目次と前回の記事
これまでに作成したモジュール
以下のリンクから、これまでに作成したモジュールを見ることができます。
| リンク | 説明 |
|---|---|
| marubatsu.py | Marubatsu、Marubatsu_GUI クラスの定義 |
| ai.py | AI に関する関数 |
| util.py | ユーティリティ関数の定義。現在は gui_play のみ定義されている |
| tree.py | ゲーム木に関する Node、Mbtree クラスの定義 |
| gui.py | GUI に関する処理を行う基底クラスとなる GUI クラスの定義 |
ルールベースの AI の一覧
ルールベースの AI の一覧については、下記の記事を参照して下さい。
ゲーム木を視覚化する GUI の改良
前回の記事で作成した、ゲーム木を視覚化する GUI を実装した Mbtre_GUI クラスには、いくつかの問題点があるので、今回の記事では Mbtree_GUI を改良することにします。
中心となるノードの強調表示
Mbtree_GUI は、下図のような部分木を描画しますが、下図では、どのノードを中心とした部分木を描画しているかがわかりづらい という問題があります。

そこで、中心となるノード を何らかの方法で 強調して描画 することにします。ノードの強調の方法には、下記のような様々な方法が考えられます。
- 色のついた外枠を描画する
- 枠線やマークを太くする
- 背景色を変える
本記事では、中心となるノードの 外枠を赤色で描画する 方法を採用しますが、上記の方法に限らず、もっと良い強調の方法を思いついた人は実装してみて下さい。
draw_board の修正
ゲーム盤 は、Marubatsu_GUI クラスの draw_board メソッドで描画するので、draw_board を ゲーム盤の外枠を描画できるように改良する という方法が考えられます。そこで、下記のように draw_board を改良することにします。
-
draw_boardに、Trueが代入されていた場合に赤枠を描画して強調するemphasize1 という仮引数を追加する - 互換性を考慮して、
emphasizeはデフォルト値をFalseとするデフォルト引数にする
ゲーム盤の枠は、正方形の形をしているので、以前の記事で説明した patches モジュールで定義された、長方形を表す Rectangle という Artist を作成する関数を利用します。
また、draw_board では、下記のプログラムのように、決着がついた ゲーム盤の背景色を変更するため に、Rectangle を使っています。
rect = patches.Rectangle(xy=(dx, dy), width=mb.BOARD_SIZE,
height=mb.BOARD_SIZE, fc=bgcolor)
ゲーム盤の外枠は、上記の Rectangle と 同じ場所と大きさで、枠だけを描画すればよい ので、下記のプログラムのように、赤色の枠線を表す ec="red"、塗りつぶさないことを表す fill=False、枠線の太さを表す lw=lw を記述することで作成することができます。
なお、外枠の太さは、内枠やマークの線の太さと同じ lw にしました。
rect = patches.Rectangle(xy=(dx, dy), width=mb.BOARD_SIZE,
height=mb.BOARD_SIZE, ec="red", fill=False, lw=lw)
下記は、draw_board をそのように修正したプログラムです。なお、外枠を描画する処理 は、ゲーム盤の背景色を変更する処理の後 で行わないと、描画した 外枠の一部が背景色の長方形で上書きされてしまう 点に注意する必要があります。
-
5 行目:デフォルト値が
Falseのデフォルト引数emphasizeを追加する -
10 ~ 13 行目:
emphasizeがTrueの場合に、赤色でゲーム盤の外枠を描画する
1 from marubatsu import Marubatsu, Marubatsu_GUI
2 import matplotlib.patches as patches
3
4 @staticmethod
5 def draw_board(ax, mb, show_result=False, emphasize=False, dx=0, dy=0, lw=2):
6 # 結果によってゲーム盤の背景色を変更する
7 if show_result:
元と同じなので省略
8
9 # emphasize が True の場合は赤色の外枠を描画する
10 if emphasize:
11 frame = patches.Rectangle(xy=(dx, dy), width=mb.BOARD_SIZE,
12 height=mb.BOARD_SIZE, ec="red", fill=False, lw=lw)
13 ax.add_patch(frame)
元と同じなので省略
14
15 Marubatsu_GUI.draw_board = draw_board
行番号のないプログラム
from marubatsu import Marubatsu, Marubatsu_GUI
import matplotlib.patches as patches
@staticmethod
def draw_board(ax, mb, show_result=False, emphasize=False, dx=0, dy=0, lw=2):
# 結果によってゲーム盤の背景色を変更する
if show_result:
if mb.status == Marubatsu.PLAYING:
bgcolor = "white"
elif mb.status == Marubatsu.CIRCLE:
bgcolor = "lightcyan"
elif mb.status == Marubatsu.CROSS:
bgcolor = "lavenderblush"
else:
bgcolor = "lightyellow"
rect = patches.Rectangle(xy=(dx, dy), width=mb.BOARD_SIZE,
height=mb.BOARD_SIZE, fc=bgcolor)
ax.add_patch(rect)
# emphasize が True の場合は赤色の外枠を描画する
if emphasize:
frame = patches.Rectangle(xy=(dx, dy), width=mb.BOARD_SIZE,
height=mb.BOARD_SIZE, ec="red", fill=False, lw=lw)
ax.add_patch(frame)
# ゲーム盤の枠を描画する
for i in range(1, mb.BOARD_SIZE):
ax.plot([dx, dx + mb.BOARD_SIZE], [dy + i, dy + i], c="k", lw=lw) # 横方向の枠線
ax.plot([dx + i, dx + i], [dy, dy + mb.BOARD_SIZE], c="k", lw=lw) # 縦方向の枠線
# ゲーム盤のマークを描画する
for y in range(mb.BOARD_SIZE):
for x in range(mb.BOARD_SIZE):
color = "red" if (x, y) == mb.last_move else "black"
Marubatsu_GUI.draw_mark(ax, dx + x, dy + y, mb.board[x][y], color, lw=lw)
Marubatsu_GUI.draw_board = draw_board
修正箇所
from marubatsu import Marubatsu, Marubatsu_GUI
import matplotlib.patches as patches
@staticmethod
-def draw_board(ax, mb, show_result=False, dx=0, dy=0, lw=2):
+def draw_board(ax, mb, show_result=False, emphasize=False, dx=0, dy=0, lw=2):
# 結果によってゲーム盤の背景色を変更する
if show_result:
元と同じなので省略
+ # emphasize が True の場合は赤色の外枠を描画する
+ if emphasize:
+ frame = patches.Rectangle(xy=(dx, dy), width=mb.BOARD_SIZE,
+ height=mb.BOARD_SIZE, ec="red", fill=False, lw=lw)
+ ax.add_patch(frame)
元と同じなので省略
Marubatsu_GUI.draw_board = draw_board
draw_node の修正
draw_board は、Node クラスの draw_node メソッド内で呼び出される ので、draw_node に対しても同様に、下記のプログラムのように仮引数 emphasize を追加し、emphasize に True が代入されていた場合にノードを強調して描画するように修正する必要があります。
-
4 行目:デフォルト値が
Falseのデフォルト引数emphasizeを追加する -
7 行目:
emphasize=emphasizeを記述してdraw_boardを呼び出すように修正する
1 from tree import Node
2 import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
3
4 def draw_node(self, ax=None, maxdepth=None, emphasize=False, size=0.25, lw=0.8, dx=0, dy=0):
元と同じなので省略
5 # 自分自身のノードを真ん中の位置になるように (dx, dy) からずらして描画する
6 y = dy + (self.height - 3) / 2
7 Marubatsu_GUI.draw_board(ax, self.mb, show_result=True, emphasize=emphasize, lw=lw, dx=dx, dy=y)
元と同じなので省略
8
9 Node.draw_node = draw_node
行番号のないプログラム
from tree import Node
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
def draw_node(self, ax=None, maxdepth=None, emphasize=False, size=0.25, lw=0.8, dx=0, dy=0):
width = 8
if ax is None:
height = len(self.children) * 4
fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(width * size, height * size))
ax.set_xlim(0, width)
ax.set_ylim(0, height)
ax.invert_yaxis()
ax.axis("off")
for childnode in self.children:
childnode.height = 4
self.height = height
# 自分自身のノードを真ん中の位置になるように (dx, dy) からずらして描画する
y = dy + (self.height - 3) / 2
Marubatsu_GUI.draw_board(ax, self.mb, show_result=True, emphasize=emphasize, lw=lw, dx=dx, dy=y)
# 子ノードが存在する場合に、エッジの線と子ノードを描画する
if len(self.children) > 0:
if maxdepth != self.depth:
plt.plot([dx + 3.5, dx + 4], [y + 1.5, y + 1.5], c="k", lw=lw)
prevy = None
for childnode in self.children:
childnodey = dy + (childnode.height - 3) / 2
if maxdepth is None:
Marubatsu_GUI.draw_board(ax, childnode.mb, show_result=True, dx=dx+5, dy=childnodey, lw=lw)
edgey = childnodey + 1.5
plt.plot([dx + 4 , dx + 4.5], [edgey, edgey], c="k", lw=lw)
if prevy is not None:
plt.plot([dx + 4 , dx + 4], [prevy, edgey], c="k", lw=lw)
prevy = edgey
dy += childnode.height
else:
plt.plot([dx + 3.5, dx + 4.5], [y + 1.5, y + 1.5], c="k", lw=lw)
Node.draw_node = draw_node
修正箇所
from tree import Node
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
-def draw_node(self, ax=None, maxdepth=None, size=0.25, lw=0.8, dx=0, dy=0):
+def draw_node(self, ax=None, maxdepth=None, emphasize=False, size=0.25, lw=0.8, dx=0, dy=0):
元と同じなので省略
# 自分自身のノードを真ん中の位置になるように (dx, dy) からずらして描画する
y = dy + (self.height - 3) / 2
- Marubatsu_GUI.draw_board(ax, self.mb, show_result=True, lw=lw, dx=dx, dy=y)
+ Marubatsu_GUI.draw_board(ax, self.mb, show_result=True, emphasize=emphasize, lw=lw, dx=dx, dy=y)
元と同じなので省略
Node.draw_node = draw_node
draw_subtree の修正
最後に、draw_node を呼び出す draw_subtree を下記のプログラムのように修正します。
-
10、11 行目:強調表示するのは
centernodeだけなので、draw_nodeを呼び出すnodeがcenternodeの場合のみemphasizeをTrueにし、emphasize=emphasizeを実引数に記述してdraw_nodeを呼び出すように修正する
1 from tree import Mbtree
2
3 def draw_subtree(self, centernode=None, ax=None, size=0.25, lw=0.8, maxdepth=2):
元と同じなので省略
4 for node in nodelist:
5 if node is None:
6 dy += 4
7 childnodelist.append(None)
8 else:
9 dx = 5 * node.depth
10 emphasize = node is centernode
11 node.draw_node(ax=ax, maxdepth=maxdepth, emphasize=emphasize, size=size, lw=lw, dx=dx, dy=dy)
元と同じなので省略
12
13 Mbtree.draw_subtree = draw_subtree
行番号のないプログラム
from tree import Mbtree
def draw_subtree(self, centernode=None, ax=None, size=0.25, lw=0.8, maxdepth=2):
if centernode is None:
centernode = self.root
self.calc_node_height(maxdepth)
width = 5 * (maxdepth + 1)
height = centernode.height
parent = centernode.parent
if parent is not None:
height += (len(parent.children) - 1) * 4
parent.height = height
if ax is None:
fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(width * size, height * size))
ax.set_xlim(0, width)
ax.set_ylim(0, height)
ax.invert_yaxis()
ax.axis("off")
nodelist = [centernode]
depth = centernode.depth
while len(nodelist) > 0 and depth <= maxdepth:
dy = 0
if parent is not None:
dy = parent.children.index(centernode) * 4
childnodelist = []
for node in nodelist:
if node is None:
dy += 4
childnodelist.append(None)
else:
dx = 5 * node.depth
emphasize = node is centernode
node.draw_node(ax=ax, maxdepth=maxdepth, emphasize=emphasize, size=size, lw=lw, dx=dx, dy=dy)
dy += node.height
if len(node.children) > 0:
childnodelist += node.children
else:
childnodelist.append(None)
depth += 1
nodelist = childnodelist
if parent is not None:
dy = 0
for sibling in parent.children:
if sibling is not centernode:
sibling.height = 4
dx = 5 * sibling.depth
sibling.draw_node(ax, maxdepth=sibling.depth, size=size, lw=lw, dx=dx, dy=dy)
dy += sibling.height
dx = 5 * parent.depth
parent.draw_node(ax, maxdepth=maxdepth, size=size, lw=lw, dx=dx, dy=0)
node = parent
while node.parent is not None:
node = node.parent
node.height = height
dx = 5 * node.depth
node.draw_node(ax, maxdepth=node.depth, size=size, lw=lw, dx=dx, dy=0)
Mbtree.draw_subtree = draw_subtree
修正箇所
from tree import Mbtree
def draw_subtree(self, centernode=None, ax=None, size=0.25, lw=0.8, maxdepth=2):
元と同じなので省略
for node in nodelist:
if node is None:
dy += 4
childnodelist.append(None)
else:
dx = 5 * node.depth
+ emphasize = node is centernode
- node.draw_node(ax=ax, maxdepth=maxdepth, size=size, lw=lw, dx=dx, dy=dy)
+ node.draw_node(ax=ax, maxdepth=maxdepth, emphasize=emphasize, size=size, lw=lw, dx=dx, dy=dy)
元と同じなので省略
Mbtree.draw_subtree = draw_subtree
上記の修正後に、下記のプログラムを実行すると、実行結果のように、中心となるノードのゲーム盤に赤い外枠が描画されるようになります。ボタンを操作してどのように描画が変化するかを実際に確認してみて下さい。
from tree import Mbtree_GUI
mbtree = Mbtree()
mbtree_gui = Mbtree_GUI(mbtree)
実行結果(下記は、深さが 0 と 7 のノードが中心となる場合です)
深さが 0 のノードが中心となる場合の表示の問題とその原因
気がついていない人が多いかもしれませんが、ノードの強調表示には一つ問題があります。それは、下図のように、深さが 0 のノードが中心となる場合は、左側の外枠 が左下図のように、他の枠と比べて 細く描画されてしまう というものです。他の深さのノードの場合は、右下図のようにそのような現象はおきません。
この問題は、深さが 0 のノードの 左側の外枠の半分 が、Axes の描画範囲の外にある事 が原因です。わかりづらいと思いますので、別の具体例を挙げて説明します。
下記は、Axes の表示範囲 の x、y 座標をそれぞれ 0 ~ 1.5 に設定 し、下記のような 左下の頂点が (0, 0) で 幅と高さが 1 の 正方形の図形の外枠を描画 するプログラムです。
- 太さが 20 の赤色の外枠を描画する
- その後に、太さが 1 の黒色の外枠を描画する
このプログラムを実行すると、実行結果のように、左と下の外枠の太さが、右と上の外枠と比べて 半分の太さで描画される ように見えます。
fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(5, 5))
ax.set_xlim(0, 1.5)
ax.set_ylim(0, 1.5)
frame1 = patches.Rectangle(xy=(0, 0), width=1, height=1, ec="red", fill=False, lw=20)
ax.add_patch(frame1)
frame2 = patches.Rectangle(xy=(0, 0), width=1, height=1, ec="black", fill=False, lw=1)
ax.add_patch(frame2)
実行結果
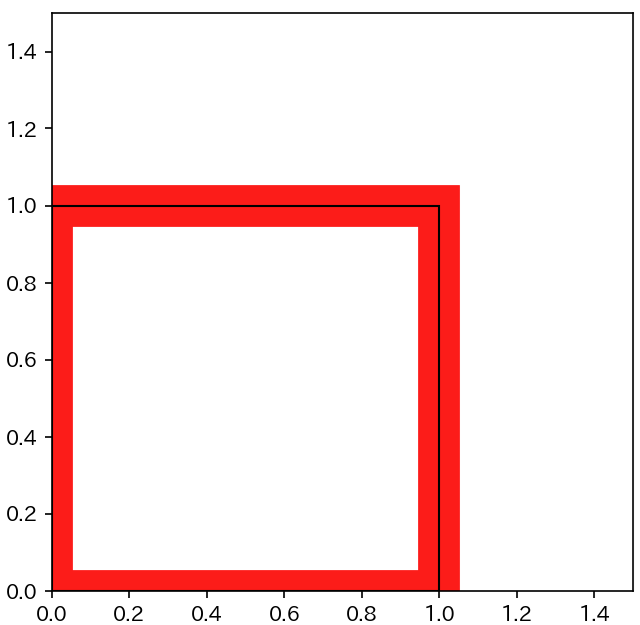
matplotlib では、図形の 外枠の枠線 は、その図形の 辺を中心とする線で描画 されるます。そのため、下図のように、外枠の枠線が太くなればなるほど、枠線は 図形の内側と外側の両方にはみ出て描画される ようになります。

上記のプログラムでは、正方形の 左と下の辺 が Axes の表示範囲の左と下にぴったりと重なるように描画 しました。そのため、枠の半分が Axes の表示範囲の外にはみ出てしまい、左と下の枠の 太さが半分になってしまいます。
深さが 0 のノードのゲーム盤は Axes の x 座標が 0 ~ 3 の範囲に描画 しました。また、前回の記事で、Mbtree_GUI では Axes の x 座標の表示範囲を 0 ~ 50 の範囲に設定 したので、深さ 0 のノードのゲーム盤は、Axes の左端にぴったりくっつくように描画 されます。これが、深さが 0 のゲーム盤の左の外枠が細く表示される原因です。
なお、実際に様々なノードを中心とする部分木を描画してみるとわかると思いますが、ゲーム盤が Axes の表示範囲の上下の端にぴったりとくっつくように描画されることはないので、ゲーム盤の上と下の外枠の太さが半分になることはありません。
ゲーム盤が Axes の表示範囲の上下の端にぴったりとくっつくように描画されない理由は、以前の記事で、ゲーム木をバランス良く描画するため、ノードを子ノードの一覧の真ん中に表示するようにしたからです。ノードの高さが最低でも 4 であるのに対し、ゲーム盤の高さは 3 なので、ゲーム盤は最低でも Axes の y 座標の表示範囲から (4 - 3) / 2 = 0.5 だけずれた位置に描画されます。
深さが 0 のノードが中心となる場合の表示の問題の修正
この問題は 図形の外枠を描画する際 に、Axes の表示範囲が図形の辺とぴったりと重ならないようにする ことで解決することができます。具体的には、Axes の x 座標の表示範囲の最小値を、例えば -1 などの、0 未満の数に変更します。
ただし、Axes の x 座標の表示範囲を 0 ~ 50 から -1 ~ 50 に変更してしまうと、Figure のサイズをそれに合わせて変更しなければ、表示される部分木が 歪んで表示されてしまうようになる 点に注意が必要です。わかりづらいかもしれないので具体例を挙げます。
下記のプログラムは、同じ大きさの 2 つの Figure に、同じ大きさの正方形を描画 する処理を行うプログラムです。ただし、片方は Axes の x 座標の表示範囲 が 0 ~ 1 で、もう片方は 0 ~ 2 に設定しています。実行結果からわかるように、同じ大きさの図形を描画 しているにも関わらず、表示される 図形の形状が異なって表示 されます。
fig1, ax1 = plt.subplots(figsize=(3, 3))
ax1.set_xlim(0, 1) # こちらは x 座標の範囲を 0 ~ 1 に設定する
ax1.set_ylim(0, 1)
frame1 = patches.Rectangle(xy=(0.25, 0.25), width=0.5, height=0.5, ec="red", fill=False, lw=1)
ax1.add_patch(frame1)
fig2, ax2 = plt.subplots(figsize=(3, 3))
ax2.set_xlim(0, 2) # こちらは x 座標の範囲を 0 ~ 2 に設定する
ax2.set_ylim(0, 1)
frame2 = patches.Rectangle(xy=(0.25, 0.25), width=0.5, height=0.5, ec="red", fill=False, lw=1)
ax2.add_patch(frame2)
実行結果
図形を正しい大きさで表示するためには、Axes の x 座標と y 座標の表示範囲の幅 と、Figure の大きさをあわせる 必要があります。あわせる方法には Axes の表示範囲をあわせる方法と、Figure の大きさをあわせる方法があります。本記事では Axes の表示範囲をあわせる方法を採用し、Figure の大きさを合わせる方法は、この後のノードで説明します。
Axes の表示範囲を合わせる場合は、Axes の表示範囲の幅を変えないようにする 必要があります。Mbtree_GUI の Axes の場合は、x 座標の表示範囲を 0 ~ 50 から -1 ~ 49 に設定する必要があります。ただし、そのように表示範囲を変更する場合は、右端のノードの表示 が、Axes の表示範囲の外に出ないことを確認する 必要があります。
右端に表示される 深さが 9 のノードのゲーム盤は、Axes の x 座標が 45 ~ 48 の範囲に描画 されます。また、深さ 9 のノードには 子ノードは存在しない ので、ゲーム盤の右にエッジを表す線を描画する必要はありません。そのため、Axes の x 座標の表示範囲を -1 ~ 49 に変更しても問題がないことがわかります。ピンとこない人は図を書いてみると良いでしょう。
Axes の y 座標の表示範囲は、update_gui で設定するので、下記のプログラムのように update_gui を修正します。
- 3 行目:Axes の x 座標の表示範囲を左に 1 だけ左にずらすように修正する
1 def update_gui(self):
2 self.ax.clear()
3 self.ax.set_xlim(-1, self.width - 1)
4 self.ax.set_ylim(0, self.height)
5 self.ax.invert_yaxis()
6 self.ax.axis("off")
7
8 maxdepth = min(self.centernode.depth + 1, 9)
9 self.mbtree.draw_subtree(self.centernode, ax=self.ax, maxdepth=maxdepth)
10
11 Mbtree_GUI.update_gui = update_gui
行番号のないプログラム
def update_gui(self):
self.ax.clear()
self.ax.set_xlim(-1, self.width - 1)
self.ax.set_ylim(0, self.height)
self.ax.invert_yaxis()
self.ax.axis("off")
maxdepth = min(self.centernode.depth + 1, 9)
self.mbtree.draw_subtree(self.centernode, ax=self.ax, maxdepth=maxdepth)
Mbtree_GUI.update_gui = update_gui
修正箇所
def update_gui(self):
self.ax.clear()
- self.ax.set_xlim(0, self.width)
+ self.ax.set_xlim(-1, self.width - 1)
self.ax.set_ylim(0, self.height)
self.ax.invert_yaxis()
self.ax.axis("off")
maxdepth = min(self.centernode.depth + 1, 9)
self.mbtree.draw_subtree(self.centernode, ax=self.ax, maxdepth=maxdepth)
Mbtree_GUI.update_gui = update_gui
上記の修正後に、下記のプログラムを実行すると、実行結果のように、深さが 0 のノードが中心となる場合の外枠の表示の問題が修正されていることが確認できます。
mbtree_gui = Mbtree_GUI(mbtree)
実行結果

また、Axes の x 座標の範囲を左にずらしたので、深さが 9 のノードを中心とした場合の表示がおかしくなっていないかを確認する必要があり、下図のように表示がおかしくならないことが確認できます。
本記事では採用しませんが、Figure の幅をあわせる方法を説明します。
まず、Axes の x 座標の表示範囲を -1 ~ 50 に変更するために、下記のプログラムのように update_gui を修正します。
- 3 行目:x 座標の表示範囲を -1 ~ 50 に修正する
1 def update_gui(self):
2 self.ax.clear()
3 self.ax.set_xlim(-1, self.width)
元と同じなので省略
4
5 Mbtree_GUI.update_gui = update_gui
行番号のないプログラム
def update_gui(self):
self.ax.clear()
self.ax.set_xlim(-1, self.width - 1)
self.ax.set_ylim(0, self.height)
self.ax.invert_yaxis()
self.ax.axis("off")
if self.centernode.depth <= 4:
maxdepth = self.centernode.depth + 1
elif self.centernode.depth == 5:
maxdepth = 7
else:
maxdepth = 9
self.mbtree.draw_subtree(self.centernode, ax=self.ax, maxdepth=maxdepth)
disabled = self.centernode.parent is None
self.set_button_status(self.left_button, disabled=disabled)
disabled = self.centernode.depth >= 6 or len(self.centernode.children) == 0
self.set_button_status(self.right_button, disabled=disabled)
disabled = self.centernode.parent is None or self.centernode.parent.children.index(self.centernode) == 0
self.set_button_status(self.up_button, disabled=disabled)
disabled = self.centernode.parent is None or self.centernode.parent.children[-1] is self.centernode
self.set_button_status(self.down_button, disabled=disabled)
Mbtree_GUI.update_gui = update_gui
修正箇所
def update_gui(self):
self.ax.clear()
- self.ax.set_xlim(0, self.width)
+ self.ax.set_xlim(-1, self.width)
元と同じなので省略
Mbtree_GUI.update_gui = update_gui
Axes の x 座標の表示範囲の幅が 50 から 51 に増えたので、それにあわせて Figure を作成する処理を行う create_widgets を下記のプログラムのように修正します。
-
3 行目:Figure の幅の計算式の
self.widthを(self.width + 1)に修正する
1 def create_widgets(self):
元と同じなので省略
2 with plt.ioff():
3 self.fig = plt.figure(figsize=[(self.width + 1) * self.size,
4 self.height * self.size])
5 self.ax = self.fig.add_axes([0, 0, 1, 1])
元と同じなので省略
6
7 Mbtree_GUI.create_widgets = create_widgets
行番号のないプログラム
def create_widgets(self):
self.left_button = self.create_button("←", 100)
self.up_button = self.create_button("↑", 100)
self.right_button = self.create_button("→", 100)
self.down_button = self.create_button("↓", 100)
with plt.ioff():
self.fig = plt.figure(figsize=[(self.width + 1) * self.size,
self.height * self.size])
self.ax = self.fig.add_axes([0, 0, 1, 1])
self.fig.canvas.toolbar_visible = False
self.fig.canvas.header_visible = False
self.fig.canvas.footer_visible = False
self.fig.canvas.resizable = False
Mbtree_GUI.create_widgets = create_widgets
修正箇所
def create_widgets(self):
元と同じなので省略
with plt.ioff():
- self.fig = plt.figure(figsize=[self.width * self.size,
- self.height * self.size])
+ self.fig = plt.figure(figsize=[(self.width + 1) * self.size,
+ self.height * self.size])
self.ax = self.fig.add_axes([0, 0, 1, 1])
元と同じなので省略
Mbtree_GUI.create_widgets = create_widgets
本記事が Figure の大きさをあわせる方法を採用しなかったのは、create_widgets の修正が必要になるからです。ただし、どちらの方法でも問題は修正できるので、どちらの修正方法を採用してかまいません。
先程の例では、Axes の x 座標の表示範囲を 0 ~ 1 から 0 ~ 2 に変更しました。この場合は、表示範囲の幅が 1 から 2 に 2 倍の変化が生じるので、Figure の大きさを変えないと、表示される図形の形が大きく変化してしまいます。
一方、Axes の x 座標の表示範囲を 0 ~ 50 から -1 ~ 50 の範囲に変更した場合は、表示範囲の幅は 50 から 51 になるため、全体の 5 % しか増えません。そのため、Figure の大きさを変更しなくても、表示の見た目がほとんど変わらないので、Figure の大きさを変更しないという方法も考えられます。
部分木の深さの改良
前回の記事では、部分木の高さが大きくなりすぎないようにする ために、部分木の深さ を中心となるノードの 子ノードまでの深さ にすることにしました。
確かにそうすることで部分木の高さを減らすことができましたが、できれば もっと深いノードまで部分木を表示したほうが、ゲーム木の 全体像を把握しやすく なります。
そこで、中心となるノードからの深さを増やした場合に、部分木の高さがいくつになるかを計算し、部分木の高さがあまり高くならない範囲のゲーム木の深さを調べる ことにします。
孫ノードまでの深さの部分木の高さの計算
まず、中心となるノードより 2 つ深い、孫ノードまでの部分木 の高さの最大値を計算します。下図は、前回の記事で子ノードまでの部分木の高さを計算する際に使った図です。
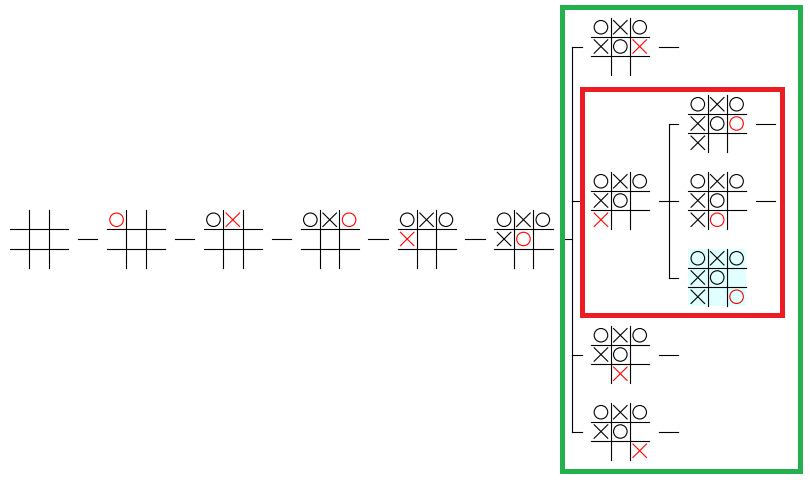
中心となるノードからの 部分木の深さが変化 した場合は、上図の 赤枠の高さは変化 しますが、緑枠の高さは変化しません。そこで、孫ノードまでの部分木 を描画する場合に、赤枠の中に最大でいくつゲーム盤が縦に表示されるかを計算することにします。
赤枠の部分に 最も多くのゲーム盤が縦に並ぶ のは、centernode の すべての子ノードが子ノードを持つ場合 です。例えば、centernode の子ノードが決着がついた局面であれば、そのノードには子ノードがないので、その分だけ縦に並ぶゲーム盤の数が少なくなります。
下図は、centernode のすべての子ノードに子ノードが存在する場合の部分木の一例で、下記のプログラムを実行することで表示することができます2。このプログラムでは、深さ 6 のノードを中心とし、深さ 8 の孫ノードまでを表示しています。
mbtree.draw_subtree(mbtree.nodelist_by_depth[6][7], maxdepth=8)
実行結果

上図の場合は、深さ 6 の孫ノードの数は「深さ 6 の子ノードの数 * 深さ 7 の子ノードの数」という式で計算することができます。深さ d の子ノードの数は 9 - d で計算できるので、中心となるノードの深さが d の場合は、深さ d の 孫ノードの数の最大値 は (9 - d) * (9 - (d + 1)) = (9 - d) * (8 - d) という式で計算できます。ただし、ゲーム木の深さは 9 までしかないので、深さ 8 の場合は 9 - 8 = 1、深さ 9 の場合は 1 になる点に注意が必要です。
前回の記事と同様に、緑枠の中に縦に並ぶゲーム盤の数の最大値は、赤枠の中の最大値 + 兄弟ノードの数 になるので、以下のようになります。
| d | 赤枠の最大値 | 兄弟ノードの数 | 最大値 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 9 * 8 = 72 | 0 | 72 |
| 1 ~ 7 | (9 - d) * (8 - d) | 9 - d | (9 - d) * (9 - d)3 |
| 8 | 1 | 9 - 8 = 1 | 2 |
| 9 | 1 | 9 - 9 = 0 | 1 |
0 から 9 までのそれぞれの深さの最大値を計算すると以下のようになります。表の 1 行目は、前回の記事で計算した centernode の子ノードまでの部分木の、2 行目は centernode の孫ノードまでの部分木の最大値を表します。
d |
0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 子ノードまでの部分木の最大値 | 9 | 16 | 14 | 12 | 10 | 8 | 6 | 4 | 2 | 1 |
| 孫ノードまでの部分木の最大値 | 72 | 64 | 49 | 36 | 25 | 16 | 9 | 4 | 2 | 1 |
上記の表から、centernode の 孫ノードまでの部分木を描画する場合 は、centernode の 深さが 5 以上の場合 の最大値は、子ノードまでの部分木の最大値である 16 以下 になることがわかります。従って、深さ 5 以上 のノードを中心とする部分木を描画する場合は、孫ノードまでの部分木を描画 しても、Axes の表示範囲内に収まる ことになります。
同様の方法で、centernode より 3 つ深い、ひ孫のノードまでの部分木 の高さの最大値を計算することにします。この場合は、赤い枠線の部分に縦に描画されるノードの最大値は、centernode の深さが d の場合は、先程と同様の考え方で (9 - d) * (8 - d) * (7 - d) になるので、それぞれの深さの最大値は下記の表のようになります。ただし、深さが 4 以下のノードの場合は、明らかに 16 を超えるので計算を省略します。
| d | 赤枠の最大値 | 兄弟ノードの数 | 最大値 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 5 | 4 * 3 * 2 = 24 | 9 - 5 = 4 | 28 |
| 6 | 3 * 2 * 1 = 6 | 9 - 6 = 3 | 9 |
| 7 | 2 * 1 = 2 | 9 - 7 = 2 | 4 |
| 8 | 1 | 9 - 8 = 1 | 2 |
| 9 | 1 | 9 - 9 = 0 | 1 |
下記は、0 から 9 までのそれぞれの深さの最大値の表に、ひ孫までの部分木の最大値を加えたものです。表から、centernode の ひ孫ノードまでの部分木を描画 する場合は、centernode の 深さが 6 以上の場合の最大値 は、子ノードまでの部分木の最大値である 16 以下になる ことがわかります。
d |
0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 子ノードまでの部分木の最大値 | 9 | 16 | 14 | 12 | 10 | 8 | 6 | 4 | 2 | 1 |
| 孫ノードまでの部分木の最大値 | 72 | 64 | 49 | 36 | 25 | 16 | 9 | 4 | 2 | 1 |
| ひ孫ノードまでの部分木の最大値 | 28 | 9 | 4 | 2 | 1 |
深さ 6 のひ孫ノードの深さ はゲーム木の深さの 最大値である 9 なので、上記から、以下の事がわかります。
-
centernodeの深さが 4 以下の場合は、子ノードまでの部分木の最大値は 16 -
centernodeの深さが 5 場合は、孫ノードまでの部分木の最大値は 16 -
centernodeの深さが 6 以上の場合は、深さ 9 までの部分木の最大値は 9
従って、下記の深さのノードまで部分木を描画する ようにしても、Axes の表示範囲内に表示が収まることがわかります。
centernode の深さ |
部分木の深さ |
|---|---|
| 4 以下 | 子ノード |
| 5 | 孫ノード |
| 6 以上 | 深さ 9 までのノード |
下記は、そのように update_gui を修正したプログラムです。
-
2 ~ 7 行目:
centernodeの深さに応じたmaxdepthを計算する
1 def update_gui(self):
元と同じなので省略
2 if self.centernode.depth <= 4:
3 maxdepth = self.centernode.depth + 1
4 elif self.centernode.depth == 5:
5 maxdepth = 7
6 else:
7 maxdepth = 9
8 self.mbtree.draw_subtree(self.centernode, ax=self.ax, maxdepth=maxdepth)
9
10 Mbtree_GUI.update_gui = update_gui
行番号のないプログラム
def update_gui(self):
self.ax.clear()
self.ax.set_xlim(-1, self.width - 1)
self.ax.set_ylim(0, self.height)
self.ax.invert_yaxis()
self.ax.axis("off")
if self.centernode.depth <= 4:
maxdepth = self.centernode.depth + 1
elif self.centernode.depth == 5:
maxdepth = 7
else:
maxdepth = 9
self.mbtree.draw_subtree(self.centernode, ax=self.ax, maxdepth=maxdepth)
Mbtree_GUI.update_gui = update_gui
修正箇所
def update_gui(self):
元と同じなので省略
- maxdepth = min(self.centernode.depth + 1, 9)
+ if self.centernode.depth <= 4:
+ maxdepth = self.centernode.depth + 1
+ elif self.centernode.depth == 5:
+ maxdepth = 7
+ else:
+ maxdepth = 9
self.mbtree.draw_subtree(self.centernode, ax=self.ax, maxdepth=maxdepth)
Mbtree_GUI.update_gui = update_gui
上記の修正後に、下記のプログラムを実行すると、実行結果のように、深さが 5 のノードが中心となる場合は孫ノードまで、深さ 6 のノードが中心となる場合は深さ 9 のノードまでの部分木が描画されるようになります。
mbtree_gui = Mbtree_GUI(mbtree)
実行結果(中心となるノードが深さ 5 と 6 の場合の図です)


中心となるノードの移動可能な範囲の改良
下記は、中心となるノードがの深さが 6 の場合と 7 の場合の図です。


よく見ると、右図は、左図の 赤枠の部分の図と同じ内容 になっていることがわかります。このように、深さが 7 以上 のノードを中心とする 部分木 は、そのノードの 深さ 6 の親ノードを中心とする部分木の一部 になってしまうので、ゲーム木の 全体像を把握するという目的 において、わざわざ 深さ 7 以上の部分木を描画 することに 意味はありません。
そこで、ボタンの操作によって、深さが 7 以上 のノードを中心とする 部分木を表示しない ように修正することにします。
下記は、そのように create_event_handler を修正したプログラムです。深さが 7 以上になる ような操作は、→ ボタン をクリックして子ノードに移動する場合 だけ なので、→ ボタン以外のイベントハンドラを修正する必要はありません。
-
3 行目:→ ボタンをクリックした時のイベントハンドラで
centernodeを移動する条件式に、centernodeの深さが 6 以下であるという条件を追加する
1 def create_event_handler(self):
元と同じなので省略
2 def on_right_button_clicked(b=None):
3 if self.centernode.depth < 6 and len(self.centernode.children) > 0:
4 self.centernode = self.centernode.children[0]
5 self.update_gui()
元と同じなので省略
6
7 Mbtree_GUI.create_event_handler = create_event_handler
行番号のないプログラム
def create_event_handler(self):
def on_left_button_clicked(b=None):
if self.centernode.parent is not None:
self.centernode = self.centernode.parent
self.update_gui()
def on_right_button_clicked(b=None):
if self.centernode.depth < 6 and len(self.centernode.children) > 0:
self.centernode = self.centernode.children[0]
self.update_gui()
def on_up_button_clicked(b=None):
if self.centernode.parent is not None:
index = self.centernode.parent.children.index(self.centernode)
if index > 0:
self.centernode = self.centernode.parent.children[index - 1]
self.update_gui()
def on_down_button_clicked(b=None):
if self.centernode.parent is not None:
index = self.centernode.parent.children.index(self.centernode)
if self.centernode.parent.children[-1] is not self.centernode:
self.centernode = self.centernode.parent.children[index + 1]
self.update_gui()
self.left_button.on_click(on_left_button_clicked)
self.right_button.on_click(on_right_button_clicked)
self.up_button.on_click(on_up_button_clicked)
self.down_button.on_click(on_down_button_clicked)
def on_key_press(event):
keymap = {
"left": on_left_button_clicked,
"right": on_right_button_clicked,
"up": on_up_button_clicked,
"down": on_down_button_clicked,
}
if event.key in keymap:
keymap[event.key]()
# fig の画像イベントハンドラを結び付ける
self.fig.canvas.mpl_connect("key_press_event", on_key_press)
Mbtree_GUI.create_event_handler = create_event_handler
修正箇所
def create_event_handler(self):
元と同じなので省略
def on_right_button_clicked(b=None):
if self.centernode.depth < 6 and len(self.centernode.children) > 0:
self.centernode = self.centernode.children[0]
self.update_gui()
元と同じなので省略
Mbtree_GUI.create_event_handler = create_event_handler
実行結果は省略しますが、上記の修正後に、下記のプログラムを実行すると、→ キーで深さが 7 以上のノードに移動できなくなることを確認して下さい。
mbtree_gui = Mbtree_GUI(mbtree)
ボタンの状態の変更
現状では、ボタンの色が常に緑色で表示されるようになっている点がわかりづらいので、クリックしても中心となるノードを 移動できない場合はボタンを灰色で表示して操作できない ように修正することにします。
ボタンの色を変更して操作できないようするメソッドは、GUI クラスの set_button_status メソッドとして定義しましたので、それを利用することができます。
GUI クラスの修正
以前の記事で、ウィジェットの状態を更新 する update_widgets_status という抽象メソッドを GUI クラスに定義し ましたが、よく考えると ウィジェットの状態の更新 は、GUI で必須となる処理ではありません。例えば、常に操作を行うことができるボタンしか存在しない GUI では、ウィジェットの状態を変更する必要はありません。
そこで、下記のプログラムのように、update_widgets_status という抽象クラスを 削除した GUI クラスを定義し直す ことにします。なお、update_widget_status メソッドの定義を削除するだけなので、行番号や、修正箇所は省略します。
GUI クラスの定義(長いのでクリックして表示して下さい)
from abc import ABCMeta, abstractmethod
import matplotlib as mlp
import ipywidgets as widgets
class GUI(metaclass=ABCMeta):
"""GUI の処理を行うクラスの基底クラス."""
def __init__(self):
# %matplotlib widget のマジックコマンドを実行する
get_ipython().run_line_magic('matplotlib', 'widget')
self.disable_shortcutkeys()
self.create_widgets()
self.create_event_handler()
self.display_widgets()
self.update_gui()
@abstractmethod
def create_widgets(self):
"""ウィジェットを作成する."""
pass
@abstractmethod
def create_event_handler(self):
"""イベントハンドラを定義する."""
pass
@abstractmethod
def display_widgets(self):
"""ウィジェットを配置して表示する."""
pass
@abstractmethod
def update_gui(self):
"""GUI の表示を更新する."""
pass
@staticmethod
def disable_shortcutkeys():
"""matplotlib の Figure のデフォルトのショートカットキー操作を禁止する."""
attrs = [ "fullscreen", "home", "back", "forward", "pan", "zoom", "save", "help",
"quit", "quit_all", "grid", "grid_minor", "yscale", "xscale", "copy"]
for attr in attrs:
mlp.rcParams[f"keymap.{attr}"] = []
@staticmethod
def create_button(description:str, width:float):
"""ボタンのウィジェットを作成する.
Args:
description:
ボタンに表示する文字列
width:
ボタンの横幅
"""
return widgets.Button(
description=description,
layout=widgets.Layout(width=f"{width}px"),
style={"button_color": "lightgreen"},
)
@staticmethod
def set_button_status(button, disabled:bool):
""" ボタンのウィジェットの状態を設定する
Args:
button:
ボタンのウィジェット
disabled:
False の場合は緑色で表示し、操作できるようにする
True の場合は灰色で表示し、操作できないようにする
"""
button.disabled = disabled
button.style.button_color = "lightgray" if disabled else "lightgreen"
update_gui の修正
Marubatsu_GUI では、update_gui で行う処理が長かったので、ウィジェットの状態の更新を行う処理 update_widgets_status というメソッドを定義し、update_gui から呼び出していましたが、Mbtree_GUI の update_gui で行う処理は短いので、その中に下記のプログラムのようにボタンの状態を更新する処理を直接記述することにします。
-
2、4、6、8:それぞれのボタンが 操作できない場合に
Trueになる条件式 を記述し、disalbedに代入する。create_event_handlerの中のボタンのイベントハンドラの中に記述する条件式を記述すれば良いと思う人がいるかもしれないが、それらはボタンを 操作できる場合にTrueになる条件式 なので、その逆を記述する必要がある -
3、5、7、9:
set_button_statusメソッドを利用して、4 つのボタンの状態を設定する
1 def update_gui(self):
元と同じなので省略
2 disabled = self.centernode.parent is None
3 self.set_button_status(self.left_button, disabled=disabled)
4 disabled = self.centernode.depth >= 6 or len(self.centernode.children) == 0
5 self.set_button_status(self.right_button, disabled=disabled)
6 disabled = self.centernode.parent is None or self.centernode.parent.children.index(self.centernode) == 0
7 self.set_button_status(self.up_button, disabled=disabled)
8 disabled = self.centernode.parent is None or self.centernode.parent.children[-1] is self.centernode
9 self.set_button_status(self.down_button, disabled=disabled)
10
11 Mbtree_GUI.update_gui = update_gui
行番号のないプログラム
def update_gui(self):
self.ax.clear()
self.ax.set_xlim(-1, self.width - 1)
self.ax.set_ylim(0, self.height)
self.ax.invert_yaxis()
self.ax.axis("off")
if self.centernode.depth <= 4:
maxdepth = self.centernode.depth + 1
elif self.centernode.depth == 5:
maxdepth = 7
else:
maxdepth = 9
self.mbtree.draw_subtree(self.centernode, ax=self.ax, maxdepth=maxdepth)
disabled = self.centernode.parent is None
self.set_button_status(self.left_button, disabled=disabled)
disabled = self.centernode.depth >= 6 or len(self.centernode.children) == 0
self.set_button_status(self.right_button, disabled=disabled)
disabled = self.centernode.parent is None or self.centernode.parent.children.index(self.centernode) == 0
self.set_button_status(self.up_button, disabled=disabled)
disabled = self.centernode.parent is None or self.centernode.parent.children[-1] is self.centernode
self.set_button_status(self.down_button, disabled=disabled)
Mbtree_GUI.update_gui = update_gui
修正箇所
def update_gui(self):
元と同じなので省略
+ disabled = self.centernode.parent is None
+ self.set_button_status(self.left_button, disabled=disabled)
+ disabled = self.centernode.depth >= 6 or len(self.centernode.children) == 0
+ self.set_button_status(self.right_button, disabled=disabled)
+ disabled = self.centernode.parent is None or self.centernode.parent.children.index(self.centernode) == 0
+ self.set_button_status(self.up_button, disabled=disabled)
+ disabled = self.centernode.parent is None or self.centernode.parent.children[-1] is self.centernode
+ self.set_button_status(self.down_button, disabled=disabled)
Mbtree_GUI.update_gui = update_gui
上記の修正後に、下記のプログラムを実行すると、実行結果のように、操作できないボタンが灰色で描画されるようになります。中心となるノードを移動して、ボタンの色が正しく表示されるようになったことを確認して下さい。
mbtree_gui = Mbtree_GUI(mbtree)
実行結果

今回の記事のまとめ
今回の記事では、ゲーム木を表示する GUI の改良をいくつか行いました。次回の記事では別の改良を行う予定です。
本記事で入力したプログラム
| リンク | 説明 |
|---|---|
| marubatsu.ipynb | 本記事で入力して実行した JupyterLab のファイル |
| marubatsu_new.py | 今回の記事で更新した marubatsu.py |
| tree_new.py | 今回の記事で更新した tree.py |
| gui_new.py | 今回の記事で更新した gui.py |
次回の記事
-
emphasize は、強調する という意味の英単語です ↩
-
mbtree.nodelist_by_depth[6][0]から順番に、そのような部分木が表示されるまでdraw_subtreeを実行して見つけました ↩ -
$x × y + x × z = x × (y + z)$ という公式を使うことで、$(9 - d) × (8 - d) + (9 - d)$ は、下記のように計算できます
$(9 - d) × (8 - d) + (9 - d)$
$= (9 - d) × (8 - d) + (9 - d) × 1$
$= (9 - d) × (8 - d + 1)$
$= (9 - d) * (9 - d)$ ↩





