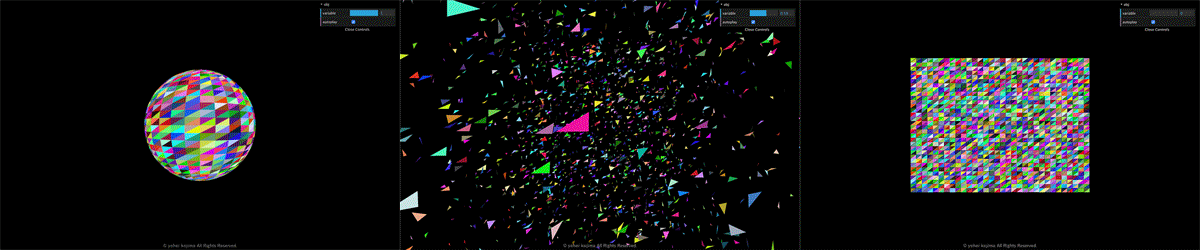こんにちは、yohei kojima です。
今回はWebGL(three.js)で変形アニメーションの作り方を解説していきます。
なんとなくシェーダーでメッシュは作れたけど、これをどうやって動かすの・・・色変えるくらいしかできない・・・みたいな方におすすめの記事です。
動きの部分だけにフォーカスし、できるだけシンプルに解説していきたい思います。
デモ
球体(Sphere)から平面(Plane)に変形します。
https://youhe.jp/demo/transform/
解説
まずベースとなるレンダラー、シーン、カメラを作成
const renderer = new THREE.WebGLRenderer();
renderer.setPixelRatio(window.devicePixelRatio);
renderer.setSize(window.ResizeWatch.width, window.ResizeWatch.height);
renderer.setClearColor(0x000000);
const container = document.getElementById("js-container");
container.appendChild(renderer.domElement);
const scene = new THREE.Scene();
const camera = new THREE.PerspectiveCamera(80, window.innerWidth / window.innerHeight, 1, 20);
camera.position.z = 10;
次にメッシュに使うジオメトリを作成します。ここが1番重要です。
オブジェクトを変形させるためには各頂点が以下を保持している必要があります。
・平面時のポジション(SphereBufferGeometry)
・球体時のポジション(PlaneBufferGeometry)
・ランダムなポジション
自前で球体と平面を定義するのは面倒なのでthree.jsのジオメトリから頂点とindexの情報を用いて作ります。
気をつける点は2つです。
①球体、平面の頂点数を同じにする
頂点数を同じにしないとどちらかのメッシュの頂点数が足りず形が崩れます。
②元のジオメトリとindexを同じにする必要がある
indexがバラバラだと頂点の位置は合っていても面が正しく作られません。
// 使用するジオメトリ
const geometry = new THREE.BufferGeometry();
// 球体ジオメトリ
const sGeometry = new THREE.SphereBufferGeometry(3.5, 32, 32);
// 球体ジオメトリのポジション
const sGeometryPosition = sGeometry.attributes.position.array;
// 平面ジオメトリ
const pGeometry = new THREE.PlaneBufferGeometry(12, 9, 32, 32);
// 平面ジオメトリのポジション
const pGeometryPosition = pGeometry.attributes.position.array;
// 平面ジオメトリのインデックス
const pGeometryIndex = pGeometry.index.array;
const count = pGeometryIndex.length * 3;
let sPosition = new Float32Array(count);
let pPosition = new Float32Array(count);
let rPosition = new Float32Array(count);
let color = new Float32Array(count);
let index = new Uint16Array(count / 3);
let r = new THREE.Vector3(0), c;
for (let i = 0; i < count / 3; i++) {
// 平面ジオメトリのインデックスから球体のポジションを代入
sPosition[i * 3 + 0] = sGeometryPosition[pGeometryIndex[i] * 3 + 0];
sPosition[i * 3 + 1] = sGeometryPosition[pGeometryIndex[i] * 3 + 1];
sPosition[i * 3 + 2] = sGeometryPosition[pGeometryIndex[i] * 3 + 2];
// 平面ジオメトリのインデックスから平面のポジションを代入
pPosition[i * 3 + 0] = pGeometryPosition[pGeometryIndex[i] * 3 + 0];
pPosition[i * 3 + 1] = pGeometryPosition[pGeometryIndex[i] * 3 + 1];
pPosition[i * 3 + 2] = pGeometryPosition[pGeometryIndex[i] * 3 + 2];
if (i % 3 == 0) {
// ランダムポジションの作成
r.x = Math.random() * 60 - 30;
r.y = Math.random() * 60 - 30;
r.z = Math.random() * 60 - 30;
// ランダムカラーの作成
c = new THREE.Color(Math.floor(Math.random() * 16777215));
}
rPosition[i * 3 + 0] = r.x;
rPosition[i * 3 + 1] = r.y;
rPosition[i * 3 + 2] = r.z;
color[i * 3 + 0] = c.r;
color[i * 3 + 1] = c.g;
color[i * 3 + 2] = c.b;
index[i] = i;
}
// 使用するジオメトリに各情報を代入
geometry.setAttribute("sPosition", new THREE.BufferAttribute(sPosition, 3));
geometry.setAttribute("pPosition", new THREE.BufferAttribute(pPosition, 3));
geometry.setAttribute("rPosition", new THREE.BufferAttribute(rPosition, 3));
geometry.setAttribute("color", new THREE.BufferAttribute(color, 3));
geometry.setIndex(new THREE.BufferAttribute(index, 1));
マテリアルを定義して先程のジオメトリと合わせてメッシュを作ります。
シェーダーは後述します。
let uniforms = {
variable: {type: "f", value: 0.0},
autoplay: {type: "bool", value: true}
};
const material = new THREE.RawShaderMaterial({
uniforms: uniforms,
vertexShader: vs,
fragmentShader: fs,
side: THREE.DoubleSide
});
const mesh = new THREE.Mesh(geometry, material);
scene.add(mesh);
update 関数を作ります。
update(frame) {
requestAnimationFrame(() => {update()});
if (uniforms.autoplay.value) {
uniforms.variable.value = (Math.cos(frame * 0.003) + 1) / 2;
}
renderer.setRenderTarget(null);
renderer.render(scene, camera);
}
最後にシェーダーを書いていきます。
ここで線形補間(mix)を使います。
mix(x, y. v)は、x(1 - v) + y * v を返します。
v = 0 の時は、x
v = 1 の時は、y
となり x ~ y の間を 0 ~ 1 で示せます。
v(variabl)の値は update() で更新しています。
今回は、途中でランダムなポジションを経由させたかったので mix を2重で使っています。
単調なアニメーションになりますが
vec3 p = mix(pPosition, sPosition, variable);
としても動きます。
precision mediump float;
uniform mat4 modelViewMatrix;
uniform mat4 projectionMatrix;
uniform float variable;
attribute vec3 sPosition;
attribute vec3 pPosition;
attribute vec3 rPosition;
attribute vec3 color;
varying vec3 vColor;
void main() {
vColor = color;
vec3 p = mix(pPosition, mix(rPosition, sPosition, variable), variable);
gl_Position = projectionMatrix * modelViewMatrix * vec4(p, 1.0);
}
precision mediump float;
varying vec3 vColor;
void main() {
gl_FragColor = vec4(vColor.rgb, 1.0);
}
これで実装は終わりです。
わからないところがあったらTwitterで聞いてください。 → yohei kojima