背景
CloudFrontを通じてS3の静的ウェブサイトを配信し、公開する手法をよく見かけますが、しっかりとしたウェブサービスを作る場合、API Gatewayをオリジンとして指定し、APIをCloudFrontで配信することも少なくないでしょう。
しかし、設定やポリシーでアクセス制限ができるS3と違って今現在API GatewayへのアクセスをCloudFrontからのみに絞ることはできません。
本文はある程度それを実現できる回避策を紹介し、そしてそれに基づいたより強固の対策も併せて紹介いたします。
結論
CloudFrontのカスタムヘッダーとAPI Gatewayのポリシー設定を通じて、実践上CloudFrontからのリクエストのみ受け付けるAPI Gatewayを作れます。さらにセキュリティ性を高めたい場合、自動的にヘッダーを変更するプログラムもご活用ください!
コードはこちら:https://github.com/zhang-hang-valuesccg/example-cloudfront-apigateway-integration
全体設計
使用環境:
- CDK: 2.162.0
- Typescript: 5.6.2
事前準備
CDKの設定を済ませた上、CDKプロジェクトを用意します:
mkdir example-cloudfront-apigateway-integration
cd example-cloudfront-apigateway-integration
cdk init -l typescript
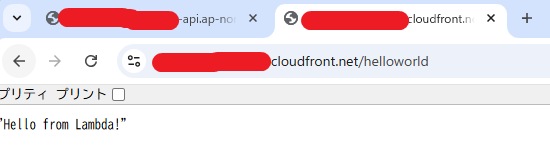
デモ用のAPIをLambda関数で用意します(ただのHello world):
import { Handler } from "aws-lambda";
export const handler: Handler = async (event) => {
const response = {
statusCode: 200,
body: JSON.stringify("Hello from Lambda!"),
};
return response;
};
上記関数を./lambdaフォルダに置きますと、プロジェクトがこんな感じになります:

必要のリソースをCDKで作ります:
// ...import everything
export class ExampleCloudfrontApigatewayIntegrationStack extends cdk.Stack {
constructor(scope: Construct, id: string, props?: cdk.StackProps) {
super(scope, id, props);
const helloworldFn = new NodejsFunction(this, "example-helloworld-fn", {
entry: "lambda/index.ts",
runtime: Runtime.NODEJS_20_X,
});
const apiPolicy = new PolicyDocument({
statements: [
new PolicyStatement({
actions: ["execute-api:Invoke"],
effect: Effect.ALLOW,
principals: [new AnyPrincipal()],
resources: [`execute-api:/*/*/*`],
}),
],
});
const api = new RestApi(this, "example-restapi", {
policy: apiPolicy,
deployOptions: {
stageName: "api",
},
});
const apiHelloworld = api.root.addResource("helloworld");
apiHelloworld.addMethod("GET", new LambdaIntegration(helloworldFn));
new Distribution(this, "example-distribution", {
defaultBehavior: {
origin: new RestApiOrigin(api),
},
});
}
}
デモ用のLambda関数をGETメソッドとしてAPI Gatewayに追加し、CloudFrontのオリジンとして指定します。アクセスできるように、API Gatewayのポリシーでアクセル権限を全開放します。
デプロイすると、CloudFrontとAPI Gateway両方のURLから関数を実行できてしまいます。
基礎編
上記のように、CloudFrontとAPI Gatewayをうまく繋げましたが、両方のURLからAPIを叩ける仕様になっていて、セキュリティ要件に満たない場合があります。
API Gateway側のURLへのアクセスをブロックするために、CloudFrontのカスタムヘッダーとAPI Gatewayのポリシー設定を活用します。
さっきのスタックに対して、以下の変更を行います:
// ...import everything
export class ExampleCloudfrontApigatewayIntegrationStack extends cdk.Stack {
constructor(scope: Construct, id: string, props?: cdk.StackProps) {
super(scope, id, props);
+ const referer = "super_complex_random_string";
const helloworldFn = new NodejsFunction(this, "example-helloworld-fn", {
entry: "lambda/index.ts",
runtime: Runtime.NODEJS_20_X,
});
const apiPolicy = new PolicyDocument({
statements: [
new PolicyStatement({
actions: ["execute-api:Invoke"],
effect: Effect.ALLOW,
principals: [new AnyPrincipal()],
resources: [`execute-api:/*/*/*`],
}),
+ new PolicyStatement({
+ actions: ["execute-api:Invoke"],
+ effect: Effect.DENY,
+ principals: [new AnyPrincipal()],
+ resources: [`execute-api:/*/*/*`],
+ conditions: {
+ StringNotEquals: {
+ "aws:Referer": referer,
+ },
+ },
+ }),
],
});
const api = new RestApi(this, "example-restapi", {
policy: apiPolicy,
deployOptions: {
stageName: "api",
},
});
const apiHelloworld = api.root.addResource("helloworld");
apiHelloworld.addMethod("GET", new LambdaIntegration(helloworldFn));
new Distribution(this, "example-distribution", {
defaultBehavior: {
- origin: new RestApiOrigin(api),
+ origin: new RestApiOrigin(api, {
+ customHeaders: {
+ Referer: referer,
+ },
+ }),
},
});
}
}
まず、refererという文字列を用意します。実際の運用では、悪意ある第三者に推測されにくい、複雑なランダム文字列を使います。
そして、API Gatewayのポリシーに「Refererヘッダーが上記のreferer文字列と同じの場合のみリクエストを通す」ステートメントを追加します。
最後に、DistributionのAPI GatewayオリジンにRefererヘッダーを付与します。
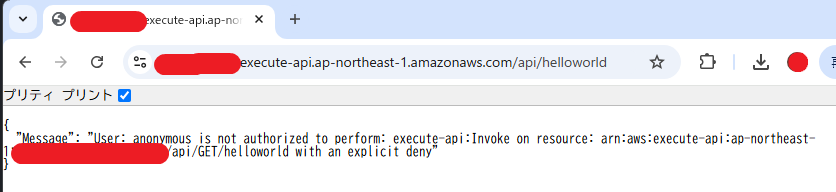
つまり、CloudFrontを通すリクエストのみに正しいRefererヘッダーが付与され、API Gatewayを通過できます。こうして、API Gatewayへの不正アクセスがポリシーにブロックされます。
API GatewayのURLからAPIをアクセスしようとすると、以下のようにできなくなりました。
応用篇
もちろん、上記の対策は完璧じゃありません。Refererヘッダーに複雑なランダム文字列を配置したとしても、時間を経てばなにかしらの形式で漏えいが発生するかもしれません。できれば、定期的にRefererヘッダーをローテーションするなどの徹底的な対策が望ましい。
応用編として、CloudFrontとAPI GatewayのRefererヘッダー設定を同時に変更できるLambda関数を作ってみます。
以下のようにLambda関数を追加し、CloudFrontとAPI Gatewayの変更権限を与えます。
// inside the stack
+ const refererUpdaterFn = new NodejsFunction(
+ this,
+ "example-referer-updater",
+ {
+ entry: "lambda/referer-updater.ts",
+ runtime: Runtime.NODEJS_20_X,
+ timeout: cdk.Duration.seconds(10),
+ environment: {
+ REST_API_ID: api.restApiId,
+ DISTRIBUTION_ID: distribution.distributionId,
+ ACCOUNT: props?.env?.account || "",
+ REGION: props?.env?.region || "",
+ },
+ }
+ );
+ distribution.grant(refererUpdaterFn, "cloudfront:*");
+ refererUpdaterFn.addToRolePolicy(
+ new PolicyStatement({
+ actions: [
+ "apigateway:PATCH",
+ "apigateway:POST",
+ "apigateway:UpdateRestApiPolicy",
+ ],
+ effect: Effect.ALLOW,
+ resources: ["arn:aws:apigateway:*::/*"],
+ })
+ );
Lambda関数がちょっと長いので本文では割愛しますが、Githubに載せますので興味ある方はこちらをチェックしてください。
簡単に説明しますと、CloudFrontのConfigを読み込み、カスタムヘッダー部分のみ書き換えて、CloudFrontクライアントのUpdateDistributionCommandでConfigをアップデートします。加えて、API Gatewayのポリシーに同様な変更を施し、API GatewayクライアントのUpdateRestApiCommandでポリシーをアップデートします。注意すべきなのは、ポリシー変更後、CreateDeploymentCommandでAPI Gatewayを再デプロイしないと新しいポリシーが反映されません。
Refereヘッダーに使う文字列ですが、cryptoかuuidなどのランダム文字列を生成できるライブラリを使うといいなと思います。
さらに、定期的にRefererヘッダーを書き換えたい場合、EventBridgeを使います。以下の設定で、毎週金曜日24時(JST)で自動的にRefererヘッダーを書き換えます:
+ new Rule(this, "example-auto-invoke", {
+ schedule: Schedule.cron({
+ hour: "15",
+ minute: "0",
+ weekDay: "FRI",
+ }),
+ targets: [
+ new LambdaFunction(refererUpdaterFn, {
+ retryAttempts: 0,
+ }),
+ ],
+ });
CloudFrontのデプロイは通常遅いますが、カスタムヘッダー設定は思ったよりはやく反映されます(原理は不明だが)のでダウンタイムの心配もそこまでしなくてよいかと。
おわりに
CloudFrontからのリクエストのみ受け付けるAPI Gatewayの作り方を紹介いたしましたが、いかがでしょうか?
こういった手法のメリットとして、以下の点が挙げられます:
- CloudFrontでCloudFront FunctionやLambda@Edgeを使って簡単な認証を配置しても、API Gateway側で叩かれる心配がなくなる
- ポリシーベースの対策であるため、費用も抑えられる(IAMは無料だから)
- 管理が楽になる。Refererヘッダーの設定と自動更新までCDKに取り込まれ、マネコンぽちぽちする必要は一切ない
もちろん、これで完璧!とは言えない点もあります:
- インフラの二重管理:応用編の中に、CDKとSDK(Referer update Lambdaの中に)両方からインフラの管理や変更を行っており、インフラの改修やメンテナンスが若干ややこしくなる
- どんなに頑張っても、Refererヘッダーの漏えいの可能性をゼロにできない。あくまで回避策で、そういった権限制限をAWS側が提供するのは一番なのだ
special thanks: @miko-t