソースを利用します。Application は複数の Environment を持つことができ、それぞれが互いに独立したネットワークやその他のインフラストラクチャリソースを持ちます。
あなたの Copilot の利用開始にあわせて Copilot は test Environment (テスト環境)を作成しますが、これとは異なる Environment、例えば production Environment (本番環境)を新たに作るというのはごく一般的なことでしょう。この production Environment は test Environment とは完全に独立したもので、production Environment 用のネットワークスタックやそこにデプロイされる Service を持ちます。独立したテスト環境と本番環境を持つことで、まずはテスト環境にデプロイし、問題ないことを確認した上で本番環境にデプロイするというオペレーションが可能になります。
下に載せた図は、API と Backend という2つの Service を持つ MyApp という Application を表しています。これら2つの Service は test と production という2つの Environment にデプロイされています。test Environment では両方の Service が1つのコンテナを実行している一方で、production Environment ではそれぞれが3つのコンテナを実行しているのが分かるでしょうか。このように、Service はデプロイ先の Environment ごとに異なる設定を持つことができます。詳しくは環境変数の利用ガイドもご覧ください。
- サービスをデプロイする環境
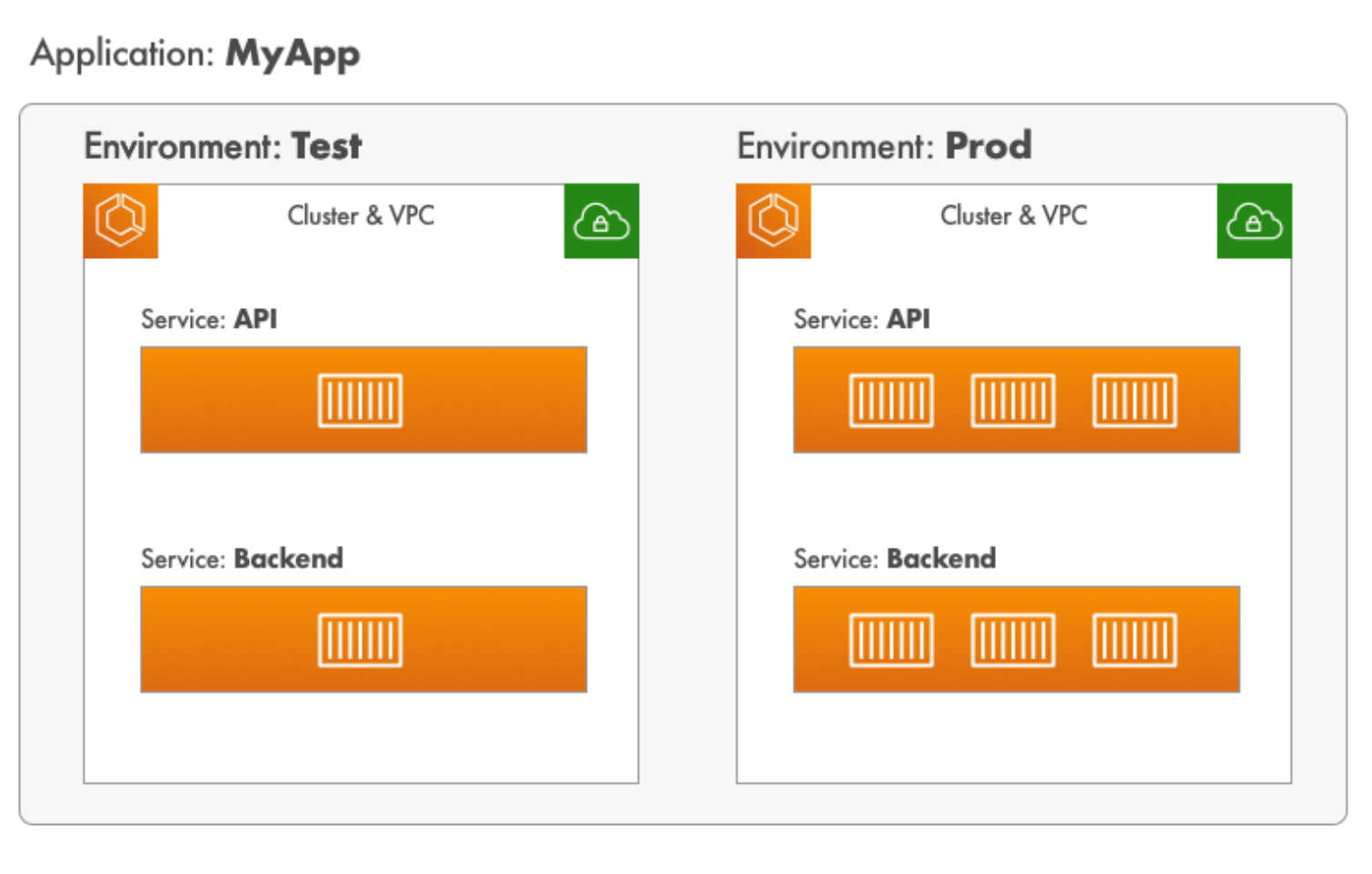
出典:AWS Copilot CLI > Concept > Envrionments
実践
前提
CloudShellでは、Copilot CLIがインストールされているため、今回はCloudShellで実行します。
バージョン確認
- バージョンを確認してみます
$ copilot --version copilot version: v1.33.3 $
環境変数の設定
- 以降で使用する環境変数を設定します
$ export APP=demo-app $ export SVC=demo-svc $ export ENV=test
アプリケーションの作成
app initを基に試します。
-
copililot app init を実行します
$ copilot app init $APP ✔ Proposing infrastructure changes for stack demo-app-infrastructure-roles - Creating the infrastructure for stack demo-app-infrastructure-roles [create complete] [44.5s] - A StackSet admin role assumed by CloudFormation to manage regional stacks [create complete] [19.3s] - An IAM role assumed by the admin role to create ECR repositories, KMS keys, and S3 buckets [create complete] [17.7s] ✔ The directory copilot will hold service manifests for application demo-app. Recommended follow-up action: - Run `copilot init` to add a new service or job to your application. $ -
copilotディレクトリができています
$ ls -laR copilot/ copilot/: total 12 drwxr-xr-x. 2 cloudshell-user cloudshell-user 4096 Jul 1 12:44 . drwxrwxrwx. 5 cloudshell-user cloudshell-user 4096 Jul 1 12:44 .. -rw-r--r--. 1 cloudshell-user cloudshell-user 22 Jul 1 12:44 .workspace $
サービスの作成
svc initを基に試します。
- copilot svc init を実行します
$ copilot svc init --name $SVC --app $APP --image nginx --port 80 --svc-type "Load Balanced Web Service" Note: It's best to run this command in the root of your workspace. ✔ Wrote the manifest for service demo-svc at copilot/demo-svc/manifest.yml Your manifest contains configurations like your container size and port. - Update regional resources with stack set "demo-app-infrastructure" [succeeded] [0.0s] Recommended follow-up actions: - Update your manifest copilot/demo-svc/manifest.yml to change the defaults. - Run `copilot svc deploy --name demo-svc --env test` to deploy your service to a test environment. $ - サービス名の下に、manifest.ymlができていました。
$ ls -laR copilot/ copilot/: total 16 drwxr-xr-x. 3 cloudshell-user cloudshell-user 4096 Jul 1 12:59 . drwxrwxrwx. 5 cloudshell-user cloudshell-user 4096 Jul 1 12:44 .. drwxr-xr-x. 2 cloudshell-user cloudshell-user 4096 Jul 1 12:59 demo-svc -rw-r--r--. 1 cloudshell-user cloudshell-user 22 Jul 1 12:44 .workspace copilot/demo-svc: total 12 drwxr-xr-x. 2 cloudshell-user cloudshell-user 4096 Jul 1 12:59 . drwxr-xr-x. 3 cloudshell-user cloudshell-user 4096 Jul 1 12:59 .. -rw-r--r--. 1 cloudshell-user cloudshell-user 1902 Jul 1 12:59 manifest.yml $ - manifestファイルを確認します。CPU 256(0.25 vCPU)、memory 512 MiBで1タスクが確保されるようです
$ cat copilot/demo-svc/manifest.yml # The manifest for the "demo-svc" service. # Read the full specification for the "Load Balanced Web Service" type at: # https://aws.github.io/copilot-cli/docs/manifest/lb-web-service/ # Your service name will be used in naming your resources like log groups, ECS services, etc. name: demo-svc type: Load Balanced Web Service # Distribute traffic to your service. http: # Requests to this path will be forwarded to your service. # To match all requests you can use the "/" path. path: '/' # You can specify a custom health check path. The default is "/". # healthcheck: '/' # Configuration for your containers and service. image: location: nginx # Port exposed through your container to route traffic to it. port: 80 cpu: 256 # Number of CPU units for the task. memory: 512 # Amount of memory in MiB used by the task. count: 1 # Number of tasks that should be running in your service. exec: true # Enable running commands in your container. network: connect: true # Enable Service Connect for intra-environment traffic between services. # storage: # readonly_fs: true # Limit to read-only access to mounted root filesystems. # Optional fields for more advanced use-cases. # #variables: # Pass environment variables as key value pairs. # LOG_LEVEL: info #secrets: # Pass secrets from AWS Systems Manager (SSM) Parameter Store. # GITHUB_TOKEN: GITHUB_TOKEN # The key is the name of the environment variable, the value is the name of the SSM parameter. # You can override any of the values defined above by environment. #environments: # test: # count: 2 # Number of tasks to run for the "test" environment. # deployment: # The deployment strategy for the "test" environment. # rolling: 'recreate' # Stops existing tasks before new ones are started for faster deployments.[cloudshell-user@ip-10-130-21-81 ~]$ $
Environmentの作成
env initを基に試します。
- Service実行用に新しいEnvironmentを作成する
- 質問に答えると、CLIはVPC、ALB、ECS ClusterなどのServiceで共有される共通インフラを作成する
-
copilot env init を実行します
$ copilot env init --name $ENV --app $APP --profile default --default-config ✔ Wrote the manifest for environment test at copilot/environments/test/manifest.yml - Update regional resources with stack set "demo-app-infrastructure" [succeeded] [0.0s] - Update regional resources with stack set "demo-app-infrastructure" [succeeded] [47.9s] - Update resources in region "us-east-2" [create complete] [46.8s] - KMS key to encrypt pipeline artifacts between stages [create complete] [15.8s] - ECR container image repository for "demo-svc" [create complete] [0.0s] - S3 Bucket to store local artifacts [create in progress] [1.3s] ✔ Proposing infrastructure changes for the demo-app-test environment. - Creating the infrastructure for the demo-app-test environment. [create complete] [42.3s] - An IAM Role for AWS CloudFormation to manage resources [create complete] [19.4s] - An IAM Role to describe resources in your environment [create complete] [17.3s] ✔ Provisioned bootstrap resources for environment test in region us-east-2 under application demo-app. Recommended follow-up actions: - Update your manifest copilot/environments/test/manifest.yml to change the defaults. - Run `copilot env deploy --name test` to deploy your environment. $ -
あらたに、environmentディレクトリができていました
$ ls -laR copilot/ copilot/: total 20 drwxr-xr-x. 4 cloudshell-user cloudshell-user 4096 Jul 1 22:33 . drwxrwxrwx. 5 cloudshell-user cloudshell-user 4096 Jul 1 12:44 .. drwxr-xr-x. 2 cloudshell-user cloudshell-user 4096 Jul 1 12:59 demo-svc drwxr-xr-x. 3 cloudshell-user cloudshell-user 4096 Jul 1 22:33 environments -rw-r--r--. 1 cloudshell-user cloudshell-user 22 Jul 1 12:44 .workspace copilot/demo-svc: total 12 drwxr-xr-x. 2 cloudshell-user cloudshell-user 4096 Jul 1 12:59 . drwxr-xr-x. 4 cloudshell-user cloudshell-user 4096 Jul 1 22:33 .. -rw-r--r--. 1 cloudshell-user cloudshell-user 1902 Jul 1 12:59 manifest.yml copilot/environments: total 12 drwxr-xr-x. 3 cloudshell-user cloudshell-user 4096 Jul 1 22:33 . drwxr-xr-x. 4 cloudshell-user cloudshell-user 4096 Jul 1 22:33 .. drwxr-xr-x. 2 cloudshell-user cloudshell-user 4096 Jul 1 22:33 test copilot/environments/test: total 12 drwxr-xr-x. 2 cloudshell-user cloudshell-user 4096 Jul 1 22:33 . drwxr-xr-x. 3 cloudshell-user cloudshell-user 4096 Jul 1 22:33 .. -rw-r--r--. 1 cloudshell-user cloudshell-user 592 Jul 1 22:33 manifest.yml $ -
environment/manifest.ymlを確認します
$ cat copilot/environments/test/manifest.yml # The manifest for the "test" environment. # Read the full specification for the "Environment" type at: # https://aws.github.io/copilot-cli/docs/manifest/environment/ # Your environment name will be used in naming your resources like VPC, cluster, etc. name: test type: Environment # Import your own VPC and subnets or configure how they should be created. # network: # vpc: # id: # Configure the load balancers in your environment, once created. # http: # public: # private: # Configure observability for your environment resources. observability: container_insights: false $
インフラのデプロイ
Envrionmentインフラをデプロイします。
env deployを基に試します
- copilot env deployを実行します
$ copilot env deploy --name $ENV ✔ Proposing infrastructure changes for the demo-app-test environment. - Creating the infrastructure for the demo-app-test environment. [update complete] [65.8s] - An ECS cluster to group your services [create complete] [2.9s] - A security group to allow your containers to talk to each other [create complete] [0.0s] - An Internet Gateway to connect to the public internet [create complete] [16.1s] - A resource policy to allow AWS services to create log streams for your workloads. [create complete] [3.5s] - Private subnet 1 for resources with no internet access [create complete] [1.7s] - Private subnet 2 for resources with no internet access [create complete] [1.7s] - A custom route table that directs network traffic for the public subnets [create complete] [9.0s] - Public subnet 1 for resources that can access the internet [create complete] [1.7s] - Public subnet 2 for resources that can access the internet [create complete] [4.5s] - A private DNS namespace for discovering services within the environment [create complete] [43.2s] - A Virtual Private Cloud to control networking of your AWS resources [create complete] [11.6s] ✔ Successfully deployed environment test $
環境の確認
VPC
ECS
ALB
サービスのデプロイ
svc deployを基に試します。
- copilot svc deployを実行します。最後にURLが表示されるのでメモしておきます
$ copilot svc deploy --name $SVC --env $ENV ・・・・省略・・・・ ✔ Deployed service demo-svc. Recommended follow-up action: - Your service is accessible at http://XXXX.us-east-2.elb.amazonaws.com over the internet. $
環境の確認
ALB
ECR
ECS
-
ECSクラスタをクリックします
-
「タスク定義」をクリックします
アクセス確認
サービスの削除
svc deleteを基に試します。
- copilot svc deleteを実行します
$ copilot svc delete -n $SVC ・・・・省略 ・・・・ ✔ Deleted service demo-svc from application demo-app. Recommended follow-up action: - Run `copilot pipeline deploy` to update the corresponding pipeline if it exists. $
ALB
ECR
ECS
考察
今回、はじめて Copilot CLIを試してみました。すぐにECSを構築でき、簡単な動作検証などに使用できそうです。
今後、活用していきたいと思います。
参考












