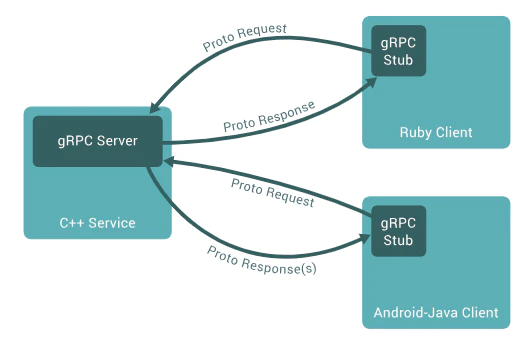
gRPCとは
Googleが開発したプロトコルの1つで主にマイクロサービス間(サーバー間)での通信に用いられる。RPC(Remote procedure call:遠隔手続き呼び出し)という技術がベースとなっている。
メリット
よくRESTful APIとの違いが挙げられますが優れている点は以下の通りです
・Protocol Buffersによるバイナリデータ転送
・HTTP/2ベースで高速
・双方向通信(WebSocketのようなもの)
Protocol Buffers とは
gRPCではProtocol Buffersのフォーマットにシリアライズしてデータをやり取りします。バイナリベースなのでキストベースのプロトコルと比較して通信における転送量を大きく削減できます。.protoファイルを書いて、コンパイラを実行すると任意の言語のクライアント・サーバー用のコードを生成します。
実践編
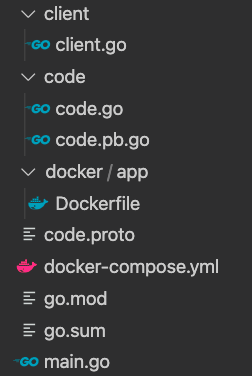
最終的なディレクトリ構成は以下のようになっています。
各種セットアップ
Protocol Buffers をインストールを行います。Homebrewがインストールされていることが前提です。
$ brew install protobuf
go mod init を行います。現在のディレクトリにおけるモジュールを外部からインポートする時のパスを設定します。
$ go mod init example.com
gRPC と Protocol Buffers のGoプラグインをインストールを行います。
$ go get -u google.golang.org/grpc
$ go get -u github.com/golang/protobuf/protoc-gen-go
Protocol Buffers を利用した開発では、まず構造化データを.proto ファイルに定義します。
// protoのバージョン
syntax = "proto3";
// パッケージ名を指定
package code;
// コードが自動生成されるディレクトリを指定しています。
option go_package = "/code";
// APIにおけるサービス定義
service CodeService {
rpc GetResult (Request) returns (Response) {}
}
// リクエストのメッセージ型を定義
message Request {
string code = 1;
}
// レスポンスのメッセージ型を定義
message Response {
string result = 1;
}
以下のコマンドでprotocを使ってGo固有のgRPCコードの生成します。
現在のディレクトリの配下にcodeディレクトリを作成されて中にcode.pb.goが作成されます。
$ protoc --go_out=plugins=grpc:. code.proto
サーバー側の実装
package main
import (
"google.golang.org/grpc"
"fmt"
"net"
"example.com/code"
)
func main() {
fmt.Println("Hello gRPC API Server !")
// listenするportを設定します
lis, err := net.Listen("tcp",":9000")
// エラーハンドリング
if err != nil {
fmt.Println(err)
}
s := code.Server{}
grpcServer := grpc.NewServer()
code.RegisterCodeServiceServer(grpcServer, &s)
// エラーハンドリング
if err := grpcServer.Serve(lis); err != nil {
fmt.Println(err)
}
}
package code
import (
"fmt"
"golang.org/x/net/context"
)
type Server struct {
}
func (s *Server) GetResult(ctx context.Context, in *Request) (*Response, error) {
// クライアントからリクエストを受け取る
fmt.Println(in.Code)
// ここでサーバーがクライアントにレスポンスを返す
return &Response{Result: result}, nil
}
クライアント側でリクエストを送信
package main
import (
"fmt"
"example.com/code"
"golang.org/x/net/context"
"google.golang.org/grpc"
)
func main() {
var conn *grpc.ClientConn
conn, err := grpc.Dial(":9000", grpc.WithInsecure())
if err != nil {
fmt.Println(err)
}
defer conn.Close()
c := code.NewCodeServiceClient(conn)
// リクエストを送信する
response, err := c.GetResult(context.Background(), &code.Request{Code: text})
if err != nil {
fmt.Println(err)
}
// サーバーからのレスポンスを表示
fmt.Println(response.Result)
}
最後に
今回はGo(クライアント)からGo(サーバー)に対してリクエストを送信するケースを考えましたがVue.jsやReactなどのクライアントと通信をする際はgRPC-Webを用います。こちらも時間ありましたら実装しようと考えていますのでよろしくお願いします。
参考文献