この記事は、Elastic stack Advent Calendar 2016の14日目の記事です。
Elasticsearchの特長はいろいろありますが、欲しい情報とどのくらいマッチしているのかという、より人間の感覚に近い形で文書を検索できる点が魅力だと思います。
Function Scoreクエリを使うとドキュメントに対して自分でスコアをつけることができるのでその方法をまとめてみました。
準備
まずはElasticsearch / Kibana環境を準備しましょう。@kokumutyoukanさんのアドベントカレンダー7日目の記事が参考になるかと思います。
Docker環境がある方は以下のdocker-compose.ymlを用意してdocker-compose upするのが早いかもしれません。
version: '2'
services:
elasticsearch:
image: elasticsearch
ports:
- 9200:9200
kibana:
image: kibana
ports:
- 5601:5601
depends_on:
- elasticsearch
クエリを試すには最低限Elasticsearchがあればできますが、Kibana 5.x のDevTool Console を使うとクエリ入力を補完してくれたり、実行や結果の確認がすぐにできて便利です。
データの準備
なかなかいいデータセットを見つけるのが難しかったので自分でダミーデータを用意しました1。内容は本のデータで以下のフィールドを持っています。
- title: タイトル
- author: 著者
- publisher: 出版社
- genre: ジャンル
- rating: 評価(1〜5)
- release_date: 発売日(12月10日から60日前までをランダムに生成)
bulk API でインポートできる形式でこちらに用意してありますのでこちらをダウンロードしてください。値にバラツキを持たせるため件数は少なめです(100件)。
データのインポート:
curl -XPOST 'localhost:9200/book/book/_bulk?pretty&refresh' --data-binary "@books.json"
Function Scoreクエリによるスコアリング
Function Scoreクエリでは次の方法でフィールドの値を使ったスコアリングができます。
- Field Value factor (値を数式でスコア生成)
- Decay functions (目的の値との近さ(距離)でスコア生成。decay=減衰)
- Script score (painlessなどのスクリプトを使ってスコア生成)
今回の記事ではScript score以外の2つを説明し、その後それらのスコアを組み合わせる方法について説明していきます。
Field Value factor (フィールドの値でスコアリング)
field_value_factor を利用するとドキュメントのフィールド値を直接スコアに利用できます。
今回用意した本のデータセットで、評価(rating)の値(1〜5で5がベスト)をそのままスコアの値に反映させる場合は次のようになります。
GET /book/book/_search?size=5
{
"query": {
"function_score": {
"query": {
"match_all": {}
},
"functions": [
{
"field_value_factor": {
"field": "rating"
}
}
]
}
}
}
上の例は最も単純な例ですが、値に関数を適用したり、null値の扱いを決めるなどいくつかオプションがあります(参考: Field Value factor)。
実行すると以下のような結果が返ります。
{
"took": 65,
"timed_out": false,
"_shards": {
"total": 5,
"successful": 5,
"failed": 0
},
"hits": {
"total": 100,
"max_score": 5,
"hits": [
{
"_index": "book",
"_type": "book",
"_id": "19",
"_score": 5,
"_source": {
"title": "Jacob Have I Loved",
"author": "Donavon Abernathy",
"publisher": "Virgin Publishing",
"genre": "Humor",
"rating": 5,
"release_date": "2016-10-21"
}
},
{
"_index": "book",
"_type": "book",
"_id": "24",
"_score": 5,
"_source": {
"title": "The Mirror Crack'd from Side to Side",
"author": "Ms. Ayana McCullough",
"publisher": "Manning Publications",
"genre": "Fiction narrative",
"rating": 5,
"release_date": "2016-11-19"
}
},
{
"_index": "book",
"_type": "book",
"_id": "25",
"_score": 5,
"_source": {
"title": "The Wives of Bath",
"author": "Mireya Heller DVM",
"publisher": "NavPress",
"genre": "Fiction in verse",
"rating": 5,
"release_date": "2016-11-09"
}
},
{
"_index": "book",
"_type": "book",
"_id": "8",
"_score": 5,
"_source": {
"title": "Time of our Darkness",
"author": "Lambert Mraz",
"publisher": "Elsevier",
"genre": "Essay",
"rating": 5,
"release_date": "2016-10-23"
}
},
{
"_index": "book",
"_type": "book",
"_id": "32",
"_score": 5,
"_source": {
"title": "Precious Bane",
"author": "Rickie Kessler III",
"publisher": "Kensington Books",
"genre": "Fiction in verse",
"rating": 5,
"release_date": "2016-11-16"
}
}
]
}
}
ratingの値が直接スコアリングの値になるため、最も高いものが返ってきています。
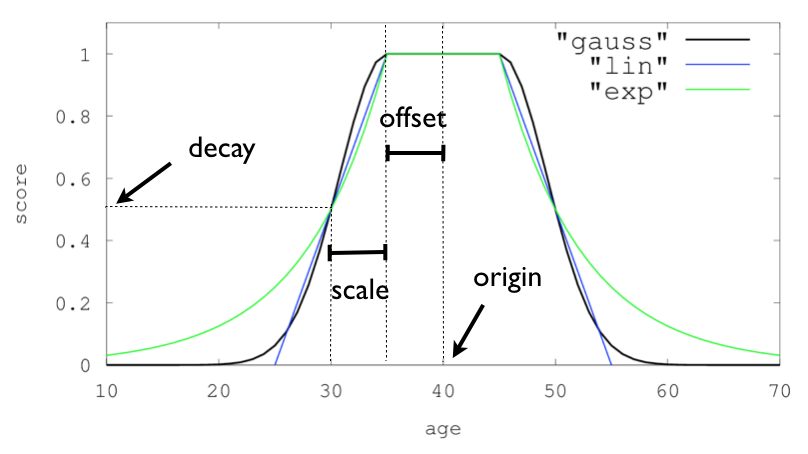
Decay functions (目的の値との近さ(距離)でスコアリング)
ドキュメントのスコアを調整するために減衰関数(線形関数、指数関数、ガウス関数)を利用できます。例えば次のようなフィールドを持つドキュメントに適用できます。
- 位置情報 - 例えば東京駅に近いホテルを列挙したいとき。
- 日付 - ドキュメントの最終更新日が新しい方がよい、など。
- 年齢 - 会員の25歳前後を中心にメールを送りたい。
サンプルのデータセットで発売日(release_date)に指数関数の減衰を適用してみます。
offsetを3日間、scaleを10日間でdecay(減衰の程度)を0.8にセットしてみます。
GET /book/book/_search?size=5
{
"query": {
"function_score": {
"query": {
"match_all": {}
},
"functions": [
{
"exp": {
"release_date": {
"scale": "10d",
"offset": "3d",
"decay": 0.8
}
}
}
]
}
}
}
各パラメータの意味は下記公式ドキュメントの図の通りです。
今回のケースではorigin(減衰の基準となる値)を省略していますが、フィールドが日時の場合のデフォルトは現在(now)です。このためクエリを実行した日時を基準にスコアリングされます。
2016年12月11日に実行した場合の結果は以下の通りです。
{
"took": 11,
"timed_out": false,
"_shards": {
"total": 5,
"successful": 5,
"failed": 0
},
"hits": {
"total": 100,
"max_score": 1,
"hits": [
{
"_index": "book",
"_type": "book",
"_id": "99",
"_score": 1,
"_source": {
"title": "nfinite Jest",
"author": "Onie Doyle",
"publisher": "Charles Scribner's Sons",
"genre": "Fiction narrative",
"rating": 4,
"release_date": "2016-12-10"
}
},
{
"_index": "book",
"_type": "book",
"_id": "46",
"_score": 1,
"_source": {
"title": "By Grand Central Station I Sat Down and Wept",
"author": "Ms. Alva Bergstrom",
"publisher": "Marshall Cavendish",
"genre": "Folklore",
"rating": 1,
"release_date": "2016-12-09"
}
},
{
"_index": "book",
"_type": "book",
"_id": "3",
"_score": 1,
"_source": {
"title": "The Wings of the Dove",
"author": "River Denesik",
"publisher": "Medknow Publications",
"genre": "Speech",
"rating": 2,
"release_date": "2016-12-10"
}
},
{
"_index": "book",
"_type": "book",
"_id": "45",
"_score": 1,
"_source": {
"title": "This Lime Tree Bower",
"author": "Kareem Moen",
"publisher": "Eel Pie Publishing",
"genre": "Realistic fiction",
"rating": 3,
"release_date": "2016-12-09"
}
},
{
"_index": "book",
"_type": "book",
"_id": "60",
"_score": 0.97308505,
"_source": {
"title": "Wildfire at Midnight",
"author": "Dawn Renner",
"publisher": "Bloodaxe Books",
"genre": "Mystery",
"rating": 1,
"release_date": "2016-12-07"
}
}
]
}
}
オフセットを3日としているため、12月10日、12月9日のデータのスコアは1となりが混ざって表示されていますが、最後のデータはオフセットよりも前の日付のためスコアが低くなっていること("_score": 0.97308505)がわかります。
複数ファンクションのトータルスコアと重み付け
functionsには複数のファンクションを指定できますが、functionsトータルのスコアはscore_modeとmax_boostによって決まります。
例として前述の2つファンクション指定した場合です。
GET /book/book/_search?size=5
{
"query": {
"function_score": {
"query": {
"match_all": {}
},
"functions": [
{
"field_value_factor": {
"field": "rating"
}
},
{
"exp": {
"release_date": {
"scale": "10d",
"offset": "3d",
"decay": 0.8
}
}
}
],
"score_mode": "multiply",
"max_boost": 10
}
}
}
score_modeはmultiply(かけ算)以外にもmaxやavgなどの関数が指定できます。そして計算後のスコアはmax_boostでリミットされます。上の例ですとどんなにスコアが大きくなる場合でも10がfunctionsの最大スコアになります。
また、各ファンクションごとに重み付けを設定することができます。例えば上記の組み合わせでratingの重みを1/5にしてみると以下のようになります。
GET /book/book/_search?size=5
{
"query": {
"function_score": {
"query": {
"match_all": {}
},
"functions": [
{
"field_value_factor": {
"field": "rating"
},
"weight": 0.2
},
{
"exp": {
"release_date": {
"scale": "10d",
"offset": "3d",
"decay": 0.8
}
}
}
],
"score_mode": "multiply",
"max_boost": 10
}
}
}
結果はratingの影響が小さくなり、ratingが低くてもrelease_dateが新しいものが上位に来るようになりました。
{
"took": 9,
"timed_out": false,
"_shards": {
"total": 5,
"successful": 5,
"failed": 0
},
"hits": {
"total": 100,
"max_score": 0.9097863,
"hits": [
{
"_index": "book",
"_type": "book",
"_id": "23",
"_score": 0.9097863,
"_source": {
"title": "A Monstrous Regiment of Women",
"author": "Skyla Gorczany",
"publisher": "Nonesuch Press",
"genre": "Narrative nonfiction",
"rating": 5,
"release_date": "2016-12-04"
}
},
{
"_index": "book",
"_type": "book",
"_id": "50",
"_score": 0.8137376,
"_source": {
"title": "The Last Temptation",
"author": "Tess Towne I",
"publisher": "André Deutsch",
"genre": "Historical fiction",
"rating": 5,
"release_date": "2016-11-29"
}
},
{
"_index": "book",
"_type": "book",
"_id": "99",
"_score": 0.8,
"_source": {
"title": "nfinite Jest",
"author": "Onie Doyle",
"publisher": "Charles Scribner's Sons",
"genre": "Fiction narrative",
"rating": 4,
"release_date": "2016-12-10"
}
},
{
"_index": "book",
"_type": "book",
"_id": "75",
"_score": 0.77822,
"_source": {
"title": "The Golden Bowl",
"author": "Vincenzo Schowalter",
"publisher": "Ballantine Books",
"genre": "Fantasy",
"rating": 5,
"release_date": "2016-11-27"
}
},
{
"_index": "book",
"_type": "book",
"_id": "56",
"_score": 0.7442526,
"_source": {
"title": "The Doors of Perception",
"author": "Lester Kerluke",
"publisher": "Canongate Books",
"genre": "Classic",
"rating": 5,
"release_date": "2016-11-25"
}
}
]
}
}
まとめると、
functionsのスコア = min(max_boost, score_mode(f1*w1, f2*w2, ..., fn*wn))
# fx: 各functionのスコア
# wx: 各functionの重み
となります。
queryとfunctionsのスコア組み合わせ
これまで説明を省いてきましたが、functionsでの評価が適用されるのはfunction_score中で指定したqueryでヒットしたドキュメントだけです。
そして、queryにもスコアがあるのでそのスコアとfunctionsのスコアを組み合わせたものが最終的なfunction_scoreクエリのスコアになります。このスコアの組み合わせ方をboost_modeで指定できます(デフォルトはmultiply)。また、queryのスコアはboostオプションでブーストできます。
function_scoreのスコア = boost_mode(queryスコア * boost, functionsスコア)
次の例はqueryのスコアを2倍に引き上げた上でfunctionsのスコアとかけ算した結果を最終的なスコア値とする場合です。
GET /book/book/_search?size=5
{
"query": {
"function_score": {
"query": {
"match": {
"title": "I"
}
},
"boost": 2,
"functions": [
{
"field_value_factor": {
"field": "rating"
},
"weight": 0.2
},
{
"exp": {
"release_date": {
"scale": "10d",
"offset": "3d",
"decay": 0.8
}
}
}
],
"score_mode": "multiply",
"boost_mode": "multiply",
"min_score": 1
}
}
}
min_scoreを指定するとfunction_scoreのスコアがその値以下のドキュメントは結果から除外されます。結果、上記の例ですとスコアが1以上の結果だけが返ってきます。
{
"took": 5,
"timed_out": false,
"_shards": {
"total": 5,
"successful": 5,
"failed": 0
},
"hits": {
"total": 3,
"max_score": 1.4026401,
"hits": [
{
"_index": "book",
"_type": "book",
"_id": "19",
"_score": 1.4026401,
"_source": {
"title": "Jacob Have I Loved",
"author": "Donavon Abernathy",
"publisher": "Virgin Publishing",
"genre": "Humor",
"rating": 5,
"release_date": "2016-10-21"
}
},
{
"_index": "book",
"_type": "book",
"_id": "33",
"_score": 1.354239,
"_source": {
"title": "As I Lay Dying",
"author": "Katelin Rau",
"publisher": "Etruscan Press",
"genre": "Speech",
"rating": 4,
"release_date": "2016-10-16"
}
},
{
"_index": "book",
"_type": "book",
"_id": "22",
"_score": 1.1626254,
"_source": {
"title": "If I Forget Thee Jerusalem",
"author": "Elsie Reichel Sr.",
"publisher": "Viking Press",
"genre": "Western",
"rating": 3,
"release_date": "2016-11-10"
}
}
]
}
}
explain API で確認する
いろいろとスコアリングを変更していくと、実際に取得されたドキュメントのスコアがどうしてこうなったのか知りたくなります。
そんな時explain API を使うと便利です。上で取得したドキュメントをexplainで見てみましょう。
GET /book/book/19/_explain
{
"query": {
"function_score": {
"query": {
"match": {
"title": "I"
}
},
"functions": [
{
"field_value_factor": {
"field": "rating"
},
"weight": 0.2
},
{
"exp": {
"release_date": {
"scale": "10d",
"offset": "3d",
"decay": 0.8
}
}
}
],
"score_mode": "multiply",
"boost": 2,
"boost_mode": "replace"
}
}
}
ちょっと長いですが、descriptionとdetailsを見ると何をどう計算しているのか分かると思います。
{
"_index": "book",
"_type": "book",
"_id": "19",
"matched": true,
"explanation": {
"value": 0.34044877,
"description": "sum of:",
"details": [
{
"value": 0.34044877,
"description": "min of:",
"details": [
{
"value": 0.34044877,
"description": "function score, score mode [multiply]",
"details": [
{
"value": 1,
"description": "function score, product of:",
"details": [
{
"value": 1,
"description": "match filter: *:*",
"details": []
},
{
"value": 1,
"description": "product of:",
"details": [
{
"value": 5,
"description": "field value function: none(doc['rating'].value * factor=1.0)",
"details": []
},
{
"value": 0.2,
"description": "weight",
"details": []
}
]
}
]
},
{
"value": 0.34044877,
"description": "function score, product of:",
"details": [
{
"value": 1,
"description": "match filter: *:*",
"details": []
},
{
"value": 0.34044877,
"description": "Function for field release_date:",
"details": [
{
"value": 0.34044877,
"description": "exp(- MIN[Math.max(Math.abs(1.477008E12(=doc value) - 1.481439186535E12(=origin))) - 2.592E8(=offset), 0)] * 2.5826799920626123E-10)",
"details": []
}
]
}
]
}
]
},
{
"value": 3.4028235e+38,
"description": "maxBoost",
"details": []
}
]
},
{
"value": 0,
"description": "match on required clause, product of:",
"details": [
{
"value": 0,
"description": "# clause",
"details": []
},
{
"value": 1,
"description": "_type:book, product of:",
"details": [
{
"value": 1,
"description": "boost",
"details": []
},
{
"value": 1,
"description": "queryNorm",
"details": []
}
]
}
]
}
]
}
}
その他
functions中でfilterを指定したり、ランダムなスコアリングをすることもできます。
興味がありましたらドキュメントを参照してみてください。
まとめ
ElasticsearchでFunction Scoreクエリを使ったスコアリングについて見てきました。
複数のファンクションを組み合わせることでかなり柔軟なスコアリングができると思います。求めているものを取得するために、どうスコアリングしたらいいか考えるだけでもワクワクしますよね。
実際に使う際には検索の精度やパフォーマンスなどを評価して、試行錯誤を繰り返すことになると思いますが、初めの一歩として参考になれば幸いです。