はじめに
以下の記事で扱った、Babylon.js の「Playing Sounds and Music」の話です。
●Babylon.js の「Playing Sounds and Music」のサンプルを 2つほど見てみる - Qiita
https://qiita.com/youtoy/items/4f66e9a5f53d9af322ca
上記では、公式サンプルを 2つほど見ていきましたが、今回はさらに他のサンプルも見ていきます。
公式ドキュメント
前回の記事の再掲になりますが、「Playing Sounds and Music」の公式ドキュメントのページは以下になります。
●Playing Sounds and Music | Babylon.js Documentation
https://doc.babylonjs.com/features/featuresDeepDive/audio/playingSoundsMusic/
ドキュメントの目次
以下も再掲ですが、ドキュメントの目次です。
- Creating an audio engine
- Playing a sound
- Streaming a sound
- Sound instances
- Looping playback
- Volume
- Stereo pan
- Spatial audio
- Attaching meshes
- Audio buses
- Main audio buses
- Intermediate audio buses
- Analyzer
- Sound buffers
- Using browser-specific audio codecs
- Browser autoplay considerations
- Playing sounds after the audio engine is unlocked
- Unmute button
- Feature requests and bug fixes
前回の記事では以下を扱いました。
- Creating an audio engine
- Playing a sound
- Streaming a sound
公式ドキュメントを見ていく
今回の内容に入っていきます。
「Sound instances」のサンプル
以下の「Sound instances」のサンプルを見てみます。
●AudioEngineV2 | Babylon.js Playground
https://playground.babylonjs.com/#1BZK59#12
コードの内容
コードは以下のとおりです。
var createScene = async function () {
// Create a basic scene
var scene = new BABYLON.Scene(engine);
scene.clearColor = BABYLON.Color3.BlackReadOnly;
scene.createDefaultEnvironment({
createGround: false,
createSkybox: false,
createDefaultCameraOrLight: false,
});
scene.createDefaultCameraOrLight(true, true, false);
scene.activeCamera.alpha = Math.PI / 2;
scene.activeCamera.radius = 0.05;
BABYLON.AppendSceneAsync("https://playground.babylonjs.com/scenes/BoomBox.glb", scene);
// Load the sound and play it three times after the audio engine is unlocked
// The `maxInstances: 2` option makes the first instance stop playing when the sound is played a third time
(async () => {
const audioEngine = await BABYLON.CreateAudioEngineAsync();
const sound = await BABYLON.CreateSoundAsync("sound", "https://assets.babylonjs.com/sound/alarm-1.mp3", {
maxInstances: 2,
});
// Wait for the audio engine to unlock
await audioEngine.unlockAsync();
sound.play(); // Instance #1
setTimeout(() => {
// Calling `play` twice more will create two new instances and make the first instance stop playing due to the `maxInstances: 2` option being set
sound.playbackRate = 2;
sound.play(); // Instance #2
sound.play(); // Instance #3
}, 4000);
})();
return scene;
};
コードの音の再生に関わる部分は以下のようです。
// Load the sound and play it three times after the audio engine is unlocked
// The `maxInstances: 2` option makes the first instance stop playing when the sound is played a third time
(async () => {
const audioEngine = await BABYLON.CreateAudioEngineAsync();
const sound = await BABYLON.CreateSoundAsync("sound", "https://assets.babylonjs.com/sound/alarm-1.mp3", {
maxInstances: 2,
});
// Wait for the audio engine to unlock
await audioEngine.unlockAsync();
sound.play(); // Instance #1
setTimeout(() => {
// Calling `play` twice more will create two new instances and make the first instance stop playing due to the `maxInstances: 2` option being set
sound.playbackRate = 2;
sound.play(); // Instance #2
sound.play(); // Instance #3
}, 4000);
})();
このサンプルでは、インスタンスを { maxInstances: 2 } という部分で最大 2つまでと制限して、音の再生を行っているようです。
そのため、コード中の #1 と #2 の部分では、処理が行われたタイミングで音を鳴らすことができる状況になるようです(インスタンスの総数が 1つ ⇒ 2つ となり、最大数の 2 を超えていないため)。この時は、#1 が鳴り始めて 4秒後に 2倍の再生速度になった #2 も鳴り始めるようです。
そして #3 の部分では、既にインスタンスが 2つ存在するため、最初に作成された #1 のインスタンスがストップし、#3 のインスタンスの再生が始まるという流れになるようです。
動作を試す
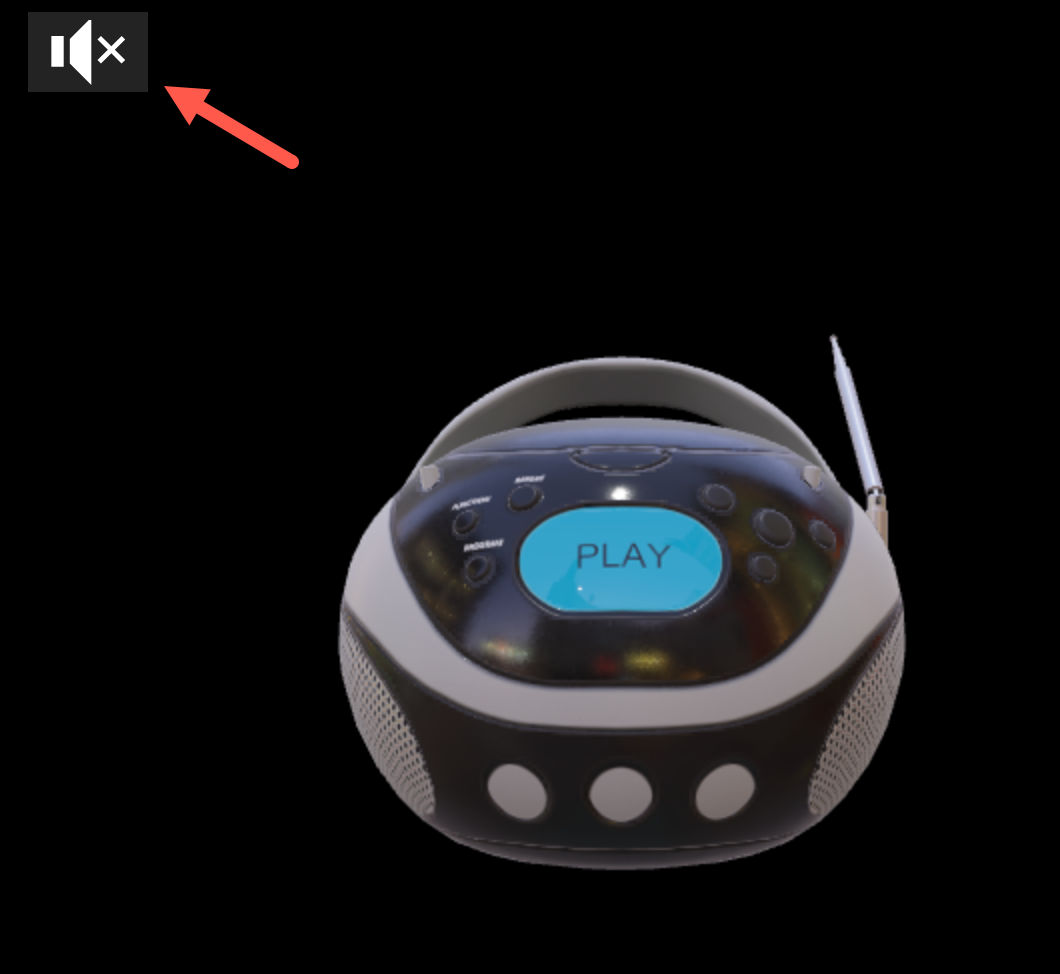
サンプルの動作を試してみます。
サンプルの動作の流れは(前回の記事で見たサンプルと同様に)、画面の左上に表示されているアイコンをクリックすると、音の再生が始まるというものでした。
アイコンをクリックすると、#1 の音の再生 ⇒ #2・#3 の再生という流れで音が鳴るのが確認できました。
「Looping playback」のサンプル
次は、以下の「Looping playback」のサンプルを見てみます。
●AudioEngineV2 | Babylon.js Playground
https://playground.babylonjs.com/#1BZK59#13
コードの内容
コードは以下のとおりです。
var createScene = async function () {
// Create a basic scene
var scene = new BABYLON.Scene(engine);
scene.clearColor = BABYLON.Color3.BlackReadOnly;
scene.createDefaultEnvironment({
createGround: false,
createSkybox: false,
createDefaultCameraOrLight: false,
});
scene.createDefaultCameraOrLight(true, true, false);
scene.activeCamera.alpha = Math.PI / 2;
scene.activeCamera.radius = 0.05;
BABYLON.AppendSceneAsync("https://playground.babylonjs.com/scenes/BoomBox.glb", scene);
// Loop a sound indefinitely after the audio engine is unlocked
// All three of the randomly chosen methods below will make the sound loop indefinitely
(async () => {
const audioEngine = await BABYLON.CreateAudioEngineAsync({ volume: 0.5 });
// Wait for the audio engine to unlock
await audioEngine.unlockAsync();
const loopMethod = 3 * Math.random();
if (loopMethod < 1) {
console.log("Looping method 1: Create the sound with the `loop: true` option set.");
const bounce = await BABYLON.CreateSoundAsync("bounce", "sounds/bounce.wav", { loop: true });
bounce.play();
} else if (loopMethod < 2) {
console.log("Looping method 2: Create the sound and set the `loop` property to true before calling `play()`.");
const bounce = await BABYLON.CreateSoundAsync("bounce", "sounds/bounce.wav");
bounce.loop = true;
bounce.play();
} else {
console.log("Looping method 3: Create the sound and set `loop: true` in the `play` function's options.");
const bounce = await BABYLON.CreateSoundAsync("bounce", "sounds/bounce.wav");
bounce.play({ loop: true });
}
})();
return scene;
};
上記の音の再生に関わる部分は、以下となるようです。
// Loop a sound indefinitely after the audio engine is unlocked
// All three of the randomly chosen methods below will make the sound loop indefinitely
(async () => {
const audioEngine = await BABYLON.CreateAudioEngineAsync({ volume: 0.5 });
// Wait for the audio engine to unlock
await audioEngine.unlockAsync();
const loopMethod = 3 * Math.random();
if (loopMethod < 1) {
console.log("Looping method 1: Create the sound with the `loop: true` option set.");
const bounce = await BABYLON.CreateSoundAsync("bounce", "sounds/bounce.wav", { loop: true });
bounce.play();
} else if (loopMethod < 2) {
console.log("Looping method 2: Create the sound and set the `loop` property to true before calling `play()`.");
const bounce = await BABYLON.CreateSoundAsync("bounce", "sounds/bounce.wav");
bounce.loop = true;
bounce.play();
} else {
console.log("Looping method 3: Create the sound and set `loop: true` in the `play` function's options.");
const bounce = await BABYLON.CreateSoundAsync("bounce", "sounds/bounce.wav");
bounce.play({ loop: true });
}
})();
return scene;
処理の内容は、音の再生のループになるようです。
そして、ドキュメントの以下に書かれた 3つのループ再生の方法を、どれか 1つランダムに選んで実行する処理になっているようです。
動作を試す
サンプルの動作を試すと、ループで音が再生されます。
コードでは、3種類のループ再生処理のいずれかが選ばれますが、設定されている音のファイルが同じなので、聞こえ方は 3つのどの処理が選ばれた時も同じになります。
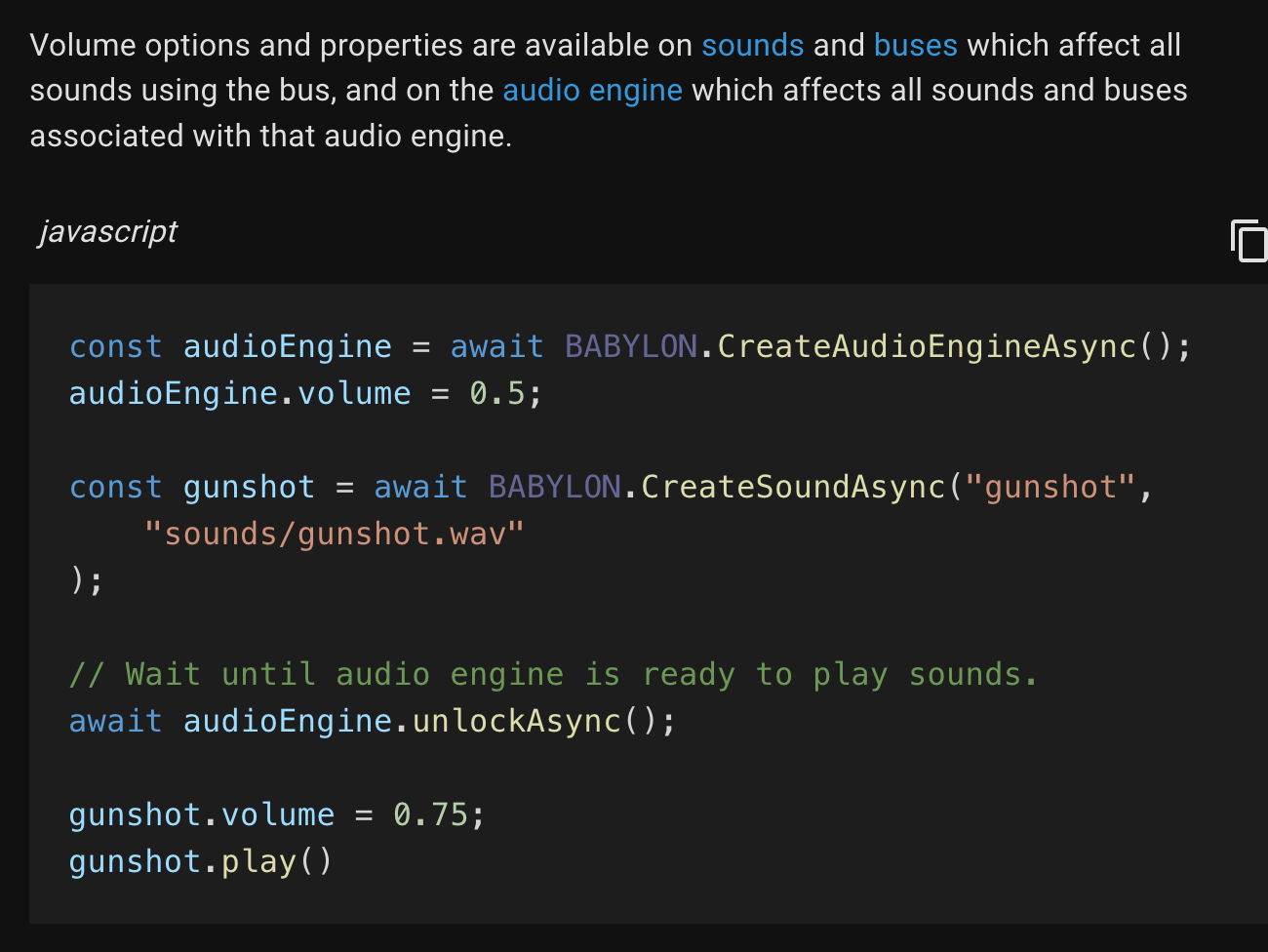
「Volume」のサンプル
Volume の部分は、プレイグラウンドのサンプルはなく、コードのサンプルが掲載されているのみのようです。
ドキュメントには、以下のコードが掲載されていました。
ボリュームは 0 が無音で 1 は 100% の音量、1 より大きな値も指定できるようです。
また、全体の音に影響を及ぼすオーディオエンジンでも、個々のサウンドでもボリュームを変えられるようです。
以下は、上で掲載したコードの抜粋ですが、1つ目がオーディオエンジンのボリュームを、2つ目は特定のサウンドの音量を設定しているものと思われます。
const audioEngine = await BABYLON.CreateAudioEngineAsync();
audioEngine.volume = 0.5;
const gunshot = await BABYLON.CreateSoundAsync("gunshot",
"sounds/gunshot.wav"
);
。。。
gunshot.volume = 0.75;
おわりに
今回、前回の記事に引き続き、Babylon.js の「Playing Sounds and Music」のサンプルを見ていきました。
前回・今回で見られていないもので、以下の Stereo pan・Spatial audio 以降の内容があります。これらも、別途、見えていければと思います。
- Stereo pan
- Spatial audio
- Attaching meshes
- Audio buses
- Main audio buses
- Intermediate audio buses
- Analyzer
- Sound buffers
- Using browser-specific audio codecs
- Browser autoplay considerations
- Playing sounds after the audio engine is unlocked
- Unmute button
- Feature requests and bug fixes